- Marten
-
- For the Wiltshire village, see Marten, Wiltshire. For the town in Bulgaria, see Marten, Bulgaria. "Martes" redirects here. For the village in Spain, see Martes, Aragon.
"Martens" redirects here. For other uses, see Martens (disambiguation).Marten 
European Pine Marten Scientific classification Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Subphylum: Vertebrata Infraphylum: Gnathostomata (unranked): Chordata Craniata Superclass: Tetrapoda Class: Mammalia Subclass: Theria Infraclass: Placentalia Superorder: Laurasiatheria Order: Carnivora Suborder: Caniformia Family: Mustelidae Subfamily: Mustelinae Genus: Martes
Pinel, 1792Species 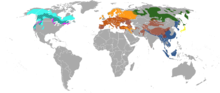
Martes range The martens constitute the genus Martes within the subfamily Mustelinae, in family Mustelidae.
Contents
Description
Martens are slender, agile animals, adapted to living in taigas, and are found in coniferous and northern deciduous forests across the northern hemisphere. They have bushy tails, and large paws with partially retractible claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark brown, depending on the species, and, in many cases, is valued by fur trappers.
Diet
Martens are omnivorous animals related to wolverines, minks, badgers, ferrets, and weasels. Their diet consists of squirrels, mice, rabbits, birds, fish, insects, and eggs, and they will also eat fruit and nuts when these are available.[1][2]
Behavior
Martens are solitary animals, meeting only to breed in late spring or early summer. Litters of up to five blind and nearly hairless kits are born in early Spring. They are weaned after around two months, and leave the mother to fend for themselves at about three to four months of age.
Etymology
The Modern English "marten" comes from the Middle English "martryn", in turn borrowed from the Anglo-French "martrine" and Old French "martre" (French "martes"), itself from a Germanic source, cf. Old English mearþ, Old Norse mörðr, Old High German and Yiddish mardar.
Species
Recent DNA research has shown that the genus Martes is in fact polyphyletic, placing Martes pennanti and Martes americana outside the genus and allying it with Eira and Gulo, to form a new New World clade.[3] The genus first evolved up to seven million years ago, during the Pliocene.
- American Marten Martes americana
- Newfoundland Pine Marten Martes americana atrata
- Yellow-throated Marten Martes flavigula
- Beech Marten Martes foina
- Nilgiri Marten Martes gwatkinsii
- Pine Marten Martes martes
- Japanese Marten Martes melampus
- Fisher Martes pennanti
- Sable Martes zibellina
Cultural references
In the Middle Ages, marten pelts were highly valued goods used as a form of payment in Slavonia, the Croatian Littoral and Dalmatia. The Croatian word for marten, kuna, is the name of the modern Croatian currency.[4] A marten is depicted on the obverse of the 1, 2 and 5 kuna coins, minted since 1993, and on the reverse of the 25 kuna commemorative coins.[5]
The Finnish communications company Nokia derives its name, via the river Nokianvirta, from a type of marten locally known as the nokia.[6]
References
- ^ Powell, Roger (1984). Macdonald, D.. ed. The Encyclopedia of Mammals. New York: Facts on File. pp. 118–119. ISBN 0-87196-871-1.
- ^ http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/43330041/ns/us_news-weird_news/
- ^ Flynn, J.J. et all (2004). "Molecular Phylogeny of the Carnivora (Mammalia): Assessing the Impact of Increased Sampling on Resolving Enigmatic Relationships". Systematic Biology 54(2): 317–337.
- ^ Croatian National Bank. First Money — History of the Croatian Currency: Kuna and lipa — the Croatian Currency. – Retrieved on 31 March 2009.
- ^ Croatian National Bank. Kuna and Lipa, Coins of Croatia: 1 Kuna Coin, 2 Kuna Coin, 5 Kuna Coin & Commemorative 25 Kuna Coins in Circulation. – Retrieved on 31 March 2009.
- ^ [1] - Retrieved on the 23rd of July 2010
Categories:- Martens
- Mustelinae
- Mammals of Canada
- Mammals of North America
- Mammals of Europe
- Mammals of Asia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
