- Chico Municipal Airport
-
Chico Municipal Airport 
USGS 2006 Orthophoto IATA: CIC – ICAO: KCIC – FAA LID: CIC Summary Airport type City of Chico Owner City of Chico Serves Chico, California Location Chico, California, 4 miles (6 km) N of downtown Chico Elevation AMSL 72.5 ft / 22 m Coordinates 39°47′43″N 121°51′30″W / 39.79528°N 121.85833°WCoordinates: 39°47′43″N 121°51′30″W / 39.79528°N 121.85833°W Runways Direction Length Surface ft m 13L/31R 6,724 2,049 Asphalt 13R/31L 3,005 916 Asphalt Helipads Number Length Surface ft m H1 64 20 Concrete Chico Municipal Airport (IATA: CIC, ICAO: KCIC, FAA LID: CIC), often called CMA, is a public airport located four miles (6 km) north of the central business district (CBD) of Chico, a city in Butte County, California, United States. The airport covers 1,475 acres (6 km²) and has two runways and one helipad. It is mostly used for general aviation, but is served by one commercial airline. The airport's fixed base operator, "Northgate Aviation". http://www.northgateaviation.com., provides fuel, maintenance, flight training and charter flights for business and personal travel.
Contents
Airline and destination
Airlines Destinations United Express operated by SkyWest Airlines San Francisco Previous air carriers include American Eagle, Hughes Air West and Reno Air Express.
History
During the late 1930s the City of Chico acquired approximately 160 acres (0.6 km²) of land five miles (8 km) north of what was then the City limits and constructed an airport hangar and runway. Until 1941, this original facility was leased to a fixed-base operator. During 1941 the City acquired an additional 1,000 acres (4 km²) for the purpose of leasing the Airport to the United States Government.
On 11 September 1941 when the City Council of Chico formally signed a lease with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers representing the War Department for the use of 1,045 acres of land at $1 per year with an option to buy. The City also provided all utilities and service roads to the field. Between four and five million dollars were allocated for construction of all needed facilities in a very short time, as at other bases. Eventually 140 buildings as well as runways, aprons and service roads were constructed.
Chico Army Airfield was under the command of the 10th Army Air Force Base Unit, AAF West Coast Training Center, Army Air Forces Training Command. Chico AAF also had five auxiliary landing fields:
- Orland Auxiliary Field No. 1 39°43′16″N 122°08′44″W / 39.72111°N 122.14556°W
- Kirkwood Auxiliary Field No. 2 39°47′20″N 122°07′31″W / 39.78889°N 122.12528°W
- Vina Auxiliary Field No. 3 39°56′54″N 121°59′29″W / 39.94833°N 121.99139°W
- Campbell Auxiliary Field No. 4 39°54′10″N 121°55′43″W / 39.90278°N 121.92861°W
- Oroville Auxiliary Field No. 5 39°34′58″N 121°38′24″W / 39.58278°N 121.64°W
On 15 April 1942, the first cadre of permanent troops who managed the field moved in. The field was officially opened as the Chico Army Flying School on April 15, 1942. The first cadets arrived on April 25, 1942 from Moffett Field where they had already completed part of their basic flying in addition to their primary training. Basic training at Chico began on July 28,1942.
An all black company was assigned to the Field in August 1942. The first WACs arrived in October 1943. A cadre of black WACs was housed on an eleven-acre site across Cohasset Road from the Field. WASPS (Women's Army Service Pilots) frequently delivered planes to the field. At its peak Chico Army Air Field had about 4,000 personnel. In the first two years, it trained 5,500 cadets and thousands of ground personnel.
In April 1944 the mission of the Field was changed from basic flying training of cadets to training of fighter pilots. An April 24,1944 the Field was transferred from the Western Flying Training Command to the IV Fighter Command.
The new command brought in pilots who had completed their basic and advanced training and received commissions prior to coming to Chico. Here they were to be taught tactics of combat flying using Bell King Cobra (P-63) planes, later switching to the twin-engine Lockheed P-38 Lightings. These were all propeller planes. In May of 1945 jet training was introduced on the P-59 jet trainers, and in July the P-51 `Mustangs. On August 25, 1945 IV Fighter Command was replaced by the 21st Bombardment Wing. Its function was to process both personnel and aircraft for overseas assignment. In October 1945 the Wing was redesignated the First Staging Command. Now the planes being processed were B-29 Superfortress bombers and crews.
Chico Army Air Field was deactivated on December 31, 1945. The property was excessed and transferred by the U.S. Army to the General Services Administration (GSA) for disposal. The lease on 1,045.3 acres was terminated on June 8, 1948. The lease termination agreement included the transfer of all U.S. Government constructed improvements to the City of Chico. GSA transferred the 10.97 acres to the City of Chico by deed dated January 28, 1949. The total acreage disposed was 1,056.27.
On 30 January 1959, the Air Force announced plans to conduct surveys in the vicinity of Beale Air Force Base to determine the feasibility for missile bases. A Titan-I ICBM was located on the north side of the airport[1] from 1962–1965, part of the Beale AFB's 851st Strategic Missile Squadron system of several ICBMs centered around Marysville. Its formal designation was Beale 851-C. The last missile was lowered into the Chico complex 4C on April 20, 1962.
The Chico missile complex was the location of two 1962 accidents. On 24 May during a contractor checkout, a terrific blast rocked launcher 1 at the complex, destroying a Titan I and causing heavy damage to the silo. On 6 June trouble again struck as a flash fire at another silo killed a worker. After the investigation, the Air Force concluded that the two separate explosions occurred because of a blocked vent and blocked valve. The silo was repaired and put back into operational service. Today, the site has all three launch silos capped, but some development has taken place on the launch area with a retention pond, some trees, and some single-story buildings being erected. It appears to be in use for some type of quarrying/grading material which is transported to construction sites in the Chico area.[2][3]
See also
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Air Force Historical Research Agency.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the Air Force Historical Research Agency.- Shaw, Frederick J. (2004), Locating Air Force Base Sites History’s Legacy, Air Force History and Museums Program, United States Air Force, Washington DC, 2004.
- Manning, Thomas A. (2005), History of Air Education and Training Command, 1942–2002. Office of History and Research, Headquarters, AETC, Randolph AFB, Texas ASIN: B000NYX3PC
- ^ "Titan I map". California Department of Toxic Substances Control. http://www.envirostor.dtsc.ca.gov/public/map.asp?global_id=04970001.
- ^ "Photos of ICBM site in Chico, California". http://news.webshots.com/album/557872339cfnyzB.
- ^ "Beale AFB History". Global Security.org. http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/facility/beale.htm.
External links
- Chico Municipal Airport
- FAA Airport Master Record for CIC (Form 5010 PDF)
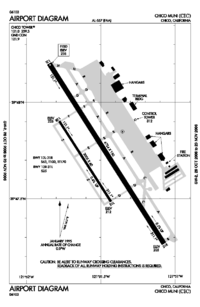
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective 20 October 2011
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KCIC
- ASN accident history for CIC
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart, Terminal Procedures for KCIC
Airfields Group Training Stations · Replacement Training Stations · Tactical Airfields
Units Commands IV Bomber Command · IV Fighter Command · IV Air Support CommandWings 21st Bombardment · Los Angeles Fighter · San Diego Fighter · San Francisco Fighter · Seattle FighterGroups Bombardment 12th Bombardment · 30th Bombardment · 41st Bombardment · 42d Bombardment · 47th Bombardment · 380th Bombardment · 385th Bombardment · 389th Bombardment · 392d Bombardment · 399th Bombardment · 449th Bombardment · 450th Bombardment · 451st Bombardment · 453rd Bombardment · 454th Bombardment · 455th Bombardment · 456th Bombardment · 461st Bombardment · 463d Bombardment · 465th Bombardment · 466th Bombardment · 470th Bombardment · 483rd Bombardment · 486th Bombardment · 491st Bombardment · 492d BombardmentFighter 1st Fighter · 14th Fighter · 20th Fighter · 35th Fighter · 51st Fighter · 55th Fighter · 78th Fighter · 81st Fighter · 82d Fighter · 328th Fighter · 329th Fighter · 339th Fighter · 354th Fighter · 360th Fighter · 363rd Fighter · 364th Fighter · 369th Fighter · 367th Fighter · 372d Fighter · 412th Fighter · 473d Fighter · 474th Fighter · 478th Fighter · 479th FighterReconnaissance 68th Reconnaissance · 69th ReconnaissanceTroop Carrier Categories:- Airports in Butte County, California
- 1941 establishments
- USAAF West Coast Training Center
- USAAF Fourth Air Force Replacement Training Stations
- Airfields of the United States Army Air Forces in California
- Chico, California
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.