- Interstate 69
-
Interstate 69 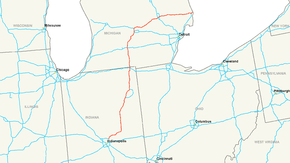
Route information Length: 355.8 mi[3] (572.6 km)
(original route; 1.73 mi (2.78 km) segment opened near Evansville, Indiana on September 29, 2009. 55.3 mi section of freeway in Kentucky designated as I-69 on October 25, 2011. 42.0 mi[1] (70.0 km) are open in MS and TN. 6.2 mile (10.0 km) section of US-77 freeway signed as I-69 completed near Corpus Christi, Texas on August 9, 2011 [2])Existed: 1956 (orig. route completed 1992) – present Major junctions Original South end: 


 I-465 / US 31 / US 52 / US 421 in Indianapolis, IN
I-465 / US 31 / US 52 / US 421 in Indianapolis, IN


 I-469 / US 24 / US 30 / US 33 in Fort Wayne, IN
I-469 / US 24 / US 30 / US 33 in Fort Wayne, IN

 I-80 / I-90 near Angola, IN
I-80 / I-90 near Angola, IN
 I-94 near Marshall, MI
I-94 near Marshall, MI
 I-96 near Lansing, MI
I-96 near Lansing, MI

 US 23 / I-75 near Flint, MI
US 23 / I-75 near Flint, MINorth end:  Highway 402 at Canadian border on Blue Water Bridge in Port Huron, MI
Highway 402 at Canadian border on Blue Water Bridge in Port Huron, MIHighway system Main route of the Interstate Highway System
Main • Auxiliary • BusinessInterstate 69 (I-69) is an Interstate Highway in the United States. It exists in two parts: a completed highway from Indianapolis, Indiana, northeast to the Canadian border in Port Huron, Michigan, and a mostly proposed extension southwest to the Mexican border in Texas. Of this extension – nicknamed the NAFTA Superhighway because it would help trade with Canada and Mexico spurred by the North American Free Trade Agreement – only three short pieces—a 6.2 mile (10.0 km) section near Corpus Christi, Texas, one in northwestern Mississippi and in the Memphis, Tennessee area and a 1.73-mile segment near Evansville, Indiana--have been built and signed as I-69 (see Interstate 69 in Mississippi and Interstate 69 in Indiana). A fourth segment of I-69 through Kentucky, 145 miles (232 km) long utilizing that state's existing parkway system and a section of Interstate 24, was established by federal legislation in 2008, but the Federal Highway Administration did not authorize the parkways to be signed as I-69 until upgrades of certain sections are complete. A 55-mile (88.5 km) section from Eddyville to Nortonville was recently approved and signed. [4].
The southern terminus of the original portion is at Interstate 465, the beltway around Indianapolis, on the northeast side of that city. I-69 heads northeast, past Anderson, Muncie, Marion, and Fort Wayne, Indiana; the latter city is served by Interstate 469, I-69's only current signed auxiliary route. After crossing the Indiana East-West Toll Road (I-80/I-90) near Angola, I-69 enters Michigan, crossing I-94 east of Battle Creek and joining with I-96 for an overlap west of Lansing. Where it splits from I-96, I-69 turns east, both in compass direction and in signed direction, and heads north of Lansing and through Flint (where it crosses I-75) to a junction with I-94 in Port Huron. The last bit of I-69 overlaps I-94 to the Blue Water Bridge across the St. Clair River, where traffic continues on Highway 402 in the Canadian province of Ontario.
The proposed extension evolved from the combination of Corridors 18 and 20 of the National Highway System as designated in the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991, but the federally recognized corridor also includes connecting and existing infrastructure, including Interstate 94 between Chicago and Port Huron and several spurs from I-69. Among these proposed spurs are an extension of Interstate 530 from Pine Bluff, Arkansas (known as "the Dickey Split," for its champion, congressman Jay Dickey), an upgrade of U.S. Route 59 from Texarkana, Texas, and a split in southern Texas to serve three border crossings at Laredo, Pharr, and Brownsville.
In August 2007, I-69 was selected by the USDOT as one of six Corridors of the Future, making it eligible for additional federal funding and streamlined planning and review. When it is finished, it may be one of the longest interstate highways not numbered with a digit ending in 0 or 5 (next to Interstate 94) and may be the longest north-south interstate highway. If the entire length of the freeway is completed, the freeway will end up being about 1800 miles in length.[citation needed]
Contents
Route description
Main articles: Interstate 69 in Indiana, Interstate 69 in Michigan, Interstate 69 in Mississippi, and Interstate 69 in TennesseeI-69 currently exists in three distinct sections: the original (with later additions), fully completed route from Indianapolis, Indiana to the Blue Water Bridge at Port Huron, Michigan, a 1.73-mile (2.78 km) section from I-64/I-164 to Indiana State Road 68 (SR 68) in southwest Indiana, and a 42-mile (68 km) section from Tunica Resorts, Mississippi to the I-40/I-69/TN-300 interchange in Memphis, Tennessee.
The new I-69 in Mississippi and Tennessee starts at an at-grade intersection with the former route of Mississippi Highway 304 in Banks, Tunica County. It continues roughly north-northeast, crossing into DeSoto County, to a partial interchange with the current route of MS 304, then runs easterly to an interchange with I-55 in northern Hernando. It then continues north, overlapping I-55 to the Tennessee state line, and continues northward concurrently with I-55 to the south side of Memphis. It then follows I-240 northward through downtown before joining I-40. Presently, the northern end of this section of I-69 is at the I-40/I-69/TN-300 interchange on the north side of Memphis. This portion of the route is the first "section of independent utility" (SUI) of the proposed extension to be signed as part of the national I-69 route, and the first portion designed as part of the extension.
The new section of Interstate 69 in southern Indiana presently begins at the I-64/I-164/SR 57 interchange north of Evansville, at the boundary between the SIU 3 ["Segment of Independent Utility"] and SIU 4; from there, it runs north to SR 68. Construction is currently underway to take the route north-northeast from there to Indiana 64 near Oakland City, which marks the end of Section 1 of SIU 3. NEPA Tier 2 Records of Decision (ROD) have been approved and final design work is presently underway to continue the highway from there north-northeast to US 50/US 150 at Washington (SIU 3, Section 2) and then on northeast to US 231 near the Crane Naval Surface Warfare Center (SIU 3, Section 3). The Tier 2 Draft Environmental Impact Statement (DEIS) has been published for the final new-terrain segment (SIU 3, Section 4), which will take I-69 from Crane NSWC northeast to SR 37 on the southwest side of Bloomington. From there, Sections 4 (Bloomington to Martinsville) and 5 (Martinsville to Indianapolis) of I-69's SIU 3 will eventually upgrade the existing SR 37 expressway corridor to full Interstate freeway standards all the way north-northeast to I-465 on the southwest side of Indianapolis.
The traditional portion of Interstate 69 in Indiana (SIU 1 of the overall national plan) starts at an interchange with I-465 in northeastern Indianapolis, running roughly northeast to near Anderson, where it turns more easterly to provide indirect access to Muncie before turning more northerly towards Fort Wayne. In Fort Wayne, I-69 roughly runs along the western edge of the city while an auxiliary route, I-469, loops east of the city. I-69 continues northerly to the Indiana East-West Toll Road near Fremont, then crosses the border into Michigan just south of Kinderhook.
I-69 in Michigan runs north passing through Coldwater and Marshall. Near Olivet, I-69 begins to turn in a northeasterly direction passing through the Lansing metropolitan area. Here I-69 is cosigned on/with I-96, the only such palindromic pairing in the Interstate Highway System. I-69 is signed east–west from Lansing through Flint to Port Huron. At its eastern terminus, I-69 joins I-94 to cross the Blue Water Bridges at the Canadian border over the St. Clair River.
Proposed extension
In 2000, Corridors 18 and 20 were split into 32 Segments of Independent Utility (SIUs) as part of the I-69 (Corridor 18) Special Environmental Study.[5] Some states use these SIU numbers to identify projects. I-94 between Chicago and Port Huron was SIU 27.
As of 2009[update], SIU 1 (all of original I-69 north of Indianapolis) and SIU 2 (which will likely use I-465 around Indianapolis, but is as yet unsigned) are open, as is the short SIU 10 in northwestern Mississippi, and part of SIU 9 in the Memphis, Tennessee area. SIUs 5 and 6 in Kentucky are built as freeways, but not yet up to Interstate standards in all areas. On June 6, 2008, President George W. Bush signed HR-1195, designating these parkways as I-69. Kentucky officials planned to place I-69 signs on the Pennyrile Parkway, Western Kentucky Parkway and Purchase Parkway in 2008, but the U.S. Federal Highway Administration (FHA) has not yet given Kentucky approval to do so.[6][7][8][9] Four SIUs in Indiana, Tennessee, and Arkansas (3, 7, 9, and 28) are under construction and portions of these SIUs are open to traffic.[10][11] Most of the remaining parts of the mainline are in the environmental impact statement (EIS) stages; the FHA has signed records of decision approving the final EIS for SIUs 11,[12] 12,[13] and 13.[14]
While federal legislation established a mandate to extend I-69 from Indiana to Texas, it did not provide funding for its construction. Therefore, it must compete against other projects for traditional funding. Despite approval of several segments, work has been completed on only a few scattered segments, due in part to increasing costs for construction materials and machinery. As a result, several states have indicated that construction of I-69 may not be possible without the use of tolls as the primary means to finance building the highway. Tennessee, Arkansas, and Mississippi passed legislation authorizing toll roads within each state. However, financing I-69 construction with tolls is highly unpopular in most areas; Indiana examined building most of SIU 3 as a toll road, but quickly reverted to making it toll-free after widespread opposition from I-69 opponents and supporters alike.
In Texas, it was originally envisioned that private firms will build, operate, then transfer portions of the highway to the state after a specified period of time. Lawmakers in Kentucky considered a bill that would authorize the re-tolling of three parkways slated to become part of I-69. Kentucky and Indiana plan to finance a new bridge across the Ohio River with tolls,[15] and Indiana governor Mitch Daniels announced in 2006 that I-69 through Indiana will be toll-free; about half of I-69 extension through southwest Indiana will be built using $700 million from the 2006 Major Moves deal, although the Major Moves legislation gives Indiana the option to place tolls on I-69 if necessary.[16]
Texas
In Texas, I-69 planning has become part of the Trans-Texas Corridor (TTC) studies. This part of the TTC, called I-69/TTC, includes I-69 and all of its spurs authorized by Congress. It will extend from three border crossings, at Laredo, McAllen, and Brownsville, along US 59, US 281, and US 77 towards Victoria. After the three branches join, I-69 will continue along the general US 59 corridor past Houston to Carthage, where it will turn easterly to Louisiana. In metro Houston, I-69 will now follow the US-59 freeway corridor through town. A planned branch continues north on US 59 from the Carthage area to Texarkana. Most of the proposed I-69 route in Texas already exists as 4-lane highways, with a lengthy freeway section stretching north and south of Houston along U.S. 59 and shorter freeway sections of U.S. 77, U.S. 83, and U.S. 281 in the Rio Grande Valley.
The I-69/TTC project has been split into 15 SIUs, which match the original ones but do not share numbers. SIUs 1 to 8 (original 16 to 23) cover the main line along the "I-69 East" branch to Brownsville. The "I-69 Central" branch to McAllen is SIUs 9, 11, and 12 (original 24 to 26). The branches to Texarkana and Laredo are SIUs 13 and 14 (original 29 and 30), and two connections near Brownsville are SIUs 10 and 15 (original 31 and 32). The I-69/TTC study also includes SIU L-CC, a connection between Laredo and Corpus Christi that was not in the 2000 study.[17] The Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) originally considered building the I-69/TTC over new terrain paralleling US-59, US-77, and US-281.
Responding to widespread opposition from environmental groups and property rights activists, TxDOT announced in June 2008 that it will complete I-69 by upgrading the existing US-59, US-77, and US-281 roadways to Interstate standards through rural areas, with bypasses around urban centers along the route. Instead of building the Trans-Texas Corridor as originally planned, TxDOT now plans to finance upgrading the existing highways to I-69 through private sector investment. Under the proposed arrangement, I-69 would remain toll-free where it overlaps pre-existing highways, while bypasses of cities may be tolled. The private firms awarded contracts for I-69 would also build and operate toll roads throughout the state; some of those revenues would then be applied to I-69 construction.
A stated goal of TxDOT's I-69 initiative is that "existing suitable freeway sections of the proposed system be designated as I-69 as soon as possible."[18] In response to TxDOT's request, a six-mile segment of US 77 between I-37 and SH 44 near Corpus Christi was approved for "I-69" designation by the Federal Highway Administration in August, 2011, and was approved by the AASHTO in October 2011.[19] Signage will be posted at an official ceremony on December 5, 2011[20]
Louisiana, Arkansas, and Mississippi
Main articles: Interstate 69 in Louisiana, Interstate 69 in Arkansas, and Interstate 69 in MississippiAs well as covering the part in Texas northeast of Nacogdoches, SIU 16 also extends into Louisiana, ending at US 171 near Stonewall. SIU 15 continues around the south and east sides of the Shreveport area, crossing I-49 and ending at I-20 near Haughton.[21] SIU 14 extends northeast from I-20 to US 82 near El Dorado, Arkansas,[22] and SIU 13 continues northeast to US 65 near McGehee, mainly paralleling US 278.[23] Also included in Corridor 18, as SIU 28, is an extension of I-530 from Pine Bluff south along the US 425 corridor to I-69 west of Monticello; a short piece at the south end opened in mid-2006 as Highway 530.[24] The Charles W. Dean Bridge, SIU 12, will cross the Mississippi River between McGehee, Arkansas and Benoit, Mississippi, while SIU 11 will parallel US 61 to Tunica Resorts.[25] SIU 10, the first completed portion of the I-69 extension, runs east from Robinsonville to I-55 near Hernando, and opened in late 2006.[26] With the record of decision signed in 2007, the FHWA authorized MDOT to add I-69 signs on I-55 from the I-55/I-69 interchange in Hernando to the Tennessee state line.
Tennessee, Kentucky, and southern Indiana
I-69 SIU 9 overlaps I-55 into Memphis, Tennessee, switching there to I-240 and then I-40 before leaving onto the short State Route 300 connection and then paralleling US 51 to near Millington. On January 18, 2008, the FHWA authorized TDOT to erect I-69 signs on I-55, I-240, and I-40 from the Mississippi state line to the I-40/TN300 interchange. The proposed Interstate 269 will bypass this part of I-69, beginning where I-69 joins I-55 in Mississippi and ending near Millington, and will include the northern part of State Route 385 near Millington. SIU 8 will continue beyond Millington, near US 51, to I-155 near Dyersburg, while SIU 7 will use the existing US 51 freeway and new bypasses to the state line at Fulton, Kentucky.[27]
In Kentucky, I-69 mostly follows existing freeways originally built as toll roads. SIU 6 follows the Purchase Parkway and I-24 from Fulton to Eddyville, while SIU 5 continues along the Wendell H. Ford Western Kentucky Parkway and Edward T. Breathitt Parkway (originally called the Pennyrile Parkway) to Henderson. While these parkways received the I-69 designation by federal legislation signed in 2008, they will require upgrading to meet Interstate standards – but will not need as much work as in other states, where entirely new highways must be built.[28] The preferred alternative for SIU 4 will leave the Breathitt Parkway near its north end and cross the Ohio River to I-164 near Evansville, Indiana, and will then use I-164 to I-64.[29]
SIU 3, connecting I-64 to I-465 in southern Indianapolis, will roughly parallel State Road 57 and State Road 37 past Bloomington.[30] Finally, it has long been assumed that SIU 2 will most likely follow I-465 around the city, though INDOT has never officially confirmed that.
On August 31, 2011, Kentucky Governor Steve Beshear announced an agreement between the state and the Federal Highway Administration which will allow the Kentucky Transportation Cabinet to erect I-69 signage along the new interstate's 17-mile overlap with Interstate 24 and the 38-mile stretch of the Wendell H. Ford Western Kentucky Parkway between I-24 and the Edward T. Breathitt Pennyrile Parkway. Signage is expected to be placed in the fall of 2011, with construction on necessary upgrades of the portion of the Western Kentucky Parkway expected to be bid in September. [31] On October 25. 2011, I-69 was officlly designated by Governor Steve Beshear along the Western Kentucky Parkway along a 55 mile stretch between Eddyville, KY and Nortonville, KY. [32]
History
A route from Indianapolis northeast via Fort Wayne to I-80/I-90 near Angola was added to the proposed "Interregional Highway System" by the early 1940s. Unlike most of the routes, it was not drawn along an existing U.S. Highway corridor, except north of Fort Wayne (where it used US 27); most of it ran roughly parallel to State Roads 9 and 37.[33] The extension beyond Angola to I-94 near Marshall actually started out as part of what evolved into I-94. On early plans, the Chicago-Detroit route would have replaced US 112 (now US 12), splitting from I-80/I-90 at South Bend.[33][34] By 1947, the route had been shifted north to present I-94, along what was then US 12, but the connection to South Bend remained, splitting at Kalamazoo.[35]
The Interstate 69 designation was assigned to the Indianapolis-Angola route in 1957, while the short South Bend-Kalamazoo route became proposed Interstate 67.[36] The I-67 designation was shifted east to the US 27 corridor by early 1958, eventually being absorbed into the extension of I-69 to I-94 near Marshall which was built in 1967.[37][38] The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1968 authorized an additional 1500 miles (2400 km) of Interstates, to be chosen by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA); among Michigan's proposals was a 156-mile (251 km) extension of I-69 northeast and east via US 27 to Lansing, M-78 to Flint, and M-21 to Port Huron.[39] However, the FHWA initially only approved the route to I-475[40] in Flint.[41] The continuation to Port Huron was eventually approved in late 1984.[citation needed] Michigan's 1241-mile (1997 km) portion of the Interstate system was completed in 1992, when the last piece of I-69 opened southwest of Lansing between I-96 and Charlotte.[42]
The Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act of 1991 included two High Priority Corridors that would later become parts of a proposed cross-country extension of I-69:[43]
- (18) Corridor from Indianapolis, Indiana, to Memphis, Tennessee, via Evansville, Indiana.
- (20) United States Route 59 Corridor from Laredo, Texas, through Houston, Texas, to the vicinity of Texarkana, Texas.
Corridor 18 was extended southwest to Houston, Texas, where it connected to Corridor 20, by the Department of Transportation and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 1993; the new definition read "Corridor from Indianapolis, Indiana, through Evansville, Indiana, Memphis, Tennessee, Shreveport/Bossier, Louisiana, and to Houston, Texas."[44] The National Highway System Designation Act of 1995 made further amendments to the description of Corridor 18, specifying that it would serve Mississippi and Arkansas, extending it south to the Mexican border in the Lower Rio Grande Valley, and adding a short connection at Brownsville, Texas. This act also specified that Corridors 18 and 20 were "future parts of the Interstate System", to become actual Interstates when built to Interstate standards and connected to other Interstates. Although the act designated Corridor 9 as Interstate 99, no number was assigned to Corridors 18 and 20 yet.[45]
The Transportation Equity Act for the 21st Century (TEA-21), enacted in 1998, greatly expanded the definition of Corridor 18 to include the existing I-69, as well as Interstate 94 between Port Huron and Chicago. A connection to Pine Bluff, Arkansas was added, and the extension to the Lower Rio Grande Valley was detailed as splitting into two routes at Victoria, one following US 77 and the other following US 59 and US 281 to the Rio Grande. This act also assigned the Interstate 69 designation to Corridors 18 and 20, with the branches on US 77 and US 281 to the Rio Grande being "I-69 East" and "I-69 Central".[46] With TEA-21, the I-69 extension took shape, and remains today as those segments.[47]
Opposition and controversy
The construction of I-69 has also angered environmentalists. In particular, the portion of the route in Indiana would run through wetlands, existing farmland, and forested areas, and cut through geologically sensitive karst topography, which environmentalists argue threatens to pollute underground water systems and harm the rare species that live there.[48] [49]
Auxiliary routes
- Interstate 269 (Tennessee/Mississippi) - under construction
- Interstate 369 (Northern Kentucky) - planned
- Interstate 469 (Indiana)
Auxiliary routes of Interstate 69 
References
- ^ Mississippi Department of Transportation, Mississippi Public Roads Selected Statistics Extent, Travel, and Designation, accessed August 2007
- ^ "Robstown highway officially becomes first stretch of Interstate 69". Corpus Christi Caller. August 9, 2011. http://www.caller.com/news/2011/aug/09/robstown-highway-officially-becomes-first-of-69/.
- ^ DeSimone, Tony (October 31, 2002). "Table 1: Main Routes of the Dwight D. Eisenhower National System Of Interstate and Defense Highways as of October 31, 2002". Route Log and Finder List. Federal Highway Administration. http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/reports/routefinder/table1.cfm.
- ^ "New Interstate 69 designated in Ky.". Nashville, TN: WSMV-TV. October 26, 2011. http://www.wsmv.com/story/15878028/new-interstate-69-designated-in-ky. Retrieved October 26, 2011.
- ^ I-69 (Corridor 18) Special Environmental Study, February 7, 2000
- ^ HR-1195 Text
- ^ "KY I-69 Designation Cruises Through Congress" (Press release). Representative Whitfield. May 4, 2008. http://whitfield.house.gov/news/press.aspx?id=228.
- ^ Interstate 69 Legislation, Tristate Homepage.com
- ^ "President Bush Signs HR-1195" (Press release). The White House. June 6, 2008. http://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2008/06/20080606-4.html.
- ^ TDOT I-69 Segment 9 Newsletter, January 2007
- ^ I-69 Indianapolis to Evansville Extension (Official Site)
- ^ Staff. "I-69 Project Page". Mississippi Department of Transportation. http://www.gomdot.com/Home/Projects/I69/Home.aspx. Retrieved November 1, 2010.
- ^ "Great River Bridge Compact Hears Update" (Press release). Arkansas Highway and Transportation Department. November 30, 2000. http://www.arkansashighways.com/News/News2000/NR00-138.htm.
- ^ "Location for Proposed I-69 in South Arkansas Receives Federal Approval" (Press release). Arkansas Highway and Transportation Department. May 24, 2006. http://www.arkansasinterstates.com/News/News%202007/News%202006/NR06-061.htm.
- ^ "Toll Seen for I-69 Bridge". Evansville Courier-Press. January 27, 2008. http://www.courierpress.com/news/2008/jan/27/toll-seenfor-i-69bridge/.
- ^ "INDOT I-69 SIU-3 Section 1 FEIS News Release" (PDF) (Press release). Indiana Department of Transportation. http://www.i69indyevn.org/PDF/Section1/pr_FEIS.pdf. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Staff. "I-69/TTC (Northeast Texas to Mexico)". Texas Department of Transportation. http://ttc.keeptexasmoving.org/projects/i69/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ Staff. "What's Next for I-69 Texas?". Texas Department of Transportation. http://www.txdot.gov/drivenbytexans/whats_next.htm. Retrieved August 2011.
- ^ "Portion of US 77 Approved as Part of U.S. Interstate System" (Press release). Texas Department of Transportation. http://www.txdot.gov/news/028-2011.htm. Retrieved August 2011.
- ^ "First I-69 signs going up on U.S. 77 in December". http://www.brownsvilleherald.com/articles/december-133075-first-going.html.
- ^ Staff. "I-69, SIU 15 Project Site". Louisiana Department of Transportation and Development. http://www.i69dotd.com/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ Staff. "Interstate 69 Shreveport to El Dorado". Arkansas Highway and Transportation Department and Louisiana Department of Transportation and Development. http://www.i69arkla.com/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ Staff. "Interstate 69 El Dorado to McGehee". Arkansas Highway and Transportation Department. http://i-69.dina.org/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ Riggin, Amy (May 26, 2006). "Interstate Plan is Moving Forward". Pine Bluff Commercial. http://www.pbcommercial.com/articles/2006/05/26/news/news2.txt.
- ^ "I-69 Robinsonville to Benoit". Mississippi Department of Transportation. http://www.msdoti69.net/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ Risher, Wayne (July 20, 2006). "New Leg of I-69 to Open on Oct. 3". The Commercial Appeal. http://www.redorbit.com/news/business/580882/new_leg_of_i69_to_open_on_oct_3_/index.html.
- ^ Staff. "Interstate 69 Project". Tennessee Department of Transportation. http://www.tdot.state.tn.us/i69/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ "Governor Fletcher Unveils I-69 Corridor Designation" (Press release). Commonwealth of Kentucky. May 15, 2006. http://www.kentucky.gov/Newsroom/governor/20060515i69.htm.
- ^ "Preferred Alternative Identified for I-69 Corridor Linking Henderson and Evansville" (Press release). Indiana Department of Transportation. February 11, 2004. http://www.kytc.state.ky.us/news/2-11-04.htm.
- ^ Staff= Indiana Department of Transportation. "Official I-69 Evansville to Indianapolis Study Homepage". http://deis.i69indyevn.org/. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ "Governor Beshear announces approval of historic I-69 agreement" (Press release). Governor of Kentucky. August 31, 2011. http://governor.ky.gov/pressrelease.htm?PostingGUID={AC96E6DB-B9F4-4698-8017-A05FF61347BA}.
- ^ "Governor puts I-69 on the map". WPSD-TV. October 25,2011. http://www.wpsdlocal6.com/news/ky-state-news/Beshear-Puts-I-69-On-The-Map-132568533.html.
- ^ a b Public Roads Administration (ca. 1943). Highway plan ca 1943.jpg Routes of the Recommended Interregional Highway System (Map). http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Interregional Highway plan ca 1943.jpg.
- ^ Public Roads Administration (1939). Highway plan 1939.jpg Proposed Interregional Highway System (Map). http://commons.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Interregional Highway plan 1939.jpg.
- ^ Public Roads Administration (August 2, 1947). Highway plan August 2, 1947 big text.jpg National System of Interstate Highways (Map). http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Interstate Highway plan August 2, 1947 big text.jpg.
- ^ Public Roads Administration (August 14, 1957). Highway plan August 14, 1957.jpg Official Route Numbering for the National System of Interstate and Defense Highways (Map). http://commons.wikimedia.org/File:Interstate Highway plan August 14, 1957.jpg.
- ^ Staff (April 25, 1958). Recommended Numbering: Interstate Highways in Michigan (Report). Michigan State Highway Department. Archived from the original on October 16, 2002. http://web.archive.org/web/20021016104545/http://nwindianahwys.homestead.com/michiplan.html.
- ^ Public Roads Administration (June 27, 1958). Highway plan June 27, 1958.jpg Official Route Numbering for the National System of Interstate and Defense Highways (Map). http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Interstate Highway plan June 27, 1958.jpg.
- ^ "State Asks 600 Miles of Extra Interstate". Ironwood Daily Globe. November 14, 1968.
- ^ Michigan Department of Transportation (1984). Official Transportation Map (Map).
- ^ Federal Highway Administration (October 1, 1970). Highway plan October 1, 1970.jpg The National System of Interstate and Defense Highways (Map). http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Interstate Highway plan October 1, 1970.jpg.
- ^ Staff. "1990s". Transportation Timeline. Michigan Department of Transportation. http://www.michigan.gov/mdot/0,1607,7-151-9620_11154_39107-106010--,00.html. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ H.R.2950
- ^ H.R. 5518
- ^ S.440
- ^ H.R. 2400
- ^ Staff. "NHS High Priority Corridors Description". Federal Highway Administration. http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/hep10/nhs/hipricorridors/hpcor.html. Retrieved August 2007.
- ^ ELPC - Indiana I-69
- ^ Bisbort, Alan. "The World This Week: Nafty Business: 'Super Corridor' will pave over the heart of America". The Valley Advocate. http://www.valleyadvocate.com/article.cfm?aid=4476.
Further reading
- Dellinger, Matt (2010). Interstate 69: The Unfinished History of the Last Great American Highway. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 1416542493.
External links
- I69Info.com
- Interstate 69 at Michigan Highways
- Highway Position: Is an Indiana Congressman introducing legislation to change the name of Interstate 69? (Snopes.com)
- Indiana Highway Ends: I-69
- I-69 Recreational Heritage Route in Southern Michigan
- Official DOT websites:
- I-69 Indianapolis-Evansville Study (Indiana Department of Transportation, SIU 3))
- Interstate 69 in Tennessee (SIUs 7, 8, and 9)
- Interstate 69 in Mississippi (SIU 11)
- McGehee to El Dorado, Ark. (SIU 13)
- El Dorado to Shreveport, La. (SIU 14)
- Shreveport bypass (SIU 15)
- KeepTexasMoving.com Trans-Texas Corridor, a Texas Department of Transportation site
- Supporters:
- Alliance for I-69 Texas, an association supporting the development of I-69 in Texas
- Hoosier Voices for I-69 Indiana based association supporting the construction of I-69 in Indiana
- Opponents:
- Citizens for Appropriate Rural Roads, an organization opposed to a new-terrain route for I-69 in Indiana.
- Clearinghouse for Actions against I-69 in Indiana a link to its listserv
- [1], I-69 Opposition News Feed
- Higgs, Steven. Twenty Years of Crimes Against Democracy: A Grassroots History of the I-69/NAFTA Highway, Bloomington, IN: Higgs Communications, 2009. ISBN 9780982531440
Main Interstate Highways (major interstates highlighted)
4 5 8 10 12 15 16 17 19 20 22 24 25 26 27 29 30 35 37 39 40 43 44 45 49 55 57 59 64 65 66 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 (W) 76 (E) 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 (W) 84 (E) 85 86 (W) 86 (E) 87 88 (W) 88 (E) 89 90 91 93 94 95 96 97 99 H-1 H-2 H-3 Unsigned A-1 A-2 A-3 A-4 PRI-1 PRI-2 PRI-3 Lists Primary Main - Intrastate - Suffixed - Temporary - Future - Gaps Auxiliary Main - Future - Unsigned Other Standards - Business - Bypassed - Tolled Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



