- Ojibwe people
-
This article is about the native North American people. For other uses of "Ojibwe", "Ojibway", or "Ojibwa", see Ojibway (disambiguation)."Chippewa" redirects here. For other uses, see Chippewa (disambiguation).
Ojibwe 
Symbol of the Anishinaabe peopleTotal population 219,711[citation needed] Regions with significant populations Canada, United States Languages English, Ojibwe
Religion Related ethnic groups Ottawa, Potawatomi and other Algonquian peoples
The Ojibwe (also Ojibwa or Ojibway) or Chippewa (also Chippeway) are among the largest groups of Native Americans–First Nations north of Mexico. They are divided between Canada and the United States. In Canada, they are the third-largest population among First Nations, surpassed only by Cree and Inuit. In the United States, they had the fourth-largest population among Native American tribes, surpassed only by Navajo, Cherokee and the Lakota. Because many Ojibwe were historically formerly located mainly around the outlet of Lake Superior, which the French colonists called Sault Ste. Marie, they referred to the Ojibwe as Saulteurs. Ojibwe who subsequently moved to the prairie provinces of Canada have retained the name Saulteaux. Ojibwe who were originally located about the Mississagi River and made their way to southern Ontario are known as the Mississaugas.[1]
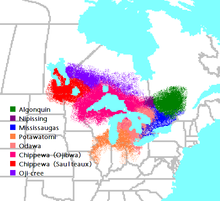
The Ojibwe peoples are a major component group of the Anishinaabe-speaking peoples, a branch of the Algonquian language family which includes the Algonquin, Nipissing, Oji-Cree, Odawa and the Potawatomi. The Ojibwe peoples number over 56,440 in the U.S., living in an area stretching across the northern tier from Michigan west to Montana.[citation needed] Another 77,940 of main-line Ojibwe; 76,760 Saulteaux and 8,770 Mississaugas, in 125 bands, live in Canada, stretching from western Quebec to eastern British Columbia.[citation needed] They are historically known for their crafting of birch bark canoes, sacred birch bark scrolls, use of cowrie shells for trading, cultivation of wild rice, and use of copper arrow points. In 1745 they adopted guns from the British to use to defeat and push the Dakota nation of the Sioux to the south.
The Ojibwe Nation was the first to set the agenda with European-Canadian leaders for signing more detailed treaties before many European settlers were allowed too far west. The Midewiwin Society is well respected as the keeper of detailed and complex scrolls of events, history, songs, maps, memories, stories, geometry, and mathematics.[2]
Contents
Name
Further information: List of Ojibwa ethnonymsThe autonym for this group of Anishinaabeg is Ojibwe (plural: Ojibweg). This name is commonly anglicized as "Ojibwa" or "Ojibway." The name "Chippewa" is an alternative anglicization. Although many variations exist in literature, "Chippewa" is more common in the United States and "Ojibwa" predominates in Canada, but both terms are used in each country. In many Ojibwe communities throughout Canada and the U.S., more members have been using the generalized name Anishinaabe(-g).
The exact meaning of the name Ojibwe is not known; the most common explanations for the name derivations are:
- from ojiibwabwe (/o/ + /jiibw/ + /abwe/), meaning "those who cook\roast until it puckers", referring to their fire-curing of moccasin seams to make them water-proof.[3] Some early sources say this name described a method of ritual torture which the Ojibwe applied to enemies.;[4]
- from ozhibii'iwe (/o/ + /zhibii'/ + /iwe/), meaning "those who keep records [of a Vision]", referring to their form of pictorial writing, and pictographs used in Midewiwin sacred rites;[5] or
- from ojiibwe (/o/ + /jiib/ + /we/), meaning "those who speak-stiffly"\"those who stammer", an exonym or name given to them by the Cree, characterizing their language as heard by different language speakers.[6]
Language
Main article: Ojibwe languageThe Ojibwe language is known as Anishinaabemowin or Ojibwemowin, and is still widely spoken, but the number of fluent speakers has declined sharply. Today, most of the language's fluent speakers are elders. A movement has picked up in recent years to revitalize the language, and restore its strength as an anchor of Ojibwe culture. The language belongs to the Algonquian linguistic group, and is descended from Proto-Algonquian. Its sister languages include Blackfoot, Cheyenne, Cree, Fox, Menominee, Potawatomi, and Shawnee. Anishinaabemowin is frequently referred to as a "Central Algonquian" language; however, Central Algonquian is an area grouping rather than a linguistic genetic one. Ojibwemowin is the fourth-most spoken Native language in North America (US and Canada) after Navajo, Cree, and Inuktitut. Many decades of fur trading with the French established the language as one of the key trade languages of the Great Lakes and the northern Great Plains.
The popularity of the epic poem The Song of Hiawatha, written by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow in 1855, publicized the Ojibwe culture. The epic contains many toponyms that originate from Ojibwe words.
History
Pre-contact and spiritual beliefs
According to their tradition, and from recordings in birch bark scrolls, many Ojibwe came from the eastern areas of North America, which they called Turtle Island, and from along the east coast. They traded widely across the continent for thousands of years and knew of the canoe routes west and a land route to the west coast. The identification of the Ojibwe as a culture or people may have occurred in response to contact with Europeans. The Europeans preferred to deal with bounded groups and tried to identify those they encountered.[7]
According to the oral history, seven great miigis (radiant/iridescent) beings appeared to the peoples in the Waabanakiing (Land of the Dawn, i.e., Eastern Land) to teach them the mide way of life. One of the seven great miigis beings was too spiritually powerful and killed the peoples in the Waabanakiing when they were in its presence. The six great miigis beings remained to teach, while the one returned into the ocean. The six great miigis beings established doodem (clans) for the peoples in the east, symbolized by animal, fish or bird species. The five original Anishinaabe doodem were the Wawaazisii (Bullhead), Baswenaazhi (Echo-maker, i.e., Crane), Aan'aawenh (Pintail Duck), Nooke (Tender, i.e., Bear) and Moozoonsii (Little Moose), then these six miigis beings returned into the ocean as well. If the seventh miigis being stayed, it would have established the Thunderbird doodem.
At a later time, one of these miigis appeared in a vision to relate a prophecy. It said that if the Anishinaabeg did not move further west, they would not be able to keep their traditional ways alive because of the many new settlements and European immigrants who would arrive soon in the east. Their migration path would be symbolized by a series of smaller Turtle Islands, which was confirmed with miigis shells (i.e., cowry shells). After receiving assurance from the their "Allied Brothers" (i.e., Mi'kmaq) and "Father" (i.e., Abnaki) of their safety to move inland, the Anishinaabeg gradually migrated along the St. Lawrence River to the Ottawa River to Lake Nipissing, and then to the Great Lakes.
The first of the smaller Turtle Islands was Mooniyaa, where Mooniyaang (present-day Montreal, Quebec) now stands. The "second stopping place" was in the vicinity of the Wayaanag-gakaabikaa (Concave Waterfalls, i.e., Niagara Falls). At their "third stopping place" near the present-day city of Detroit, Michigan, the Anishinaabeg divided into six groups, of which the Ojibwe was one. The first significant new Ojibwe culture-centre was their "fourth stopping place" on Manidoo Minising (Manitoulin Island). Their first new political-centre was referred as their "fifth stopping place", in their present country at Baawiting (Sault Ste. Marie).
Continuing their westward expansion, the Ojibwe divided into the "northern branch," following the north shore of Lake Superior, and "southern branch," along its south shore. As the peoples continued to migrate westward, the "northern branch" divided into a "westerly group" and a "southerly group". The "southern branch" and the "southerly group" of the "northern branch" came together at their "sixth stopping place" on Spirit Island (46°41′15″N 092°11′21″W / 46.6875°N 92.18917°W) located in the St. Louis River estuary of the present-day Duluth/Superior region. The people were directed in a vision by the miigis being to go to the "place where there is food (i.e., wild rice) upon the waters." Their second major settlement, referred as their "seventh stopping place", was at Shaugawaumikong (or Zhaagawaamikong, French, Chequamegon) on the southern shore of Lake Superior, near the present La Pointe, Wisconsin.
The "westerly group" of the "northern branch" migrated along the Rainy River, Red River of the North, and across the northern Great Plains until reaching the Pacific Northwest. Along their migration to the west, they came across many miigis, or cowry shells, as told in the prophecy.
Post-contact with Europeans
The first historical mention of the Ojibwe occurs in the French Jesuit Relation of 1640, a report by the missionary priests to their superiors in France. Through their friendship with the French traders (coureur des bois and voyageurs), the Ojibwe gained guns, began to use European goods, and began to dominate their traditional enemies, the Lakota and Fox to their west and south. They drove the Sioux from the Upper Mississippi region to the area of the present-day Dakotas, and forced the Fox down from northern Wisconsin. The latter allied with the Sauk for protection.
By the end of the 18th century, the Ojibwe controlled nearly all of present-day Michigan, northern Wisconsin, and Minnesota, including most of the Red River area. They also controlled the entire northern shores of lakes Huron and Superior on the Canadian side and extending westward to the Turtle Mountains of North Dakota. In the latter area, the French Canadians called them Ojibwe or Saulteaux.
The Ojibwe (Chippewa) were part of a long-term alliance with the Anishinaabe Ottawa and Potawatomi peoples, called the Council of Three Fires. They fought against the Iroquois Confederacy, based mainly to the southeast of the Great Lakes in present-day New York, and the Sioux. The Ojibwe expanded eastward, taking over the lands along the eastern shores of Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. In part due to its long trading alliance, the Ojibwe allied with the French against Great Britain and its colonists in the Seven Years' War (also called the French and Indian War).[8] After losing the war, in 1763 France was forced to cede "its" colonial claims to lands in Canada and east of the Mississippi River to Britain. After adjusting to British colonial rule, the Ojibwe allied with them and against the United States in the War of 1812. They had hoped a British victory could protect against United States settlers' encroachment on their territory.
Following the war, the United States government tried to forcibly remove all the Ojibwe to Minnesota west of Mississippi River. The Ojibwe resisted, and there were violent confrontations. In the Sandy Lake Tragedy, the US killed several hundred Ojibwe. Through the efforts of Chief Buffalo and the rise of popular opinion in the US against Ojibwe removal, the bands east of the Mississippi were allowed to return to reservations on ceded territory. A few families were removed to Kansas as part of the Potawatomi removal.
In British North America, the Royal Proclamation of 1763 following the Seven Years' War governed the cession of land by treaty or purchase . Subsequently France ceded most of the land in Upper Canada to Great Britain. Even with the Jay Treaty signed between the Great Britain and the United States, the newly formed United States did not fully uphold the treaty. Illegal United States immigration into Ojibwe and other Native American lands continued, and the tribes retaliated in the series of battles called the Northwest Indian War. As it was still preoccupied by war with France, Great Britain ceded to the United States much of the lands in Ohio, Indiana, Michigan, parts of Illinois and Wisconsin, and northern Minnesota and North Dakota to settle the boundary of their holdings in Canada.
Many of the land cession treaties the British made with the Ojibwe provided for their rights for continued hunting, fishing and gathering of natural resources after land sales. The government signed numbered treaties in northwestern Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and Alberta. British Columbia had no signed treaties until the late 20th century, and most areas have no treaties yet. The government and First Nations are continuing to negotiate treaty land entitlements and settlements. The treaties are constantly being reinterpreted by the courts because many of them are vague and difficult to apply in modern times. The numbered treaties were some of the most detailed treaties signed for their time. The Ojibwe Nation set the agenda and negotiated the first numbered treaties before they would allow safe passage of many more British settlers to the prairies.
Often, earlier treaties were known as "Peace and Friendship Treaties" to establish community bonds between the Ojibwe and the European settlers. These earlier treaties established the groundwork for cooperative resource-sharing between the Ojibwe and the settlers. The United States and Canada viewed later treaties offering land cessions as offering territorial advantages. The Ojibwe did not understand the land cession terms in the same way because of the cultural differences in understanding the uses of land. The governments of the US and Canada considered land a commodity of value that could be freely bought, owned and sold.
The Ojibwe believed it was a fully shared resource, along with air, water and sunlight. At the time of the treaty councils, they could not conceive of separate land sales or exclusive ownership of land. Consequently, today in both Canada and the US, legal arguments in treaty-rights and treaty interpretations often bring to light the differences in cultural understanding of treaty terms to come to legal understanding of the treaty obligations.[9]
During its Indian Removal of the 1830s, US government attempted to relocate tribes from the east to the west of the Mississippi River as the white pioneers increasingly migrated west. By the late 19th century, the government policy was to move tribes onto reservations within their territories. The government attempted to do this to the Anishinaabe in the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan.
Culture
 Details of Ojibwe Wigwam at Grand Portage by Eastman Johnson, c. 1906
Details of Ojibwe Wigwam at Grand Portage by Eastman Johnson, c. 1906
The Ojibwe live in groups (otherwise known as "bands"). Most Ojibwe, except for the Great Plains bands, lived a sedentary lifestyle, engaging in fishing and hunting to supplement the women's cultivation of numerous varieties of maize and squash, and the harvesting of manoomin (wild rice). Their typical dwelling was the wiigiwaam (wigwam), built either as a waginogaan (domed-lodge) or as a nasawa'ogaan (pointed-lodge), made of birch bark, juniper bark and willow saplings.
They developed a form of pictorial writing, used in religious rites of the Midewiwin and recorded on birch bark scrolls and possibly on rock. The many complex pictures on the sacred scrolls communicate much historical, geometrical, and mathematical knowledge. Ceremonies also used the miigis shell (cowry shell), which is found naturally in distant coastal areas. Their use of such shells demonstrates there was a vast trade network across the continent at some time. The use and trade of copper across the continent has also been proof of a large trading network that took place for thousands of years, as far back as the Hopewell culture. Certain types of rock used for spear and arrow heads were also traded over large distances. The use of petroforms, petroglyphs, and pictographs was common throughout the Ojibwe traditional territories. Petroforms and medicine wheels were a way to teach the important concepts of four directions and astronomical observations about the seasons, and to use as a memorizing tool for certain stories and beliefs.
During the summer months, the people attend jiingotamog for the spiritual and niimi'idimaa for a social gathering (pow-wows or "pau waus") at various reservations in the Anishinaabe-Aki (Anishinaabe Country). Many people still follow the traditional ways of harvesting wild rice, picking berries, hunting, making medicines, and making maple sugar. Many of the Ojibwe take part in sun dance ceremonies across the continent. The sacred scrolls are kept hidden away until those who are worthy and respect them are given permission to see and interpret them properly.
The Ojibwe would bury their dead in a burial mound. Many erect a jiibegamig or a "spirit-house" over each mound. A traditional burial mound would typically have a wooden marker, inscribed with the deceased's doodem (clan sign). Because of the distinct features of these burials, Ojibwe graves have been often looted by grave robbers. In the United States, many Ojibwe communities safe-guard their burial mounds through the enforcement of the 1990 Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act.
The Ojibwe viewed the world in two genders: animate and inanimate, rather than male and female. As an animate, a person could serve the society as a male-role or a female-role. John Tanner and the anthropologist Hermann Baumann have documented that Ojibwe peoples do not live according to the European ideas of gender and its roles. Individuals known as egwakwe (or Anglicised to "agokwa"), contribute in ways that cross European gender lines. Though these egwakweg may contribute to their communities in whatever way brings out their best character, these documented male-to-female transsexual midew among the Ojibwe were more readily noticed by the ethnic European documenters.[10] A well-known egwakwe warrior and guide in Minnesota history was Ozaawindib.
Several Ojibwe bands in the United States cooperate in the Great Lakes Indian Fish & Wildlife Commission, which manages the treaty hunting and fishing rights in the Lake Superior-Lake Michigan areas. The commission follows the directives of U.S. agencies to run several wilderness areas. Some Minnesota Ojibwe tribal councils cooperate in the 1854 Treaty Authority, which manages their treaty hunting and fishing rights in the Arrowhead Region. In Michigan, the Chippewa-Ottawa Resource Authority manages the hunting, fishing and gathering rights about Sault Ste. Marie, and the resources of the waters of lakes Michigan and Huron. In Canada, the Grand Council of Treaty #3 manages the Treaty 3 hunting and fishing rights related to the area around Lake of the Woods.
Kinship and clan system
Main article: Anishinaabe clan systemOjibwe understanding of kinship is complex, and includes not only the immediate family but also the extended family. It is considered a modified bifurcate merging kinship system. As with any bifurcate-merging kinship system, siblings generally share the same kinship term term with parallel cousins, because they are all part of the same clan. The modified system allows for younger siblings to share the same kinship term with younger cross-cousins. Complexity wanes further from the speaker's immediate generation, but some complexity is retained with female relatives. For example, ninooshenh is "my mother's sister" or "my father's sister-in-law"—i.e., my parallel-aunt, but also "my parent's female cross-cousin". Great-grandparents and older generations, as well as great-grandchildren and younger generations, are collectively called aanikoobijigan. This system of kinship speaks of the nature of the Anishinaabe's philosophy and lifestyle, that is, of interconnectedness and balance among all living generations, as well as of all generations of the past and of the future.
The Ojibwe people were divided into a number of odoodeman (clans; singular: doodem) named primarily for animals and birds totems (pronounced doodem). The five original totems were Wawaazisii (Bullhead), Baswenaazhi ("Echo-maker", i.e., Crane), Aan'aawenh (Pintail Duck), Nooke ("Tender", i.e., Bear) and Moozwaanowe ("Little" Moose-tail). The Crane totem was the most vocal among the Ojibwe, and the Bear was the largest — so large, in fact, that it was sub-divided into body parts such as the head, the ribs and the feet.
Traditionally, each band had a self-regulating council consisting of leaders of the communities' clans, or odoodemaan. The band was often identified by the principal doodem. In meeting others, the traditional greeting among the Ojibwe peoples is, "What is your 'doodem'?" ("Aaniin gidoodem?" or "Awanen gidoodem?") to establish social conduct by identifying each of the parties as family, friends or enemies. Today, the greeting has been shortened to "Aaniin."[citation needed]
Spiritual beliefs
Main article: Anishinaabe traditional beliefsThe Ojibwe have a number of spiritual beliefs passed down by oral tradition under the Midewiwin teachings. These include a creation story and a recounting of the origins of ceremonies and rituals. Spiritual beliefs and rituals were very important to the Ojibwe because spirits guided them through life. Birch bark scrolls and petroforms were used to pass along knowledge and information, as well as for ceremonies. Pictographs were also used for ceremonies.
The sweatlodge is still used during important ceremonies about the four directions, when oral history is recounted. Teaching lodges are common today to teach the next generations about the language and ancient ways of the past. The traditional ways, ideas, and teachings are preserved and practiced in such living ceremonies. The Ojbwe crafted the dreamcatcher. They believe that if one is hung above the head of a sleeper, it will catch and trap bad dreams, preventing them from reaching the dreamer. Traditional Ojibwe use dreamcatchers only for children, as they believe that adults should be able to interpret their dreams, good or bad and use them in their lives.
Popular culture
In legends and fiction
- The legend of the Ojibwe Wendigo, in which tribesmen identify with a cannibalistic monster and prey on their families, is a story with many meanings. One points to the consequences of greed and the destruction that results from it. Thomas Pynchon, Ramsey Campbell and Stephen King reference this story in their fiction.
- The novelist Louise Erdrich is Anishinaabe. She has written about characters from her culture in Tracks, Love Medicine, and The Bingo Palace.
- In his story, "Fathers and Sons", Ernest Hemingway uses two Ojibwe as secondary characters.[citation needed]
- Winona LaDuke is a popular political and intellectual voice for the Anishinaabe people.
- The Medicine woman Keewaydinoquay Peschel has written books on ethnobotany and books for children.
- The literary theorist and writer Gerald Vizenor has drawn extensively on Anishinaabe philosophies of language.
- The writer William Kent Krueger has written a series of crime novels chronicling the adventures of a character named Corcoran “Cork” O’Connor, the Ojibwe sheriff of Aurora, Minnesota. The novels expresses how Cork uses his Ojibwe heritage and Anglo-American culture to solve local crimes. Ojibwe spirituality is an important element of the subtext of many of the storylines.
In music
- Composer Ferde Grofe composed a movement, "Father of the Waters", of his Mississippi Suite, which represents the Chippewa Indians and the headwaters of the Mississippi.
In television
- In several episodes of the HBO series The Sopranos (e.g., "Mayham" and "The Fleshy Part of the Thigh"), an Ojibwe Indian saying is left by the bedside of Tony Soprano whilst he recovers from a gunshot wound: "Sometimes I go about in pity for myself, and all the while, a great wind carries me across the sky".
Bands
In his History of the Ojibway People (1855), William W. Warren recorded 10 major divisions of the Ojibwe in the United States. He mistakenly omitted the Ojibwe located in Michigan, western Minnesota and westward, and all of Canada. When identified major historical bands located in Michigan and Ontario are added, the count becomes 15[citation needed]:
English Name Ojibwe Name
(in double-vowel spelling)Location Saulteaux Baawitigowininiwag Sault Ste. Marie area of Ontario and Michigan Border-Sitters Biitan-akiing-enabijig St. Croix-Namakegon River valleys in eastern Minnesota and northern Wisconsin Lake Superior Band Gichi-gamiwininiwag south shore of Lake Superior Mississippi River Band Gichi-ziibiwininiwag upper Mississippi River in Minnesota Rainy Lake Band Goojijiwininiwag Rainy Lake and River, about the northern boundary of Minnesota Ricing-Rails Manoominikeshiinyag along headwaters of St. Croix River in Wisconsin and Minnesota Pillagers Makandwewininiwag North-central Minnesota and Mississippi River headwaters Mississaugas Misi-zaagiwininiwag north of Lake Erie, extending north of Lake Huron about the Mississaugi River Algonquins (Nipissing) Odishkwaagamiig Quebec-Ontario border, about Lake Nipissing Dokis Band N/A Along French River region in Ontario, near Lake Nipissing Ottawa Lake (Lac Courte Oreilles) Band Odaawaa-zaaga'iganiwininiwag Lac Courte Oreilles, Wisconsin Bois Forte Band Zagaakwaandagowininiwag north of Lake Superior Lac du Flambeau Band Waaswaaganiwininiwag head of Wisconsin River Muskrat Portage Band Wazhashk-Onigamininiwag northwest side of Lake Superior at the Canadian border Nopeming Band Noopiming Azhe-ininiwag northeast of Lake Superior and west of Lake Nipissing These 15 major divisions developed into the following Ojibwe Bands and First Nations of today. Bands are listed under their respective tribes where possible.[citation needed] See also the listing of Saulteaux communities.
- Aamjiwnaang First Nation
- Aroland First Nation
- Batchewana First Nation of Ojibways
- Bay Mills Indian Community
- Biinjitiwabik Zaaging Anishnabek First Nation
- Chapleau Ojibway First Nation
- Chippewas of Kettle and Stony Point
- Chippewas of Lake Simcoe and Huron (Historical)
- Beausoleil First Nation
- Chippewas of Georgina Island First Nation
- Chippewas of Rama First Nation (formerly known as Chippewas of Mnjikaning First Nation)
- Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation
- Chippewa of the Thames First Nation
- Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory (Historical)
- Chippewa Cree Tribe of Rocky Boys Indian Reservation
- Curve Lake First Nation
- Cutler First Nation
- Dokis First Nation
- Eabametoong First Nation
- Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa and Chippewa Indians
- Garden River First Nation
- Grassy Narrows First Nation (Asabiinyashkosiwagong Nitam-Anishinaabeg)
- Islands in the Trent Waters
- Keeseekoowenin Ojibway First Nation
- Koocheching First Nation
- Lac des Mille Lacs First Nation
- Lac La Croix First Nation
- Lac Seul First Nation
- Lake Nipigon Ojibway First Nation
- Lake Superior Chippewa Tribe
- Bad River Chippewa Band
- Lac Vieux Desert Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Keweenaw Bay Indian Community
- L'Anse Band of Chippewa Indians
- Ontonagon Band of Chippewa Indians
- Lac Courte Oreilles Band of Lake Superior Chippewa Indians
- Bois Brule River Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Chippewa River Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Lac Courte Oreilles Band of Lake Superior Chippewa Indians
- Removable St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin
- Lac du Flambeau Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Sokaogon Chippewa Community
- St. Croix Chippewa Indians of Wisconsin
- Little Traverse Bay Bands of Odawa Indians
- Magnetawan First Nation
- Minnesota Chippewa Tribe
- Mississaugi First Nation
- Bois Forte Band of Chippewa
- Bois Forte Band of Chippewa
- Lake Vermilion Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Little Forks Band of Rainy River Saulteaux
- Fond du Lac Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Grand Portage Band of Chippewa
- Leech Lake Band of Ojibwe
- Cass Lake Band of Chippewa
- Lake Winnibigoshish Band of Chippewa
- Leech Lake Band of Pillagers
- Removable Lake Superior Bands of Chippewa of the Chippewa Reservation
- White Oak Point Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- Mille Lacs Band of Ojibwe
- Mille Lacs Indians
- Sandy Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- Rice Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- St. Croix Band of Chippewa Indians of Minnesota
- Kettle River Band of Chippewa Indians
- Snake and Knife Rivers Band of Chippewa Indians
- White Earth Band of Chippewa
- Gull Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- Otter Tail Band of Pillagers
- Rabbit Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- Removable Mille Lacs Indians
- Removable Sandy Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- Rice Lake Band of Mississippi Chippewa
- Bois Forte Band of Chippewa
- North Caribou Lake First Nation
- Ojibway Nation of Saugeen First Nation
- Ojibways of the Pic River First Nation
- Osnaburg House Band of Ojibway (Historical)
- Cat Lake First Nation
- Mishkeegogamang First Nation (formerly known as New Osnaburgh First Nation)
- Slate Falls First Nation
- Pembina Band of Chippewa Indians (Historical)
- Pikangikum First Nation
- Poplar Hill First Nation
- Red Lake Band of Chippewa Indians
- Lac des Bois Band of Chippewa Indians
- Sagamok Anishnawbek First Nation
- Saginaw Chippewa Tribal Council
- Sault Tribe of Chippewa Indians
- Saulteaux First Nation
- Shawanaga First Nation
- Southeast Tribal Council
- Berens River First Nation
- Bloodvein First Nation
- Brokenhead First Nation
- Buffalo Point First Nation (Saulteaux)
- Hollow Water First Nation
- Black River First Nation
- Little Grand Rapids First Nation
- Pauingassi First Nation (Saulteaux)
- Poplar River First Nation
- Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians
- Wabaseemoong Independent Nation
- Wabauskang First Nation
- Wabun Tribal Council
- Beaverhouse First Nation
- Brunswick House First Nation
- Chapleau Ojibwe First Nation
- Matachewan First Nation
- Mattagami First Nation
- Wahgoshig First Nation
- Wabigoon Lake Ojibway Nation
- Wahnapitae First Nation
- Washagamis Bay First Nation
- Whitefish Bay First Nation
- Whitefish Lake First Nation
- Whitefish River First Nation
- Whitesand First Nation
- Whitewater Lake First Nation
- Wikwemikong Unceded First Nation
Other tribes known by their Ojibwe/Ottawa names
Known
NameOjibwe
NameOjibwe
MeaningOwn
NameArkansas (Quapaw) Aakaanzhish(ag) Dang little Kansas Ugahxpa (down-stream people) Assiniboine Asiniibwaan(ag) Stoney Cookers Nakota (allies) Blackfoot Makadewanazid(ag) Black-foot Niitsítapi (original people) Chipewyan Ojiibwayaan(ag) Pointed Skin Dënesųłiné Eskimo Ashki-amaw Eats It Raw Inupiaq Flathead Nebagindibe(g) Flat-head Salish Iroquois Naadowe(g) Massassauga Rattlesnake Akunęhsyę̀niʼ in Tuscarora, Rotinonsionni in Mohawk Kansas Aakaans(ag) [Lives at the] Little Hell-hole Kaw (People of the South Wind) Kaskaskia Gaaskaaskeyaa(g) Hide-scraper Kickapoo Giiwigaabaw(ag) Stands here-and-there Kiikaapoa Menominee Omanoominii(g) Wild Rice People Omāēqnomenew Miami Omaamii(g) Downstream people Myaamia Micmac Miijimaa(g) Allied-Brothers Mi'kmaq / L'nu Moingwena Moowiingwenaa(g) Have a Filthy Face Ottawa Odaawaa(g) Trader Odawa Potawatomi Boodewaadamii(g) Fire Keeper Bodéwadmi Sauk/Sac Ozaagii(g) [Lives at the] Outlet Asakiwaki Shawnee Zhaawanoo(g) Southerners Chowanoc Sioux Naadowensiw(ag) Little like the Iroquois Aioe-Dakota-Lakota-Nakota Snake (Shoshoni) Ginebigowinini(wag) Snake People Panamint (grass house), Tukuaduka (sheep eaters), or Toi Ticutta (cattail eaters) Wea Waawiyaataan(oog) [Those at the] Rounded [Lake] Waayaahtanwa Winnebago Wiinibiigoo(g) [Lives at the] Stinking Waters Ho-Chunk ([people of the] Big Voice) Notable people
- Ah-shah-way-gee-she-go-qua (Aazhawigiizhigokwe/Hanging Cloud) (Warrioress)
- David Wayne "Famous Dave" Anderson (Business Entrepreneur)
- Arron Asham (Canadian professional ice hockey player for the Pittsburgh Penguins)
- Edward Benton Banai (Writer)
- Dennis Banks (Political Activist)
- James Bartleman (Diplomat, Author)
- Adam Beach (Actor, Writer)
- Carl Beam (Artist)
- Jason Behr (Actor)
- Archibald "Grey Owl" Belaney (Naturalist and Writer) —English, but presented himself an Ojibwe
- Clyde Bellecourt (Social Activist)
- Vernon Bellecourt (Social Activist)
- Chief Bender (Baseball player)
- Benjamin Chee Chee (Artist)
- Henry Boucha (American former professional ice hockey player, United States Hockey Hall of Fame)
- Al Hunter (Poet and Writer)
- George Copway (Missionary and Writer)
- Eddy Cobiness (Artist)
- Jim Denomie (Artist)
- Patrick DesJarlait (Commercial Artist)
- Louise Erdrich (Writer)
- Phil Fontaine (Politician)
- William Gardner—(One of the Untouchables)
- Carl Gawboy (Artist, Historian)
- Gordon Henry Jr. (Writer)
- Tara Hedican (World Junior Wrestling Champion 2001)
- Virgil Hill (Boxer)
- Vincent J Holland-Mason (Young Atlanta icon, Writer, Broadcastor)
- Basil Johnston (Historian and Cultural Essayist)
- Peter Jones (Missionary and Writer)
- Ke-che-waish-ke (Gichi-Weshkiinh/Buffalo) (Chief)
- Maude Kegg (Author, Cultural Embassidor)
- Winona LaDuke (Activist and Writer)
- Carole LaFavor (Writer)
- Joe Lumsden (Chairman, Sault Tribe of Chippewa Indians)
- Loma Lyns (Singer, Songwriter)
- Karinn Martel (Poet and Author of the Vampires and Chocolate Book Series)
- Cody McCormick (Canadian professional ice hockey player for the Colorado Avalanche)
- Rod Michano (AIDS Activist/Educator)
- Norval Morrisseau (Artist)
- Ted Nolan (Canadian former professional ice hockey player and coach, Jack Adams Award winner)
- Jim Northrup (Columnist)
- O-zaw-wen-dib (Ozaawindib/Yellow Head) (Warrioress, Guide)
- Francis Pegahmagabow, warrior
- Leonard Peltier (Political Activist, Prisoner)
- Mel Pervais (Entrepreneur)
- Tommy Prince (Soldier)
- D'Arcy Rheault (Writer, Philosopher, College Professor)
- Buffy Sainte-Marie (Singer)
- Keith Secola (Rock and Blues Singer)
- Chris Simon (Canadian professional ice hockey player, Stanley Cup winner w/ 1996 Colorado Avalanche)
- John Smith/Gaa-binagwiiyaas) (Chief)—reported to have lived 137 years
- Drew Hayden Taylor (Playwright, Author and Journalist)
- Roy Thomas (Artist)
- Anton Treuer (Writer, Historian, Professor of Ojibwe)
- David Treuer (Writer)
- Dale Turner (Dartmouth College Professor)
- Shania Twain (Singer)—non-Ojibwe of Cree heritage adopted by her Ojibwe stepfather
- E. Donald Two-Rivers (Poet, Playwright)
- Alfred Michael "Chief" Venne (Athletic manager and coach)
- Gerald Vizenor (Writer)
- Wawatam (Chief)
- Waabaanakwad (White Cloud) (Chief)
- John Whitecloud (Radio Personality)
- William Whipple Warren (Historian, Politician)
- Gregory L. Ybarra (N8HXQ ARES/RACES Radio Officer and Genesee County Emergency Coordinator).
Ojibwe treaties
- Tribal Treaty Administrants
- 1854 Treaty Authority—1854CT
- Chippewa Ottawa Resource Authority—1836CT fisheries
- Grand Council of Treaty 3—Treaty 3
- Grand Council of Treaty 8—Treaty 8
- Great Lakes Indian Fish & Wildlife Commission—1837CT, 1836CT, 1842CT and 1854CT
- Nishnawbe Aski Nation—Treaty 5 and Treaty 9
- Red Lake Band of Chippewa—1886CT and 1889CT
- Union of Ontario Indians—RS, RH1, RH2, misc. pre-confederation treaties
- Treaties with France
- La Grande Paix de Montréal (1701)
- Treaties with Great Britain
- Treaty of Fort Niagara (1764)
- Treaty of Fort Niagara (1781)
- Indian Officers' Land Treaty (1783)
- The Crawford Purchases (1783)
- Between the Lakes Purchase (1784)
- The McKee Purchase (1790)
- Between the Lakes Purchase (1792)
- Chenail Ecarte (Sombra Township) Purchase (1796)
- London Township Purchase (1796)
- Land for Joseph Brant (1797)
- Penetanguishene Bay Purchase (1798)
- St. Joseph Island (1798)
- Toronto Purchase (1805)
- Head-of-the-Lake Purchase (1806)
- Lake Simcoe-Lake Huron Purchase(1815)
- Lake Simcoe-Nottawasaga Purchase (1818)
- Ajetance Purchase (1818)
- Rice Lake Purchase (1818)
- The Rideau Purchase (1819)
- Long Woods Purchase (1822)
- Huron Tract Purchase (1827)
- Saugeen Tract Agreement (1836)
- Manitoulin Agreement (1836)
- The Robinson Treaties
- Ojibewa Indians of Lake Superior (1850)
- Ojibewa Indians of Lake Huron (1850)
- Manitoulin Island Treaty (1862)
- Treaties with Canada
- Treaty No. 1 (1871)—Stone Fort Treaty
- Treaty No. 2 (1871)
- Treaty No. 3 (1873)—Northwest Angle Treaty
- Treaty No. 4 (1874)—Qu'Appelle Treaty
- Treaty No. 5 (1875)
- Treaty No. 6 (1876)
- Treaty No. 8 (1899)
- Treaty No. 9 (1905–1906)—James Bay Treaty
- Treaty No. 5, Adhesions (1908–1910)
- The Williams Treaties (1923)
- The Chippewa Indians
- The Mississauga Indians
- Treaty No. 9, Adhesions (1929–1930)
- Treaties with the United States
- Treaty of Fort McIntosh (1785)
- Treaty of Fort Harmar (1789)
- Treaty of Greenville (1795)
- Fort Industry (1805)
- Treaty of Detroit (1807)
- Treaty of Brownstown (1808)
- Treaty of Springwells (1815)
- Treaty of St. Louis (1816)—Ottawa, Ojibwe, and Potawatomi
- Treaty of Miami Rapids (1817)
- St. Mary's Treaty (1818)
- Treaty of Saginaw (1819)
- Treaty of Saúlt Ste. Marie (1820)
- Treaty of L'Arbre Croche and Michilimackinac (1820)
- Treaty of Chicago (1821)
- Treaty of Prairie du Chien (1825)
- Treaty of Fond du Lac (1826)
- Treaty of Butte des Morts (1827)
- Treaty of Green Bay (1828)
- Treaty of Prairie du Chien (1829)
- Treaty of Chicago (1833)
- Treaty of Washington (1836)—Ottawa & Chippewa
- Treaty of Washington (1836)—Swan Creek & Black River Bands
- Treaty of Detroit (1837)
- Treaty of St. Peters (1837)—White Pine Treaty
- Treaty of Flint River (1837)
- Saganaw Treaties
- Treaty of Saganaw (1838)
- Supplemental Treaty (1839)
- Treaty of La Pointe (1842)—Copper Treaty
- Isle Royale Agreement (1844)
- Treaty of Potawatomi Creek (1846)
- Treaty of Fond du Lac (1847)
- Treaty of Leech Lake (1847)
- Treaty of La Pointe (1854)
- Treaty of Washington (1855)
- Treaty of Detroit (1855)—Ottawa & Chippewa
- Treaty of Detroit (1855)—Sault Ste. Marie Band
- Treaty of Detroit (1855)—Swan Creek & Black River Bands
- Treaty of Sac and Fox Agency (1859)
- Treaty of Washington (1863)
- Treaty of Old Crossing (1863)
- Treaty of Old Crossing (1864)
- Treaty of Washington (1864)
- Treaty of Isabella Reservation (1864)
- Treaty of Washington (1866)
- Treaty of Washington (1867)
Gallery
-
A-na-cam-e-gish-ca (Aanakamigishkaang/"[Traces of] Foot Prints [upon the Ground]"), Ojibwe chief, painted by Charles Bird King
-
Bust of Aysh-ke-bah-ke-ko-zhay (Eshkibagikoonzhe or "Flat Mouth"), a Leech Lake Ojibwe chief
-
Chief Beautifying Bird (Nenaa'angebi), by Benjamin Armstrong, 1891
-
Bust of Beshekee, war chief, modeled 1855, carved 1856
-
Hanging Cloud, a female Ojibwe warrior
-
Kay be sen day way We Win, by Eastman Johnson, 1857
-
Kei-a-gis-gis, a Plains Ojibwe woman, painted by George Catlin
-
Milwaukee Ojibwe woman and baby, courtesy of the Wisconsin Historical Society
-
"One Called From A Distance" (Midwewinind) of the White Earth Band, 1894.
Notes
- ^ "First Nations Culture Areas Index". the Canadian Museum of Civilization. http://www.civilization.ca/cmc/exhibitions/tresors/ethno/etb0170e.shtml.
- ^ "Anishinabe". eMuseum @ Minnesota State University. Minnesota State University. Mankato. http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/history/mncultures/anishinabe.html. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
- ^ "Microsoft Word - dictionary best for printing 2004 ever finalpdf.doc" (PDF). http://www.humiliationstudies.org/documents/DaffernMultilingualDictionary.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-02.
- ^ Warren, William W. (1885; reprint: 1984) History of the Ojibway People. ISBN 0-87351-162-X
- ^ Louise Erdrich, Books and Islands in Ojibwe Country (2003)[dead link]
- ^ Johnston, Basil. (2007) Anishinaubae Thesaurus ISBN 0-87013-753-0
- ^ Anthony, David. The Horse, the Wheel and Language, Princeton University Press, 2007, p. 102
- ^ Gevinson, Alan. "Which Native American Tribes Allied Themselves with the French?" Teachinghistory.org, accessed 23 September 2011.
- ^ "The Atlas of Canada: Historical Indian Treaties". http://atlas.nrcan.gc.ca/site/english/maps/historical/indiantreaties/historicaltreaties. Retrieved 2010-05-09.
- ^ Feinberg, Leslie: Transgender Warriors, New York: Beacon Press, 1996, p. 40
References
- F. Densmore, Chippewa Customs (1929, repr. 1970)
- H. Hickerson, The Chippewa and Their Neighbors (1970)
- R. Landes, Ojibwa Sociology (1937, repr. 1969)
- R. Landes, Ojibwa Woman (1938, repr. 1971)
- F. Symington, The Canadian Indian (1969)
Further reading
- Aaniin Ekidong: Ojibwe Vocabulary Project. St. Paul: Minnesota Humanities Center, 2009.http://www.amazon.com/s/ref=nb_sb_ss_i_0_6?url=search-alias%3Dstripbooks&field-keywords=aaniin+ekidong&sprefix=aaniin
- Bento-Banai, Edward (2004). Creation- From the Ojibwa. The Mishomis Book.
- Danziger, E.J., Jr. (1978). The Chippewa of Lake Superior. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
- Densmore, F. (1979). Chippewa customs. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press. (Published originally 1929)
- Grim, J.A. (1983). The shaman: Patterns of religious healing among the Ojibway Indians. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
- Gross, L.W. (2002). The comic vision of Anishinaabe culture and religion. American Indian Quarterly, 26, 436-459.
- Howse, Joseph. A Grammar of the Cree Language; With which is combined an analysis of the Chippeway dialect. London: J.G.F. & J. Rivington, 1844.
- Johnston, B. (1976). Ojibway heritage. Toronto: McClelland and Stewart.
- Long, J. Voyages and Travels of an Indian Interpreter and Trader Describing the Manners and Customs of the North American Indians, with an Account of the Posts Situated on the River Saint Laurence, Lake Ontario, & C., to Which Is Added a Vocabulary of the Chippeway Language ... a List of Words in the Iroquois, Mehegan, Shawanee, and Esquimeaux Tongues, and a Table, Shewing the Analogy between the Algonkin and the Chippeway Languages. London: Robson, 1791.
- Nichols, J.D., & Nyholm, E. (1995). A concise dictionary of Minnesota Ojibwe. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
- Treuer, Anton. The Assassination of Hole in the Day. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 2011.
- Treuer, Anton. Ojibwe in Minnesota. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society, 2010. Ojibwe in Minnesota. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 2010.
- Treuer, Anton. Living Our Language: Ojibwe Tales & Oral Histories. St. Paul: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 2001. http://www.amazon.com/Living-Our-Language-Ojibwe-Histories/dp/0873514041/ref=sr_1_2?ie=UTF8&s=books&qid=1274417157&sr=8-2
- Vizenor, G. (1972). The everlasting sky: New voices from the people named the Chippewa. New York: Crowell-Collier Press.
- Vizenor, G. (1981). Summer in the spring: Ojibwe lyric poems and tribal stories. Minneapolis: The Nodin Press.
- Vizenor, G. (1984). The people named the Chippewa: Narrative histories. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
- Warren, William W. (1851). History of the Ojibway People.
- White, Richard (1991). The Middle Ground: Indians, Empires, and Republics in the Great Lakes Region, 1650-1815 (Studies in North American Indian History) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England, ISBN 0-521-37104-X
- White, Richard (July 31, 2000). Chippewas of the Sault. The Sault Tribe News.
- Wub-e-ke-niew. (1995). We have the right to exist: A translation of aboriginal indigenous thought. New York: Black Thistle Press.
External links
- Great Lakes Indian Fish & Wildlife Commission
- Chief Buffalo and Benjamin Armstrong
- Ojibwe culture and history, a lengthy and detailed discussion
- Kevin L. Callahan's An Introduction to Ojibway Culture and History
- Ojibwe Song Pictures, recorded by Frances Desmore
- Digital recreation of the 'Chippewa' entry from Handbook of American Indians North of Mexico, edited by Frederick Webb Hodge
- Ojibwa migration through Manitoba
- video: The Making of an Ojibwe Hand Drum
- Nindoodemag: The Significance of Algonquian Kinship Networks in the Eastern Great Lakes Region, 1600–1701
- Ojibwe Waasa-Inaabidaa—PBS documentary featuring the history and culture of the Anishinaabe-Ojibwe people of the Great Lakes (United States-focused).
- Ojibwe migratory map from Ojibwe Waasa-Inaabidaa
- Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture - Chippewa
- 1836 Chippewa-Ottawa Resource Authority
- Grand Council of Treaty #3
- Batchewana First Nation of Ojibways
- Red Cliff Band of Lake Superior Chippewa
- Mississaugi First Nation
- Southeast Tribal Council
- Wabun Tribal Council
Categories:- Ojibwe
- Anishinaabe peoples
- Anishinaabe lands
- Algonquian ethnonyms
- Algonquian peoples
- Great Lakes tribes
- Plains tribes
- First Nations in Alberta
- First Nations in Ontario
- First Nations in Manitoba
- First Nations in Saskatchewan
- First Nations in Quebec
- Native American tribes in Michigan
- Native American tribes in Minnesota
- Native American tribes in Montana
- Native American tribes in North Dakota
- Native American tribes in Wisconsin
- Upper Peninsula of Michigan
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.