- 1930s
-
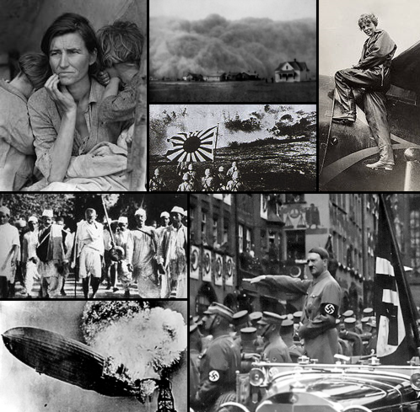
"'30s" and "thirties" redirect here. For decades comprising years 30–39 of other centuries, see List of decades.From left, clockwise: Dorothea Lange's photo of the homeless Florence Thompson show the effects of the Great Depression; Due to the economic collapse, the farms become dry and the Dust Bowl spreads through America; The Battle of Wuhan during the Second Sino-Japanese War; Aviator Amelia Earhart becomes a national icon; German dictator Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party attempted to establish a New Order of absolute Nazi German hegemony in Europe, which culminated in 1939 when Germany invaded Poland, leading to the outbreak of World War II; The Hindenburg explodes over a small New Jerseian airfield, effectively ending commercial airship travel; Mohandas Gandhi walks to the Indian Ocean in the Salt March of 1930.

Millennium: 2nd millennium Centuries: 19th century – 20th century – 21st century Decades: 1900s 1910s 1920s – 1930s – 1940s 1950s 1960s Years: 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 1938 1939 Categories: Births – Deaths – Architecture
Establishments – DisestablishmentsThe 1930s, or the Thirties, was the decade that started on January 1, 1930 and ended on December 31, 1939. It was the fourth decade of the 20th century.
After the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the largest stock market crash in American history, most of the decade was consumed by an economic downfall called The Great Depression that had a traumatic effect worldwide. In response, authoritarian regimes emerged in several countries in Europe, in particular the Third Reich in Germany. Weaker states such as Ethiopia, China, and Poland were invaded by expansionist world powers, ultimately leading to World War II by the decade's end. The decade also saw a proliferation in new technologies, including intercontinental aviation, radio, and film.
Contents
Politics and wars
Wars
 The Colombian Army countering a Peruvian attack during the Colombia–Peru War
The Colombian Army countering a Peruvian attack during the Colombia–Peru War
- Colombia–Peru War (1 September 1932 – 24 May 1933) - fought between the Republic of Colombia and the Republic of Peru.
- Chaco War (15 June 1932 – 10 June 1935) - the war was fought between Bolivia and Paraguay over the disputed territory of Gran Chaco resulting in an overall Paraguayan victory in 1935. An agreement dividing the territory was made in 1938, officially ending outstanding differences and bringing an official "peace" to the conflict.
- Second Sino-Japanese War (7 July 1937 – 9 September 1945) - fought between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The Second Sino-Japanese War was the largest Asian war in the twentieth century.[1] It also made up more than 50% of the casualties in the Pacific War.
- World War II outbreaks on September 1, 1939.
Internal conflicts
- Spanish Civil War (17 July 1936 – 1 April 1939) - Germany and Italy back anti-communist Falange forces of Francisco Franco. The Soviet Union and international communist parties (see Abraham Lincoln Brigade) back the left-wing republican faction in the war. The war ends in April 1939 with Franco's nationalist forces defeating the republican forces. Franco becomes Head of State of Spain, President of Government and de facto dictator. The Republic gives way to the Spanish State, an authoritarian dictatorship.
- Castellammarese War (1929 - 10 September 1931).
Major political changes
The rise of Nazism
 German dictator Adolf Hitler (right) and Italian dictator Benito Mussolini (left) pursue agendas of territorial expansion for their countries in the 1930s, eventually leading to the outbreak of World War II in 1939.
German dictator Adolf Hitler (right) and Italian dictator Benito Mussolini (left) pursue agendas of territorial expansion for their countries in the 1930s, eventually leading to the outbreak of World War II in 1939.
- Adolf Hitler and the National Socialist German Worker's Party (Nazi Party) rise to power in Germany in 1933, forming a fascist regime committed to repudiating the Treaty of Versailles, persecuting and removing Jews and other minorities from German society, expanding Germany's territory, and opposing the spread of communism.
- Hitler pulls Germany out of the League of Nations, but hosts the 1936 Summer Olympics to show his new reich to the world as well as the supposed Athleticism of his Aryan troops/athletes.
- Neville Chamberlain, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (1937–1940), attempts the appeasement of Hitler in hope of avoiding war by allowing the dictator to annex the Sudetenland (the western regions of Czechoslovakia). Later signing the Munich Agreement and promising constituents "Peace for our time". He was ousted in favor of Winston Churchill in May 1940, after the Invasion of Norway.[2]
- The assassination of the German diplomat Ernst vom Rath by a German-born Polish Jew triggers the Kristallnacht (The Night of Broken Glass) held between the 9 to 10 November 1938 and carried out by the Hitler Youth, the Gestapo and the SS during which the Jewish population living in Nazi Germany and Austria were attacked - 91 Jews were murdered and 25,000 to 30,000 were arrested and placed in concentration camps. 267 synagogues were destroyed and thousands of homes and businesses were ransacked. Kristallnacht also served as a pretext and a means for the wholesale confiscation of firearms from German Jews.
- Germany and Italy pursue territorial expansionist agendas. Germany demands the annexation of the Federal State of Austria and German-populated territories in Europe. From 1935 to 1936, Germany receives the Saar, remilitarizes the Rhineland. Italy initially opposes Germany's aims on Austria but the two countries resolve their differences in 1936 in the aftermath of Italy's diplomatic isolation following the start of the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. Germany becoming Italy's only remaining ally. Germany and Italy improve relations by forming an alliance against communism in 1936 with the signing of the Anti-Comintern Pact. Germany annexes Austria in the event known as the Anschluss. The annexation of Sudetenland followed after negotiations which resulted in the Munich Agreement of 1938. The Italian invasion of Albania in 1939 succeeds in turning the Kingdom of Albania to an Italian protectorate. The vacant throne was claimed by Victor Emmanuel III of Italy.[3] Germany receives the Memel territory from Lithuania, occupies Czechoslovakia, and finally invades the Second Polish Republic. The final event resulting in the outbreak of World War II.
- Multiple countries in the Americas including Canada, Cuba, and the United States controversially deny asylum to hundreds of Jewish German refugees on the MS St. Louis who are fleeing Germany in 1939 which under the Nazi regime was pursuing a racist agenda of anti-Semitic persecution. In the end, no country accepted the refugees and the ship returns to Germany with most of its passengers on board, while some commit suicide based on the prospect of returning to Nazi-run Germany.
United States
- Franklin D. Roosevelt is elected President of the United States in November 1932. Roosevelt initiates a widespread social welfare strategy called the "New Deal" to combat the economic and social devastation of the Great Depression. The economic agenda of the "New Deal" was a radical departure from previous laissez-faire economics.
Colonization
- The Ethiopian Empire is invaded by the Kingdom of Italy during the Second Italo-Abyssinian War from 1935 to 1936. The occupied territory merges with Eritrea and Italian Somaliland into the colony of Italian East Africa.
- The Empire of Japan captures Manchuria in 1931, creating the puppet state of Manchukuo. A puppet government was created, with Puyi, the last Qing Dynasty Emperor of China, installed as the nominal regent and emperor.[4]
Decolonization and independence
- Mohandas Gandhi lead the non-violent Satyagraha movement in the Declaration of the Independence of India and the Salt March in March 1930.
Disasters
- The German dirigible airship Hindenburg explodes in the sky above Lakehurst, New Jersey, United States on May 6, 1937. 36 people are killed. The event leads to an investigation of the explosion and the disaster causes major public distrust of the use of hydrogen-inflated airships and seriously damages the reputation of the Zeppelin company.
- The New London School in New London, Texas is destroyed by an explosion, killing in excess of 300 students and teachers (1937).
- The New England Hurricane of 1938, which became a Category 5 hurricane before making landfall as a Category 3. The hurricane was estimated to have caused property losses estimated at US$306 million ($ 4.72 billion in 2010), killed between 682 and 800 people, and damaged or destroyed over 57,000 homes, including famed actress Katharine Hepburn's, who had been staying in her family's Old Saybrook, Connecticut beach home when the hurricane struck.
- The Dust Bowl, or Dirty Thirties: a period of severe dust storms causing major ecological and agricultural damage to American and Canadian prairie lands from 1930 to 1936 (in some areas until 1940). Caused by extreme drought, coupled with decades of extensive farming without crop rotation, fallow fields, cover crops, or other techniques to prevent erosion, and heavy winds, it affected an estimated 100,000,000 acres (400,000 km2) of land (traveling as far east as New York and the Atlantic Ocean), caused mass migration (which was the inspiration for the Pulitzer Prize winning The Grapes of Wrath by John Steinbeck), food shortages, multiple deaths and illness from sand inhalation (see History in Motion), and a severe reduction in the going wage rate.
- The 1938 Yellow River flood pours out from Huayuankou, China in 1938, inundating 54,000 km2 (21,000 sq mi) of land, and takes an estimated 500,000 lives.
Assassinations
The 1930s were marked by several notable assassinations:
- U.S. presidential candidate Huey Long assassinated (1935).
- Engelbert Dollfuss, Chancellor of Austria and leading figure of Austrofascism, is assassinated in 1934 by Austrian Nazis. Germany and Italy nearly clash over the issue of Austrian independence despite close ideological similarities of the Italian Fascist and Nazi regimes.
- Alexander I of Yugoslavia is assassinated in 1934 during a visit to Marseille, France. His assassin was Vlado Chernozemski, a member of the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization. The IMRO was a political organization that fought for secession of Vardar Macedonia from Yugoslavia.[5]
International issues
- The NSDAP (Nazi Party) under Adolf Hitler wins the German federal election, March 1933. Hitler becomes Chancellor of Germany. Following the 1934 death in office of Paul von Hindenburg, President of Germany, Hitler's cabinet passed a law proclaiming the presidency vacant and transferred the role and powers of the head of state to Hitler as Führer und Reichskanzler (leader and chancellor). The Weimar Republic effectively gives way to Nazi Germany, a Totalitarian autocratic national socialist dictatorship.
- The Great Depression seriously affects the economic, political, and social aspects of society across the world.
- Major conflict occurs across the world such as the Chaco War, the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, the Spanish Civil War, the Chinese Civil War, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the outbreak of World War II on September 1, 1939.
- Collapse of the League of Nations as countries like Germany, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan abdicate the League.
Europe
- In 1930, Miguel Primo de Rivera, Prime Minister of Spain and head of a military dictatorship is forced to resign in response to a financial crisis. (Part of the Great Depression). Alfonso XIII of Spain, who had previously backed the dictatorship, attempts to return gradually to the previous system and restore his prestige. This failed utterly, as the King was considered a supporter of the dictatorship, and more and more political forces called for the establishment of a republic. In 1931, republican and socialist parties won a major victory in the local elections, while the monarchists were in decline. Street riots ensued, calling for the removal of the monarchy. The Spanish Army declared that they would not defend the King. Alfonso flees the country, effectively abdicating and ending the Bourbon Restoration phase which had started in the 1870s. A Second Spanish Republic emerges.
- In the Soviet Union, agricultural collectivization and rapid industrialization take place.[6]
- More than 25 million people migrate to cities in the Soviet Union.
- Anglo-German Naval Agreement is signed in 1935, removing the Treaty of Versailles' level of limitation on the size of the Kriegsmarine (German Navy). The agreement allows Germany to build a larger naval force.
- Éamon de Valera introduces a new constitution for the Irish Free State in 1937, effectively ending its status as a British Dominion.
- The "Great Purge" of "Old Bolsheviks" from the Communist Party of the Soviet Union takes place from 1936 to 1938, as ordered by Soviet Union leader Joseph Stalin, resulting in hundreds of thousands of people being killed. This purge was due to mistrust and political differences, as well as the massive drop in Grain produce. This was due to the method of collectivization in Russia. The Soviet Union produced 16 million lbs of grain less in 1934 compared to 1930. This led to the starvation of millions of Russians.
- The 1937 World's Fair in Paris, France displays the growing political tensions in Europe. The pavilions of the rival countries of Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union face each other. Germany at the time was internationally condemned for Luftwaffe (its air force) having performed a bombing of the Basque town of Guernica in Spain during the Spanish Civil War. Spanish artist Pablo Picasso depicted the bombing in his masterpiece painting Guernica at the World Fair, which was a surrealist depiction of the horror of the bombing.
Africa
Hertzog of South Africa, whose National Party had won the 1929 election alone, after splitting with the Labour Party, received much of the blame for the devastating economic impact of the depression.
Americas
 Amelia Earhart in 1935.
Amelia Earhart in 1935.
- Canada and other countries under the British Empire sign the Statute of Westminster in 1931 establishing effective parliamentary independence of Canada from the parliament of the United Kingdom.
- United States Marine Corps general Smedley Butler confesses to the U.S. Congress in 1934 that a group of industrialists contacted him, requesting his aid to overthrow the U.S. government of Roosevelt and establish what he claimed would be a fascist regime in the United States.
- Newfoundland voluntarily returns to British colonial rule in 1934 amid its economic crisis during the Great Depression with the creation of the Commission of Government, a non-elected body.
- Canadian Prime Minister W. L. Mackenzie King meets with German Führer Adolf Hitler in 1937 in Berlin. King is the only North American head of government to meet with Hitler.
- Amelia Earhart receives major attention in the 1930s as the first woman pilot to conduct major air flights. Her disappearance for unknown reasons in 1937 while on flight prompted search efforts which failed.
- Southern Great Plains devastated by decades-long Dust Bowl
- In 1932 the Cipher Bureau broke the German Enigma cipher and overcame the ever-growing structural and operating complexities of the evolving Enigma machine with plugboard, the main German cipher device during World War II.
- Board of Temperance Strategy established in U.S. to fight repeal of prohibition
- Getúlio Vargas became the President of Brazil after the 1930 coup d'état.
Asia
 Mohandas Gandhi on the Salt March in 1930.
Mohandas Gandhi on the Salt March in 1930.
- Major international media attention follows Mohandas Gandhi's peaceful resistance movement against the British colonial rule in India.
- Chinese Communist Party leader Mao Zedong forms the small enclave state called the Chinese Soviet Republic in 1931.
- The Gandhi–Irwin Pact is signed by Mohandas Gandhi and Viceroy of India, Lord Irwin on March 5, 1931. Gandhi agrees to end the campaign of civil disobedience being carried out by the Indian National Congress (INC) in exchange for Irwin accepting the INC to participate in roundtable talks on British colonial policy in India.
- The Government of India Act of 1935 is passed in the British Raj, separating Burma into a separate British colony and increasing political autonomy of the princely states in India.
- Mao Zedong's Chinese communists begin a large retreat from advancing nationalist forces, called the Long March beginning in October 1934 and ending in October 1936 resulting in the collapse of the Chinese Soviet Republic.
- Colonial India's Muslim League leader Muhammed Ali Jinnah delivers his "Day of Deliverance" speech on December 2, 1939, calling upon Muslims to begin to engage in civil disobedience against the British colonial government starting on December 12. Jinnah demands redress and resolution to tensions and violence occurring between Muslims and Hindus in India. Jinnah's actions are not supported by the largely Hindu-dominated Indian National Congress whom he had previously closely allied with. The decision is seen as part of an agenda by Jinnah to support the eventual creation of an independent Muslim state called Pakistan from British Empire.
Australia
- Australia and New Zealand sign the Statute of Westminster in 1931 which established legislative equality between the self-governing dominions of the British Empire and the United Kingdom, with a few residual exceptions. The Parliament of Australia and Parliament of New Zealand gain full legislative authority over their territories, no longer sharing powers with the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
Economics
- The Great Depression occurred during the 1930s.
- Economic interventionist policies increase in popularity as a result of the Great Depression in both authoritarian and democratic countries. In the western world, Keynesianism replaces classical economic theory.
- Rapid industrialization takes place in the Soviet Union.
- Prohibition in the United States finally ended in 1933. On December 5, 1933, the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment repealed the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution.
Technology
Many technological advances occurred in the 1930s, including:
- On March 8, 1930, the first frozen foods of Clarence Birdseye were sold in Ringfield, Massachusetts, United States.
- Ub Iwerks produced the first Color Sound Cartoon in 1930, a Flip the Frog cartoon entitled: "Fiddlesticks";
- In 1930, Warner Brothers released the first All-Talking All-Color wide-screen movie, Song of the Flame; in 1930 alone, Warner Brothers released ten All-Color All-Talking feature movies in Technicolor and scores of shorts and features with color sequences;
- Air mail service across the Atlantic Ocean began;
- Radar was invented, known as RDF (Radio Direction Finding), such as in British Patent GB593017 by Robert Watson-Watt in 1938;
- In 1933, the 3M company marketed Scotch Tape;
- In 1931, RCA Victor introduced the first long-playing phonograph record.
- In 1935, the British London and North Eastern Railway introduced the A4 Pacific, designed by Nigel Gresley. Just three years later, one of these, No. 4468 Mallard, would become the fastest steam locomotive in the world.
- In 1936, Kodachrome is invented, being the first color film made by Eastman Kodak.
- In 1936, The first regular high-definition (then defined as at least 200 lines) television service from the BBC, based at Alexandra Palace in London, officially begins broadcasting.
- Nuclear fission discovered by Otto Hahn, Lise Meitner and Fritz Strassman in 1939.
- The Volkswagen Beetle, one of the best selling automobiles ever produced, had its roots in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s. Created by Ferdinand Porsche and his chief designer Erwin Komenda. The car would prove to be successful, and is still in production today.
- First intercontinental commercial airline flights.
- The chocolate chip cookie was accidentally developed by Ruth Graves Wakefield in 1930 which was very popular.
- The Frying Pan was the first electric lap steel guitar ever produced.
- Edwin Armstrong invented wide-band frequency modulation radio in 1933.
- The Bass guitar was invented by Paul Tutmarc of Seattle, Washington in 1936.
Popular culture
Radio
- Radio becomes dominant mass media in industrial nations.
Music
Main article: 1930s in music- "Swing" music starts becoming popular (from 1935 onward). It gradually replaces the sweet form of Jazz that had been popular for the first half of the decade.
- "Delta Blues" music, the first recorded in the late 1920s, was expanded by Robert Johnson and Skip James, two of the most important and influential acts of "Blues" genre.
- Django Reinhardt and Stéphane Grappelli led the development of Gypsy jazz.
- Sergei Rachmaninoff composed Rhapsody on a Theme of Paganini in 1934.
- Charlie Christian becomes the first electric guitarist to be in a multiracial band with Benny Goodman and Lionel Hampton in 1939.
Film
- Disney's Snow White and the Seven Dwarves was released in 1937.
- The Little Princess was released in 1939.
- The Wizard of Oz was released in 1939
In the art of film making, the Golden Age of Hollywood entered a whole decade, after the advent of talking pictures ("talkies") in 1927 and full-color films in 1930: more than 50 classic films were made in the 1930s: most notable were Gone With The Wind and The Wizard of Oz.
- The soundtrack and photographic technology prompted many films to be made or re-made, such as the 1934 version of Cleopatra, using lush art deco sets which won an Academy Award (see films 1930–1939 in: Academy Award for Best Cinematography);
- Universal Pictures begins producing its distinctive series of horror films, which came to be known as the Universal Monsters, featuring what would become iconic representations of literary and mythological monsters, the horror films (or monster movies) included many cult classics, such as Dracula, Frankenstein, The Mummy, Jekyll/Hyde, King Kong, The Hunchback of Notre Dame, and other films about wax museums, vampires and zombies, leading to the 1941 film The Wolf Man These films led to the stardom of stars such as Bela Lugosi, Lon Chaney Jr, and Boris Karloff.
- Recurring series' and serials included: Laurel and Hardy, the Marx Brothers, Tarzan, Charlie Chan, Alfred Hitchcock films, Our Gang, and the filming of "superheroes" such as The Phantom
Sports
- 1936 Berlin Olympics
- First Jules Rimet Cup hosted in Uruguay in 1930
Architecture
See also: :Category:1930s architecture The Empire State Building became the world's tallest building when completed in 1931.
The Empire State Building became the world's tallest building when completed in 1931.
- The world's tallest building (for the next 35 years) was constructed, opening as the Empire State Building on May 3, 1931 in New York City, USA;
- The Golden Gate Bridge was constructed, opening on May 27, 1937 in San Francisco, USA;
Literature and art
- Height of the Art Deco movement in North America and Western Europe.
- Notable poetry include W. H. Auden's Poems.
- Notable literature includes F. Scott Fitzgerald's Tender Is the Night (1934), J.R.R. Tolkien's The Hobbit (1937), Aldous Huxley's Brave New World (1932), John Steinbeck's Grapes of Wrath (1939) and Of Mice and Men (1937), Ernest Hemingway's To Have and Have Not (1937), John Dos Passos's U.S.A trilogy, William Faulkner's As I Lay Dying (1930) and Absalom, Absalom! (1936), John O'Hara's Appointment in Samarra (1934) and Butterfield 8 (1935).
- Notable "hardboiled" crime fiction includes Raymond Chandler's The Big Sleep, James M. Cain's The Postman Always Rings Twice (1934).
- Notable plays include Thorton Wilder's Our Town (1938).
- Near the end of the decade, two of the world's most iconic superheroes and recognizable fictional characters were introduced in comic books; Superman first appeared in 1938, and Batman in 1939.
- The pulp fiction magazines began to feature distinctive, gritty adventure heroes that combined elements of hard boiled detective fiction and the fantastic adventures of the earlier pulp novels. Two particularly noteworthy characters introduced were Doc Savage and The Shadow, who would later influence the creation of characters such as Superman and Batman.
Visual arts
See also: Social Realism and History of paintingSocial Realism became an important art movement during the Great Depression in the United States in the 1930s. Social realism generally portrayed imagery with socio-political meaning. Other related American artistic movements of the 1930s were American scene painting and Regionalism which were generally depictions of rural America, and historical images drawn from American history. Precisionism with its depictions of industrial America was also a popular art movement during the 1930s in the USA. During the Great Depression the art of Photography played an important role in the Social Realist movement. The work of Dorothea Lange, Walker Evans, Margaret Bourke-White, Lewis Hine, Edward Steichen, Gordon Parks, Arthur Rothstein, Marion Post Wolcott, Doris Ulmann, Berenice Abbott, Aaron Siskind, Russell Lee, Ben Shahn (as a photographer) among several others were particularly influential.
The Works Progress Administration part of the Roosevelt Administration's New Deal sponsored the Federal Art Project, the Public Works of Art Project, and the Section of Painting and Sculpture which employed many American artists and helped them to make a living during the Great Depression.
Mexican muralism was a Mexican art movement that took place primarily in the 1930s. The movement stands out historically because of its political undertones, the majority of which of a Marxist nature, or related to a social and political situation of post-revolutionary Mexico. Also in Latin America Symbolism and Magic Realism were important movements.
In Europe during the 1930s and the Great Depression, Surrealism, late Cubism, the Bauhaus, De Stijl, Dada, German Expressionism, Expressionism, Symbolist and modernist painting in various guises characterized the art scene in Paris and elsewhere.
People
World leaders
 Emperor Hirohito in 1935. He was the last divine Emperor of Japan
Emperor Hirohito in 1935. He was the last divine Emperor of Japan
 Adolf Hitler wins a popular election and then establishes a dictatorship in Germany whose expansionist ambitions lead to the outbreak of World War II in Europe.
Adolf Hitler wins a popular election and then establishes a dictatorship in Germany whose expansionist ambitions lead to the outbreak of World War II in Europe.
 Franklin D. Roosevelt, as President of the United States initiates major economic reform in the United States.
Franklin D. Roosevelt, as President of the United States initiates major economic reform in the United States.
- Prime Minister James Scullin (Australia)
- Prime Minister Joseph Lyons (Australia)
- Prime Minister Sir Earle Page (Australia)
- President Getúlio Vargas (Brazil)
- Prime Minister Richard Bedford Bennett, 1st Viscount Bennett (Canada)
- Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King (Canada)
- President Chiang Kai-shek (China)
- President Lin Sen (China)
- King Fuad I (Egypt, Sudan, Nubia, Kordofan & Darfur)
- Taoiseach Éamon de Valera (Éire)
- Emperor Haile Selassie I (Ethiopia)
- President Paul von Hindenburg (Germany)
- Führer Adolf Hitler (Germany)
- Governor-General Lord Edward Irwin (British India)
- Governor-General The Marquess of Linlithgow (British India)
- Mahatma Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (India)
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel (India)
- Jawaharlal Nehru (India)
- Rezā Shāh Pahlavi (Iran/Persia)
- King Faisal I (Iraq)
- King Ghazi (Iraq)
- King Faisal II (Iraq)
- President W.T. Cosgrave (Irish Free State)
- President Éamon de Valera (Irish Free State)
- King Victor Emmanuel III (Italy)
- Prime Minister Benito Mussolini (Italy)
- Emperor Hirohito (Japan)
- Emir Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah (Kuwait)
- President Lázaro Cárdenas (Mexico)
- Sultan Mohammed V (Morocco)
- Prime Minister Michael Joseph Savage (New Zealand)
- Marshal Józef Piłsudski Józef Piłsudski (Poland)
- Minister of foreign Józef Beck (Poland)
- Prime Minister António de Oliveira Salazar (Portugal)
- Prime Minister James Barry Munnik Hertzog (South Africa)
- General Secretary Joseph Stalin (Soviet Union)
- President Niceto Alcalá-Zamora (Spain)
- Prime Minister Manuel Azaña (Spain)
- Prime Minister Alejandro Lerroux (Spain)
- President Hashim al-Atassi (Syria)
- President Bahij al-Khatib (Syria)
- Bey (Crown Prince) Ahmad II (Tunisia)
- President Mustafa Kemal Atatürk (Turkey)
- King George V (United Kingdom)
- King Edward VIII (United Kingdom)
- King George VI (United Kingdom)
- Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald (United Kingdom)
- Prime Minister Stanley Baldwin (United Kingdom)
- Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain (United Kingdom)
- President Herbert Hoover (United States)
- President Franklin D. Roosevelt (United States)
- Holy Father Pope Pius XI (Vatican)
Sports figures
Global
- Cliff Bastin (English footballer)
- Donald Bradman (Australian cricketer)
- Haydn Bunton, Sr (Australian Rules Footballer)
- Jack Crawford (tennis)
- Jack Dyer (Australian rules football player)
- Walter Hammond (English cricketer)
- Eddie Hapgood (English footballer)
- George Headley (West Indies cricketer)
- Alex James (Scottish footballer)
- Douglas Jardine (English cricketer)
- Harold Larwood (English cricketer)
- Jack Lovelock (New Zealand runner)
- Fred Perry (English tennis player)
- Leonard Hutton, English cricketer
- Percy Williams (sprinter)
- Dhyan Chand, Indian hockey player
- Lala Amarnath, Indian cricketer
 Joe Louis American world heavyweight boxing champion.
Joe Louis American world heavyweight boxing champion.
 Jesse Owens shook racial stereotypes both with Nazis and segregationists in the USA at the 1936 Berlin Olympics.
Jesse Owens shook racial stereotypes both with Nazis and segregationists in the USA at the 1936 Berlin Olympics.
United States
See also: History of baseball in the United States- Joe Louis (boxing)
- Lou Ambers (boxing)
- Henry Armstrong (boxing)
- Max Baer (boxing)
- Cliff Battles (halfback)
- Jay Berwanger (halfback)
- James J. Braddock (boxing)
- Ellison M. ("Tarzan") Brown (marathon)
- Don Budge (tennis)
- Tony Canzoneri (boxing)
- Mickey Cochrane (baseball)
- Buster Crabbe (swimming)
- Glenn Cunningham (running)
- Dizzy Dean (baseball)
- Joe DiMaggio (baseball)
- Babe Didrikson (track)
- Leo Durocher (baseball)
- Turk Edwards (tackle)
- Jimmie Foxx (baseball)
- Lou Gehrig (baseball)
- Hank Greenberg (baseball)
- Lefty Grove (baseball)
- Dixie Howell (halfback)
- Don Hutson (end)
- Cecil Isbell (quarterback)
- Bobby Jones (golf)
- John A. Kelley (marathon)
- Nile Kinnick (halfback)
- Tommy Loughran (boxing)
- Alice Marble (tennis)
- Ralph Metcalfe (sprinter)
- Bronko Nagurski (fullback)
- Mel Ott (baseball)
- Jesse Owens (sprinter)
- Bobby Riggs (tennis)
- Barney Ross (boxing)
- Al Simmons (baseball)
- Helen Stephens (track)
- Eddie Tolan (sprinter)
- Ellsworth Vines (tennis)
- Stella Walsh (sprinter)
- Frank Wykoff (sprinter)
Entertainers
 Walt Disney introduces each of the Seven Dwarfs in a scene from the original 1937 Snow White
Walt Disney introduces each of the Seven Dwarfs in a scene from the original 1937 Snow White
- Louis Armstrong
- Fred Astaire
- Carl Barks
- John Barrymore
- Wallace Beery
- Humphrey Bogart
- Charles Boyer
- James Cagney
- Frank Capra
- Charlie Chaplin
- Claudette Colbert
- Gary Cooper
- Joan Crawford
- Bing Crosby
- Bette Davis
- Errol Flynn
- Henry Fonda
- Joan Fontaine
- John Ford
- Olivia De Havilland
- Walt Disney
- Clark Gable
- Greta Garbo
- Judy Garland
- Cary Grant
- Katharine Hepburn
- Leslie Howard
- Boris Karloff
- Buster Keaton
- Laurel and Hardy
- Vivien Leigh
- The Marx Brothers
- Paul Muni
- Laurence Olivier
- Edward G. Robinson
- Ginger Rogers
- Mickey Rooney
- James Stewart
- Barbara Stanwyck
- Shirley Temple
- The Three Stooges
- Spencer Tracy
- John Wayne
- Orson Welles
Musicians
-
George Gershwin in 1937, the year of his death
-
Carl van Vechten, Bessie Smith, 1936. She was an early blues singer, was known for her powerful voice.
-
Lead Belly and his wife Martha Promise Ledbetter in Wilton, Conn., February 1935. On January 20 of the same year, the two were married at Mary Elizabeth Barnicle's Wilton farmhouse, and on the same day Lead Belly made the first recording of "Alberta" there for John Lomax and the Library of Congress.
-
Composer and jazz pianist Fats Waller in 1938
-
Cab Calloway and The Cotton Club Orchestra, 1934 photo of His High-de-Highness of Ho-de-Ho and the band
- Harold Arlen
- Louis Armstrong
- Fred Astaire
- Count Basie
- Cab Calloway
- Eddie Cantor
- Nat King Cole
- Noël Coward
- Bing Crosby
- Vernon Duke
- Jimmy Durante
- Duke Ellington
- Ella Fitzgerald
- George Gershwin
- Ira Gershwin
- Benny Goodman
- Coleman Hawkins
- Billie Holiday
- Lena Horne
- Al Jolson
- Jerome Kern
- Lead Belly
- Glenn Miller
- Édith Piaf
- Cole Porter
- Ma Rainey
- Django Reinhardt
- Bill "Bojangles" Robinson
- Rodgers and Hart
- Frank Sinatra
- Bessie Smith
- Fats Waller
- Ethel Waters
Influential artists
-
Theo van Doesburg, Simultaneous Counter-Composition, 1930, Museum of Modern Art, New York City, co-founder of De Stijl
-
Joaquín Torres García, 1932, Latin American abstract Symbolism
-
Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, The Junkerboden Under Snow, (1936–1938)
Painters and sculptors
Muralists
-
Diego Rivera, Recreation of Man at the Crossroads (renamed Man, Controller of the Universe), originally created in 1934, Mexican muralism movement
- Santiago Martínez Delgado
- Pedro Nel Gómez
- José Orozco
- Diego Rivera
- David Siqueiros
Photography
-
Dorothea Lange, Migrant Mother, 1936. Depictions of pea pickers in California, centering on Florence Owens Thompson, age 32, a mother of seven children, in Nipomo, California, March 1936.
-
Walker Evans, Allie Mae Burroughs, 1935-1936, a symbol of the Great Depression
-
Carl Van Vechten, Salvador Dalí and Man Ray in Paris, June 16, 1934, making "wild eyes"
- Ansel Adams
- Margaret Bourke-White
- Walker Evans
- Lewis Hine
- Dorothea Lange
- Gordon Parks
- Man Ray
- Edward Steichen
- Carl Van Vechten
- Edward Weston
See also
- 1930s in television
- 1930s in literature
- 30s in the 30s - Shanghai - Cotton's - November 20, 2010
Timeline
The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade:
1930 • 1931 • 1932 • 1933 • 1934 • 1935 • 1936 • 1937 • 1938 • 1939
References
- ^ Bix, Herbert P. "The Showa Emperor's 'Monologue' and the Problem of War Responsibility", Journal of Japanese Studies, Vol. 18, No. 2. (Summer, 1992), pp. 295–363.
- ^ Hunt, Lynn. "The Making of the West: Peoples and Cultures" Vol. C since 1740.Bedford/St. Martin's, 2009.
- ^ Zabecki, David T. (1999). World War II in Europe: an encyclopedia. New York: Garland Pub. pp. p1353. ISBN 0-8240-7029-1. http://books.google.com/?id=gYDN-UfehEEC&pg=PA1353&dq=albania+%22Italian+protectorate%22.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica article on Manchukuo
- ^ "The first central committee of IMRO. Memoirs of d-r Hristo Tatarchev", Materials for the Macedonian liberation movement, book IX (series of the Macedonian scientific institute of IMRO, led by Bulgarian academician prof. Lyubomir Miletich), Sofia, 1928, p. 102 , поредица "Материяли за историята на македонското освободително движение" на Македонския научен институт на ВМРО, воден от българския академик проф. Любомир Милетич, книга IX, София, 1928.
- ^ A. L. Unger (January 1969). "Stalin's Renewal of the Leading Stratum: A Note on the Great Purge". Soviet Studies 20 (3): 321–330. doi:10.1080/09668136808410659. JSTOR 149486.
- ^ "National Park History: “The Spirit of the Civilian Conservation Corps”". Nationalparkstraveler.com. http://www.nationalparkstraveler.com/2008/09/park-history-spirit-civilian-conservation-corps. Retrieved 2010-09-04.
- ^ http://www.allmusic.com/artist/p91178
- ^ http://www.allmusic.com/cg/amg.dll
External links
- Heroes of the 1930s - slideshow by Life magazine
- The Dirty Thirties — Images of the Great Depression in Canada
- America in the 1930s Extensive library of projects on America in the Great Depression from American Studies at the University of Virginia
- The 1930s Timeline year by year timeline of events in science and technology, politics and society, culture and international events with embedded audio and video. AS@UVA
- Gardiner, Juliet, The Thirties: An Intimate History. London, Harper Press, 2010. ISBN 978-0-00-724076-0
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.