- Cree
-
Not to be confused with the Creek people.
Cree
nēhilaw
nēhiyaw camp near Vermilion, Alberta, in 1871 Total population over 200,000 Regions with significant populations Canada, United States Languages Related ethnic groups The Cree are one of the largest groups of First Nations / Native Americans in North America, with 200,000 members living in Canada. In Canada, the major proportion of Cree live north and west of Lake Superior, in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and the Northwest Territories, although 15,000 live in eastern Quebec.[1]
In the United States, this Algonquian-speaking people lived historically from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share a reservation with the Ojibwe (Chippewa).[2]
The documented westward migration over historic time has been strongly associated with their roles as middle men and hunters in the North American Fur Trade.[3]
Contents
Tribes
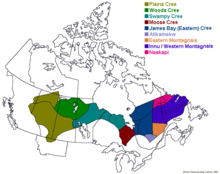
The Cree Nation is generally divided into eight groups (some political, others cultural):
- Naskapi (Innu) and
- Montagnais (Innu) are inhabitants of an area they refer to as Nitassinan. Their territories comprise most of the present-day political jurisdictions of eastern Quebec and Labrador. Their cultures are differentiated, as the Naskapi are still caribou hunters and more nomadic than the Montagnais, but the Montagnais have more settlements. The total population of the two groups in 2003 was about 18,000 people, of which 15,000 lived in Quebec. Their dialects and languages are the most distinct from the Cree spoken by the groups west of Lake Superior.
- Attikamekw are inhabitants of the area they refer to as Nitaskinan (Our Land), in the upper St. Maurice River valley of Quebec (about 300 km north of Montreal). Their population is around 4,500.
- James Bay Cree - Grand Council of the Crees; approximately 16,357 Cree (Iyyu in Coastal Dialect / Iynu in Inland Dialect) of the James Bay and Nunavik regions of Northern Quebec.
- Moose Cree - Moose Factory[4] in the Cochrane District, Ontario; this group lives on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River, at the southern end of James Bay.
- Swampy Cree - this group lives in northern Manitoba along the Hudson Bay coast and adjacent inland areas to the south and west, and in Ontario along the coast of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Some also in eastern Saskatchewan around Cumberland House. It has 4,500 speakers.
- Woods Cree group in northern Alberta and Saskatchewan.
- Plains Cree 34,000 people in Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and Montana.
Collectively the Cree used the autonym Nēhilawē (those who speak our language).[5] They used "Cree" to refer to their people only when speaking the languages of the European colonists, French or English.[6]
Skilled American bison hunters and horsemen, the Plains Cree were allied with the Assiniboine and the Saulteaux before they encountered French settlers in the 18th century.
Name
The name "Cree" is derived from the Algonkian-language exonym Kiristino, which the Ojibwa used for tribes around Hudson Bay. The French colonists and explorers, who spelled the term Kilistinon, Kiristinon, and Cristinaux, used the term for numerous tribes which they encountered north of Lake Superior, in Manitoba, and west of there.[7] The French used these terms to refer to various groups of peoples in Canada, some of which are now better distinguished as Severn Anishinaabe (Ojibwa), who speak languages different from the Algonkian or the Cree.[8] Depending on the community, the Cree may call themselves by the following names: the nēhiyaw, nīhithaw, nēhilaw, and nēhinaw; or ininiw, ililiw, iynu (innu), or iyyu. These names are derived from the historical autonym nēhiraw (uncertain meaning) or from the historical autonym iriniw (meaning "person"). Cree using the latter autonym tend to be those living in the territories of Quebec and Labrador.[9]
Language
The Cree language (also known in the most broad classification as Cree-Montagnais, Cree-Montagnais-Naskapi, to show the groups included within it) is the name for a group of closely related Algonquian languages spoken by approximately 117,000 people across Canada, from the Northwest Territories to Labrador. It is the most widely spoken aboriginal language in Canada.[10] The only region where Cree has official status is in the Northwest Territories, together with eight other aboriginal languages.[11][12]
The two major groups: Nehiyaw and Innu, speak a mutually intelligible, Cree dialect continuum, which can be divided by many criteria. In a dialect continuum, "It is not so much a language, as a chain of dialects, where speakers from one community can very easily understand their neighbours, but a Plains Cree speaker from Alberta would find a Quebec Cree speaker difficult to speak to without practice."[13]
One major division between the groups is that the Eastern group palatalizes the sound /k/ to either /ts/ (c) or to /tʃ/ (č) when it precedes front vowels. There is also a major difference in grammatical vocabulary (particles) between the groups. Within both groups, another set of variations has arisen around the pronunciation of the Proto-Algonquian phoneme *l, which can be realized as /l/, /r/, /y/, /n/, or /ð/ (th) by different groups. Yet in other dialects, the distinction between /eː/ (ē) and /iː/ (ī) has been lost, merging to the latter. In more western dialects, the distinction between /s/ and /ʃ/ (š) has been lost, both merging to the former.
If the consonants /p/ /t/ /c/ and /k/* used in Cree are compared[14] to their English counterparts, it is noticeable that there is little distinction of voicing. In English, voicing marks the difference of meaning in words such as "bin : pin". Since there is not distinction of voicing in Cree, it is common for variants of /t/ to sound more like [d] without any difference in meaning.[15]
Victor Gollum lists Cree in the Encyclopedia of the World's Endangered Languages as one of fifty-fve languages that have more than 1,000 speakers which are being actively acquired by children.[16]
In Canada
The Cree are the largest group of First Nations in Canada, with over 200,000 members and 135 registered bands.[17] This large population may be a result of the Crees' traditional openness to inter-tribal marriage. Together, their reserve lands are the largest of any First Nations group in the country.[17] The largest Cree band and the second largest First Nations Band in Canada after the Six Nations Iroquois is the Lac La Ronge Band in northern Saskatchewan.
The Métis (from French Métis - any person of mixed ancestry) are people of mixed ancestry, such as Nehiyaw (or Anishinaabe) and French, English, or Scottish heritage. According to Indian and Northern Affairs Canada, the Métis were historically the children of French fur traders and Nehiyaw women or, from unions of English or Scottish traders and northern Dene women (Anglo-Métis). Generally in academic circles, the term Métis can be used to refer to any combination of persons of mixed Native American and European heritage, although historical definitions for Métis remain. Canada's Indian and Northern Affairs broadly define Métis as those persons of mixed First Nation and European ancestry.
In the United States
At one time the Cree were located in northern Minnesota, North Dakota and Montana. Today they live as part of the federally recognized Chippewa Cree tribe, located on the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation in Montana. They share the reservation with the Pembina Band of Chippewa Indians, who form the "Chippewa" half of the Chippewa Cree tribe. (In Canada the Chippewa are known as Ojibwa.) Traditionally, the southern limits of the Cree territory in the United States were the Missouri River and the Milk River in Montana.
Cree First Nation communities
1 Naskapi (Iyiyiw and Innu)
- Kawawachikamach
- Natuashish
2 Montagnais
a Eastern Montagnais (Innu)- Mingan
- Uashat-Maliotenam
- Matimekosh
- Natashquan
- Pakua-Shipi
- La Romaine
- Sheshatshiu
b Western Montagnais (Nehilaw and Ilniw)
- Mashteuiatsh
- Betsiamites
- Essipit
3 Atikamekw (Nehiraw)
- Atikamekw d'Opitciwan
- Les Atikamekw de Manawan
- Conseil des Atikamekw de Wemotaci
4 James Bay Cree
a Northern James Bay Cree (Iyiyiw)- Cree Nation of Chisasibi
- Eastmain First Nation (also Southern James Bay Cree)
- Cree Nation of Wemindji
- Cree Nation of Whapmagoostui
b Southern James Bay Cree (Iyniw (inland) and Iyyiw (coastal))
- Eastmain First Nation (also Northern James Bay Cree)
- Cree Nation of Mistissini
- Cree Nation of Nemaska
- Oujé-Bougoumou First Nation – Oujé-Bougoumou, Quebec
- The Crees of the Waskaganish First Nation
- Waswanipi Cree First Nation
5 Moose Cree (Mōsonī / ililī)
6 Swampy Cree (Maškēkowak / nēhinawak)
- Attawapiskat First Nation – Attawapiskat, Ontario
- Black Sturgeon First Nation
- Brunswick House First Nation (also Ojibwa)
- Chapleau Cree First Nation
- Chemawawin Cree Nation (also Rocky Cree)
- Constance Lake First Nation (also Ojibwa)
- Cumberland House Cree Nation
- Fisher River Cree Nation
- Flying Post First Nation (also Ojibwa)
- Fort Albany First Nation (also known as Albany First Nation) - Fort Albany, Ontario
- Fort Severn First Nation
- Fox Lake Cree Nation
- Kashechewan First Nation
- Marcel Colomb First Nation
- Matachewan First Nation (also Ojibwa)
- Mathias Colomb First Nation (also Rocky Cree)
- Misipawistik Cree Nation (formerly known as Grande Rapids First Nation)(also Rocky Cree)
- Missanabie Cree First Nation
- Mosakahiken Cree Nation
- Neskantaga First Nation
- Opaskwayak Cree Nation – The Pas, Manitoba
- Red Earth Cree Nation (also Woods Cree)
- Sapotaweyak Cree Nation
- Shamattawa Cree Nation
- Shoal Lake Cree Nation (also Woods Cree)
- Tataskweyak Cree Nation
- Taykwa Tagamou Nation (formerly known as New Post First Nation)
- War Lake First Nation
- Weenusk First Nation
- Wuskwi Sipihk First Nation
- York Factory First Nation
7 Woodland Cree
a Rocky Cree (Asinīskāwiyiniwak)- Barren Lands First Nation
- Bunibonibee Cree Nation (formerly known as Oxford House First Nation)
- Chemawawin Cree Nation (also Swampy Cree)
- God’s Lake First Nation
- Manto Sipi Cree Nation
- Mathias Colomb First Nation (also Swampy Cree)
- Misipawistik Cree Nation (formerly known as Grand Rapids First Nation)(also Swampy Cree)
- Moose Lake First Nation
- Nelson House Band of Cree (Historical)
- Norway House Cree Nation
- Pimicikamak
- Split Lake First Nation
- The Pas First Nation
b Woods Cree (Sakāwithiniwak / nīhithawak)
- Bigstone Cree Nation
- Canoe Lake First Nation(also Bush Cree)
- Driftpile First Nation
- Duncan's First Nation
- Fort McMurray First Nation (also Chipewyan)
- Grouard First Nation
- Green Lake Band of Cree (historical)
- Lac La Ronge First Nation (formerly known as Lac La Ronge Indian Band)
- La Ronge & Stanley Mission Band of Cree Indians (Historical), which divided and then re-amalgamated:
- James Roberts Band of Cree Indians (Historical)
- Amos Charles Band of Cree Indians (Historical)
- La Ronge & Stanley Mission Band of Cree Indians (Historical), which divided and then re-amalgamated:
- Montreal Lake First Nation
- Peter Ballantyne Cree Nation
- Lac La Ronge First Nation (formerly known as Lac La Ronge Indian Band)
- Heart Lake First Nation
- Kapawe'no First Nation
- Little Red River Cree Nation
- Loon River First Nation
- Lubicon Lake Indian Nation
- Mikisew Cree First Nation
- Red Earth Cree Nation (also Swampy Cree)
- Sawridge First Nation
- Shoal Lake Cree Nation (also Swampy Cree)
- Sturgeon Lake Cree Nation
- Sucker Creek First Nation
- Swan River First Nation
- Wabasca First Nation
- Whitefish Lake First Nation 128
8 Plains Cree (Paskwāwiyiniwak / nēhiyawak)
a Downstream People (Māmihkiyiniwak)- Cowessess First Nation
- Little Black Bear First Nation
- Muscowpetung First Nation (also Saulteaux)
- Nekaneet First Nation
- Ochapowace First Nation
- One Arrow First Nation
- Peepeekisis First Nation
- Star Blanket First Nation
i Calling River / Qu'Appelle Cree (Kātēpwēwi-sīpīwiyiniwak)
- Ocean Man First Nation (also Assiniboine and Saulteaux)
- Pheasant Rump Nakota Nation (also Nakoda and Saulteaux)
- Whitebear First Nation
ii Rabbit skins (Wāpošwayānak)
- Kahkewistahaw First Nation
- Okanese First Nation (also Saulteaux)
- Pasqua First Nation (also Saulteaux)
- Sakimay First Nation (also Saulteaux)
iii Touchwood Hills Cree (Pasākanacīwiyiniwak)(also Saulteaux) – Punnichy, Saskatchewan
- Daystar First Nation
- Gordon First Nation
- Kawacatoose First Nation
- Muskowekwan First Nation
iv Cree-Assiniboine / Young Dogs (Nēhiyawi-pwātak)
- Piapot First Nation (also Assiniboine)
b Upstream People (Natimiyininiwak)
- Beaver Lake Cree Nation – Lac la Biche, Alberta
- Big Island Lake First Nation (also known as Joseph Bighead First Nation)
- Chippewa-Cree Indians of the Rocky Boy’s Reservation, Montana (also Ojibwa)
- Frog Lake First Nation
- Kehewin Cree Nation
- Lucky Man First Nation
- Moosomin First Nation
- Mosquito Grizzly Bear's Head First Nation (also Nakoda)
- Muskeg First Nation
- Pelican Lake First Nation
- Saulteaux First Nation (also Saulteaux)
- St. Peter's Band of Cree and Saulteaux (Historical)(also Saulteaux)
- Muskoday First Nation (formerly: John Smith First Nation) – Muskoday, Saskatchewan
- Peguis First Nation – Peguis, Manitoba
- Sturgeon Lake First Nation
- Thunderchild First Nation
- Waterhen Lake First Nation
- Witchekan Lake First Nation
i Beaver Hills Cree (Amiskwacīwiyiniwak)
- Alexander First Nation (also Wapski Mahikan Society) – Morinville, Alberta
- Alexis Nakota First Nation (also Nakoda)
- Enoch Cree Nation – Winterburn, Alberta
- Ermineskin Cree Nation – Hobbema, Alberta
- Louis Bull First Nation – Hobbema, Alberta
- Montana First Nation – Hobbema, Alberta
- O'Chiese First Nation(also Saulteaux)
- Onion Lake Cree Nation
- Paul First Nation (also Nakoda) – Duffield, Alberta
- Saddle Lake Cree First Nation
- Blue Quills Band of Cree (Historical)
- Saddle Lake Band of Cree (Historical)
- Wahsatenaw Band of Cree (Historical)
- Whitefish (Goodfish) Lake First Nation
- Samson Cree Nation – Hobbema, Alberta
- Sunchild First Nation
ii House Cree (wāskahikaniwiyiniwak)
iii Parklands Cree / Willow Cree (Paskokopāwiyiniwak)
- Beardy's and Okemasis First Nations
- James Smith First Nation
- Peter Chapman Cree Nation (incorporated into James Smith First Nation, but with some legal status as a separate entity).[18]
iv River Cree (Sīpīwininiwak)
- Little Pine First Nation
- Poundmaker First Nation
- Red Pheasant Cree Nation
- Sweetgrass First Nation
v Northern Plains Cree / Western Woodland Cree / Bush Cree (Sakāwiyiniwak)
- Big River First Nation
- Canoe Lake First Nation (also Woods Cree)
- Flying Dust First Nation
- Island Lake First Nation
- Makwa Sahgaiehcan First Nation
Notable Cree Chiefs
- Mistāwasis ("Big Child", also known as Pierre Belanger), Chief of the Parklands/Willow Cree (Paskokopāwiyiniwak), born about 1813. He was one of the influential chiefs of the House Cree or Wāskahikaniwiyiniwak, supplied between 1852–1854 Fort Carlton with bison meat and pemmican, acquired in his youth by constant military conflicts the respect of Crowfoot, the chief of the Siksika, the Blackfoot called Mistāwasis respectfully “The Iron Buffalo of the Plains”)[19]
- Ahtahkakoop ("Starblanket"), Chief of the House Cree (Wāskahikaniwiyiniwak). He was born about 1815-16, signed together with his cousin, Mistāwasis in 1876 the Treaty 6 at Fort Carlton, where he agreed that his group were settled into a reserve near the present-day Prince Albert, died 4 December 1896 at the age of 81 years)[20]
- Ahchuchhwahauhhatohapit (Ahchacoosacootacoopits - ‘Starblanket’,[21] Chief of a band of Calling River Cree (Kātēpwēwi-sīpīwiyiniwak), born about 1845 in the lower Qu’Appelle Valley, son of Wāpiy-mōsētōsis ("White Calf"), his tribal group was closely associated with the Ka Kichi Wi Winiwak under the leadership of chief Kakeesheway (‘Loud Voice’), and a close ally of Payipwāt ("Piapot"), the chief of the Cree-Assiniboine or "Young Dogs", 1879 after the disappearance of the bison Ahchuchhwahauhhatohapit settled on a reserve in the File Hills of the lower Qu'Appelle Valley, died 1917 in the Star Blanket reserve, Saskatchewan)[22]
- Payipwāt (or Piapot: "[One who Knows the] Secrets of the Sioux"), also known as "Hole in the Sioux" or Kisikawasan - ‘Flash in the Sky’, Chief of the Cree-Assiniboine or the Young Dogs with great influence on neighboring Assiniboine, Downstream People, southern groups of the Upstream People and Saulteaux (Plains Ojibwa), born 1816, kidnapped as a child by the Sioux,[23] he was freed about 1830 by Plains Cree, significant Shaman,[24] most influential chief of the feared Young Dogs,[25] convinced the Plains Cree to expand west in the Cypress Hills, the last refugee for bison groups, therefore disputed border area between Sioux, Assiniboine, Siksika Kainai and Cree, refused to participate in the raid on a Kainai camp near the present Lethbridge, Alberta, then the Young Dogs and their allies were content with the eastern Cypress Hills to the Milk River, Montana, does not participate at the negotiations on the Treaty 4 of 1874, he and Cheekuk, the most important chief of the Plains Ojibwa in the Qu'Appelle area, signed on 9 September 1875 the treaty only as preliminary contract, tried with the chiefs of the River Cree Minahikosis ("Little Pine") and Mistahi-maskwa ("Big Bear") to erect a kind of Indian Territory for all the Plains Cree, Plains Ojibwa and Assiniboine - as Ottawa refused, he asked 1879-80 along with Kiwisünce (cowessess- 'Little Child')[26] and the Assiniboine for adjacent reserves in the Cypress Hills, Payipwāt settled in a reserve about 37 miles northeast of Fort Walsh, Minahikosis ("Little Pine") and Papewes (‘Lucky Man’) asked successfully for reserves near the Assiniboine or Payipwāt - this allowed the Cree and Assiniboine to preserve their autonomy - because they went 1881 in Montana on bison hunting, stole Absarokee horses and alleged cattle killed, arrested the U.S. Army the Cree-Assiniboine group, disarmed and escorted them back to Canada - now unarmed, denied rations until the Cree and Assiniboine gave up their claims to the Cypress Hills and went north - in the following years the reserves changed several times and the tribes were trying repeated until to the Northwest Rebellion in 1885 to build an Indian Territory, Payipwāt remained under heavy guard, until his death he was a great spiritual leader, therefore Ottawa deposed Payipwāt on 15 April 1902 as chief, died in April 1908 on Piapot Reserve, Saskatchewan)[27]
- Kee-a-kee-ka-sa-coo-way (‘The Man Who gives the War Whoop’), Chief of the Plains Cree, was in the middle of the 19th century the leading chief of the Plains Cree, had also a large following among the Plains Ojibwa around Fort Pitt, his sub-chief was Mukitou (‘Black Powder’), the father of Mistahi-maskwa.
- Mistahi-maskwa (recorded as Mistihui'muskwa or as Mistahimusqua; better known as Big Bear in English and as Gros Ours in French), Chief of the Plains Cree, born about 1825, son of the Ojibwa-Chief Mukitou (‘Black Powder’), mastered his native language, the Cree language, as well as Ojibwe language, led the last resistance to the dispersal of the Cree on many reservations and asked for a big total reserve, a revolt of the young warriors under the leadership of one of his sons in 1885 destroyed these plans, died 17 January 1888 on the Poundmaker reservation in North Battleford in Saskatchewan.
- Kapapamahchakwew (Kā-papāmahcahkwêw, Kapapa Machatiwe, Papamahchakwayo, French: ‘Esprit Errant’, better known as Wandering Spirit, war chief of the Plains Cree under Mistahimaskwa, born 1845 near Jackfish Lake, Saskatchewan, committed on 2 April 1885, the so-called Frog Lake massacre, killed the Indian Agent Thomas Quinn and eight whites and one Métis, surrendered in July at Fort Pitt, was hanged on 27 November 1885 in Battleford, Saskatchewan)[28]
- Kamiokisihkwew (Miyo Kisikaw - Fine Day,[29] Chief of the Plains Cree, born 1850 in the Battle River region, died 193[?], was a shaman and war chief under Pitikwahanapiwiyin`s River Cree, during the North-West Rebellion Battleford was sacked by River Cree, subsequently Fine Day was as war chief the leader in the uprising, defeated the Canadian army in the Battle of Cut Knife, later joined a group of Plains Cree under the leadership of Chief Wikaskokiseyin(‘Sweet Grass’), whose chief he became later)
- Pitikwahanapiwiyin (Pîhtokahânapiwiyin - ‘Poundmaker’,[30][31] Chief of the River Cree, born about 1842 in the North Battleford Region in Saskatchewan; son of Sikakwayan (‘Skunk Skin’), an shaman of the Assiniboine and a Franco-Canadian Métisse, the sister of Chief Mistāwasis ("Big Child"), Chief of a band consisting of Plains River Cree (Sīpīwininiwak-paskwāwiyiniwak), Woods River Cree (‘Sīpīwininiwak-sakāwiyiniwak’), Western Woodland Cree (Sakāwiyiniwak) and Nakoda (Stoney), was adopted in 1873 by the Siksika chief Crowfoot as son, lived several years by the Blackfeet-name Makoyi-koh-kin (‘Wolf Thin Legs’) under the Siksika, returned to the Cree, became counselor of the Chief Pihew-kamihkosit (‘Red Pheasant’), was involved in the negotiations for the Treaty 6 in 1876 and went in 1879 in the Poundmaker reservation, later he participated in the siege of Battleford and the Battle of Cut Knife, died 4 July 1886 in Blackfoot Crossing, Alberta)[32]
- Wikaskokiseyin (Wee-kas-kookee-sey-yin, better known as Chief Sweet Grass, Chief of the Plains Cree, his mother was a captured Absaroke, as he grew up he was also called Apistchi-okimas- 'Little Chief', signed the Treaty 6 on 9 September 1876 at Fort Pitt, along with bands of Woodland Cree, Chipewyan, some Saulteaux, only a quarter of the participating groups were Plains Cree, while his successor as chief Wah-wee-oo-kah-tah-mah-hote ('Strike him on the back') signed the Treaty 6 at Fort Carlton on the 28th August 1876 together with the Willow Cree, died 11 January 1877 in a shootout accident on the Plains, probably at Saint-Paul-des-Cris, Alberta)[33]
- Peechee (Pesew - ‘Mountain Lion’, also known as Louis Piche), Chief of the Asini Wachi Nehiyawak and later the head chief of the 'Rocky/Mountain Cree' or Asini Wachi Wi Iniwak, born about 1821, introduced under the Asini Wachi Wi Iniwak the Catholic rite, his three sons, Piyesew Chak, Keskayiwew('Bobtail') and Ermineskin were also significant chiefs, Pesew and his elder son Chak Piyesew were killed during a gambling dispute in 1843, among his sons-in-law were the chiefs Samson, Chiniki, Bearspaw, Capote Blank and Jacques Cardinal)[34]
- Ermineskin (‘One with teh skin like a ermine’,[35] Sehkosowayanew, Sikosew Inew, also known as Baptiste Piche, Chief of the Bear Hills Cree (Maskwa Wachi-is Ininiwak), son of Pesew (‘Mountain Lion’), brother-in-law of Pitikwahanapiwiyin)[36]
- Keskayiwew (Kiskiyew, Kiskiyo - Bobtail, also known as Alexis Piche, Chief of the Bear Hills Cree (Maskwa-wachi-is Ininiwak), son of Pesew (‘Mountain Lion’), brother of Ermineskin, became chief after the death of his older brother, was elected instead of Maskepetoon ('Broken Arm') to the chieftainship of the Rocky Cree and later became head chief of the Western Cree(‘Pakisimotan Wi Iniwak’) and soon after became the head chief of all the groups of the Upstream People)
- Kamdyistowesit (Kanaweyihimitowin,[37] ‘Beardy’, French: ‘Barbu’, Chief of the Parklands or Willow Cree, born 1828 near Duck Lake, became in the 1870th chief, married Yaskuttsu-s,[38] the half-sister of chief Küpeyakwüskonam (‘One Arrow’), among the members of his tribal group were many Métis descendants of the Hudson's Bay Company employee George Sutherland)[39]
- Küpeyakwüskonam (Kupeyakwuskonam, Kah-pah-yak-as-to-cum - One Arrow, French: ‘Une Flèche’, Chief of the Parklands or Willow Cree, born 1815 in the Saskatchewan River Valley, son of George Sutherland (‘Okayasiw’) and his second wife Paskus (‘Rising’), tried to prevent in 1876 negotiations on the Treaty 6 at Fort Carlton along with Kamdyistowesit ('Beardy') and Saswaypew ('Cut Nose'), but finally signed on August 28 the treaty, in August 1884 he attended a meeting with chief Mistahimaskwa ('Big Bear') and Papewes (‘Papaway’ - 'Lucky Man'), his tribal group joined first the Métis in 1885, died on 25 April 1886 in the prison)[40]
- Minahikosis (Little Pine, French: ‘Petit Pin’, Chief of the Plains Cree, born about 1830 in the vicinity of Fort Pitt, Saskatchewan, his mother was a Blackfeet, became famous in the 1860s, as armed Plains Cree to find the last remaining bison, penetrated more and more into the territory of the Blackfoot Confederacy, led three years bitter resistance, signed however, in view of his starving people in 1879 the Treaty 6, and moved into a reserve at the foot of Blue Hill along the Battle River, his reputation was comparable to that of Mistahimaskwa' ('Big Bear'))[41]
- Papewes (Papaway - ‘Lucky Man’, Chief of the Plains River Cree (Sīpīwininiwak-paskwāwiyiniwak), born in the late 1830s near Fort Pitt, was in the 1870s a leader of Mistahimaskwa´s Plains River Cree, as the bison disappeared, signed along with Little Pine on the 2nd July 1879 for the 470 members of his tribal group an annex to the Agreement No. 6 at Fort Walsh, in vain he asked for a reserve in the Cypress Hills and the Buffalo Lake, so many members went back to Mistahimaskwa ("Big Bear") or joined Minahikosis ("Little Pine"), Papewes asked 1884 in vain a reserve adjacent to the reserves of Pitikwahanapiwiyin (' Poundmaker'), Minahikosis and Mistahimaskwa, during the rebellion of 1885 were the two groups of Papewes and Minahikosis scattered and some of their members fled in the U.S., 1886 settled the remaining members of the two groups in the Little Pine's reserve[42] died 1901 nahe Fort Assiniboine, Montana)[43]
- Saswaypew (Sayswaypus, Seswepiu - ‘Cut Nose’, Chief of the Parklands or Willow Cree, son of Wimtchik, a Franco-Canadian Métis, married One Arrow’s sister Nawapukayus, his sisters Ayamis and Minuskipuihat were both married to ‘One Arrow’, Kamdyistowesit (‘Beardy’) and he were brother-in-law, because both were married to daughters of George Sutherland)
- Maskepetoon (Maski Pitonew - ‘Broken Arm’, ‘Crooked Arm’, later called Peacemaker, Chief of a group of Rocky /Mountain Cree or Asini Wachi Wi Iniwak, born about 1807 in the Saskatchewan River region, because of his bravery he was called by the hostile Blackfoot Mon-e-ba-guh-now or Mani-kap-ina (‘Young Man Chief’), turned later to the Methodist missionaries, what him and his followers brought into conflict with the Catholic free Rocky Cree under the leadership of Pesew, moved to the reserve and was soon known as the Peacemaker, was killed in 1869 in a Blackfoot camp in Alberta by the enemy war chief Big Swan, in an attempt to make peace between the two peoples unarmed)[44]
- Pihew-kamihkosit (Pee-yahn-kah-nihk-oo-sit, better known as Red Pheasant, Chief of the Plains River Cree, brother and counselor of the chief Wuttunee (‘Porcupine’), signed on 23 August 1876 on behalf of his brother Wuttunee the Treaty 6, he was then regarded as a so called Treaty Chief by the Canadian government, moved with his tribal group 1878 onto the present Red Pheasant Reserve, about 33 km south of North Battleford, Saskatchewan)[45]
- Peayasis (better known as François Desjarlais, Chief of the Beaver River Cree or Amisk Sipi Wi Iniwak, a subgroup of the Woodland Cree (Sakāwithiniwak), born 1824 at the Beaver River, son of Ladoucoeur dit Desjarlais and Josephte Suzette Cardinal, signed on 8 August 1876 the Treaty 6, participated in battle of Battle River)
- Kahkewistahaw, Chief of the Rabbit Skin Cree (Wāpošwayānak) and Saulteaux, signed in 15 September 1874 the Treaty 4, his tribal group was hunting in the area around Wood Mountain and the Cypress Hills and went back to the Qu'Appelle Valley to get once in the year their payments and gifts until a reserve was established in 1881)[46][47]
- Paskwüw (Paskwa, Pisqua, usually called Pasquah - ‘The Plain’; French: Les Prairies), Chief of the Plains Cree, born 1828, son of the famous chief Mahkaysis, 1874 his tribal group were making their living with bison hunting in the vicinity of today's Leech Lake, Saskatchewan, they had also created gardens and raised a small herd of cattle, in September 1874 Pasqua took part in the negotiations on the Treaty 4 in Qu'Appelle Valley, he asked the Canadian government for the payment of £ 300,000 to the tribes, which the Hudson's Bay Company had received for the sale of Rupert's land to Canada, despite the refusal of Canada he finally signed the treaty and moved to a reserve five miles west of Fort Qu'Appelle, stayed out with his tribal group from the Northwest Rebellion of 1885, died in March 1889 he succumbed to the tuberculosis)[48]
- Petequakey (‘Comes to Us With the Sound of Wings’, better known as Isidore Cayen dit Boudreau, Chief of the Parklands or Willow Cree at Muskeg Lake, born in St. Boniface, Manitoba, as son of Pierre Narcisse Cayen dit Boudreau and Adelaide Catherine Arcand (‘Kaseweetin’), though he was a Métis he became chief of the Willow Cree an the Métis, who were living with the Cree, brother and counselor of chief Kee-too-way-how (a.k.a. Alexander Cayen dit Boudreau), after Kee-too-way-how had left the reserve on the Muskeg Lake to live around Batoche, became Petequakey chief (1880–1889) of the remaining Cree and Métis living in the reserve, he participated on 26 March 1885 along with the Métis leader Gabriel Dumont at the battle at Duck Lake, thereafter he led his tribal group to St. Laurent to participate in the defense of Batoche, one of the largest Métis settlements and the seat of the Saskatchewan's provisional government during the rebellion)[49]
- Kee-too-way-how (‘Sounding With Flying Wings’, better known as Alexander Cayen dit Boudreau, Chief of the Parklands or Willow Cree at Muskeg Lake, born 1834 St. Boniface, Manitoba, son of Pierre Narcisse Cayen dit Boudreau and Adelaide Catherine Arcand (‘Kaseweetin’), though he was of Métis descent he became chief of the Willow Cree and the Métis, who were living with the Cree, brother of Petequakey (‘Isidore Cayen dit Boudreau’), lived along Duck Lake, signed 1876 Treaty 6 and settled in a reserve at Muskeg Lake - that was later named after his brother Petequakey - but left the reserve in 1880 and lived again in the following years close to St. Laurent de Grandin mission, played a prominent role during the Northwest Rebellion of 1885 in which he participated in every battle, served also as an emissary of the Métis leader Gabriel Dumont to ask the Assiniboine for support, on 23 May 1885 he also submitted the declaration of surrender of Pitikwahanapiwiyin ('Poundmaker') to General Middleton, was captured on the 1st June 1885, in the subsequent trial of Kee-too-way-how at Regina, Louis Cochin testified that he and the carters in the camp of Pitikwahanapiwiyin survived only thanks to the intercession by Kee-way-too-how and its people, despite the positive testimony, he was on 14 August 1885 sentenced to imprisonment for seven years for his involvement in the Métis rebellion, died 1886).
Notable Cree
- Janice Acoose, author, of Sakimay (Saulteaux) and Ninankawe Marival Métis ancestry
- Nathaniel Arcand, actor
- Irene Bedard, actress
- Mary Katherine Campbell, former Miss America pageant titleholder
- Harold Cardinal, writer, political leader, teacher, and lawyer
- Lorne Cardinal, actor
- Tantoo Cardinal, actor
- Jonathan Cheechoo, NHL hockey player
- Theoren Fleury, retired NHL hockey player, humanitarian, spokesperson, and author
- Michael Greyeyes, actor
- Tomson Highway, playwright, librettist of the first Cree-language opera
- Tyson Houseman, actor
- Cody Lightning, actor
- Wilton Littlechild, lawyer, former Member of Parliament
- Delia Opekokew, lawyer and activist
- Bronson Pelletier, actor
- Roméo Saganash, Member of Parliament for Abitibi—Baie-James—Nunavik—Eeyou, Quebec
- Buffy Sainte-Marie, singer
- Cree Summer, singer/actress
- Richard Throssel (1882–1933), photographer
- Michelle Thrush, actor
- Gordon Tootoosis, actor
- Shania Twain, singer/songwriter
- Alfred Young Man (b. 1948), educator, writer, curator, artist
See also
- Cree language
- Cree syllabics
- Iynu
- James Bay Cree hydroelectric conflict
- Métis
- Michif
- Oji-Cree
- Okichitaw
- Politics of Saskatchewan
Notes
-
- ^ "Culture Areas Index". the Canadian Museum of Civilization. http://www.civilization.ca/cmc/exhibitions/tresors/ethno/etb0170e.shtml.
- ^ "Gateway to Aboriginal Heritage". Canadian Museum of Civilization Corporation. http://www.civilization.ca/cmc/exhibitions/tresors/ethno/etb0000e.shtml.
- ^ Alexander Mackenzie, [1] Voyages from Montreal Through the Continent of North America to the Frozen and Pacific Oceans in 1789 and 1793.
- ^ a b Moose Cree First Nation community profile
- ^ "[T]heir native name", David Thompson, Travels in Western North America 1784-1812, Victor G. Hopwood, ed., Toronto: Macmillan of Canada, 1971
- ^ David Pentland, "Synonymy", in Handbook of North American Indians, vol. 6, June Helm, ed., Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1981, p. 227
- ^ David Thompson noted, "The French Canadians...call them 'Krees', a name which none of the Indians can pronounce...", "Life with the Nahathaways", in David Thompson: Travels in Western North America 1784-1812, Victor G. Hopwood, ed., Toronto: Macmillan of Canada, 1971, p. 109.
- ^ Adolph M. Greeberg, James Morrison[disambiguation needed
 ], "Group Identities in the Boreal Forest: The Origin of the Northern Ojibwa", Ethnohistory 29(2):75-102 (1982)
], "Group Identities in the Boreal Forest: The Origin of the Northern Ojibwa", Ethnohistory 29(2):75-102 (1982) - ^ David H. Pentland, "Synonymy", in "West Main Cree", in Handbook of North American Indians, v. 6, June Helm, ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C., 1981, p. 227.
- ^ Statistics Canada: 2006 Census
- ^ Northwest Territories Official Languages Act, 1988 (as amended 1988, 1991-1992, 2003)
- ^ "Languages of Canada", Ethnologue: Languages of the World. Note: The western group of languages includes Swampy Cree, Woods Cree and Plains Cree. The eastern language is called Moose Cree. Retrieved 21 September 2008.
- ^ "Cree", Language Geek. Retrieved 21 September 2008.
- ^ * Most dialects have these consonants.
- ^ Wolfart, H. C., and Janet F. Carroll. Meet Cree: A Guide to the Language : Second Edition, New York: University of Alberta, 1981
- ^ C. Moseley (April 23, 2007), Encyclopedia of the World's Endangered Languages (Curzon Language Family Series), Routledge, pp. 3–4, ISBN 9780700711970, 070071197X, http://openlibrary.org/books/OL7763711M/Encyclopedia_of_the_World's_Endangered_Languages_(Curzon_Language_Family_Series)
- ^ a b Source: Canadian Geographic
- ^ http://esask.uregina.ca/entry/peter_chapman_first_nation.html
- ^ Mistawasis First Nation
- ^ AHTAHKAKOOP FIRST NATION
- ^ not to confused with the Ahtahkakoop (‘Starblanket’), Chief of the House Cree (Wāskahikaniwiyiniwak)
- ^ Ahchuchhwahauhhatohapit
- ^ Nehiyawak Leadership
- ^ by his knowledge of Sioux spirituality and medicine the Cree called him Payipwāt - 'One who knows the secrets of the Sioux'
- ^ they had more than any other Cree-Group adapted to the life on the Plains, were known as horse thieves and warriors, and as they drove little trade, they were feared by the Hudson's Bay Company as troublemakers
- ^ KIWISÜNCE
- ^ PAYIPWAT
- ^ Cree Nation
- ^ not to be confused with the Ojibwe Chief Mino-giizhig ("Fine Day")
- ^ Poundmaker was given his name because he had a special skill in the construction of the Buffalo Pound's for slaying of grazing bison
- ^ Back to Batoche
- ^ Pitikwahanapiwiyin
- ^ Treaty 6 - The Signing
- ^ Peechee's Band
- ^ clue to his Métis descent, as the ermine fur is white in winter and brown in summer - as well as the skin of a Métis
- ^ The People Who Own Themselves
- ^ Beardy's Okemasis First Nation
- ^ was the daughter of George Sutherland’s first wife Papamikiwis (‘Swinger’)
- ^ Indians Who Fought in the 1185 Resistance
- ^ One Arrow
- ^ Little Pine First Nation
- ^ Lucky Man Cree Nation
- ^ PAPEWES
- ^ Maskepetoon
- ^ Red Pheasant First Nation
- ^ Kahkewistahaw First Nation
- ^ Kahkewistahaw band
- ^ PASKWÜW
- ^ Métis Who Withdrew From Treaty
References
- Grant, Bruce (2000). The Concise Encyclopedia of the American Indian. New York: Wings Books. ISBN 0-517-69310-0.
- Stevens, James R. (1971). Sacred Legends of the Sandy Lake Cree. McClelland and Stewart Ltd..
External links
- Cree cultural site
- The East Cree language web
- The Cree-Innu linguistic atlas
- Grand Council of the Crees (GCC) website
- The Plains Cree - Ethnographic, Historical and Comparative Study by David Mandelbaum
- Lac La Ronge Band website
- Little Red River Cree Nation website
- Brief history of Cree from Canadian Geographic
- CBC Digital Archives - James Bay Project and the Cree
- Pimooteewin, a first Cree language opera
- Fisher River Cree Nation Official Website
- The Gift of Language and Culture website
- Cree language Wikipedia
- CBC Digital Archives – Eeyou Istchee: Land of the Cree
- On the Path of the Elders
First Nations in Alberta Cultural areas Plains · SubarticNumbered Treaties Ethno-cultural groups and languages Beaver / Daneẕaa (language) · Blackfoot / Niitsítapi (language) · Chipewyan / Denésoliné (language) · Cree / Nēhilawē (Woodland Cree) (language [plains variant]) · Sarcee / Tsuu T'ina (language) · Saulteaux / Nakawē (language) · Stoney / Nakoda (language)
First Nation
governments (bands)Alexander · Alexis · Athabasca Chipewyan · Bearspaw · Beaver · Beaver Lake Cree · Bigstone Cree · Chiniki · Chipewyan Prairie · Cold Lake · Dene Tha' · Driftpile · Duncan's · Enoch Cree · Ermineskin Cree · Fort McKay · Fort McMurray · Frog Lake · Heart Lake · Horse Lake · Kainai · Kapawe'no · Kehewin Cree · Little Red River Cree · Loon River · Louis Bull · Lubicon Lake · Mikisew Cree · Montana · O'Chiese · Paul · Piikani · Saddle Lake · Samson Cree · Sawridge · Siksika · Smith's Landing · Sturgeon Lake · Sucker Creek · Sunchild · Swan River · Tallcree · Tsuu T'ina · Wesley · Whitefish Lake (Atikameg) · Whitefish Lake (Goodfish) · Woodland CreeCategories:- Cree
- First Nations in the Northwest Territories
- First Nations in Alberta
- First Nations in Saskatchewan
- First Nations in Manitoba
- First Nations in Ontario
- First Nations in Quebec
- Native American tribes
- First Nations in British Columbia
- Algonquian peoples
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.