- Mi'kmaq people
-
Míkmaq Grand Council Flag of the Mi'kmaq Nation[1] Total population 60,000 Regions with significant populations Canada (New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Quebec), United States (Maine) Languages Religion Christianity, Míkmaq Traditionalism and Spirituality, others
Related ethnic groups other Algonquian peoples
The Míkmaq (English /ˈmɪkˌmæk/; Mi'kmaq: [miːɡmax]) are a First Nations people, indigenous to the northeastern region of New England, Canada's Atlantic Provinces, and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec. The nation has a population of about 40,000 (plus 21,429 in the Qalipu First Nation[2]), of whom nearly 9,100 speak the Míkmaq language.[3][4] Once written in Míkmaq hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the standard Latin alphabet.
The ethnonym has traditionally been spelled Micmac in English, but the natives have used different spellings: Mi’kmaq (singular Mi’kmaw) by the Míkmaq of Prince Edward Island and Nova Scotia, Miigmaq (Miigmao) by the Míkmaq of New Brunswick, Mi’gmaq by the Listuguj Council in Quebec, or Mìgmaq (Mìgmaw) in some native literature.[5] Until the 1980s, "Micmac" remained the most common spelling in English. Although still used, for example, in Ethnologue, this spelling has fallen out of favour in recent years. Most scholarly publications use the preferred native spelling of Mi'kmaq.[6] The Míkmaq prefer to use one of the three current Míkmaq orthographies when writing in English or French.[7] They consider the English spelling to be "colonially tainted."[5]
On September 26th, 2011 the Government of Canada announced the recognition of Canada's newest Mi'kmaq First Nations Band, the Qalipu First Nations in Newfoundland and Labrador. The new landless band has accepted 20,000 applications to become part of the band. Its members are recognized as Status Indians, joining other organized Mi'kmaq bands recognized in the Northeast of Canada.[8][9]
Contents
Etymology
Lnu (the adjectival and singular noun, previously spelled "L'nu"; the plural is Lnúk, Lnu’k, Lnu’g, or Lnùg) is the self-recognized term for the Míkmaq of New Brunswick, Newfoundland, Nova Scotia, Quebec and Maine, meaning "human being" or "the people".[10]
Various explanations exist for the origin of the term Míkmaq. The Mi'kmaw Resource Guide states that "Míkmaq" means "the family":
The definite article "the" suggests that "Mi'kmaq" is the undeclined form indicated by the initial letter "m". When declined in the singular it reduces to the following forms: nikmaq - my family; kikmaq - your family; wikma - his/her family. The variant form Mi'kmaw plays two grammatical roles: 1) It is the singular of Mi'kmaq and 2) it is an adjective in circumstances where it precedes a noun (e.g. mi'kmaw[sic?] people, mi'kmaw treaties, mi'kmaw person, etc.)[11]
However, there are other hypotheses:
The name "Micmac" was first recorded in a memoir by de La Chesnaye in 1676. Professor Ganong in a footnote to the word megamingo (earth), as used by Marc Lescarbot, remarked "that it is altogether probable that in this word lies the origin of the name Micmac." As suggested in this paper on the customs and beliefs of the Micmacs, it would seem that megumaagee the name used by the Micmacs, or the Megumawaach, as they called themselves, for their land, is from the words megwaak, "red", and magumegek, "on the earth", or as Rand recorded, "red on the earth," megakumegek, "red ground," "red earth." The Micmacs, then, must have thought of themselves as the Red Earth People, or the People of the Red Earth. Others seeking a meaning for the word Micmac have suggested that it is from nigumaach, my brother, my friend, a word that was also used as a term of endearment by a husband for his wife... Still another explanation for the word Micmac suggested by Stansbury Hagar in "Micmac Magic and Medicine" is that the word megumawaach is from megumoowesoo, the name of the Micmacs' legendary master magicians, from whom the earliest Micmac wizards are said to have received their power.[12]
Members of the Mi'kmaq First Nation historically referred to themselves as Lnu, but used the term níkmaq (my kin) as a greeting. The French initially referred to the Míkmaq as Souriquois"[13] and later as Gaspesiens or (through English) "Mickmakis". The British originally referred to them as Tarrantines.[14]
History
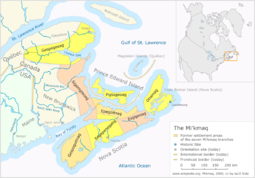
The Mi'kmaw territory was divided into seven traditional "districts". Each district had its own independent government and boundaries. The independent governments had a district chief and a council. The council members were band chiefs, elders, and other worthy community leaders. The district council was charged with performing all the duties of any independent and free government by enacting laws, justice, apportioning fishing and hunting grounds, making war, suing for peace, etc.
The Seven Mi'kmaq Districts are Kespukwitk, Sikepnékatik, Eskíkewaq, Unamákik, Piktuk aqq Epekwitk, Sikniktewaq, and Kespékewaq.
In addition to the district councils, there was also a Grand Council or Santé Mawiómi. The Grand Council was composed of "Keptinaq", or captains in English, who were the district chiefs. There were also Elders, the Putús (Wampum belt readers and historians, who also dealt with the treaties with the non-natives and other Native tribes), the women council, and the Grand Chief. The Grand Chief was a title given to one of the district chiefs, which was usually from the Mi'kmaq district of Unamáki or Cape Breton Island. This title was hereditary and usually went to the Grand Chief's eldest son. The Grand Council met on a little island on the Bras d'Or lake in Cape Breton called "Mniku", on a reserve today called Chapel Island or Potlotek. To this day, the Grand Council still meets at the Mniku to discuss current issues within the Mi'kmaq Nation.
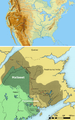
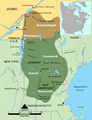
The Mi'kmaq were members of the Wapnáki (Wabanaki Confederacy), an alliance with four other Algonquian-language nations: the Abenaki, Penobscot, Passamaquoddy, and Maliseet. The allied tribes ranged from present-day New England in the United States to the Maritime Provinces of Canada. At the time of contact with the French (late 16th century), they were expanding from their maritime base westward along the Gaspé Peninsula /St. Lawrence River at the expense of Iroquoian-speaking tribes, hence the Míkmaq name for this peninsula, Kespek ("last-acquired"). On June 24 1610, Grand Chief Membertou converted to Catholicism and was baptised. He concluded an alliance with the French Jesuits which affirmed the right of Mi'kmaq to choose Catholicism and\or Mi'kmaw tradition
Eighteenth Century
The Mi'kmaq, as allies with the French, were amenable to limited French settlement in their midst. After France lost political control of Acadia in 1710, the Mí'kmaq engaged in warfare against the British throughout Dummer's War, King George's War, Father Le Loutre's War and the French and Indian War (Seven Years' War). Along with Acadians, the Mi'kmaq used military force to resist the founding of British (Protestant) settlements in Halifax, Dartmouth, Lawrencetown and Lunenburg. During the French and Indian War, the Mi'kmaq assisted the Acadians in resisting the British during the Expulsion of the Acadians. The military resistance ended with the French defeat at the Siege of Louisbourg (1758) in Cape Breton. After the war, the Mi'kmaq soon found themselves overwhelmed by increasing numbers of British people, who seized much of their land without payment.
Between 1725 and 1779, the Mí'kmaq signed a series of peace and friendship treaties with Great Britain, but none of these was a land cession treaty. The nation historically consisted of seven districts, which was later expanded to eight with the ceremonial addition of Great Britain at the time of the 1749 treaty. Chief Jean-Baptiste Cope signed a Peace Treaty in 1752 on behalf of the Shubenacadie Mi'kmaq.[15]
Later the Mí'kmaq also settled Newfoundland, as the unrelated Beothuk tribe became extinct. Mí'kmaq delegates concluded the first international treaty, the Treaty of Watertown, with the United States soon after it declared its independence in July 1776. These delegates did not officially represent the Mi'kmaq government, although many individual Mi'kmaq did privately join the Continental army as a result.
On August 31, 2010, the governments of Canada and Nova Scotia signed an historic agreement with the Mi'kmaq Nation, establishing a process whereby they must consult with the Mi'kmaq Grand Council before engaging in any activities or projects that affect the Mi'kmaq in Nova Scotia — which covers most, if not all, actions these governments might take within that jurisdiction. This is the first such collaborative agreement in Canadian history including all the First Nations within an entire province.[16]
Míkmaq First Nation subdivisions
Míkmaw names in the table are spelled according to several orthographies. The Míkmaw orthographies in use are Míkmaw pictographs, the orthography of Silas Tertius Rand, the Pacifique orthography, and the most recent Smith-Francis orthography, which has been adopted throughout Nova Scotia and in most Míkmaw communities.
Community Province/State Town/Reserve Est. Pop. Míkmaq name Abegweit First Nation  Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward IslandScotchfort, Rocky Point, Morell 396 Epekwitk Acadia  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaYarmouth 996 Malikiaq Annapolis Valley  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaCambridge Station 219 Kampalijek Aroostook Band of Micmac  Maine
MainePresque Isle 920 Ulustuk Bear River First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaBear River 272 Lsetkuk Buctouche First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickBuctouche 80 Puktusk Burnt Church First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickBurnt Church 14 1,488 Esk inuopitijkChapel Island First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaChapel Island 576 Potlotek Eel Ground First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickEel Ground 844 Natuaqanek Eel River Bar First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickEel River Bar 589 Ugpi'gangij Elsipogtog First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickBig Cove 3000+ Lsipuktuk Eskasoni First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaEskasoni 3,800+ Wékistoqnik Fort Folly First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickDorchester 105 Amlamkuk Kwesawék Micmacs of Gesgapegiag  Quebec
QuebecGesgapegiag 1,174 Keskapekiaq Nation Micmac de Gespeg  Quebec
QuebecFontenelle 490 Kespék Glooscap First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaHantsport 360 Pesikitk Indian Island First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickIndian Island 145 Lnui Menikuk Lennox Island First Nation  Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward IslandLennox Island 700 Lnui Mnikuk Listuguj Mi'gmaq First Nation  Quebec
QuebecListuguj Mi'gmaq First Nation 3,166 Listikujk Membertou First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaSydney 1,051 Maupeltuk Metepenagiag Mi'kmaq Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickRed Bank 527 Metepnákiaq Miawpukek First Nation  Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and LabradorConne River 2,366 Miawpukwek Qalipu First Nation  Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and LabradorNewfoundland and Labrador 21,429[17] Qalipu[18][19] Millbrook First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaTruro 1400 Wékopekwitk Pabineau First Nation  New Brunswick
New BrunswickBathurst 214 Kékwapskuk Paq’tnkek First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaAfton 500 Paqtnkek Pictou Landing First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaTrenton 547 Puksaqtéknékatik Indian Brook First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaIndian Brook (Shubenacadie) 2,120 Sipekníkatik Wagmatcook First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaWagmatcook 623 Waqm itkukWaycobah First Nation  Nova Scotia
Nova ScotiaWhycocomagh 900 Wékoqmáq Demographics
Year Population Verification 1500 4,500 Estimation 1600 3,000 Estimation 1700 2,000 Estimation 1750 3,000 Estimation 1800 3,100 Estimation 1900 4,000 Census 1940 5,000 Census 1960 6,000 Census 1972 10,000 Census 1998 15,000 SIL 2006 20,000 Census The pre-contact population is estimated at 3,000-30,000.[20] In 1616, Father Biard believed the Míkmaq population to be in excess of 3,000, but he remarked that, because of European diseases, there had been large population losses during the 16th century. Smallpox, wars and alcoholism led to a further decline of the native population, which was probably at its lowest in the middle of the 17th century. Then the numbers grew slightly again, before becoming apparently stable during the 19th century. During the 20th century, the population was on the rise again. The average growth from 1965 to 1970 was about 2.5%.
Celebrations
In the Canadian provinces of Nova Scotia and Newfoundland and Labrador, October is celebrated as Míkmaq History Month and the entire Nation celebrates Treaty Day annually on October 1. This was first signified in the year, 1752, with the Peace and Friendship Treaty (also called the Treaty of 1752) signed by Jean-Baptiste Cope of Shubenacadie and the king's representative. It was stated that the natives would be given gifts annually,"as long as they continued in Peace."[21]
Folklore
In Mi'kmaq mythology, evil and wickedness among men causes them to kill each other. This causes great sorrow to the creator-sun-god, who weeps tears that become rains sufficient to trigger a deluge. The people attempt to survive by traveling in bark canoes, but only a single old man and woman survive to populate the earth.[22]
- See also: Glooscap
Notable Míkmaq
- Dr. Daniel N. Paul, C.M., O.N.S., Mi'kmaq Elder, author (We Were Not the Savages), Mi'kmaq tribal historian, columnist, human rights activists (See www.danielnpaul.com)
- Grand Chief Gabriel Sylliboy, Grand Chief of the Mi'kmaq Nation
- Étienne Bâtard (18th century), warrior
- Noel Jeddore, Saqmaw forced into exile (1865–1944)
- Kevin Cloud
- Thomas Clair, actor who appeared in The New World
- Anna Mae Pictou Aquash, activist (1946–1976)
- Henri Membertou, kji-saqmaw/puowin (c.1525-1611)
- Rita Joe, poet
- Donald Marshall Jr.
- Chad Denny, ice hockey player for the Lewiston MAINEiacs and Atlanta Thrashers draftee
- Ashton Bernard, ice hockey player for the Cape Breton Screaming Eagles and New Jersey Devils draftee
- Lionel Little Eagle Pinn, Kitpoviosee, Writer
- Sandy McCarthy, played for the Calgary Flames ice hockey team
- Everett Sanipass, played for the Quebec Nordiques ice hockey team
- Ciara Loyer, played for the kickboxing team in British Columbia
- Lee (Harvey) Cremo, musician (1938–1999)
- Chief Noel Doucette (1938–1996)
- Noel Knockwood, Mi'kmaq Grand Council member and spiritual leader of the Mi'kmaq People
- L'kimu, legendary Mi'kmaq Chief
- Randi O'Brien, 2009 Aboriginal Achievement Award Winner
- Desiree Poirier Lessard, founder of the community Good News, Good Deeds
Pre-contact culture
Housing
Mi'kmaq people lived in structures called wigwams. Saplings, which were usually spruce, were cut down and bent over a circle drawn on the ground. These saplings were lashed together at the top, and then covered with birch bark. The Mi'kmaq had two different sizes of wigwams. The smaller size could hold 10-15 people and the larger size 15-20 people. Wigwams could be either conical or domed in shape.
Food and hunting
The Mi'kmaq were semi-nomadic. During the summer they spent most of their time on the shores harvesting seafood; during the winter they would move inland to the woods to hunt. The most important animal hunted by the Mi'kmaq was the moose which provided food, clothing, cordage, and other things. Other animals hunted/trapped included deer, caribou, bear, rabbit, beaver, and others. The weapon used most for hunting was the bow and arrow. The Mi'kmaq made their bows from maple. The mik'maq people would store lobsters in the ground for later consumption.[citation needed]
Hunting a moose
The moose was the most important animal to the Mi'kmaq. It was their second main source of meat, clothing and cordage, which were all crucial commodities. The Mi'kmaq usually hunted moose in groups of 3 to 5 men. Before the moose hunt, the Mi'kmaq would starve their dogs for 2 days to make them fierce in helping to finish off the moose. To kill the moose, they would injure it first, by using a bow and arrow or other weapons, and after it was down, they would move in on it and finish it off with spears and their dogs. The guts would then be fed to the dogs. During this whole process, the men would try to direct the moose in the direction of the camp, so that the women would not have to go as far to drag the moose back. A boy became a man in the eyes of the community after he had killed his first moose. It was only then that he had earned the right to marry.
Other
One spiritual capital of the Míkmaq nation is Mniku, the gathering place of the Míkmaq Grand Council or Santé Mawiómi, Chapel Island in the Bras d'Or Lakes of Cape Breton Island. The island is also the site of the St. Anne Mission, an important pilgrimage site for the Míkmaq. The island has been declared a historic site.[23]
See also
Notes
- ^ Flags of the World
- ^ Qalipu First Nations Official Website http://qalipu.ca/membership-programs-and-services/membership/
- ^ Lewis, M. Paul (2009). "Micmac". Ethnologue. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=mic. Retrieved October 13, 2011.
- ^ Statistics Canada 2006
- ^ a b Emmanuel Metallic et al., 2005, The Metallic Mìgmaq-English Reference Dictionary
- ^ Mi'kmaq Landscapes by Anne-Christine Hornborg (2008), p. 3
- ^ "it is now the preferred choice of our People." Daniel Paul, We Were Not the Savages, 2000, p. 10
- ^ Press Release, September 26,2011 "Government of Canada announces creation of Qalipu Mi'kmaq First Nation Band", Market Watch, 26 September 2011
- ^ Qalipu First Nations Official Website http://www.qalipu.com/default.asp
- ^ The Nova Scotia Museum's Míkmaq Portraits database
- ^ Mi'kmaw Resource Guide, Eastern Woodlands Publishing (1997)
- ^ cited in Paul to Marion Robertson, Red Earth: Tales of the Micmac, with an introduction to their customs and beliefs (1965) p. 5.
- ^ Relations des Jésuites de la Nouvelle-France
- ^ Lydia Affleck and Simon White. "Our Language". Native Traditions. http://www.peicaps.org/betweengen/circle/language.html. Retrieved 2006-11-08.
- ^ Historian William Wicken notes that there is controversy about this assertion. While there are claims that Cope made the treaty on behalf of all the Mi'kmaq, there is no written documentation to support this assertion (See William Wicken. Mi'kmaq Treaties on Trial: History, Land, and Donald Marshall Jr. University of Toronto Press. 2002. p. 184).
- ^ Mi'kmaq of Nova Scotia, Province of Nova Scotia and Canada Sign Landmark Agreement
- ^ Qalipu First Nations Official Website http://qalipu.ca/membership-programs-and-services/membership/
- ^ 'Government of Canada Announces the Creation of the Qalipu First Nation Band' by Marketwire http://www.marketwatch.com/story/government-of-canada-announces-the-creation-of-the-qalipu-mikmaq-first-nation-band-2011-09-26
- ^ Press Release September 26, 2011 http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/09/26/idUS146921+26-Sep-2011+MW20110926
- ^ Dickshovel - Micmac
- ^ Treaty of 1752|http://www.ainc-inac.gc.ca/al/hts/tgu/pubs/pft1752/pft1752-eng.asp
- ^ Canada's First Nations - Native Creation Myths
- ^ CBCnews. Cape Breton Míkmaq site recognized
References
- Bock, Philip K. 1978. "Micmac." pp. 109–122. In Handbook of North American Indians. Vol. 15. Northeast. Bruce G. Trigger, editor. Smithsonian Institution Press.
- Davis, Stephen A. 1998. Míkmaq: Peoples of the Maritimes, Nimbus Publishing.
- Magocsi, Paul Robert (ed.). Encyclopedia of Canada's Peoples, Toronto, University of Toronto Press, 1999.
- Paul, Daniel N. 2000. We Were Not the Savages: A Míkmaq Perspective on the Collision Between European and Native American Civilizations, Fernwood Pub.
- Prins, Harald E. L. 1996. The Míkmaq: Resistance, Accommodation, and Cultural Survival (Case Studies in Cultural Anthropology), Wadsworth.
- Rita Joe, Lesley Choyce. 2005. The Míkmaq Anthology, Nimbus Publishing (CN), 2005, ISBN 1-895900-04-2
- Robinson, Angela 2005. Tán Teli-Ktlams
itasit (Ways of Believing): Míkmaw Religion in Eskasoni, Nova Scotia. Pearson Education, ISBN 0-13-177067-5. - Whitehead, Ruth Holmes. 2004. The Old Man Told Us: Excerpts from Míkmaq History 1500-1950, Nimbus Publishing, 2004, ISBN 0-921054-83-1
- Wicken, William C. 2002. Míkmaq Treaties on Trial: History, Land, and Donald Marshall Junior, University of Toronto Press.
- http://www.cmmns.com/KekinamuekPdfs/Ch2screen.pdf
Documentary film
- Our Lives in Our Hands (Míkmaq basketmakers and potato diggers in northern Maine, 1986) [1]
Maps
Maps showing the approximate locations of areas occupied by members of the Wabanaki Confederacy (from north to south):
-
Eastern Abenaki (Penobscot, Kennebec, Arosaguntacook, Pigwacket/Pequawket)
-
Western Abenaki (Arsigantegok, Missisquoi, Cowasuck, Sokoki, Pennacook
External links
- First Nations Profiles
- [2]
- Micmac History
- Míkmaq Portraits Collection
- Míkmaq Dictionary Online
- The Micmac of Megumaagee
- Míkmaq Learning Resource
 "Micmacs". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913.
"Micmacs". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. 1913.- Unama'ki Institute of Natural Resources
Categories:- Mi'kmaq
- Algonquian peoples
- First Nations in Atlantic Canada
- First Nations in Quebec
- Native American tribes in Maine
- Algonquian ethnonyms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.