- Saskatoon
-
Saskatoon — City — Downtown Saskatoon 
Flag
SealNickname(s): S'toon, The City of Bridges, The Hub City, Toontown, POW City, Paris of the Prairies[1] Motto: "Commerce Industry Education" Coordinates: 52°08′N 106°41′W / 52.133°N 106.683°W Country Canada Province Saskatchewan Establishment 1883 Incorporation 1906 Government - Mayor Don Atchison - Governing body Saskatoon City Council - MP List of MPs- Kelly Block (CPC) - Saskatoon-Rosetown-Biggar
- Brad Trost (CPC) - Saskatoon-Humboldt
- Maurice Vellacott (CPC) - Saskatoon-Wanuskewin
- Lynne Yelich (CPC) - Blackstrap
- MLAs List of MLAs- Cam Broten (NDP) - Saskatoon Massey Place
- Jennifer Campeau (SKP) - Saskatoon Fairview
- Danielle Chartier (NDP) - Saskatoon Riversdale
- Ken Cheveldayoff (SKP) - Saskatoon Silver Springs
- David Forbes (NDP) - Saskatoon Centre
- Paul Merriman (SKP) - Saskatoon Sutherland
- Don Morgan (SKP) - Saskatoon Southeast
- Rob Norris (SKP) - Saskatoon Greystone
- Roger Parent (SKP) - Saskatoon Meewasin
- Cathy Sproule (NDP) - Saskatoon Nutana
- Corey Tochor (SKP) - Saskatoon Eastview
- Gordon Wyant (SKP) - Saskatoon Northwest
Area[2] - City 170.8 km2 (65.9 sq mi) Elevation[2] 481.5 m (1,580 ft) Population (2006 Census) - City 202,340 - Density 1,184.4/km2 (3,067.6/sq mi) - Metro 233,923 Demonym Saskatonian Time zone CST (UTC−6) Area code(s) 306 GDP per capita C$26,551 (est. 2005) Median income per household C$68,300 (2006) Pronunciation /ˌsæskəˈtuːn/ Website www.saskatoon.ca 1 Source: Canada 2006 Census[3] Saskatoon is a city in central Saskatchewan, Canada, on the South Saskatchewan River. Residents of the city of Saskatoon are called Saskatonians. The city is surrounded by the Rural Municipality of Corman Park No. 344.
Saskatoon is the most populous city in the province of Saskatchewan, and has been since the mid-1980s when it surpassed the provincial capital of Regina.[4] The city had a population of 202,340 in the Canada 2006 Census,[5] with a civic estimate of 231,900 in 2010.[6] The city's census metropolitan area had a population of 233,923 in the 2006 Census.[7] Statistics Canada estimated Saskatoon's CMA population as 265,000 as of July 1, 2010.[8]
Etymology
The name Saskatoon [in Cree: sâskwatôn, "Saskatoon" or the locatives: misâskwatôminihk, lit: "at the saskatoon berry", misâskwatôminiskâhk, "at the place of many saskatoon berries", mînisihk "at the berry"] comes from the Cree inanimate noun misâskwatômina "saskatoon berries", which refers to the sweet, violet-coloured berry that grows in the area. It is also popularly described as the "Bridge City," for its seven river crossings.[9]
History
In 1882, the Toronto-based Temperance Colonization Society was granted 21 sections of land straddling the South Saskatchewan River, between what is now Warman and Dundurn.[10] The aim of the group was to escape the liquor trade in that city and set up a "dry" community in the Prairie region.[10] The following year settlers, led by John Neilson Lake, arrived on the site of what is now Saskatoon and established the first permanent settlement.[10] The settlers travelled by railway from Ontario to Moose Jaw and then completed the final leg via horse-drawn cart as the railway had yet to be completed to Saskatoon.[10]
In 1885 the Northwest Rebellion affected the tiny community in a variety of ways. Chief Whitecap and Charles Trottier passed through the present day University campus on their way to join Louis Riel's armed forces at Batoche, Saskatchewan. Following the fighting at the Battle of Fish Creek, and the Battle of Batoche, wounded Canadian soldiers convalesced at the Marr Residence which is today a historic site. A few died in care and were buried in the Pioneer Cemetery near the Exhibition Grounds.
A town charter for the west side of the river was obtained in 1903 (Nutana became a village in that year). In 1906 Saskatoon became a city with a population of 4,500, which included the communities of Saskatoon, Riversdale, and Nutana. In 1955 Montgomery Place and in 1956 the neighbouring town of Sutherland were annexed by the fast growing City of Saskatoon.[11]
Demographics
Census Population 1901 113 1911 12,004 1921 25,739 1931 43,291 1941 42,320 1951 53,268 1961 95,526 1971 126,449 1981 154,210 1991 186,058 2001 196,811 2006 202,340 Est. 2008 209,400 Est. 2009 218,900 Est. 2010 223,200 The 2006 census listed Saskatoon as the largest city of Saskatchewan with a residential population of 202,340, which grew 2.8 per cent from 2001.[12] A study released in July 2008 found that Saskatoon's population fell by approximately 2,000 people during the previous sixteen months, as more people move out of the city proper and into "bedroom communities" and adjacent Alberta.[13] At the end of 2008, the City of Saskatoon claimed a population of 209,400.[2]
According to the 2006 census, 18% of the population consists of youths under the age of 15, while those over 65 constitute 13% of the population. The median age of Saskatoon residents is 35.5 years of age, four years younger than Canada as a whole. [14]
Canada census – Saskatoon Community Profile 2006 2001 Population:
Land area:
Population density:
Median age:
Total private dwellings:
Mean household income:202,340 (2.8% from 2001)
170.83 km2 (65.96 sq mi)
1,184.4 /km2 (3,068 /sq mi)
35.9 (males: 34.2, females: 37.4)
89,646
$49,313196,811 (1.6% from 1996)
148.34 km2 (57.27 sq mi)
1,326.8 /km2 (3,436 /sq mi)
34.3 (males: 33.1, females: 35.5)
84,281
$41,991References: 2006[15] 2001[16] The above land area figure was provided by the City of Saskatoon in January 2006 and takes into account recent annexations up to that point. It does not include the two large annexations of land that occurred in the summer of 2010. These portions of land have been zoned under the provincial land management acts.
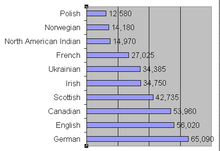 Ethno-cultural Groups in Metropolitan Saskatoon, out of 222,635 (number is greater than 222,635 because many reported more than one ethnicity)[17]
Ethno-cultural Groups in Metropolitan Saskatoon, out of 222,635 (number is greater than 222,635 because many reported more than one ethnicity)[17]
In terms of race, according to the 2001 census,[18] 190,120 or 85.4% of the city's population were white Canadians, 19,900 or 8.9% were Aboriginals, with less than 5% belonging to other visible minorities such as Han Chinese, South Asians, etc. combined.
Some 78.5% of Saskatoon's inhabitants profess to be Christian, mostly Protestant (40.1%) and Roman Catholic (32.5%).[19] Another 19.6% of Saskatoon's inhabitants do not profess a religious faith at all.[19] Minority faiths include Sikhism, Buddhism (0.7%), Judaism, Hinduism, and Islam (0.6%).[19]
Aboriginal peoples
The Saskatoon area was inhabited long before any permanent settlement was established, to which the ongoing archaeological work at Wanuskewin Heritage Park and other locations bears witness. Canada's First Nations population has been increasingly urbanized, and nowhere is that more apparent than in Saskatoon, where the First Nations population increased by 382% from 1981 to 2001;[20] however, a portion of this increase, possibly as much as half, is believed to be due to more people identifying themselves as Aboriginal in the census rather than migration or birth rate. Saskatoon has a higher percentage of First Nations population than any other major Canadian city[21] at nearly 9%, although Winnipeg and Regina both exceed 8%; in certain neighbourhoods such as Pleasant Hill, this percentage exceeds 40%. Most First Nations residents are of Cree or Dakota cultural background although to a lesser extent Saulteaux, Assiniboine, and Dene communities also exist.
Saskatoon also has a substantial Métis population and is close to the historically significant Southbranch Settlements to the north, as well as the Prairie Ronde settlement near Dundurn, Saskatchewan.
Health
The Saskatoon Health Region is responsible for health care delivery in the region. The health region operates three hospitals within the city boundaries, these include Royal University Hospital, Saskatoon City Hospital, and St. Paul's Hospital (Saskatoon). Royal University Hospital is a teaching and research hospital that operates in partnership with the University of Saskatchewan. The health region also operates hospitals in smaller neighboring communities.[22] In addition to hospitals the health region operates long-term care facilities, clinics and other health care services.
Recent data suggests that Saskatchewan has the highest rate of new HIV cases in Canada[23] and that 1/4 cases of HIV infected babies are from Saskatchewan.[24] This increase in HIV cases has been in part attributed to growing IV drug use, a gang problem, poverty and prostitution in the city of Saskatoon, which has a higher rate of HIV than other areas.[24][25][26]
Economy
Main article: Economy of SaskatoonThe economy of Saskatoon has been associated with potash, oil and agriculture (specifically wheat), resulting in the moniker POW.[27] Various grains, livestock, oil and gas, potash, uranium, gold, diamond, coal and their spin off industries fuel the economy.[28][29] The world's largest publicly traded uranium company, Cameco, and the world's largest potash producer, PotashCorp, have corporate headquarters in Saskatoon. Nearly two-thirds of the world's recoverable potash reserves are located in the Saskatoon region.[2] Innovation Place founded in 1980 brings together almost 150 agriculture, information technology, and environmental, life sciences and agricultural biotechnology industries in a science park or technology park setting.[30]
Saskatoon's other nickname, Hub city refers its ideal central location for distribution and logistics.[27] Saskatoon John G. Diefenbaker International Airport with 105,620 aircraft movements in 2008 was listed as the 19th busiest airport in Canada.[31][32]
Saskatoon is developing the South Central Business District, or block 146, which is called the River Landing Project.[33][34][35] Long range planning is underway for an expected population of 270,000 by 2025 (2000 estimate).[36]
Saskatoon is expected to see a 1.7 percent growth in gross domestic product for the year 2009.[28] The city saw a 3.4% growth in 2004, 5.1% increase in 2005 and a 2.8% increase in 2006. Saskatoon held Canada's No. 1 economic growth spot for Canada in 2005 according to the Conference Board of Canada.[37][38] The Conference Board again predicted the city would rate first for economic increase in 2008, showing a growth rate of 5.2%. The Saskatoon Regional Economic Development Authority (SREDA) has also been ranked amongst Canada's top ten economic growth groups by Site Selection magazine.[39]
Recent provincial government forecasts are calling for a $1.05 Billion deficit for 2009, the second largest deficit of all time,[40] and the Conference Board of Canada is predicting a "near term" employment drop for Saskatoon and area, while nearby Regina is predicted to post the best employment growth in Western Canada.[41]
Pike Lake and Blackstrap Provincial Parks are 40 km (25 mi) south of the city. Blackstrap Park is often used for school field trips. Batoche is located 90 km (56 mi) north of the city.
Geography
Saskatoon lies on a long belt of rich, potassic chernozem in middle-southern Saskatchewan and is found in the Aspen parkland biome. The lack of surrounding mountainous topography gives the city a relatively flat grid, though the city does sprawl over a few hills and into a few valleys. The lowest point in the city is the river, while the highest point is disputed between the suburb of Sutherland in the east side and the Silverwood-River Heights areas in the city's north end. Saskatoon, on a cross-section from west to east, has a general decline in elevation above sea level heading towards the river, and on the east bank of the river, the terrain is mostly level until outside the city, where it begins to decrease in elevation again.
Saskatoon is divided into east and west sides by the South Saskatchewan River. It is then divided into Suburban Development Areas (SDA) which are composed of neighbourhoods.[42]


Saskatoon skyline and the South Saskatchewan River Climate
Saskatoon is in the aspen parkland biome and experiences warm summers and very cold winters (plant hardiness zone 2B[43]). Its climatic zone is humid continental (Koppen climate classification Dfb).
The city has four distinct seasons. Average temperatures range from −17°C (-1°F) in January to 19°C (66°F) in July.[44] Saskatoon is fairly dry, with the summer being the wettest season. A positive aspect of the low precipitation is that Saskatoon is sunnier than average in Canada as a result, averaging 2,380.8 hours of bright sunshine annually.[45] The extreme temperatures are also more tolerable on account of the typically low humidity. The summer months can get hot at times, but the average summer high is 24°C (75°F). Thunderstorms are common in the summer months and can be severe with torrential rain, hail, high winds, intense lightning and, on rare occasion, tornados. The frost-free growing season generally lasts from mid-May to mid-September,[46] but due to Saskatoon's northerly location, damaging frosts have occurred as late as June 14[47] and again as early as August.[citation needed]
The lowest temperature ever recorded in Saskatoon was −50°C (-58°F) in 1893. The lowest wind chill ever recorded was −62°C (-80°F).[48] The highest temperature ever recorded in Saskatoon was 40.6°C (105.1°F) on 5 June 1988.[49]
The "Blizzard of 2007" was described by many residents as the worst they had seen and paralyzed the city with its low visibility, extreme cold and large volume of snow.[50] Winds rose to over 90 kilometres per hour and an estimated 25 centimetres (9.8 inches) of snow fell throughout the day.[51] Many area residents took refuge overnight at area work places, shopping centres, hospitals and the university.
Climate data for Saskatoon (Saskatoon International Airport, normals 1971–2000) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Record high °C (°F) 10
(50)12.8
(55.0)22.8
(73.0)33.3
(91.9)37.2
(99.0)40.6
(105.1)40
(104)38.6
(101.5)35.3
(95.5)32.2
(90.0)21.7
(71.1)14.4
(57.9)40.6
(105.1)Average high °C (°F) −11.8
(10.8)−7.8
(18.0)−0.7
(30.7)10.6
(51.1)18.4
(65.1)22.6
(72.7)24.9
(76.8)24.4
(75.9)18.0
(64.4)10.8
(51.4)−1.5
(29.3)−9.2
(15.4)8.2 Daily mean °C (°F) −17.1
(1.2)−13
(9)−5.8
(21.6)4.4
(39.9)11.5
(52.7)16.0
(60.8)18.2
(64.8)17.3
(63.1)11.2
(52.2)4.5
(40.1)−6.2
(20.8)−14.3
(6.3)2.2 Average low °C (°F) −22.3
(−8.1)−18.2
(−0.8)−10.9
(12.4)−1.9
(28.6)4.5
(40.1)9.4
(48.9)11.4
(52.5)10.2
(50.4)4.4
(39.9)−1.9
(28.6)−10.9
(12.4)−19.3
(−2.7)−3.8 Record low °C (°F) −48.9
(−56.0)−50
(−58)−43.3
(−45.9)−28.3
(−18.9)−12.8
(9.0)−3.3
(26.1)−0.6
(30.9)−2.8
(27.0)−11.1
(12.0)−25.6
(−14.1)−39.4
(−38.9)−43.9
(−47.0)−50
(−58)Precipitation mm (inches) 15.2
(0.598)10.3
(0.406)14.7
(0.579)23.9
(0.941)49.4
(1.945)61.1
(2.406)60.1
(2.366)38.8
(1.528)30.7
(1.209)16.7
(0.657)13.3
(0.524)15.9
(0.626)350
(13.78)Rainfall mm (inches) 0.6
(0.024)0.5
(0.02)2.3
(0.091)14.4
(0.567)46.8
(1.843)61.1
(2.406)60.1
(2.366)38.8
(1.528)29
(1.14)8.6
(0.339)2.0
(0.079)0.9
(0.035)265.2
(10.441)Snowfall cm (inches) 17.9
(7.05)12.3
(4.84)14.1
(5.55)9.7
(3.82)2.2
(0.87)0
(0)0
(0)0
(0)1.5
(0.59)7.7
(3.03)13.4
(5.28)18.5
(7.28)97.2
(38.27)Avg. precipitation days 11.3 8.3 8.1 8 9.6 12.2 11.4 9.4 8.1 6.2 8.4 10.7 111.7 Avg. rainy days .5 .4 1.6 5.3 9.3 12.2 11.4 9.4 7.8 4.3 1.4 .8 64.4 Avg. snowy days 11.9 8.9 7.5 4.1 .8 0 0 0 .6 2.7 8.5 11.7 56.7 Sunshine hours 105.5 132.8 171.9 227.1 272.0 284.2 320.7 286.3 182.8 159.9 98.9 86.3 2,328.5 Source: Environment Canada[52] Security
The Saskatoon Police Service is the primary police service for the city of Saskatoon and holds both Municipal and Provincial Jurisdiction. The following services also have jurisdiction in Saskatoon: Corman Park Police Service, Royal Canadian Mounted Police, Canadian National Railway Police Service and the Canadian Pacific Railway Police Service. As of 2009 the SPS had 475 sworn members and 107 civilian positions.[53] During the 1980s the city saw a large number of situations where the result was a shootout between suspects and the police. It was known as the Shootouts of the Eighties. Probably the most famous incident was the Canarama Mall Shootout. In 1978 Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) Constable Thomas Brian King was attacked and shot to death in Saskatoon.
Crime
The 2006 census crime data, released July 18, 2007, showed Saskatoon leading Canada in violent crime, with 1,606 violent crimes per 100,000 residents annually. However, crime statistics produced by the Saskatoon Police Service shows that crime is on the decline. Saskatoon saw a 71% drop in murders last year (a total of 2, compared to 7 in 2007). In 2008 total crimes against people fell 8.06% and total crimes against property fell by 8.22%.[54]
There were accusations in the early 1990s that the Saskatoon police were engaging in starlight tours, where officers would arrest Aboriginal men and drive them out of the city in the dead of winter to abandon them. The majority of the accusations turned out to be false however there were several starlight tours which took place.[55][56]
Main sights
One of the city's landmarks is the Delta Bessborough Hotel, known to locals as the Bez. Built by the Canadian National Railway, it was among the last railway hotels to be started before the Great Depression of the 1930s brought their era to a close. Although the building was completed in 1932, it did not open its doors until 1935 due to the Depression. The Bessborough and the Mendel Art Gallery are currently the only major structures located on the river side of Spadina Crescent. One of the most frequently circulated photographs depicting Saskatoon is of the hotel framed in one of the arches of the Broadway Bridge.[57] An interesting footnote related to the Bessborough Hotel is that the structure is slowly sliding towards the South Saskatchewan River located directly behind the hotel. It is reported the structure is moving toward the river at approximately 1" per year.
The Meewasin Valley Trail follows the South Saskatchewan River through Saskatoon. Summer activities include cycling, jogging and walking through parks and natural areas. Cross-country skiing is popular during the winter months, along with skating in Kiwanis Memorial Park. Access points are found throughout the city with interpretive signage and washrooms located along the route. There are parks throughout the Meewasin Valley, with washrooms, picnic facilities, and lookout points along the river bank.[58]
In the winter the Meewasin Skating Rink is open free to the public; it is located in Kiwanis Memorial Park beside the Delta Bessborough hotel. The outdoor rink has been open since 1980.
For years, a parcel of land west of the Victoria Bridge, south of 19th Street, and east of Avenue C has been the subject of on-again, off-again redevelopment plans. The site formerly held the Saskatoon Arena, a power plant, a branch of the Royal Canadian Legion, and the head offices of the Saskatoon Public School Division; all these structures have been demolished to make way for redevelopment, with plans for same dating back to the 1980s. The most recent version of the plan called River Landing is ongoing.[59] Calgary developer Lake Placid has proposed a 200 million dollar mega hotel/condo project to be built on the site although Lake Placid had difficulty securing financing and missed an October 30, 2009, deadline to submit a 4.5 million dollar payment for the parcel of land which seemingly killed the deal.[60][61] On November 16, 2009, it was revealed by Lake Placid that the financing should be secure within a week.[62] In April 2010, Saskatoon City Council voted in favour of entering new negotiations with Lake Placid over the site.[63]
As of May 2010, landscaping and the development of the Frank & Ellen Remai Arts Centre a new performance venue for the Persephone Theatre had been completed on River Landing, joining a senior citizens residence that had been built in River Landing in the 1990s. The Saskatoon Farmers' Market and some commercial sites have also been developed. Future plans separate from Lake Placid include the development of a new art gallery to replace the Mendel Art Gallery by 2014.[64]
Other landmarks in the city include the iconic Traffic Bridge (which as of summer 2011 is expected to be demolished and replaced by a new structure), the University of Saskatchewan campus, and the large Viterra grain terminal which has dominated the western skyline of the city for decades and is large enough to be visible from Pike Lake Provincial Park 32 km away.
Transportation
Saskatoon is located on the Yellowhead Highway spur of the Trans-Canada Highway system, also known as Highway 16, which connects Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Alberta, and British Columbia. Highways 5, 7, 11, 12, 14, 41, 219, 684, and 762 all meet at Saskatoon, with highway 60 terminating just west of the city limits.
The following bridges cross the South Saskatchewan River in Saskatoon (in order from upstream):
- Grand Trunk Bridge (rail)
- Circle Drive South Bridge (Under Construction)
- Senator Sid Buckwold Bridge
- Traffic Bridge (closed indefinitely as of August 24, 2010)[65]
- Broadway Bridge
- University Bridge
- CPR Bridge (rail)
- Circle Drive Bridge
Construction of Saskatoon's ring road, Circle Drive, began in the mid-1960s, and is yet to be completed as of mid-2010. Its remaining missing link is in the southwest; on June 20, 2008, the mayor announced that funding for the $300 million project from the federal, provincial and city governments is now in place to build the Circle Drive South Bridge, a six-lane bridge and 7 km of freeway to complete the south portion of the road. Construction of the project, which will include a new river crossing and several interchanges, commenced in 2010 and is expected to be completed in 2012.[66]
The Canadian Pacific Railway and the Canadian National Railway have connections to Saskatoon. Both railways operate intermodal facilities and trans-load centers; while Canadian National Railway also operates an automotive transfer facility.[67] Saskatoon is a stop on The Canadian passenger transcontinental rail route operated by Via Rail. The Saskatoon railway station is located in the west end of the city; it was opened in the late 1960s as a replacement for Saskatoon's original main station which was located on 1st Avenue downtown—the relocation of the station sparked a major redevelopment of the downtown that included the construction of the Midtown Plaza, TCU Place (aka Centennial Auditorium) and other developments. The many provincial transportation connections and geographic location of Saskatoon give it one of its nicknames The Hub City. The Saskatchewan Railway Museum is located just outside the city. Recent debates about moving all the railways out of the city are raising questions about a future LRT system, but the city's Mayor says the population is too small.
Saskatoon/John G. Diefenbaker International Airport provides scheduled and charter airline service for the city, and is a significant hub for mining and remote locations in Northern Saskatchewan. Non-stop scheduled destinations include Calgary, Chicago, Denver, Edmonton, Las Vegas, Minneapolis, Ottawa, Prince Albert, Regina, Toronto, Vancouver, and Winnipeg. Seasonal and Charter service is provided to Mexico, Cuba, Dominican Republic, and Churchill, MB. Air Canada, Westjet and Purolator Courier all have cargo facilities at the airport. Saskatoon/Corman Air Park is a general aviation airport located 15 km south-east of Saskatoon.
Transit services in Saskatoon are provided by Saskatoon Transit. The route system was revamped on July 2, 2006, creating increased access to most parts of the city. An up to date schedule is posted at Saskatoon Transit Route & Schedule Adjustments
The Saskatchewan Transportation Company connects Saskatoon via bus service to nearly 200 towns and villages in the province.[68] The Saskatoon bus terminal is also served by Greyhound Canada inter-provincial service between Manitoba and Alberta.
Education
Saskatoon has a number of higher education institutions:
- University of Saskatchewan
- St. Thomas More College is a Catholic federated college of the University of Saskatchewan. Affiliated with the University of Saskatchewan are the Lutheran Theological Seminary, College of Emmanuel and St. Chad (Anglican Church of Canada), and St. Andrew's College (United Church of Canada). All three are located on the university campus.
- The First Nations University of Canada Saskatoon campus is located at the corner of 7th Ave. N. & Duke St., with the main campus in Regina.
- Saskatchewan Institute of Applied Sciences and Technology
- Gabriel Dumont Institute
- SBC: Saskatoon Business College
- Western Academy of Broadcasting
- Saskatchewan Indian Institute of Technologies
Saskatoon has 78 elementary schools and 14 high schools, serving about 37,000 students. Saskatoon has three main school boards, The Saskatoon Public School Division, the Saskatoon Catholic School Division and the Conseil des Ecoles Fransaskoises.
Saskatoon is home to six units of the Canadian Cadet Movement:
- 45 Sea Cadet Corps
- 107 Air Cadet Squadron
- 328 Medical Cadet Corps - Homepage
- 702 Air Cadet Squadron
- 2293 The North Saskatchewan Regiment Royal Canadian Army Cadet Corps - Homepage
- 3071 The North Saskatchewan Regiment Royal Canadian Army Cadet Corps - Homepage
The western annexation of what is now called the Blairmore SDA also brought the Yarrow Youth Farm within the city limits; operated by the Province of Saskatchewan, this is a correction facility for at-risk youth. The City's current Projected Growth Map indicates that the farm is expected to be incorporated within planned development of the region.[69]
Arts and culture
Galleries and museums
The Mendel Art Gallery is situated on the bank of the South Saskatchewan River. Its permanent collection exceeds 5,000 works of art. In 2005, it began a major renovation project that will expand the size of the gallery by seventy per cent. In September 2005, however, the City of Saskatoon announced that it had entered discussions with the Mendel to the end of having the Mendel abandon its renovation/expansion project in favor of instead relocating the facility to a new arts and culture centre that is planned for the south downtown area.
The Art Gallery of Saskatchewan was announced in April 2009 as the replacement for the Mendal Art Gallery, which will be constructed at River Landing, around the previously constructed Remai Arts Centre, which houses the Persephone Theatre company. The Art Gallery will be built matching contributions of $13 million from the Government of Canada and the Government of Saskatchewan. The City of Saskatoon and other key partners have also committed funding in support of this project. The total estimated costs for the Gallery, which will serve as the destination centre for the River Landing project, will be approximately $51 million.[70]
Currently, the City of Saskatoon is waiting for design proposals on the Art Gallery of Saskatchewan. According to the Mendal Art Gallery website, the new Gallery will be a multi-storey building, adjacent to Persephone Theatre, in the range of 80,000 square feet (7,400 m2). The facility will allow up to three times the present available gallery space and will include studio and classroom space for education programs including an adaptive community studio and lecture theatre, meeting rooms and space for administrative functions. Emphasis will be placed on meeting functional requirements while also providing an appropriate signature architectural presence in the city’s south downtown. The atrium that is visualized for the front of the Gallery will provide not only adequate space for Gallery functions and activities and special public events but will also be a gathering place at River landing and will include visitor services and a gift shop. There will also be a bistro, restaurant and catering support and the site will incorporate 250-stall underground parking.[71] The decision to drop the Mendel name has been controversial.[72][73][74]
The Ukrainian Museum of Canada is also located on the banks of the South Saskatchewan River. The foremost attraction for Ukrainian culture in Saskatoon, it houses various artifacts such as textiles, tools, musical instruments and clothing, and displays them for public viewing. It has branches in Vancouver, Edmonton, Calgary, Winnipeg and Toronto.
The Meewasin Valley Centre, in Friendship Park, has information on Saskatoon's history, the South Saskatchewan River, and the future of the Meewasin Valley.[75]
Saskatoon is also home of the Saskatchewan Western Development Museum. This museum, one of four throughout the province, documents early pioneer life in Saskatchewan. It is noted for its interior recreation of a "Boom Town" main street, including one original building relocated from its original site. The Saskatchewan Railway Museum is located just outside the city and includes displays of rolling stock and historic railway buildings from various parts of the province.
The Forestry Farm Park and Zoo is a National Historic Site situated in the north east region of the city. The Forestry Farm was a historic nursery (dating from 1913) responsible for growing many of the trees planted within the prairie provinces. In 1966 the nursery operations were discontinued and part of the region turned into a municipal park. The city zoo is also housed within the park and features over 80 species of animals.[76] Wanuskewin Heritage Park is a National Historic Site situated five km to the north of Saskatoon. It is an Aboriginal archaeological site and features displays, special events, and activities, recent renovations are on hold due to a lack of funds during the renovations.
Events and festivals
Saskatoon's major arts venue is TCU Place, which is located adjacent to Midtown Plaza downtown. Since opening in 1967, it has hosted scores of concerts, theatrical performances, live events such as the Telemiracle telethon, high school graduation and university convocation ceremonies, and conventions. It is also home to the Saskatoon Symphony Orchestra. It recently underwent a multi-million dollar renovation to its main theatre (named in honor of former mayor and senator Sidney Buckwold).
For rock concerts and major shows, Credit Union Centre is the main venue. It is Saskatchewan's largest arena, with a capacity of 15,000 for sporting events and 14,000 for concerts. Musical acts from Saskatoon include Joni Mitchell, Kyle Riabko, Wide Mouth Mason, The Northern Pikes, The Sheepdogs, and The Deep Dark Woods, as well as countless others popular at both local and regional levels.
Saskatoon hosts many festivals and events in the summer, including the Shakespeare on the Saskatchewan Festival, the Jazz Festival, the Saskatchewan Children's Festival, the Saskatoon Fringe Theatre Festival (a showcase of alternative theatre), Saskatoon Folkfest (a cultural festival), Doors Open Saskatoon and the Canada Remembers Airshow.
For over 25 years, Saskatoon has hosted a gathering of antique automobiles, (mainly from the 1960s) that has grown into an event called "Cruise Weekend". The event is usually held on the last weekend (Friday, Saturday and Sunday) in August. Activities include a poker derby, dances, and a show 'N' shine with over 800 cars from all over western Canada. No admission is charged and everyone is free to walk around and enjoy the atmosphere.
The city's annual exhibition (now called the Saskatoon Exhibition but also known in previous years as Pioneer Days and "The Ex") is held every August at Prairieland Park. In the late 1990s, the Saskatoon Exhibition was rescheduled to August so that it no longer was in direct competition with the Calgary Stampede, which frequently overlapped the event.
Saskatoon was the 2007 host city for the Juno Awards, Canada's foremost music industry honours.
Live theatre
Live theatre is a central, vibrant part of Saskatoon's culture. Saskatoon is host to a number of live theatre venues such as the Persephone Theatre, which is located in the Remai Arts Centre at River Landing in downtown Saskatoon, The Refinery and the Saskatchewan Native Theatre Company. Saskatoon is also home to performance groups such as: Shakespeare on the Saskatchewan, Saskatoon Opera Association, Live Five, Troup du Jour, Saskatoon Gateway Players and Saskatoon Summer Players. Local improv groups such as The No-No's and Saskatoon Soaps have weekly and monthly performances respectively at various venues around the city.
Saskatoon also boasts the only burlesque group in the Prairies, the Rosebud Burlesque.
Movie theatres
Saskatoon, given its size, has few movie theatres. There is only one single-screen theatre in the city - the Broadway Theatre, which primarily shows arthouse films - while the two-screen Roxy Theatre is an "atmospheric-style" second-run theatre that reopened in 2005 after sitting unused for over a decade. The remainder of the city's theatres are multiplexes. The only movie theatre in the downtown core is the Galaxy Cinemas; the Capitol 4 shut down on April 3, 2008.[77] The city's other movie theatres are the Rainbow Cinemas (a second-run cinema) and the Centre Cinemas, located adjacent to each other in The Centre mall on the city's east side.
Music
The Canadian rock band The Sheepdogs are from Saskatoon.
Royal presence
Saskatoon has welcomed members of Canada's Royal Family since 1919. The Queen most recently visited for the a gala concert at Credit Union Centre, before a live audience of 12,000 and television viewers nationwide in 2005. The Queen was presented with the key to the city on the same visit, after touring the Canadian Light Source Synchrotron and greeting thousands of well-wishers on a walkabout at the University of Saskatchewan. Sovereigns and consorts who have visited include Edward VIII as Prince of Wales in 1919, King George Vl and Queen Elizabeth in 1939, and Elizabeth II and the Duke of Edinburgh, as Princess Elizabeth in 1951 and afterwards as Queen in 1959, 1978, 1987 and 2005. Other members of the Royal Family who have visited include Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon in 1980, the Prince of Wales (Charles) in 2001, the Princess Anne in 1982 and (as Princess Royal) in 2004, the Duke and Duchess of York (Andrew and Sarah) in 1989, and the Prince Edward in 1978. Governors General and Lieutenant Governors also pay regular visits to Saskatoon. Saskatonian Ray Hnatyshyn is credited with popularising his office as Governor General from 1990 to 1995. Lieutenant Governors Barnhart, Fedoruk, McNab, Monroe, Porteous and Worobetz were all former residents of Saskatoon.
Connections to the crown include the royal namesakes of about one hundred neighbourhoods, parks, streets, schools and other places. These include King George, Queen Elizabeth and Massey Place neighbourhoods, and Victoria, Coronation and Princess Diana parks. It was at one time considered that Saskatoon's Broadway Bridge would be renamed George V Bridge.[78] Landmarks and institutions also have connections and these include the Royal University Hospital, one of four royal designations in Saskatchewan. Grade schools named for royals include Ecole Victoria School, King George School, Queen Elizabeth School, Prince Philip School and Princess Alexandra School. Existing and historic hotels with royal namesakes include the King George Hotel, the King Edward Hotel, the Queen's Hotel and the Patricia Hotel. The Hotel Bessborough was named for a Canadian Governor General who visited the landmark under construction in the 1930s. The Queen Elizabeth Power Station is located within the city and named after Queen Elizabeth. The Prince of Wales Promenade along the South Saskatchewan River is a focal point on the riverfront trails. In 2002, 378 Saskatoon residents were presented with Canada's Golden Jubilee Medal by vice-regals to commemorate the fiftieth anniversary of the Queen's accession to the throne.[79]
Sports and recreation
Ice hockey is one of the most popular sports in Saskatoon and is home to numerous amateur teams such as the Saskatoon Blades of the WHL, who host their games in Credit Union Centre (formerly known as Saskatchewan Place). Saskatoon is also home to amateur teams at the Junior B and Midget AAA levels, as well as several youth teams. Saskatoon was a major league hockey city from 1921 to 1926 when the WCHL/WHL Sheiks/Crescents played. They made it as far as the league semi-finals twice, not far enough to challenge for the Stanley Cup. The biggest chance for a return of major professional hockey came in 1982. Bill Hunter, a local sports promoter, attempted to purchase the St. Louis Blues of the NHL and move it to Saskatoon, but the move was prevented by the league. This was due to Saskatchewan's and especially Saskatoon's small size in relation to both St. Louis and the other cities in the NHL at the time. However, it did cause the building of the Credit Union Centre, on the city's northern edge. Credit Union Centre Recent renovations will increase seating capacity to over 15,000 for hockey games in time for the facililty to host the 2010 World Junior Hockey tournament,as well as several new box suites to be added. A proposal by Ice Edge Holdings, who are the front runners to buy the Phoenix Coyotes, would move some of the Coyotes' home games to Saskatoon. Also in 2004 with Edmonton looking for a new WHL team, Oilers President and CEO Patrick Laforge offered the Edmonton Roadrunners franchise of the American Hockey League to the city of Saskatoon in exchange for the Saskatoon Blades franchise. However the deal never worked out, with the Roadrunners suspending operations and remaining dormant until 2010 when the team moved to Oklahoma City.
As for women's hockey, there is a strong youth female hockey presence in Saskatoon with a Midget AAA team and several youth teams in the city.
Canadian football is one of the most successful on field sports in Saskatoon. The University of Saskatchewan Huskies are one of the top University football programs in Canada, with three Vanier Cup national championships and 19 Hardy Trophy Canada West championships. The Huskies have made nine Vanier Cup appearances since 1990, and were the first team from outside of Ontario to host the Vanier Cup, hosting the game in 2006. As well, the Saskatoon Hilltops of the Canadian Junior Football League host their games at Gordie Howe Bowl. The Hilltops have won 12 national junior championships throughout their history. As well, many Saskatonians support the Saskatchewan Roughriders of the CFL.
The Saskatoon Yellow Jackets college summer league baseball team is a member of the Western Major Baseball League and play their games at Cairns Field. They are not affiliated with any Major League Baseball team nor do they carry any professional players. In the past other teams have attempted to grace Saskatoon's professional sports landscape including the Saskatoon Riot, (named after the Toronto Blue Jays won the World Series in 1993)Saskatoon Smokin' Guns, Saskatoon Stallions and the latest being the Saskatoon Legends. However, there is hope that the Golden Baseball League will find an owner for its proposed Saskatoon franchise and begin play in 2010 or 2011 at Cairns Field.
The University of Saskatchewan Huskies play Canadian Interuniversity Sport league games at the University Campus. Their facilities include 4,997 seat Griffiths Stadium, 700 seat Rutherford Arena, and the state-of-the-art Physical Activity Complex, which is completely new with the exception of a small swimming pool which was not updated, that opened in August 2003 with the opening of the new College of Kinesiology Building. The Huskies participate in twelve sports at the CIS level and have been most successful in football(Conference champions 18 times/National champions 3 times),[80] men's volleyball(Conference champions 11 times/National champions 4 times)[81] and men's and women's Track and Field(Conference champions 37 times/ National champions 12 times).[82]
In 2007, two new sports teams came into being in Saskatoon, the Saskatchewan SWAT of the Rocky Mountain Lacrosse League and the Saskatoon Accelerators in the Canadian Major Indoor Soccer League. The Accelerators play at Credit Union Centre, while the SWAT split their games between Credit Union Centre and Kinsmen Arena in their first season, eventually moving to Archibald Arena in 2009.
Motor racing is a popular sport in Saskatoon. Saskatchewan International Raceway has been in operation for over 40 years; SIR is home to 1/4 mile NHRA drag racing and holds racing events from May to September. As well, just north of the city lies Auto Clearing Motor Speedway; the track is home to local stock car racing, as well as races for several different Western Canadian series. 2009 saw the NASCAR Canadian Tire Series make its inaugural stop at Auto Clearing Motor Speedway, signaling a move to a larger profile track in Saskatoon.
For horse racing fans, Marquis Downs at Prairieland Park offers live horse racing from May to October.
Saskatoon is also home to two full size soccer facilities. Saskatoon Soccer Centre controls both buildings. Henk Ruys has four hardcourt indoor fields while the Sasktel Soccer Centre has two outdoor full size fields and one indoor full sized field as well as two tiled fields.
On the recreation side, Lions Skatepark was built in the Riversdale area in 2003. As well Saskatoon is home to several golf courses and various parks which include tennis courts, ball diamonds and soccer pitches for spring, summer and fall use and outdoor rinks for winter use. Blackstrap Ski Hill is also located 30 minutes south of the city, however, has been closed for both 2006 and 2007 seasons due to financial difficulty.
See: List of Sports Franchises in Saskatoon
Facilities and services
Local media
Shopping centres
- Midtown Plaza
- Market Mall
- The Centre
- The Mall at Lawson Heights
- Confederation Mall
- Preston Crossing
- College Park Mall
- Mount Royal Mall
- Antique Mall
- Stonegate Shopping Centre
- Scotia Centre Mall
- River City Mall
Law and order
- Saskatoon Police Service (Primary)
- Saskatoon Correctional Centre
- Corman Park Police Service (In Partnership with SPS)
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police (In Partnership with SPS)
Hospitals
- Royal University Hospital
- Saskatoon City Hospital
- St. Paul's Hospital
Sister cities
 Umeå, Sweden
Umeå, Sweden Shijiazhuang, China
Shijiazhuang, China Cologne, Germany
Cologne, Germany Tampere, Finland
Tampere, Finland Chernivtsi, Ukraine
Chernivtsi, Ukraine Midland, Texas, USA
Midland, Texas, USA Kitahiroshima, Japan
Kitahiroshima, Japan Ulsan, South Korea
Ulsan, South Korea Oxford, United Kingdom
Oxford, United Kingdom Kabul, Afghanistan
Kabul, Afghanistan Sangsar, Iran
Sangsar, Iran
Notable people
Main article: List of people from SaskatoonSaskatoon in popular culture
Farley Mowat's 1961 novella, Owls in the Family, is set in Saskatoon and includes references to several area landmarks, including The Railroad Bridge. His 1957 book The Dog Who Wouldn't Be concerns his childhood in Saskatoon in the 1920s and 1930s.
"Runnin' Back to Saskatoon" is a 1972 song by The Guess Who. Saskatoon is also mentioned in the City and Colour song "Comin' Home".[83]
Surrounding communities
Saskatoon is surrounded by several smaller communities, a number of which make up the larger Saskatoon census metropolitan area.

Langham
DalmenyWarman
MartensvilleAberdeen 
Asquith
Grandora
St. Denis  Saskatoon
Saskatoon 

Vanscoy Furdale
Grasswood
DundurnClavet References
- ^ Edmonton Journal, "Paris of the Prairies", April 30, 2007
- ^ a b c d "Quick Facts". City of Saskatoon. http://www.saskatoon.ca/QUICK%20FACTS/Pages/Quick%20Facts.aspx. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada and census subdivisions (municipalities), 2006 and 2001 censuses - 100% data". 2.statcan.ca. 2008-11-05. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/popdwell/Table.cfm?T=301&S=3&O=D. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Population Estimate & Projection". City of Saskatoon. http://www.saskatoon.ca/DEPARTMENTS/Community%20Services/PlanningDevelopment/FutureGrowth/DemographicAndHousingData/Pages/PopulationEstimateProjection.aspx. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ^ "Statistics Canada 2006 Community Profiles: Saskatoon". 2.statcan.ca. 2010-12-07. http://www12.statcan.ca/census-recensement/2006/dp-pd/prof/92-591/details/page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=4711066&Geo2=PR&Code2=47&Data=Count&SearchText=Saskatoon&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom=. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Population Estimate & Projection". Saskatoon.ca. 2010-12-31. http://www.saskatoon.ca/DEPARTMENTS/Community%20Services/PlanningDevelopment/FutureGrowth/DemographicAndHousingData/Pages/PopulationEstimateProjection.aspx. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ Statistics Canada 2006 Community Profiles: Saskatoon CMA.
- ^ "Section 1: Census metropolitan areas". Annual Demographic Estimates: Subprovincial Areas. Statistics Canada. February 3, 2011. http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/91-214-x/2009000/part-partie1-eng.htm. Retrieved 2011-02-03.
- ^ "Travel: Saskatoon". The Weather Network. http://www.theweathernetwork.com/index.php?product=travellers&pagecontent=CASK0276. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ a b c d "A History of Saskatoon to 1914". web.archive.org. July 2005. Archived from the original on 2006-10-03. http://web.archive.org/web/20061003192952/http://www.saskatoon100.ca/docs/SaskatoonHistoryto1914.pdf. Retrieved 2009-04-04.
- ^ O'Brien, Jeff; Ruth W. Millar, William P. Delainey (2006). Roberta Coulter. ed. Saskatoon: A History in Photographs. Coteau Books. p. 88. ISBN I-55050-336-7.
- ^ Saskatoon population up 2.8%, Regina up 0.6%, CBC News (Canadian Press), March 13, 2007.
- ^ By The StarPhoenix (Saskatoon) July 24, 2008 (2008-07-24). "City population sinks". Canada.com. http://www.canada.com/saskatoonstarphoenix/news/story.html?id=4c0536a2-24b0-40d6-9cc7-e87c286159a9. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "High percentage of seniors, kids in Saskatchewan: StatsCan - Saskatchewan - CBC News". Cbc.ca. 2007-07-17. http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/saskatchewan/story/2007/07/17/census-saskatchewan.html. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "2006 Community Profiles". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. 2009-02-24. http://www12.statcan.ca/census-recensement/2006/dp-pd/prof/92-591/index.cfm?Lang=E. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ "2001 Community Profiles". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. 2007-02-01. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/profil01/CP01/Index.cfm?Lang=E. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ "Statistics Canada, 2001 census". 0.statcan.gc.ca. 2009-08-14. http://www40.statcan.gc.ca/l01/cst01/demo27u-eng.htm. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Statistics Canada, 2001 Census". 2.statcan.ca. 2010-03-09. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census01/products/standard/themes/RetrieveProductTable.cfm?Temporal=2001&PID=58628&METH=1&APATH=3&PTYPE=55440&THEME=44&FREE=0&AID=0&FOCUS=0&VID=0&GC=99&GK=NA&SC=1&CPP=99&SR=1&RL=0&RPP=9999&D1=0&D2=0&D3=0&D4=0&D5=0&D6=0&GID=431629. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ a b c "Statistics Canada, 2001 Census". 2.statcan.ca. 2002-03-12. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/profil01/CP01/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=4711066&Geo2=PR&Code2=47&Data=Count&SearchText=saskatoon&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All&Custom=. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ Aboriginal Conditions in Census Metropolitan Areas, 1981-2001, Statistics Canada, ISBN 0-662-40884-5, Table 1.
- ^ Aboriginal Conditions in Census Metropolitan Areas, 1981-2001, Statistics Canada, ISBN 0-662-40884-5, Figure 3.
- ^ "Saskatoon Health Region List of Hospitals". Saskatoonhealthregion.ca. http://www.saskatoonhealthregion.ca/your_health/facilities_hospitals.htm. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Health officials seek answers to spike in Saskatchewan HIV cases". CBC News. 2009-03-24. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2009/03/24/hiv-prostituion.html.
- ^ a b "Saskatchewan accounts for a quarter of Canada's HIV babies". CBC News. 2009-03-24. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2009/03/23/hiv-babies.html?ref=rss&loomia_si=t0:a16:g2:r1:c0.206439:b23288122.
- ^ "Saskatoon clinic 'struggling' with explosion of HIV". CBC News. 2009-03-25. http://www.cbc.ca/health/story/2009/03/25/hiv-clinic.html?ref=rss&loomia_si=t0:a16:g2:r5:c0.152625:b23259742.
- ^ "Saskatchewan's HIV infection rate a 'crisis': top health doctor". CBC News. 2009-03-19. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2009/03/19/hiv-rate.html.
- ^ a b Parker, Rob. "How Saskatoon Got the Nickname POW". http://www.marketmyarticle.com/Article/How-Saskatoon-Got-the-Nickname-POW/1816. Retrieved 2009-04-25.
- ^ a b AHN staff (April 6, 2009). "Saskatoon Emerges As Fastest Growing City In Canada". AHN. http://www.allheadlinenews.com/articles/7014690196. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ "Saskatchewan's Economy -". About Saskatchewan/Economy. Government of Saskatchewan. http://www.gov.sk.ca/Default.aspx?DN=8f48fa79-d320-48d8-bc6a-f414d4c59694. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ^ "Innovation Place Saskatoon". http://www.innovationplace.com/innovation-place.php. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ "TP141 - Aircraft Movement Statistics". Tc.gc.ca. 2011-01-12. http://www.tc.gc.ca/policy/report/tp141e/tp141.htm. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ Passenger Traffic Passenger statistics from airport
- ^ River Landing. Retrieved February 4, 2007.
- ^ The Partnership. Retrieved February 4, 2007.
- ^ "Direct Control District No. 1 (DCD1) for The South Downtown". City of Saskatoon. August 27, 2004. http://www.saskatoon.ca/DEPARTMENTS/Community%20Services/PlanningDevelopment/FutureGrowth/Documents/DCD1_Guidelines.pdf. Retrieved 2010-11-10.
- ^ "Future Growth Study". City of Saskatoon. June 2000. http://www.saskatoon.ca/DEPARTMENTS/Community%20Services/PlanningDevelopment/NeighbourhoodPlanning/Documents/future_growth_study.pdf. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ "Saskatoon—Canadian leader in economic growth in 2005.(gross domestic product)". Sask Business. March 1, 2006. http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-147297681.html. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ "Saskatoon—Canadian leader in economic growth with GDP of seven per cent in 2005.(SASKATOON UPDATE)(gross domestic product)". Sask Business. November 1, 2005. http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1G1-139566970.html. Retrieved 2009-04-25.
- ^ "Economic News—September 19, 2008 - Enterprise Saskatchewan -". Government of Saskatchewan. http://www.enterprisesaskatchewan.ca/enr091908. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ Blevins, Kevin (November 19, 2009). "Saskatchewan deficit projected to reach $1.05 billion". Regina Leader-Post. CanWest. http://communities.canada.com/reginaleaderpost/blogs/bestfromthenewsroom/archive/2009/11/19/breaking-news-saskatchewan-deficit-projected-to-reach-1-05-billion.aspx. Retrieved 2010-04-13.
- ^ Scott, Neil (November 27, 2009). "Regina only Western Canadian city with positive near-term employment prospects: report". Regina Leader-Post (CanWest).
- ^ "City Planning". City of Saskatoon. Archived from the original on 2008-06-07. http://web.archive.org/web/20080607104710/http://www.saskatoon.ca/org/city_planning/. Retrieved 2009-07-10.
- ^ http://www.theweathernetwork.com/gardening/cask0276
- ^ "Canadian Climate Normals 1961-1990". http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_1961_1990_e.html?province=ALL&stationID=1474&stationName=saskatoon&searchType=BeginsWith.
- ^ "Canadian Climate Normals 1961-1990". http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_1961_1990_e.html?province=ALL&stationID=1474&stationName=saskatoon&searchType=BeginsWith. Retrieved 2009-07-05.
- ^ http://www.victoryseeds.com/frost/saskatchewan.html
- ^ "Backgrounder: What is the Climate Reference Station (CRS)?". http://www.gov.sk.ca/adx/aspx/adxGetMedia.aspx?mediaId=941&PN=Shared. Retrieved 2009-10-31.
- ^ "National Climate Data and Information Archive". http://www.climate.weatheroffice.ec.gc.ca/climate_normals/results_e.html?Province=ALL&StationName=saskatoon&SearchType=BeginsWith&LocateBy=Province&Proximity=25&ProximityFrom=City&StationNumber=&IDType=MSC&CityName=&ParkName=&LatitudeDegrees=&LatitudeMinutes=&LongitudeDegrees=&LongitudeMinutes=&NormalsClass=A&SelNormals=&StnId=3328&. Retrieved 2009-03-29.
- ^ Osborn, Liz. "Hottest Spots in Canada". Current Results. http://www.currentresults.com/Weather-Extremes/Canada/hottest.php. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ "Worst blizzard in years blasts Saskatchewan". CBC News. 2007-01-10. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2007/01/10/sask-storm.html.
- ^ "Blizzard blasts Saskatoon". .canada.com. 1955-12-12. http://www2.canada.com/reginaleaderpost/news/story.html?id=1c4514e7-f28f-4411-806b-92e6eb45d337. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ Environment Canada—Canadian Climate Normals 1971–2000. Retrieved 09 July 2009.
- ^ http://www.police.saskatoon.sk.ca/pdf/annual_reports/2009_Annual_Report.pdf
- ^ http://www.police.saskatoon.sk.ca/pdf/Monthend_Summary_Report_for_December_2008.pdf
- ^ "New film renews community discussion about Aboriginal freezing deaths in Saskatoon". Dispatch (University of Regina). http://www.uregina.ca/alumni/news-aen-nfrcdaafdis.htm. Retrieved 15 February 2010.
- ^ "Saskatoon police chief admits starlight cruises are not new". Windspeaker (Aboriginal Multimedia Society of Alberta). July 1, 2003. http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Saskatoon+police+chief+admits+starlight+cruises+are+not+new.%28inquiry...-a0105369747. Retrieved 15 February 2010.
- ^ "History of Saskatoon, Saskatchewan". Saskatoonkiosk.ca. http://www.saskatoonkiosk.ca/history.php. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Meewasin Trail and Facilities". http://www.meewasin.com/facilities/trail/. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
- ^ "River Landing - Saskatchewan's premier residential and destination tourist centre!". Riverlanding.ca. http://www.riverlanding.ca/. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "River Landing Village". Lakeplacidsaskatoon.com. 1999-12-04. http://www.lakeplacidsaskatoon.com/. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ Lake Placid fails deadline[dead link]
- ^ "Money for Saskatoon complex coming, developer says". CBC News. 2009-11-17. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2009/11/17/sl-lake-placid911.html.
- ^ Lake Placid Back in the Game
- ^ "Funds pledged for $51M Saskatoon art gallery". CBC News. 2009-09-23. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2009/09/23/sk-saskatoon-art-gallery.html.
- ^ "Traffic Bridge Closed Immediately Until Further Notice". City of Saskatoon. August 24, 2010. http://www.saskatoon.ca/FORUM/Traffic%20Detours/Pages/TrafficBridgetobeClosedImmediatelyUntilFurtherNotice.aspx. Retrieved 2010-09-03.
- ^ Saskatoon's south bridge finally becoming a reality, Saskatoon StarPhoenix, June 20, 2008. Retrieved July 11, 2008.
- ^ "Proximity Railway Map for Saskatoon" (PDF). http://proximityissues.ca/Maps/RAC-2004-Saskatoon.pdf. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ Saskatchewan Transportation Company (2009-08-20). "STC, The Saskatchewan Transportation Company Home Page". Stcbus.com. http://www.stcbus.com/. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ City of Saskatoon, Projected Growh Map, October 10, 2008 (accessed Nov. 16, 2008)
- ^ "Art Gallery of Saskatchewan at River Landing". http://www.riverlanding.ca/project_update/phase1/destination_centre/index.html. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ^ "Mendel Art Gallery provides impetus for new building". http://www.mendel.ca/ags/index.html. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ^ "CBC News: Mendel art gallery gets makeover in Saskatoon: new home, new name". 2009-04-03. http://www.cbc.ca/canada/saskatchewan/story/2009/04/03/gallery-saskatoon.html. Retrieved 2010-07-26.
- ^ "Save the Mendel website". http://www.savethemendel.org. Retrieved 2010-07-26.
- ^ "Saskatoon StarPhoenix: Mendel memory may disappear". http://www2.canada.com/saskatoonstarphoenix/news/forum/story.html?id=aafa65c0-e5ba-40ff-bc38-42cae8f6bf6d. Retrieved 2010-07-26.
- ^ "Meewasin Valley Centre". http://www.meewasin.com/education/meewasin_valley/index.php. Retrieved 2008-03-10.
- ^ Zoo Brochure[dead link]
- ^ "Downtown Capitol Theatre to close for good April 3". The StarPhoenix. 2008-03-23. http://www.canada.com/saskatoonstarphoenix/story.html?id=181aa6f7-6840-4853-afb6-37079da4caa0&k=60279. Retrieved 2008-04-03.
- ^ Key to Landmarks[dead link]
- ^ Government House Canadian Honours database[dead link]
- ^ "U of S Huskie Athletics". Huskies.usask.ca. http://huskies.usask.ca/Home_Left/mens_sports/football/legacy.php. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "U of S Huskie Athletics". Huskies.usask.ca. http://huskies.usask.ca/Home_Left/mens_sports/volleyball/legacy.php. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "U of S Huskie Athletics". Huskies.usask.ca. http://huskies.usask.ca/Home_Left/mens_sports/track_field/legacy.php. Retrieved 2011-05-05.
- ^ "Comin' Home Lyrics". Sing365.com. http://www.sing365.com/music/lyric.nsf/Comin%27-Home-lyrics-City-And-Colour/87A04CAF0ADDED97482571260008AB7C. Retrieved 2010-05-15.
External links
Coordinates: 52°08′N 106°41′W / 52.133°N 106.683°W
- City of Saskatoon Official Website
- Tourism Saskatoon
- City of Saskatoon - Official Community Plan - Bylaw No. 8769
- Narratives of Saskatoon 1882-1912
- Saskatoon on Google Maps
- Pike Lake Provincial Park
- Black Strap Provincial Park
- Parks Canada (English)
- Map of Saskatoon at Statcan
- The Encyclopedia of Saskatchewan - Saksatoon
 Subdivisions of Saskatchewan
Subdivisions of SaskatchewanSubdivisions Communities Cities Estevan · Flin Flon (part) · Humboldt · Lloydminster (part) · Martensville · Meadow Lake · Melfort · Melville · Moose Jaw · North Battleford · Prince Albert · Regina · Saskatoon · Swift Current · Weyburn · YorktonTopics  Category ·
Category ·  Portal ·
Portal ·  WikiProject
WikiProjectCensus metropolitan areas (CMAs) in Canada by size Toronto, ON · Montreal, QC · Vancouver, BC · Ottawa, ON · Calgary, AB · Edmonton, AB · Quebec City, QC · Winnipeg, MB · Hamilton, ON · London, ON · Cambridge-Kitchener-Waterloo, ON · St. Catharines-Niagara, ON · Halifax, NS · Oshawa, ON · Victoria, BC · Windsor, ON · Saskatoon, SK · Regina, SK · Sherbrooke, QC · St. John's, NL · Barrie, ON · Kelowna, BC · Abbotsford, BC · Greater Sudbury, ON · Kingston, ON · Saguenay, QC · Trois-Rivières, QC · Guelph, ON · Moncton, NB · Brantford, ON · Thunder Bay, ON · Saint John, NB · Peterborough, ON
Categories:- Saskatoon
- Populated places established in 1883
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.