- Telecommunications in Bangladesh
-
The liberalisation of Bangladesh’s telecommunications sector began with small steps in 1989 with the issuance of a licence to a private operator for the provision of inter alia cellular mobile services to compete with the previous monopoly provider of telecommunications services the Bangladesh Telegraph and Telephone Board (BTTB). Significant changes in the number of fixed and mobile services deployed in Bangladesh occurred in the late 1990s and the number of services in operation have subsequently grown exponentially in the past five years.
The incentives both from government and public sectors have helped to grow this sector.It is now one of the biggest sector of Bangladesh. As a populous country, it's huge market has attracted many foreign investors to invest in this sector
Contents
Telecommunication
The telecom sector in Bangladesh is rapidly emerging. Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC) is the regulatory authority for this sector, overseeing licensing, policy etc.
Calling Code: +880 – SubCodes
Landmarks in the history of telecom industry in Bangladesh[1]
- 1853 : Telegraph branch under Posts and Telegraph Department, British India.
- 1971 : Reconstructed as Bangladesh Telegraph and Telephone Department under Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications.
- 1975 : Reconstructed as Telegraph and Telephone Board.
- 1979 : Reconstructed as Bangladesh Telegraph and Telephone Board (BTTB) with right to issue license for telecom and wireless services.
- 1981 : Digital Telex Exchange in Bangladesh.
- 1983 : Automatic Digital ITX started in Dhaka.
- 1985 : Coinbox Telephone service introduced in Bangladesh by BTTB.
- 1989 : GENTEX Telegraph messaging service introduced in Bangladesh.
- 1989 : Bangladesh Rural Telecom Authority got license to operate exchanges in 200 upazilla.
- 1989 : Sheba Telecom got license to operate exchange is 199 upazilla.
- 1989 : Cellular mobile phone company Pacific Bangladesh Telephone Limited and Bangladesh Telecom got license.
- 1995 : Card Telephone service introduced in Bangladesh by BTTB and TSS.
- 1995 : Regulatory power of BTTB transferred to Ministry (MoPT).
- 1995 : 2nd and 3rd ITX installed in Dhaka.
- 1996 : GrameenPhone got cellular mobile Telephone license.
- 1996 : Telecom Malaysia International Bangladesh got cellular mobile license.
- 1998 : Telecom Policy.
- 2000 : Global Telecom Service (GTS) Telex Exchange venture with British Teleco.
- 2001 : Telecommunication Act, to establish Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC).
- 2002 : ICT Policy.
- 2004 : Teletalk cellular mobile launched.
- 2005 : Egypt-based Orascom acquired Sheba Telecom
- 2006 : NGN introduced in BTTB.
- 2008 : BTTB converted into Bangladesh Telecommunications Company Limited (BTCL) with 100% shares owned by Government.
- 2008 : Japanese NTT DoCoMo bought 30 percent stake in Aktel
- 2009 : Bharti Airtel acquired 70 percent stake in Warid Telecom
- 2009 : Internet Protocol Telephony Service Provider (IPTSP) Operators launched.
Structure
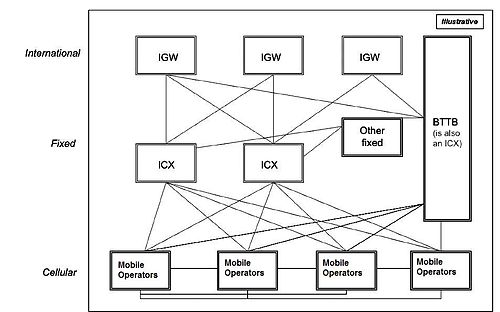
As defined in the National Telecommunications Policy 1998 and International Long Distance Telecommunications Services (ILDTS) Policy 2007, all mobile operators is to interconnect through Interconnection Exchange (ICX) and all international calls to be handled by International Gateway (IGW) which is to be connected to the mobile and fixed operators through the ICXs.
The Interconnection Exchange (ICX) will receive all calls from the mobile and fixed operators whenever the call is made to other network and will pass it to the destination network if the call is local, and will pass to the IGWs if the call is international. ICX will also deliver calls received from IGWs where the call is destined. [2]
Below illustrate the structure of interconnection between different interfaces.
PSTN
The PSTN or fixed operators in Bangladesh are:
- BTCL (former BTTB)
- Peoples Telecommunication and Information Services Ltd.
- Ranks Telecom Ltd. – Currently off air
- Tele Barta Ltd. – branded under the nameJubok phone
- Jalalabad Telecom Ltd. – branded under the name Bijoy Phone
- Onetel Communication Ltd.
- National Telecom Ltd.
- Westec Ltd.
- Dhaka Telephone Co. Ltd.
- Integrated Services Limited (ISL) – branded under the name Sheba Phone
- S.A Telecom System Ltd.
- Banglaphone Ltd.
The number of PSTN subscribers in Bangladesh as of February 2009 was 1.372 million.[3]
Mobile Phone Operators
There are 6 mobile phone operators in Bangladesh. These are:
1. Grameenphone Ltd.: Branded as Grameenphone
2. Axiata Bangladesh Ltd: Branded as Robi
3. Sheba Telecom Ltd.: Branded as Banglalink
4. Pacific Bangladesh Telephone Ltd.: Branded as Citycell
5. Teletalk Bangladesh Ltd.: Branded as Teletalk
6. Airtel Bangla Ltd. Branded as Airtel
The number of mobile phone subscribers in Bangladesh as of February 2009 was 45.21 million.[4], rising to 76.43 million at the end of June 2011[5].
Long Distance Operators (as per ILDTS Policy 2007)
On February 25, 2008 the Bangladesh Telecommunications Regulatory Commission awarded licenses for two Interconnection Exchanges (ICX), three International Gateways (IGw), and one International Internet Gateway (IIG) to six firms through an open auction in February 2008. The incumbent BTTB got the same licenses too. Here is the list of all operators:
International Gateway (IGW) Operators
1. Bangla Trac Communications Limited
2. Mir Telecom
4. BTCL
Interconnection Exchange (ICX) operators
1. Getco Telcommunications Ltd.
3. BTCL
International Internet Gateway (IIG) Operator
2. BTCL
Internet Protocol Telephony Service Provider (IPTSP) Operators
The IPTSP operators in Bangladesh are:
- Nationwide:
1. HRC Technologies Limited (GETCO Online Ltd.)
3. Information Services Network Limited
4. Agni Systems Ltd.
5. Innovative Online Limited
6. Dhakacom Limited
7. Connect BD Ltd.
8. Digital Connectivity Limited
9. BTS Communications (BD) Ltd
10. Royal Green Online Limited
11. Global Access Limited
12. Access Telecom (BD) Ltd.
13. Ranks ITT Ltd.
14. BDCOM Online Ltd.
15. Broad Band Telecom Services Limited
16. Link 3 Technologies Ltd
17. BRACNet Limited
18. Metronet Bangladesh Limited
19. Communication One (Pvt.) Limited
20. Telnet Communication Limited
21. X-Net Limited
22. Bangladesh Internet Exchange Limited
23. Nreach Net (Pvt.) Limited
24. Advanced Data Networks System Limited
25. Akij Online Limited
26. Bangladesh Export Import Company Limited
27. IDS Bangladesh
28. IS PROS LIMITED
29. Idea Networks And Communications Ltd
30. Pritty International (Pvt) Limited
31. Akceycom Limited
- Central:
1. Grameen Cybernet Limited
2. Fusion Net
3. M/s. Media & Multimedia
4. Next Online Limited
5. J F Optical Services
6. IT Connect Limited
7. Sine-10 (BD) Ltd.
8. SADIATEC Ltd
- Zonal:
1. Chittagong Online Limited
2. Chittagong Telecom Services Limited
3. HN TELECOM
On August 18, 2009 the Bangladesh Telecommunications Regulatory Commission awarded licenses for IPTSP. IPTSP operators are regulated by the BTRC.[6]
Radio
Radio broadcast stations: AM 12, FM 12, shortwave 2, community radio 1, internet radios
Radios: 6.15 million (1997)
The government owned Betar-Radio Bangladesh operates from Dhaka and other local districts. Currently, the private FM radio channels are very popular. They are trying to attract young people by broadcasting music and news. The operating private radio channels include:
- Radio Today FM
- Radio Foorti FM
- Radio Amar FM
- Radio Metrowave
- ABC Radio
Television
Television broadcast stations: 16 (1999)
Televisions: 770,000 (1997)
The number of private satellite channels is growing. The first private channel in Bangladesh was ATN Bangla.
Internet
Main article: Internet in BangladeshThe first connectivity of internet was only in 1996. Though It was somewhat late, over the past few years the growth is rapid. The government's high internet tariff is impeding the growth of this sector. Recently the government is decided to reduce the tariff 50%.[7]
Internet country code: .bd
Internet Service Providers (ISPs): As of 2005 more than 180 Internet Service Providers are operating in the country.[8] ISP's are regulated by the Bangladesh telecommunication regulatory commission (BTRC).
Internet users: The number of internet users in Bangladesh as of March 2009 is over 600,000 compared to 100,000 in 2000.[9] However, only 0.3% of the population use the internet and thus making Bangladesh the lowest usage percentage per population of the internet in the world with the exception of North Korea, Myanmar and Sierra Leone.[10]
But on April, 2010 Akhtaruzzaman Manju, president of Internet Service Providers' Association of Bangladesh, told Xinhua that the country's six cell phone operators and Interent Service Providers have so far provided over 800,000 internet connections. "We've estimated that nearly 10 million people in the country are using 800,000 internet connections on sharing basis," he said, adding the number of internet users in the country is increasing yearly by around 15–16 percent.[11]
The number of Internet subscribers in Bangladesh is likely to reach 18.3 million by the year 2020– translating to a 32 percent household Internet penetration at around the same time”, says a study by an international research group.
“This increased internet penetration would resulted in 2.6 per cent contribution to the country’s GDP by 2020 while creating 129 thousand more jobs by the same year” the research added.[12]
Broadband Internet Access
Though broadband internet access is available it charges high for high speed connection than other south Asian countries, though this is rapidly changing. Broadband internet and e-commerce in Bangladesh is slowly progressing.WiMAX service is now available from some internet service providers. In Bangladesh Broadband is legally defined as 128/128 kbit/s, which is not in line with ITU.[13] Therefore most of the Broadband internet services and also subscribers are using bandwidth that may not be considered a broadband in other countries and may not be broadband in international standards .
International
There are 6 satellite earth stations. Talimabad, Betbunia are two of them.Some info shows that the number is now 7.
Submarine cables
SEA-ME-WE 4 or South-East Asia – Middle East – Western Europe 4 . The landing site is Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh.
See also
- Doel (laptop)
- Media of Bangladesh
- Telecom System in Bangladesh
- List of Bangladeshi TV and radio Channels
References
- ^ http://www.btcl.gov.bd/home/main/museum/museum.php Chronological Development of Telecommunication
- ^ http://www.btrc.gov.bd/policy/Telecom_Policy_1998.pdf National Telecommunications Policy 1998
- ^ Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission
- ^ Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission
- ^ TelecomsMarketResearch
- ^ Internet Protocol Telephony Service Provider (IPTSP)
- ^ Xinhua
- ^ ISPs association Bangladesh
- ^ #BD moble Internet Usage Stats
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.istockanalyst.com/article/viewiStockNews/articleid/4072376
- ^ http://mskhalid.wordpress.com/2010/01/26/internet-subscribers-may-reach-18-3m-by-2020-the-financial-express-22-january-2010/
- ^ http://www.itu.int/osg/spu/publications/birthofbroadband/faq.html
Telecommunications in Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territories- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Hong Kong
- Macau
Categories:- Telecommunications by country
- Communications in Bangladesh
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.