- Anishinaabe
-
Anishinaabe or Anishinabe—or more properly Anishinaabeg or Anishinabek, which is the plural form of the word—is the autonym often used by the Odawa, Ojibwe, and Algonquin peoples. They all speak closely related Anishinaabemowin/Anishinaabe languages, of the Algonquian language family.
The meaning of Anishnaabeg is "First" or "Original-Peoples". Another definition - possibly reflecting a traditionalist's viewpoint with a certain moral dimension - refers to "the good humans", or good people, meaning those who are on the right road/path given to them by the Creator or Gichi-Manidoo (Great Spirit). The Ojibwe scholar, linguist and author Basil Johnston, who explains the name in a creationist context, states that its literal translation is "Beings Made Out of Nothing", or "Spontaneous Beings", since they had been created by divine breath and were made up of flesh and blood and a soul or spirit - instead of rock, or fire, or water, or wind.[1]
Not all Anishinaabemowin speakers, however, call themselves Anishinaabeg. The Ojibwe people who moved to what are now the prairie provinces of Canada call themselves Nakawē(-k) and their branch of the Anishinaabe language, Nakawēmowin. (The French ethnonym for the group was the Saulteaux). Particular Anishinaabeg groups have different names from region to region.
There are many variant spellings of the Anishinaabe name, depending on the transcription scheme and also on whether the name is singular or plural. Therefore, different spelling systems may indicate vowel length or spell certain consonants differently (Anishinabe, Anicinape); meanwhile, variants ending in -eg/ek (Anishinaabeg, Anishinabek) come from an Algonquian plural, while those ending in an -e come from an Algonquian singular.
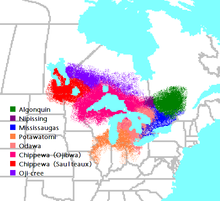
The name Anishinaabe is realised as Nishnaabe in some parts of North America, most prominently among the Odawa. The cognate Neshnabé comes from the Potawatomi, a people long allied with the Odawa and Ojibwe in the Council of Three Fires. Identified as Anishinaabe, but not part of the Council of Three Fires, are the Nipissing, Mississauga and Algonquin.
Closely related to the Ojibwe and speaking a language mutually intelligible with Anishinaabemowin (Anishinaabe language) are the Oji-Cree (also known as "Severn Ojibwe"). Their most common autonym is Anishinini (plural: Anishininiwag) and they call their language Anishininiimowin.
Among the Anishinaabeg, the Ojibwe collectively call the Nipissings and the Algonquins Odishkwaagamii (those who are at the end of the lake),[2] while those among the Nipissings who identify themselves as Algonquins call the Algonquins proper Omàmiwinini (those who are downstream).[3]
History
According to Anishinaabeg tradition, and from records of wiigwaasabak (birch bark scrolls), the people migrated from the eastern areas of North America, and from along the East Coast. In myth, the homeland was called Turtle Island.
Oral traditions among the Anishinaabeg tell a variety of creation stories. According to the oral history, seven great miigis (radiant/iridescent beings in human form) appeared to the Anishinaabe peoples in the Waabanakiing (Land of the Dawn, i.e. Eastern Land) to teach the people about the midewiwin life-style. One great miigis was too spiritually powerful and would kill people in the Waabanakiing whenever they were in its presence. This being later returned to the depths of the ocean, leaving the six great miigis to teach the people.
Each of the six miigis established separate doodem (clans) for the people. Of these doodem, five clan systems appeared: i) Awaazisii (Bullhead), ii) Baswenaazhi (Echo-maker, i.e., Crane), iii) Aan'aawenh (Pintail Duck), iv) Nooke (Tender, i.e., Bear), and v) Moozoonii (Little Moose). Later a sixth was added. vi) Waabizheshi (Marten).
After founding the doodem, the six miigis returned to the depths of the ocean as well. Some oral histories surmise that if the seventh miigis had stayed, it would have established the Animikii Thunderbird doodem.
The powerful miigis returned in a vision relating a prophecy to the people. It said that the Anishinaabeg needed to move west to keep their traditional ways alive, because of the many new settlements and people not of Anishinaabe blood who would soon arrive. The migration path of the Anishinaabe peoples would become a series of smaller Turtle Islands, confirmed by the miigis shells (i.e., cowry shells). After receiving assurance from their "Allied Brothers" (i.e., Mi'kmaq) and "Father" (i.e., Abnaki) of their safety in crossing other tribal territory, the Anishinaabeg moved inland. They advanced along the St. Lawrence River to the Ottawa River and through to Lake Nipissing, and then to the Great Lakes.
The first of these smaller Turtle Islands was Mooniyaa, where Mooniyaang (Montreal, Quebec) now stands. Here the Anishinaabeg divided into two groups: one that travelled up and settled along the Ottawa River, and the core group who proceeded to the "second stopping place" near Niagara Falls.
By the time the Anishinaabeg established their "third stopping place" near the present city of Detroit, the Anishinaabeg had divided into six distinct nations: Algonquin, Nipissing, Mississauga, Ojibwa, Odawa and Potawatomi. While the Odawa established their long-held cultural centre on Manitoulin Island, the Ojibwe established their centre in the Sault Ste. Marie region of Ontario, Canada. With expansion of trade with the French and later the British, fostered by availability of European small arms, members of the Council of Three Fires expanded southward to the Ohio River, southwestward along the Illinois River, and westward along Lake Superior, Lake of the Woods and the northern Great Plains. In their western expansion, the Ojibwa again divided, forming the Saulteaux, the seventh major branch of the Anishinaabeg: .
As the Anishinaabeg moved inland, through both alliances and conquest, they incorporated various other closely related Algonquian peoples into the Anishinaabe Nation. These included, but were not limited to, the Noquet (originally part of the Menomini Tribe) and Mandwe (originally part of the Fox). Other incorporated groups can generally be identified by the individual's Doodem (Clan). Migizi-doodem (Bald Eagle Clan) generally identifies those whose ancestors were Americans and Ma'iingan-doodem (Wolf Clan) as Santee Sioux.
Other Anishinaabe doodem migrated out of the core Anishinaabeg groupings, such as the Nibiinaabe-doodem (Merman Clan), which is now the "Water-spirit Clan" of the Winnebagos. Anishinaabe peoples now reside throughout North America, in both the northern United States and southern Canada, chiefly around the Great Lakes and Lake Winnipeg.
After this migration, and the immigration of European newcomers to North America, many Anishinaabeg groups later entered into treaties with the governments of the Dominion of Canada and the United States. Treaty 3 (of the Numbered Treaties) in Canada was signed in 1873 between the Anishinaabe (Ojibwa) people west of the Great Lakes and the government of Canada.[4] Through other treaties and resulting relocations, some Anishinaabeg now reside in the states of Kansas, Oklahoma, South Dakota, and Montana in the United States, and the provinces of Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia in Canada.
Historical relations between the Anishinaabeg and other indigenous groups
Historical relations between the Anishinaabeg and European settlers
The first of the Anishinaabeg to encounter European settlers were those of the Three Fires Confederation, within the states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, and Pennsylvania in the territory of the present-day United States, and southern Ontario and Quebec of Canada. Although there were many peaceful interactions between the Anishinaabeg and the European settlers, there were also times of turmoil and war. Warfare cost many lives on both sides.
The Anishinaabe dealt with Europeans through the fur trade, intermarriage, and performance as allies. Europeans traded with the Anishinaabe for their furs in exchange for goods, and also hired the men as guides throughout the lands of North America. The Anishinaabeg (as well as other Aboriginal groups) began to intermarry with fur traders and trappers. Some of their descendants would later create the Métis ethnic group. Fur traders were generally capitalists with significant backing. They tended to marry daughters of chiefs, with both sides forming high-status alliances. The explorers, trappers and other European workers married or had unions with other Anishinaabeg women, and their descendants tended to form the Métis.
In French North America
The earliest Europeans to encounter native peoples in the Great Lakes area were the French voyageurs. They were mainly trappers rather than settlers. Such explorers gave French names to many places in present-day Minnesota and Wisconsin.
In British North America
The ethnic identities of the Ojibwa, Ottawa, and Potawatomi did not develop until after the Anishinaabeg reached Michilimackinac on their journey westward from the Atlantic coast. Using the Midewiwin scrolls, Potawatomi elder Shup-Shewana dated the formation of the Council of Three Fires to 796 AD at Michilimackinac.
In this Council, the Ojibwe were addressed as the "Older Brother," the Odawa as the "Middle Brother," and the Potawatomi as the "Younger Brother." Consequently, when the three Anishinaabe nations are mentioned in this specific order: Ojibwe, Odawa, and Potawatomi, it is an indicator implying Council of Three Fires as well. Each tribe had different functions: the Ojibwa were the "keepers of the faith," the Odawa the "keepers of trade," and the Potawatomi are the "keepers/maintainers of/for the fire" (boodawaadam). This was the basis for their exonyms of Boodewaadamii (Ojibwe spelling) or Bodéwadmi (Potawatomi spelling).
The Ottawa (also Odawa, Odaawa, Outaouais, or Trader) are a Native American and First Nations people. Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa (or Anishinaabemowin in Eastern Ojibwe syllabics) is the third most commonly spoken Native language in Canada (after Cree and Inuktitut), and the fourth most spoken in North America (behind Navajo, Cree, and Inuktitut). Potawatomi is a Central Algonquian language. It is spoken around the Great Lakes in Michigan and Wisconsin, as well as in Kansas in the United States. In southern Ontario in Canada, it is spoken by fewer than 50 people.
Though the Three Fires had several meeting places, they preferred Michilimackinac due to its central location. The Council met for military and political purposes. The Council maintained relations with fellow Anishinaabeg nations: the Ozaagii (Sac), Odagaamii (Meskwaki), Omanoominii (Menominee), Wiinibiigoo (Ho-Chunk), Naadawe (Iroquois Confederacy), Nii'inaawi-Naadawe (Wyandot), Naadawensiw (Sioux), Wemitigoozhi (France), Zhaaganaashi (England) and the Gichi-mookomaan (the United States). After the Europeans came into the country, the French built Fort Michilimackinac in the 18th century. After the Seven Years' War, the victorious English took over the fort, also using it as a trading post.
Through the totem-system (a totem is any entity which watches over or assists a group of people, such as a family, clan or tribe.[5] ) and promotion of trade, the Council generally had a peaceful existence with its neighbours. However, occasional unresolved disputes erupted into wars. The Council notably fought against the Iroquois Confederacy and the Sioux. During the Seven Years' War, the Council fought against England.[citation needed]
The Anishinaabeg established a relationship with the British similar to that they had with the French. They formed the Three Fires Confederation in reaction to conflict with encroaching settlers and continuing tensions with the British Canadian government, as well as that of the new United States.
In the United States
The Three Fires Confederacy had conflict with the new United States after the American Revolution, as settlers kept encroaching on their territory. The Council became the core member of the Western Lakes Confederacy (also known as "Great Lakes Confederacy"), joining together with the Wyandots, Algonquins, Nipissing, Sacs, Meskwaki and others.
During the Northwest Indian War and the War of 1812, the Three Fires Confederacy fought against the United States. Many Anishinaabe refugees from the Revolutionary War, particularly Odawa and Potawatomi, migrated north to British-held areas.
Those who remained in the east were subjected to the 1830 Indian Removal policy of the United States; among the Anishinaabeg, the Potawatomi were most affected. The Odawa had been removed from the settlers' paths, so only a handful of communities experienced removal. For the Ojibwa, removal attempts culminated in the Sandy Lake Tragedy and several hundred deaths. The Potawatomi avoided removal only by escaping into Ojibwa-held areas and hiding from US officials.
William Whipple Warren (1825–1853), a United States man of mixed-Ojibwe and European descent, became an interpreter, assistant to a trader to the Ojibwe, and legislator of the Minnesota Territory. A gifted storyteller and historian, he collected native accounts and wrote the History of the Ojibway People, Based Upon Traditions and Oral Statements, first published by the Minnesota Historical Society in 1885, some 32 years after his early death from tuberculosis. Given his Anglo-American father Lyman Marcus Warren and American education, the Indians of the time did not consider William one of them. They did think of him as a friend and half-brother, because he knew the Ojibwe language and much about the culture from his Ojibwe-French mother, Marie Cadotte.[6] His work covered much of the culture and history of the Ojibwe, gathered from stories of the nation.
Warren identified the Crane and Loon clans as the two Chief clans among his mother's Anishinaabe people. Crane Clan was responsible for external governmental relationships, and Loon Clan was responsible for internal governance relationships. Warren believed that the British and United States governments had deliberately destroyed the clan system, or the polity of governance, when they forced indigenous nations to adopt representative government and direct elections of chiefs. Further, he believed such destruction led to many wars among the Anishinaabe. He also cited the experiences of other Native Nations in the US (such as the Creek, Fox and others). His work in its entirety demonstrated the significance of the clan system.[6]
After the Sandy Lake Tragedy, the government changed its policy to relocating tribes onto reservations, often by consolidating groups of communities. Conflict continued through the 19th century, as Native Americans and the United States had different goals. After the Dakota War of 1862, many Anishinaabe communities in Minnesota were relocated and further consolidated.
In Canada
Population estimates indicate that the Anishinaabeg population in the United States is more numerous than that of Canada, but census reports are criticized as being inaccurate.
The Canadian Anishinaabeg are descended from the northern Lake Superior Anishinaabeg, whose original homeland was probably in the vicinity of the eastern upper peninsula of Michigan. They separated, with one group going down into Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, southern Ontario and Pennsylvania, while another group migrated straight westward. The ancestors of the Canadian Anishinaabeg moved to the north, and then to the west. They migrated to eastern British Columbia in the 19th century.
Scholars of the Anishinaabeg will eventually learn if all Anishinaabeg are descended from those Anishinaabeg of the eastern upper peninsula of Michigan, or if they are descended from the Algonquin Anishinaabeg of Quebec. The people's history points to the upper peninsula of Michigan as their land of formation.
The Anishinaabeg of Canada have managed to withstand the efforts of the European settlers and hold onto their languages. An estimated 50,000 Canadian Anishinaabeg speak their native tongue. From Quebec to the eastern lands of British Columbia, the Anishinaabeg reserves are, for the most part, smaller in size than those in the US, a factor which may have helped them preserve the languages.
Relations today between the Anishinaabeg and their neighbours
Other indigenous groups
There are many Anishinaabeg reserves and reservations; in some places the Anishinaabeg share some of their lands with others, such as the Cree, the Dakota, Delaware, and the Kickapoo, among others. The Anishnabek who "merged" with the Kickapoo tribe may now identify as being Kickapoo in Kansas and Oklahoma. The Prairie Potawatomi were the Ojibwe, Odawa and Potawatomi of Illinois and Wisconsin who were relocated to Kansas during the 19th century.
Canada
The Anishinaabe of Manitoba, particularly those along the east side of Lake Winnipeg, have had longstanding historical conflicts with the Cree people.
United States
The relationships between the various Anishinaabe communities with the United States government have been steadily improving since the passage of the Indian Reorganization Act. Several Anishinaabe communities still experience tensions with the state governments, county governments and with non-Native American individuals and their groups.
In contemporary times, the Anishinaabe have worked to renew the clan system as a model for self-governance. They have drawn from the work of Ojibwe educator Edward Benton-Banai, who emphasizes education based on one's own culture. They believe using the clan system will also be a basis of cultural and political revitalization of the people.[citation needed]
Major issues facing the various Anishinaabe communities are:
- cultural and language preservation or revitalization;
- full and independent federal recognition: some Anishinaabe communities are recognized by county or state governments, or are recognized by the federal government only as part of another tribe;
- treaty rights: traditional means of support (hunting, fishing and gathering), establishment of reservations or upholding of the reservation boundaries per treaties and their amendments;
- personal health: diabetes and asthma affect many Anishinaabe communities at a rate higher than the general population; and
- social disparity: many Anishinaabeg suffer poor education, high unemployment, substance abuse/addiction and domestic violence at rates higher than the general population.
Anishinaabe in popular culture
A fictional Anishinaabe clan in Ontario, the Mtigwaki, were featured in the comic strip For Better or For Worse from 2005–2006.
The popular book "Keeper N' Me" also reflects on the people and the traditions of the Anishinaabe people.
See also
- Algonquin (Omaamiwinini)
- Anishinaabe/Tribal Political Organizations
- Midewiwin
- Mississaugas (Misi-zaagiing)
- Nipissing (Odishkwaagamii)
- Oji-Cree/Severn Ojibwa (Anishinini)
- Oji-Cree language (Anishininiimowin)
- Ojibwa/Chippewa (Ojibwe)
- Odawa (Odaawaa/Ottawa)
- Odawa language
- Potawatomi (Boodewaadamii/Bodéwadmi)
- Saulteaux/Plains Ojibwa (Nakawē)
References
- ^ Johnston, Basil. 1990. Ojibway Heritage, p. 15. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln and London.
- ^ Baraga, Frederic. 1878. A Dictionary of the Otchipwe Language, explained in English. Montréal: Beauchemin & Valois.
- ^ Cuoq, Jean André. 1886. Lexique de la Langue Algonquine. Montréal: J. Chapleau & Fils.
- ^ Alexander Morris, The Treaties of Canada with the Indians, Belfords , Clarke & Co., Toronto (1880)
- ^ Merriem-Webster Online, http://www.merriam-webster.com/
- ^ a b William W. Warren, History of the Ojibway People, new intro and ed. by Theresa Schenk, St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 1885; reprint, 2009, pp. iii-xxi, accessed 22 Feb 2010
- Bento-Banai, Edward (2004). Creation—From the Ojibwa, The Mishomis Book.
- Cappel, Constance. Odawa Language and Legends: Andrew J. Blackbird and Raymond Kiogima. Xlibris, 2006. ISBN 1599269201 (Foundation for Endangered Languages Award)
- Warren, William W. History of the Ojibway People. Borealis Books (St. Paul, MN: 1984).
- White, Richard (July 31, 2000). "Chippewas of the Sault", The Sault Tribe News.
Further reading
- Cappel, Constance. The Smallpox Genocide of the Odawa Tribe at L'Arbre Croche, 1763: The History of a Native American People. Lewiston, NY: The Edwin Mellen Press, 2007. ISBN 0773452206
- Long, J. Voyages and Travels of an Indian Interpreter and Trader Describing the Manners and Customs of the North American Indians, with an Account of the Posts Situated on the River Saint Laurence, Lake Ontario, & C., to Which Is Added a Vocabulary of the Chippeway Language ... a List of Words in the Iroquois, Mehegan, Shawanee, and Esquimeaux Tongues, and a Table, Shewing the Analogy between the Algonkin and the Chippeway Languages. London: Robson, 1791.
- Moose, Lawrence L. Aaniin Ekidong: Ojibwe Vocabulary Project. St. Paul: Minnesota Humanities Center, 2009.
- Treuer, Anton. Living Our Language: Ojibwe Tales & Oral Histories. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 2001. ISBN 0873514041
- Treuer, Anton. Ojibwe in Minnesota. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 2010. ISBN 9780873517683
- Warren, William W. (1851). History of the Ojibway People.
- White, Richard (1991) The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region, 1650–1815 (Studies in North American Indian History) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England, ISBN 0-521-37104-X
External links
- Anishinabek Nation - Union of Ontario Indians
- Algonquin Anishinabeg Nation Tribal Council
- Sault Ste. Marie Tribe of Chippewa Indians History
- Bemaadizing: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Indigenous Life (An online journal)
- ‘Living’ Cybercartographic Atlas of Indigenous Artifacts and Knowledge
- "The Anishinaabe-Ojibwe people of the Great Lakes", Ojibwe Waasa-Inaabidaa, (US-focused), Public Broadcasting Service/PBS.
- Ojibwe migratory map, Ojibwe Waasa-Inaabidaa
Categories:- Great Lakes tribes
- First Nations in Ontario
- First Nations in Quebec
- First Nations in Manitoba
- First Nations in Saskatchewan
- Indigenous peoples of the Subarctic
- Native American tribes in Michigan
- Native American tribes in Indiana
- Native American tribes in Wisconsin
- Native American tribes in Minnesota
- Native American tribes in North Dakota
- Native American tribes in Montana
- Native American tribes in Kansas
- Native American tribes in Oklahoma
- Potawatomi
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.