- Telecommunications in Barbados
-
Communications in Barbados refers to the telephony, internet, postal, radio, and television systems of Barbados. Barbados has long been an informational and communications centre in the Caribbean region. Electricity coverage throughout Barbados is good and reliable. Usage is high and provided by a service monopoly, Barbados Light & Power Company Ltd. (a division of Canada-based Emera).
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) call sign prefix allocated for all radio and television broadcasts in Barbados is 8P, and this replaced the former ZN as a British territory.
Contents
History
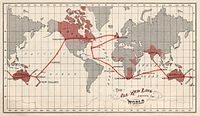 The All Red Line cable for the British Empire. Barbados(Barbadoes) functioned as a interconnection-point between Bermuda and Ascension Island in the Atlantic Ocean. c.a. 1903
The All Red Line cable for the British Empire. Barbados(Barbadoes) functioned as a interconnection-point between Bermuda and Ascension Island in the Atlantic Ocean. c.a. 1903
Barbados has had various forms of Communications as early as the 1840s. Some of the earliest expressions of inter-island communication includes a number of signal stations built along the high points of the island to relay acts of transgression towards the island to the Saint Ann's Garrison on the south-west coast. The first telephone network in the country was developed in 1884.[1] As the former British Empire's All Red Line came into existence during the early 1900s, Barbados played an importain role as a crucial link in the trans-Atlantic communications network. By 1935 a hard wired cable-based radio network was later deployed throughout the country to broadcast the Rediffusion service directly from London to homes and business across Barbados.[2] In 2001 the Government of Barbados and the local Incumbent Local Exchange Carrier (ILEC) provider, Cable & Wireless signed a MOU beginning a phased process of liberalisation of the international segment of Barbados' telecommunications sector.[3] The process was aimed at bringing Barbados' sector into compliance with the World Trade Organisation (WTO). The plan outlined the first phase commencing on 1 December 2001 and the entire process ending with full liberalisation being achieved on 1 August 2003. As these target dates were missed, the Phase I process was later commenced on 1 November 2002, with Phase II and III beginning on 16 November 2003 and 21 February 2004 respectively. Full liberalisation was attained in February, 2005, for the international telecommunications services market.[4]
Telephone
The rate of telecommunications penetration in Barbados ranks among the highest in the world. According to the International Telecommunication Union, telephone service for the period 2000-2004, stated Barbados had 124 telephones in usage for every 100 people.[5] Telecommunications are virtually universally accessible to all.
- Telephones - main lines in use
- 134,900 (2005)
- county comparison to the world: 133
- Telephones - mobile cellular
- 237,100 (2006)
- county comparison to the world: 165
- Telephone system
-
- general assessment: fixed-line teledensity of roughly 50 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone density of about 85 per 100 persons
- domestic: island-wide automatic telephone system
- international access code: +1.246 (in the North American Numbering Plan, Area code 246);
-
- landing point for:
-
- 1) the East Caribbean Fiber System (ECFS) submarine cable with links to 13 other islands in the eastern Caribbean extending from the British Virgin Islands to Trinidad;
- 2); the Antilles Crossing Phase 1 link to the US Virgin Islands via Saint Lucia;
- satellite earth stations - 1 (Intelsat - Atlantic Ocean); tropospheric scatter to Trinidad and Saint Lucia (2007)
Broadcasting
- Radio broadcast stations
- AM 2, FM 6, shortwave 0 (2004)
-
- (VOB-AM 790 (Gospel), 8PX-AM 900 (CBC)
- (BBS 90.7FM, PBS 91.9FM, BBC 92.1FM, VOB 92.9FM, CBC 94.7FM, HOTT 95.3FM, Mix 96.9FM, Gospel 97.5FM, The One 98.1FM, WE 99.9FM(SVG), Q 100.7FM, SLAM 101.1FM, Faith 102.1FM, Love 104.1FM, Radio GED 106.1 FM)
-
- Radios
- 237,000 (1997)
- Television broadcast stations
- 1 (plus two cable channels) (2004)
-
- 8PX-TV (C.B.C. TV8)
- Public Broadcast Service (PBS) -- Scheduled for 2009
-
- Televisions
- 76,000 (1997)
Internet
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
- 3+ (1999)
- (Cable & Wireless(CaribSurf), TeleBarbados/Freemotion.bb, Sunbeach Communications)
- Internet country code
- .BB
- Internet hosts
- 104 (2008)
- county comparison to the world: 178
- Internet users
- 160,000 (2005)
- county comparison to the world: 131
Broadband Internet access
Globally, the country of Barbados was ranked by the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) and UNICEF to be one of the most wired countries in the world on a per capita basis. The report entitled "State Of The World's Children 2007" stated Barbados had rate of Internet usage which was 55 users for every 100 people. This ranking meant that only 13 nations: Australia, Canada, Finland, South Korea, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, San Marino, Singapore, Sweden, Britain and the United States had a higher ratios per head of population. In so scoring this placed Barbados in the lead for the Caribbean and Latin America regions.
Telephone services in Barbados are provided by: LIME (Incumbent), Digicel, Sunbeach, WIISCOM, Internet services in the country are provided by: CariAccess, CaribSurf, Sunbeach Communications, TeleBarbados/Freemotion.bb, WI-NET INC.
ADSL services are widely available, as are Frame Relay and other more advanced services.
See also
References
- ^ About us - History: Cable & Wireless Barbados
- ^ STARCOM Network Inc. -- Our History of Broadcasting Excellence
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ Best, Tony (2006-12-27). "Barbados 'well wired'". Nation Newspaper. Archived from the original on 2007-12-23. http://web.archive.org/web/20071223220250/http://www.nationnews.com/story/319373050722253.php. Retrieved 2009-06-30.
 This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document 2004, 2006 and 2009/index.html "2000, 2004, 2006 and 2009 edition".
This article incorporates public domain material from the CIA World Factbook document 2004, 2006 and 2009/index.html "2000, 2004, 2006 and 2009 edition".
External links
- telecoms.gov.bb - Government of Barbados' Telecommunications unit
- The Telecommunications Act, 2001
- Statistic by the Government of Barbados as of 2010
Telecommunications (general) History Beacons · Broadcasting · Computer networks · Drums · Electrical telegraphy · Fax · Heliography · Hydraulic telegraphs · Internet · Mass media · Mobile phones · Optical telegraphy · Photophone · Radio · Radiotelephone · Satellite communications · Telegraphy · Telephones · Telephone patent controversies · Television · Undersea telegraph lines · Videophones
Pioneers Alexander Graham Bell · Alfred Vail · Alexander Popov · Charles Wheatstone · Claude Chappe · Edwin Armstrong · Elisha Gray · Guglielmo Marconi · Jagadish Bose · Johann Philipp Reis · John Logie Baird · Lee De Forest · Nikola Tesla · Philo Farnsworth · Reginald Fessenden · Tim Berners-Lee · Vint Cerf · Vladimir ZworykinMediums Coaxial cable · Free-space optical · Landlines · Optical fiber · Radio waves · Terrestrial microwaveNetworks Advanced Research Projects Agency · BITNET · Ethernet · FidoNet · ISDN · Internet · Local area · Mobile/Cellular · NGN · Packet switched · Public Switched Telephone · Radio · Television · Telex · Wide area · World Wide Web · WirelessGeographic Telecommunications in Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Telecommunications in North America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Navassa Island
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
Telecommunications in South America Sovereign states Dependencies and
other territoriesTelecommunications in Oceania Sovereign states - Australia
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Fiji
- Indonesia
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
Dependencies and
other territories- American Samoa
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Easter Island
- French Polynesia
- Guam
- Hawaii
- New Caledonia
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Pitcairn Islands
- Tokelau
- Wallis and Futuna
Telecommunications in Africa Sovereign
states- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Swaziland
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
States with limited
recognition- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
- Somaliland
Dependencies and
other territories- Canary Islands / Ceuta / Melilla / Plazas de soberanía (Spain)
- Madeira (Portugal)
- Mayotte / Réunion (France)
- Saint Helena / Ascension Island / Tristan da Cunha (United Kingdom)
- Western Sahara
Telecommunications in Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territories- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Hong Kong
- Macau
Telecommunications in the Americas - North America
- South America
Sovereign states - Antigua and Barbuda
- Argentina
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Bolivia
- Brazil
- Canada
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- Ecuador
- El Salvador
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Suriname
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
- Uruguay
- Venezuela
Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Falkland Islands
- French Guiana
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Navassa Island
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- US Virgin Islands
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

