- Coloroid
-
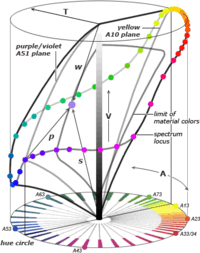 The Coloroid color space, showing the cylindrical geometry of luminosity (V), hue (A) and saturation (T), the relative components of pure hue (s), white (w) and black (s) that can be used to mix any hue within a single hue plane, and the relative areas of all possible (spectrally defined) colors and material (pigmented surfaces) colors.
The Coloroid color space, showing the cylindrical geometry of luminosity (V), hue (A) and saturation (T), the relative components of pure hue (s), white (w) and black (s) that can be used to mix any hue within a single hue plane, and the relative areas of all possible (spectrally defined) colors and material (pigmented surfaces) colors.
The Coloroid Color System is a colour space developed between 1962 and 1980 by Prof. Antal Nemcsics at the Budapest University of Technology and Economics for use by "architects and visual constructors". Since August 2000, the Coloroid has been registered as Hungarian Standard MSZ 7300.[1]
Like the OSA-UCS and Munsell systems, the Coloroid attempts to model a perceptually uniform color space or UCS. However the UCS standard applied in the Coloroid system is equal appearing increments in color when the entire range of colors is presented to the viewer, in contrast to the standard of equal "just noticeable" or small color differences between pairs of similar colors presented in isolation.[2][3]
Colors in the Coloroid color space are fundamentally specified according to the perceptual attributes of "luminosity" (luminance factor, V), "saturation" (excitation purity, T) and hue (the matching or dominant spectral wavelength, A).
The VAT components are used to define a cylindrical color geometry, with V as the achromatic vertical axis (lightness or brightness), T as the horizontal distance from the achromatic axis (chroma), and A as the hue angle around the hue circle. The circumferential limits of this cylinder are defined by the spectrum locus, or colors as they appear in a single wavelength of light (or a mixture of single "violet" and "red" wavelengths); this ambit varies vertically in V around the hue circle, showing whether the relative luminance or brightness of each wavelength is high (yellow hue) or low (violet blue hue). This defines the outer perceptual limits of the color space.
Within this is the smaller perceptual volume defined by the limit of colors it is possible to reproduce with physical media (material colors). Here the VAT perceptual attributes can be approximately matched using the three stimulus or material color components of pure hue or pure colorant (p), white colorant (w) and black colorant (s) in relative proportions whose sum must always equal 1. (Implicitly, p may be any matching single "spot" colorant or matching mixture of two "primary" colorants.)
The Coloroid technical documentation defines the conceptual equations necessary to transform the Coloroid perceptual components VAT into the corresponding stimulus components, using the CIE XYZ 1931 colormatching functions with the D65 CIE illuminant. Hues are identified according to the hue angle ψ, measured on the CIE 1931 xy chromaticity plane. These stimulus attributes in turn must be standardized or gamut mapped into a specific colorant system or color reproduction technology in order to reproduce the Coloroid color space as physical color exemplars or a color atlas. However, a Coloroid Colour Atlas[4] is available that provides color exemplars at 16 levels of lightness out to as many as 13 increments in saturation for each of for 48 hue planes.
Within the Coloroid system, color harmonies or "harmonics" can be defined through simple linear or geometrical combinations of colors.[5]
References
- ^ Nemcsics, Antal (2003). "Coloroid Colour System". Hungarian Electronic Journal of Sciences. [1]
- ^ Nemcsics, Antal (1980). "The Coloroid color space". Color Research & Application 5 (2): 113–120. doi:10.1002/col.5080050214. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/114180073/abstract.
- ^ Nemcsics, Antal (1987). "Color space of the Coloroid color system". Color Research & Application 12 (3): 135–146. doi:10.1002/col.5080120307. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/114183043/abstract.
- ^ Nemcsics, Antal (1985). Coloroid Colour Atlas. Innofinance (Révai Printing House), Budapest.
- ^ Neuman, László, Nemcsics, Antal & Neuman, Attila (2005). Computational Color Harmony based on Coloroid System. Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna University of Technology.
See also
External links
- Coloroid color space, handprint.com.
Color space List of color spaces · Color models CIE RGB color spaces · sRGB · Adobe · Wide Gamut · ProPhoto · scRGB
YUV Other See color vision for the vision capacities of organisms or machines. Categories:- Color space
- Color stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
