- Aminolevulinic acid
-
δ-Aminolevulinic acid 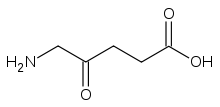
Systematic (IUPAC) name 5-amino-4-oxo-pentanoic acid Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Identifiers CAS number 106-60-5 
ATC code L01XD04 PubChem CID 137 DrugBank APRD00793 ChemSpider 134 
UNII 88755TAZ87 
KEGG D07567 
ChEBI CHEBI:356416 
ChEMBL CHEMBL601 
Chemical data Formula C5H9NO3 Mol. mass 131.13 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)δ-Aminolevulinic acid (dALA or δ-ALA or 5ala or 5-aminolevulinic acid ) is the first compound in the porphyrin synthesis pathway, the pathway that leads to heme in mammals and chlorophyll in plants.
In plants, production of δ-ALA is the step on which the speed of synthesis of chlorophyll is regulated. Plants that are fed by external δ-ALA accumulate toxic amounts of chlorophyll precursor, protochlorophyllide, indicating that the synthesis of this intermediate is not suppressed anywhere downwards in the chain of reaction. Protochlorophyllide is a strong photosensitizer in plants.
Contents
Production
In non-photosynthetic eukaryotes such as animals, insects, fungi, and protozoa, as well as the α-proteobacteria group of bacteria, it is produced by the enzyme ALA synthase, from glycine and succinyl CoA. This reaction is known as the Shemin pathway.
In plants, algae, bacteria (except for the α-proteobacteria group) and archaea, it is produced from glutamic acid via glutamyl-tRNA and glutamate-1-semialdehyde. The enzymes involved in this pathway are glutamyl-tRNA synthetase, glutamyl-tRNA reductase, and glutamate-1-semialdehyde aminotransferase. This pathway is known as the C5 or Beale pathway.[1][2]
Clinical significance
It elicits synthesis and accumulation of fluorescent porphyrins (protoporphyrin IX) in epithelia and neoplastic tissues, among them malignant gliomas. It is used to visualise tumorous tissue in neurosurgical procedures. Studies have shown that the intraoperative use of this guiding method may reduce the tumour residual volume and prolong progression-free survival in patients suffering from this disease.[3]
Aminolevulinic acid is also a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy.
Cancer diagnosis
Photodynamic detection (PDT) is the use of photosensitive drugs with a light source of the right wavelength for the detection of cancer, using fluorescence of the drug. PDT treatment possibilities include those for cancer of the prostate, breast, giant BCC (skin), cervix, recurrent bladder, vulvar, brain (human glioblastoma cells), HPV, lung, stomach, head and neck, penis, and colon, as well as those for leukemia, Barrett's oesophagus, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), Bowen's disease, and other types of cancer.
References
- ^ Beale, Samuel I. (1990) Biosynthesis of the tetrapyrrole pigment precursor, d-aminolevulinic acid, from glutamate. Plant Physiology, 93(4), 1273-1279
- ^ Willows R.D. (2004) Chlorophylls In: Encyclopaedia of Plant and Crop Science. pp 258-262, Ed: Robert M. Goodman. Marcel Dekker Inc, ISBN 0-8247-4268-0
- ^ Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ (2006). "Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial". Lancet Oncol. 7 (5): 392–401. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70665-9. PMID 16648043.
See also
Porphyrin biosynthesis early mitochondrial: D-Aminolevulinic acid
cytosolic: Porphobilinogen · Hydroxymethylbilane · Uroporphyrinogen III · Coproporphyrinogen III
late mitochondrial: Protoporphyrinogen IX · Protoporphyrin IXHeme degradation
and excretionBreakdown of hemeIntestine, excretion in fecesKidney, excretion in urinebiochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iCategories:- Biomolecules
- Amines
- Carboxylic acids
- Antineoplastic drugs
- Light therapy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
