- PAL
-
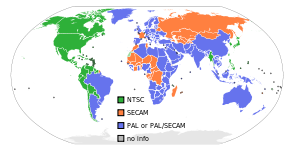
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system. The articles on broadcast television systems and analogue television further describe frame rates, image resolution and audio modulation. For discussion of the 625-line / 50 field (25 frame) per second television standard, see 576i.
Contents
History
In the 1950s, the Western European countries commenced planning to introduce colour television, and were faced with the problem that the NTSC standard demonstrated several weaknesses, including colour tone shifting under poor transmission conditions. To overcome NTSC's shortcomings, alternative standards were devised, resulting in the development of the PAL and SECAM standards. The goal was to provide a colour TV standard for the European picture frequency of 50 fields per second (50 hertz), and finding a way to eliminate the problems with NTSC.
PAL was developed by Walter Bruch at Telefunken in Germany. The format was unveiled in 1963, with the first broadcasts beginning in the United Kingdom in 1964 and Germany in 1967,[1] though the one BBC channel initially using the broadcast standard only began to broadcast in colour from 1967. Telefunken PALcolor 708T was the first PAL commercial TV set. It followed by Loewe S 920 & F 900
Telefunken was later bought by the French electronics manufacturer Thomson. Thomson also bought the Compagnie Générale de Télévision where Henri de France developed SECAM, the first European Standard for colour television. Thomson, now called Technicolor SA, also owns the RCA brand and licenses it to other companies; Radio Corporation of America, the originator of that brand, created the NTSC colour TV standard before Thomson became involved.
The term PAL is often used informally and somewhat imprecisely to refer to the 625-line/50 Hz (576i) television system in general, to differentiate from the 525-line/60 Hz (480i) system generally used with NTSC. Accordingly, DVDs are labelled as either PAL or NTSC (referring informally to the line count and frame rate) even though technically the discs do not have either PAL or NTSC composite colour. The line count and frame rate are defined as EIA 525/60 or CCIR 625/50; PAL and NTSC are only the method of embedding colour in the transmission.
Colour encoding
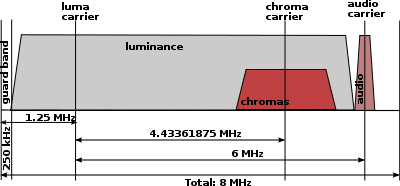
Both the PAL and the NTSC system use a quadrature amplitude modulated subcarrier carrying the chrominance information added to the luminance video signal to form a composite video baseband signal. The frequency of this subcarrier is 4.43361875 MHz for PAL, compared to 3.579545 MHz for NTSC. The SECAM system, on the other hand, uses a frequency modulation scheme on its two line alternate colour subcarriers 4.25000 and 4.40625 MHz.
The name "Phase Alternating Line" describes the way that the phase of part of the colour information on the video signal is reversed with each line, which automatically corrects phase errors in the transmission of the signal by cancelling them out, at the expense of vertical frame colour resolution. Lines where the colour phase is reversed compared to NTSC are often called PAL or phase-alternation lines, which justifies one of the expansions of the acronym, while the other lines are called NTSC lines. Early PAL receivers relied on the human eye to do that cancelling; however, this resulted in a comb-like effect known as Hanover bars on larger phase errors. Thus, most receivers now use a chrominance delay line, which stores the received colour information on each line of display; an average of the colour information from the previous line and the current line is then used to drive the picture tube. The effect is that phase errors result in saturation changes, which are less objectionable than the equivalent hue changes of NTSC. A minor drawback is that the vertical colour resolution is poorer than the NTSC system's, but since the human eye also has a colour resolution that is much lower than its brightness resolution, this effect is not visible. In any case, NTSC, PAL, and SECAM all have chrominance bandwidth (horizontal colour detail) reduced greatly compared to the luminance signal.
The 4.43361875 MHz frequency of the colour carrier is a result of 283.75 colour clock cycles per line plus a 25 Hz offset to avoid interferences. Since the line frequency (number of lines per second) is 15625 Hz (625 lines x 50 Hz / 2), the colour carrier frequency calculates as follows: 4.43361875 MHz = 283.75 * 15625 Hz + 25 Hz.
The original colour carrier is required by the colour decoder to recreate the colour difference signals. Since the carrier is not transmitted with the video information it has to be generated locally in the receiver. In order that the phase of this locally generated signal can match the transmitted information, a 10 cycle burst of colour subcarrier is added to the video signal shortly after the line sync pulse, but before the picture information, during the so called back porch. This colour burst is not actually in phase with the original colour subcarrier, but leads it by 45 degrees on the odd lines and lags it by 45 degrees on the even lines. This swinging burst enables the colour decoder circuitry to distinguish the phase of the R-Y vector which reverses every line.
PAL vs. NTSC
NTSC receivers have a tint control to perform colour correction manually. If this is not adjusted correctly, the colours may be faulty. The PAL standard automatically cancels hue errors by phase reversal, so a tint control is unnecessary. Chrominance phase errors in the PAL system are cancelled out using a 1H delay line resulting in lower saturation, which is much less noticeable to the eye than NTSC hue errors.
However, the alternation of colour information — Hanover bars — can lead to picture grain on pictures with extreme phase errors even in PAL systems, if decoder circuits are misaligned or use the simplified decoders of early designs (typically to overcome royalty restrictions). In most cases such extreme phase shifts do not occur. This effect will usually be observed when the transmission path is poor, typically in built up areas or where the terrain is unfavourable. The effect is more noticeable on UHF than VHF signals as VHF signals tend to be more robust.
In the early 1970s some Japanese set manufacturers developed decoding systems to avoid paying royalties to Telefunken. The Telefunken license covered any decoding method that relied on the alternating subcarrier phase to reduce phase errors. This included very basic PAL decoders that relied on the human eye to average out the odd/even line phase errors. One solution was to use a 1H delay line to allow decoding of only the odd or even lines. For example, the chrominance on odd lines would be switched directly through to the decoder and also be stored in the delay line. Then, on even lines, the stored odd line would be decoded again. This method effectively converted PAL to NTSC. Such systems suffered hue errors and other problems inherent in NTSC and required the addition of a manual hue control.
PAL and NTSC have slightly divergent colour spaces, but the colour decoder differences here are ignored.
PAL vs. SECAM
SECAM is an earlier attempt at compatible colour television which also tries to resolve the NTSC hue problem. It does so by applying a different method to colour transmission, namely alternate transmission of the U and V vectors and frequency modulation, while PAL attempts to improve on the NTSC method.
SECAM transmissions are more robust over longer distances than NTSC or PAL. However, owing to their FM nature, the colour signal remains present, although at reduced amplitude, even in monochrome portions of the image, thus being subject to stronger cross colour. Like PAL, a SECAM receiver needs a delay line.
PAL signal details
For PAL-B/G the signal has these characteristics.
Parameter Value Pixel Clock frequency
(digital sources with 704
or 720 active Pixel/Line)13.5 MHz Bandwidth 5 MHz[2] Horizontal sync polarity Negative Total time for each line 64.000 µs[3][4] Front porch (A) 1.65+0.4
−0.1 µsSync pulse length (B) 4.7±0.20 µs Back porch (C) 5.7±0.20 µs Active video (D) 51.95+0.4
−0.1 µs(Total horizontal sync time 12.05 µs)
After 0.9 µs a 2.25±0.23 µs colorburst of 10±1 cycles is sent. Most rise/fall times are in 250±50 ns range. Amplitude is 100% for white level, 30% for black, and 0% for sync.[3] The CVBS electrical amplitude is Vpp 1.0 V and impedance of 75 Ω.[5]
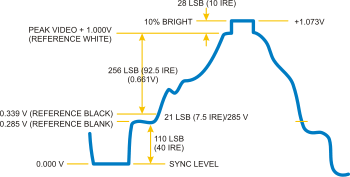 The composite video (CVBS) signal used in systems M and N before combination with a sound carrier and modulation onto an RF carrier.
The composite video (CVBS) signal used in systems M and N before combination with a sound carrier and modulation onto an RF carrier.
The vertical timings are:
Parameter Value Vertical lines 313 (625 total) Vertical lines visible 288 (576 total) Vertical sync polarity Negative (burst) Vertical frequency 50 Hz Sync pulse length (F) 0.576 ms (burst)[6] Active video (H) 18.4 ms (Total vertical sync time 1.6 ms)
As PAL is interlaced, every two fields are summed to make a complete picture frame.
Luminance, Y, is derived from red, green, and blue (R'G'B') signals:[4]
- Y = 0.299R' + 0.587G' + 0.114B'
U and V are used to transmit chrominance. Each has a typical bandwidth of 1.3 MHz.
- U = 0.492(B' − Y)
- V = 0.877(R' − Y)
Composite PAL signal = Y + Usin(ωt) + Vcos(ωt) + timing[4] where ω = 2πFSC.
Subcarrier frequency FSC is 4.43361875 MHz (±5 Hz) for PAL-B/D/G/H/I/N.
PAL broadcast systems
This table illustrates the differences:
PAL B PAL G, H PAL I PAL D/K PAL M PAL N Transmission Band VHF UHF UHF/VHF* VHF/UHF VHF/UHF VHF/UHF Fields 50 50 50 50 60 50 Lines 625 625 625 625 525 625 Active lines 576 576 582** 576 480 576 Channel Bandwidth 7 MHz 8 MHz 8 MHz 8 MHz 6 MHz 6 MHz Video Bandwidth 5.0 MHz 5.0 MHz 5.5 MHz 6.0 MHz 4.2 MHz 4.2 MHz Colour Subcarrier 4.43361875 MHz 4.43361875 MHz 4.43361875 MHz 4.43361875 MHz 3.575611 MHz 3.58205625 MHz Sound Carrier 5.5 MHz 5.5 MHz 6.0 MHz 6.5 MHz 4.5 MHz 4.5 MHz * System I has never been used on VHF in the UK.
** The UK's adoption of 582 active lines[7] has no significant impact on either non system I receivers or non system I source material as the extra lines are not within the normal display area and do not contain anything in the other standards anyway. All Digital TV broadcasts and digital recordings (e.g. DVDs) conform to the 576 active line standard.PAL-B/G/D/K/I
The majority of countries using PAL have television standards with 625 lines and 25 frames per second, differences concern the audio carrier frequency and channel bandwidths. Standards B/G are used in most of Western Europe, Australia and New Zealand, standard I in the UK, Ireland, Hong Kong, South Africa and Macau, standards D/K in most of Central and Eastern Europe and Standard D in mainland China. Most analogue CCTV cameras are Standard D.
Systems B and G are similar. System B is used for 7 MHz-wide channels on VHF, while System G is used for 8 MHz-wide channels on UHF (and Australia uses System B on UHF). Similarly, Systems D and K are similar except for the bands they use: System D is only used on VHF, while System K is only used on UHF. Although System I is used on both bands, it has only been used on UHF in the United Kingdom due to 405-line TV services on VHF operating until the 1980s.
PAL-M (Brazil)
In Brazil, PAL is used in conjunction with the 525 line, 29.97 frame/s system M, using (very nearly) the NTSC colour subcarrier frequency. Exact colour subcarrier frequency of PAL-M is 3.575611 MHz. Almost all other countries using system M use NTSC.
The PAL colour system (either baseband or with any RF system, with the normal 4.43 MHz subcarrier unlike PAL-M) can also be applied to an NTSC-like 525-line (480i) picture to form what is often known as "PAL-60" (sometimes "PAL-60/525", "Quasi-PAL" or "Pseudo PAL"). PAL-M (a broadcast standard) however should not be confused with "PAL-60" (a video playback system — see below).
PAL-N (Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay)
In Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay the PAL-N variant is used. It employs the 625 line/50 field per second waveform of PAL-B/G, D/K, H, I, but on a 6MHz channel with a chrominance subcarrier frequency of 3.582 MHz very similar to NTSC.
VHS tapes recorded from a PAL-N or a PAL-B/G, D/K, H, I broadcast are indistinguishable because the downconverted subcarrier on the tape is the same. A VHS recorded off TV (or released) in Europe will play in colour on any PAL-N VCR and PAL-N TV in Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay. Likewise, any tape recorded in Argentina or Uruguay off a PAL-N TV broadcast, can be sent to anyone in European countries that use PAL (and Australia/New Zealand, etc.) and it will display in colour. This will also play back successfully in Russia and other SECAM countries, as the USSR mandated PAL compatibility in 1985 - this has proved to be very convenient for video collectors.
People in Uruguay, Argentina and Paraguay usually own TV sets that also display NTSC-M, in addition to PAL-N. Direct TV also conveniently broadcasts in NTSC-M for North, Central and South America. Most DVD players sold in Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay also play PAL discs - however, this is usually output in the European variant (colour subcarrier frequency 4.433618 MHz), so people who own a TV set which only works in PAL-N (plus NTSC-M in most cases) will have to watch those PAL DVD imports in black and white as the colour subcarrier frequency in the TV set is the PAL-N variation, 3.582056 MHz.
In the case that a VHS or DVD player works in PAL (and not in PAL-N) and the TV set works in PAL-N (and not in PAL), there are two options:
- images can be seen in black and white, or
- an inexpensive transcoder (PAL -> PAL-N) can be purchased in order to see the colours
Some DVD players (usually lesser known brands) include an internal transcoder and the signal can be output in NTSC-M, with some video quality loss due to the system's conversion from a 625/50 PAL DVD to the NTSC-M 525/60 output format. A few DVD players sold in Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay also allow a signal output of NTSC-M, PAL, or PAL-N. In that case, a PAL disc (imported from Europe) can be played back on a PAL-N TV because there are no field/line conversions, quality is generally excellent.
Extended features of the PAL specification, such as Teletext, are implemented quite differently in PAL-N. PAL-N supports a modified 608 closed captioning format that is designed to ease compatibility with NTSC originated content carried on line 18, and a modified teletext format that can occupy several lines.
PAL-L
The PAL L (Phase Alternating Line with L-sound system) standard uses the same video system as PAL-B/G/H (625 lines, 50 Hz field rate, 15.625 kHz line rate), but with 6 MHz video bandwidth rather than 5.5 MHz. This requires the audio subcarrier to be moved to 6.5 MHz. An 8 MHz channel spacing is used for PAL-L.
System A
The BBC tested their pre-war 405 line monochrome system with all three colour standards including PAL, before the decision was made to abandon 405 and transmit colour on 625/System I only.
PAL interoperability
The PAL colour system is usually used with a video format that has 625 lines per frame (576 visible lines, the rest being used for other information such as sync data and captioning) and a refresh rate of 50 interlaced fields per second (i.e. 25 full frames per second), such systems being B, G, H, I, and N (see broadcast television systems for the technical details of each format).
This ensures video interoperability. However as some of these standards (B/G/H, I and D/K) use different sound carriers (5.5MHz, 6.0MHz 6.5MHz respectively), it may result in a video image without audio when viewing a signal broadcast over the air or cable. Some countries in Eastern Europe which formerly used SECAM with systems D and K have switched to PAL while leaving other aspects of their video system the same, resulting in the different sound carrier. Instead, other European countries have changed completely from SECAM-D/K to PAL-B/G.[8]
The PAL-N system has a different sound carrier, and also a different colour subcarrier, and decoding on incompatible PAL systems results in a black and white image without sound. The PAL-M system has a different sound carrier and a different colour subcarrier, and does not use 625 lines or 50 frames/second. This would result in no video or audio at all when viewing a European signal.
Multisystem PAL support and "PAL 60"
Recently manufactured PAL television receivers can typically decode all of these systems except, in some cases, PAL-M and PAL-N. Many of receivers can also receive Eastern European and Middle Eastern SECAM, though rarely French-broadcast SECAM (because France uses the unique positive video modulation) unless they are manufactured for the French market. They will correctly display plain CVBS or S-video SECAM signals. Many can also accept baseband NTSC-M, such as from a VCR or game console, and RF modulated NTSC with a PAL standard audio subcarrier (i.e. from a modulator), though not usually broadcast NTSC (as its 4.5 MHz audio subcarrier is not supported). Many sets also support NTSC with a 4.43 MHz subcarrier.
Many 1990s onwards VCR players sold in Europe can play back NTSC tapes/discs. When operating in this mode most of them do not output a true (625/25) PAL signal, but rather a hybrid consisting of the original NTSC line standard (525/30), but with colour converted to PAL 4.43 MHz - this is known as "PAL 60" (also "quasi-PAL" or "pseudo PAL") with "60" standing for 60 Hz (for 525/30), instead of 50 Hz (for 625/25). Some video game consoles also output a signal in this mode. Most newer television sets can display such a signal correctly, but some will only do so (if at all) in black and white and/or with flickering/foldover at the bottom of the picture, or picture rolling (however, many old TV sets can display the picture properly by means of adjusting the V-Hold and V-Height knobs — assuming they have them). Some TV tuner cards or video capture cards will support this mode (although software/driver modification can be required and the manufacturers' specs may be unclear). A "PAL 60" signal is similar to an NTSC (525/30) signal, but with the usual PAL chrominance subcarrier at 4.43 MHz (instead of 3.58 as with NTSC and South American PAL variants) and with the PAL-specific phase alternation of the red colour difference signal between the lines.
Most European DVD players output a true NTSC-M signal when playing NTSC discs, which many modern European TV sets can resolve.
Countries and territories using PAL
Over 120 countries and territories use or once used the terrestrial PAL system. Many of these are currently converting terrestrial PAL to DVB-T (PAL still often used by cable TV or in conjunction with a digital standard, such as DVB-C).
PAL B, G, D, K or I
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Albania (DVB-T introduction started in 2004)
Albania (DVB-T introduction started in 2004) Angola
Angola Ascension Island (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012, simulcast in DVB-T)
Ascension Island (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012, simulcast in DVB-T) Australia (DVB-T introduction started in 2001, PAL-B to be abandoned for DVB-T by 2013)
Australia (DVB-T introduction started in 2001, PAL-B to be abandoned for DVB-T by 2013) Bahrain (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Bahrain (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Bangladesh
Bangladesh Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana
Botswana Brunei
Brunei Bulgaria (migrated from SECAM 1994–1996) (set to migrate to DVB-T in 2012, although such broadcasts are currently only available in Sofia)
Bulgaria (migrated from SECAM 1994–1996) (set to migrate to DVB-T in 2012, although such broadcasts are currently only available in Sofia) Cameroon
Cameroon Cape Verde
Cape Verde China (PAL-D, digital broadcast using DMB-T/H)
China (PAL-D, digital broadcast using DMB-T/H) Chile (historic[citation needed], Chile adopted NTSC-M and now will be abandoned for ISDB-T)
Chile (historic[citation needed], Chile adopted NTSC-M and now will be abandoned for ISDB-T) Christmas Island (see Australia)
Christmas Island (see Australia) Cook Islands (see New Zealand)
Cook Islands (see New Zealand) Croatia (PAL broadcast abandoned by the end of 2010; broadcasting now in DVB-T, introduction started in 2005)
Croatia (PAL broadcast abandoned by the end of 2010; broadcasting now in DVB-T, introduction started in 2005) Cyprus
Cyprus Czech Republic (migrated from SECAM 1992–1994) (DVB-T introduction started in 2006, PAL to be abandoned for DVB-T by 2012)
Czech Republic (migrated from SECAM 1992–1994) (DVB-T introduction started in 2006, PAL to be abandoned for DVB-T by 2012) East Timor (Timor-Leste)
East Timor (Timor-Leste) Egypt (migrated from SECAM 1990–1992)
Egypt (migrated from SECAM 1990–1992) Eritrea
Eritrea Ethiopia
Ethiopia Falkland Islands (UHF only)
Falkland Islands (UHF only) Fiji
Fiji Gambia
Gambia Georgia (used SECAM, completely migrated to PAL-D/K in 2000s)
Georgia (used SECAM, completely migrated to PAL-D/K in 2000s) Germany (East Germany used SECAM, after reunification migrated to PAL in early 1990s; PAL broadcast abandoned at the end of 2008; DVB-T introduction started in 2003)
Germany (East Germany used SECAM, after reunification migrated to PAL in early 1990s; PAL broadcast abandoned at the end of 2008; DVB-T introduction started in 2003) Ghana
Ghana Gibraltar
Gibraltar Greece (State TV ERT migrated from SECAM in ca. 1992- private channels use PAL since their launch in 1989 - DVB-T introduction started in 2006.)
Greece (State TV ERT migrated from SECAM in ca. 1992- private channels use PAL since their launch in 1989 - DVB-T introduction started in 2006.) Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Guinea
Guinea Hong Kong (PAL-I, DMB-T/H introduced since 31 December 2007, PAL-I broadcast planned to be abandoned in 2015)
Hong Kong (PAL-I, DMB-T/H introduced since 31 December 2007, PAL-I broadcast planned to be abandoned in 2015) Hungary (migrated from SECAM 1995–1996; PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 31 December 2014; is converting to DVB-T)
Hungary (migrated from SECAM 1995–1996; PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 31 December 2014; is converting to DVB-T) Iceland
Iceland India
India Indonesia (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2018; simulcast in DVB-T since 2008)
Indonesia (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2018; simulcast in DVB-T since 2008) Iran
Iran Iraq (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Iraq (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Ireland (VHF and UHF)
Ireland (VHF and UHF) Israel (PAL transmitter shutdown started 31 March 2011 and completed on 13 June 2011; converted to DVB-T)
Israel (PAL transmitter shutdown started 31 March 2011 and completed on 13 June 2011; converted to DVB-T) Italy (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012, already abandoned in some provinces; currently converting to DVB-T)
Italy (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012, already abandoned in some provinces; currently converting to DVB-T) Jordan (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Jordan (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Kenya
Kenya Kosovo
Kosovo Kuwait
Kuwait Laos
Laos Lebanon (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Lebanon (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Lesotho
Lesotho Liberia
Liberia Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Lithuania (migrated from SECAM 1997–1999; PAL to be abandoned by 29 October 2012, Simulcast in DVB-T)
Lithuania (migrated from SECAM 1997–1999; PAL to be abandoned by 29 October 2012, Simulcast in DVB-T)
 Macau (PAL-I, digital broadcast using DMB-T/H)
Macau (PAL-I, digital broadcast using DMB-T/H) Macedonia (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012; DVB-T introduction started in 2005)
Macedonia (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012; DVB-T introduction started in 2005) Malawi
Malawi Malaysia (Preliminary DVB-T Trials ended, further trials planned. Set top box and Digital TV not yet available on sale, but USB DVB-T receivers for viewing on a computer are widely available now. Plans to abandon PAL broadcast by 2015)
Malaysia (Preliminary DVB-T Trials ended, further trials planned. Set top box and Digital TV not yet available on sale, but USB DVB-T receivers for viewing on a computer are widely available now. Plans to abandon PAL broadcast by 2015) Maldives
Maldives Moldova
Moldova Montenegro
Montenegro Morocco
Morocco Mozambique
Mozambique Namibia
Namibia Nepal
Nepal Netherlands (Broadcasting now in DVB-T)
Netherlands (Broadcasting now in DVB-T) New Zealand (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012–2017, simulcast in DVB-S (since 2007) & DVB-T (gradually rolled out since mid-2008 starting with major centres))
New Zealand (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012–2017, simulcast in DVB-S (since 2007) & DVB-T (gradually rolled out since mid-2008 starting with major centres)) Nigeria
Nigeria Norfolk Island (see Australia)
Norfolk Island (see Australia) North Korea
North Korea Oman (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Oman (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Pakistan
Pakistan Palestine (Gaza & West Bank, DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Palestine (Gaza & West Bank, DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Poland (migrated from SECAM 1993–1995; PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2013; is converting to DVB-T)
Poland (migrated from SECAM 1993–1995; PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2013; is converting to DVB-T) Portugal, including
Portugal, including  Madeira and
Madeira and  Azores (PAL broadcast to be fully abandoned by 2011, DVB-T simulcast since 2007)
Azores (PAL broadcast to be fully abandoned by 2011, DVB-T simulcast since 2007) Qatar (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Qatar (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Romania (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2010–2011; is converting to DVB-T since early 2007)
Romania (PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2010–2011; is converting to DVB-T since early 2007) Samoa (Samoa is converting to NTSC and probably ATSC)
Samoa (Samoa is converting to NTSC and probably ATSC) Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Serbia (DVB-T introduction started in 2005, PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2015)
Serbia (DVB-T introduction started in 2005, PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2015) Seychelles
Seychelles Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Singapore (DVB-T introduction started in 2004, PAL to be fully abandoned by 2015-2020)
Singapore (DVB-T introduction started in 2004, PAL to be fully abandoned by 2015-2020) Slovakia (migrated from SECAM 1992–1994; PAL to be fully abandoned by 2012, converted to DVB-T)
Slovakia (migrated from SECAM 1992–1994; PAL to be fully abandoned by 2012, converted to DVB-T) Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Somalia
Somalia South Africa (PAL to be abandoned by 2013, is converting to DVB-T)
South Africa (PAL to be abandoned by 2013, is converting to DVB-T) South Sudan
South Sudan Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Sudan
Sudan Swaziland
Swaziland Syria
Syria Tanzania
Tanzania Thailand
Thailand Tonga (Tonga is converting to NTSC and probably ATSC)
Tonga (Tonga is converting to NTSC and probably ATSC) Tristan da Cunha
Tristan da Cunha Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey Uganda
Uganda Ukraine (along with SECAM)
Ukraine (along with SECAM) United Kingdom (UHF only, PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012, already abandoned in some regions. Simulcast in DVB-T. DVB-T introduction started in 1998, DVB-T2 added from 2009.)
United Kingdom (UHF only, PAL broadcast to be abandoned by 2012, already abandoned in some regions. Simulcast in DVB-T. DVB-T introduction started in 1998, DVB-T2 added from 2009.) Vanuatu
Vanuatu Vatican City
Vatican City Vietnam
Vietnam Yemen (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment)
Yemen (DVB-T introduction currently in assessment) Zambia
Zambia Zanzibar
Zanzibar Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
PAL-M
 Brazil (simulcast with digital format in SBTVD-T, an update to ISDB-T, started in December 2007. PAL broadcast continues until 2016)
Brazil (simulcast with digital format in SBTVD-T, an update to ISDB-T, started in December 2007. PAL broadcast continues until 2016)
PAL-N
 Argentina (H264 video over ISDB-T, at 576i@50Hz (SD) or 1080i@50Hz (HD))
Argentina (H264 video over ISDB-T, at 576i@50Hz (SD) or 1080i@50Hz (HD)) Paraguay
Paraguay Uruguay (will use ISDB-T, but no date decided yet)
Uruguay (will use ISDB-T, but no date decided yet)
Countries and territories that once used PAL
Country Switched to Switchover completed  Andorra
AndorraDVB-T 25 September 2007  Austria
AustriaDVB-T 7 June 2011  Belgium
BelgiumDVB-T 1 March 2010  Croatia
CroatiaDVB-T 5 October 2010  Denmark
DenmarkDVB-T 1 November 2009  Estonia
EstoniaDVB-T 1 July 2010  Finland
FinlandDVB-T 1 September 2007  Israel
IsraelDVB-T 13 June 2011  Latvia
LatviaDVB-T 1 June 2010  Luxembourg
LuxembourgDVB-T 1 September 2006  Malta
MaltaDVB-T 31 October 2011  Netherlands
NetherlandsDVB-T 14 December 2006  Norway
NorwayDVB-T 1 December 2009  Slovenia
SloveniaDVB-T 1 December 2010  Spain
SpainDVB-T 3 April 2010  Sweden
SwedenDVB-T 29 October 2007  Switzerland
SwitzerlandDVB-T 26 November 2007 See also
- PALplus
- Broadcast television systems
- ATSC Standards
- BTSC
- NTSC
- NTSC-J
- RCA
- SECAM
- Moving image formats
- Early television stations
- Digital television
- Broadcast safe
- PAL region
- Differential gain
References
- ^ The standard that defines the PAL system was published by the International Telecommunications Union in 1998 and has the title Recommendation ITU-R BT.470-6, Conventional Television Systems
- ^ "PGC categories - Countries using PAL standard". http://www.dvd-replica.com/DVD/palnations.php. 090426 dvd-replica.com
- ^ a b "Horizontal Blanking Interval of 405-, 525-, 625- and 819-Line Standards". http://www.pembers.freeserve.co.uk/World-TV-Standards/HBI.pdf. 090426 pembers.freeserve.co.uk
- ^ a b c "NTSC, PAL, and SECAM Overview". http://www.deetc.isel.ipl.pt/Analisedesinai/sm/downloads/doc/ch08.pdf. 090426 deetc.isel.ipl.pt page 52
- ^ "empty". http://www.thomsongrassvalley.com/docs/Manuals/cameras/ldk5400/3922-496-46791.s03.v01.pdf. 090426 thomsongrassvalley.com
- ^ "empty". http://www.pembers.freeserve.co.uk/World-TV-Standards/VBI-625-PAL.pdf. 090426 pembers.freeserve.co.uk
- ^ Report 308-2 of the XIIth Pleniary Assembly of the CCIR - Characteristics of Monochrome Television Systems
- ^ "Changes to the terrestrial television systems in Central and East European countries". EBU. http://tech.ebu.ch/docs/i/i033.pdf. Retrieved 11 September 2010.
External links
- More information about TV standards
- Review of the different refresh rates of PAL, NTSC and motion picture films
- Australian VHF/UHF PAL B/G Television System Datasheet
- Convert PAL DVD to NTSC DVD
Broadcast video formats Television 525 lines625 linesHidden signalsDefunct systemsInterlacedMPEG-2 standardsMPEG-4 AVC standards- AC-3 (5.1)
- DTS
- MPEG-1 Audio Layer II
- MPEG Multichannel
- PCM
- LPCM
- AAC
- HE-AAC
Hidden signalsDigital cinema Technical issues Color space CIE RGB color spaces · sRGB · Adobe · Wide Gamut · ProPhoto · scRGB
YUV Other Telecommunications (general) History - Beacons
- Broadcasting
- Computer networks
- Drums
- Electrical telegraphy
- Fax
- Heliography
- Hydraulic telegraphs
- Internet
- Mass media
- Mobile phones
- Optical telegraphy
- Photophone
- Radio
- Radiotelephone
- Satellite communications
- Telegraphy
- Telephones
- Telephone patent controversies
- Television
- Undersea telegraph lines
- Videophones

Pioneers Mediums - Coaxial cable
- Free-space optical
- Landlines
- Optical fiber
- Radio waves
- Terrestrial microwave
Networks Geographic Telecommunications in Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Telecommunications in North America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Navassa Island
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
Telecommunications in South America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territoriesTelecommunications in Oceania Sovereign states - Australia
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Fiji
- Indonesia
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
Telecommunications in Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Telecommunications in Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territories- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Hong Kong
- Macau
Categories:- Color space
- Video formats
- Television technology
- Television terminology
- ITU-R recommendations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.