- Interstate 99
-
Interstate 99 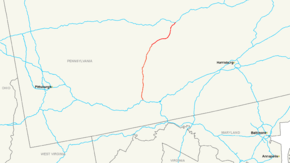
Map of southwestern Pennsylvania and vicinity with I-99 highlighted in redRoute information Maintained by PennDOT Length: 85.6 mi[2] (137.8 km) Existed: November 6, 1998[1] – present Major junctions South end: 


 I-70 / I-76 / US 220 / Penna. Tpk. near Bedford
I-70 / I-76 / US 220 / Penna. Tpk. near Bedford PA 56 near Cessna
PA 56 near Cessna
 US 22 near Altoona
US 22 near Altoona
 US 322 near State College
US 322 near State College
 PA 26 near Pleasant Gap
PA 26 near Pleasant GapNorth end: 
 I-80 / US 220 near Bellefonte
I-80 / US 220 near BellefonteHighway system Main route of the Interstate Highway System
Main • Auxiliary • BusinessRoads in Pennsylvania
Interstate • US • State • Legislative←  PA 98
PA 98PA 99  →
→Interstate 99 (I-99) is an intrastate Interstate Highway located in central Pennsylvania in the United States. The southern terminus of the route is at exit 146 of the Pennsylvania Turnpike (I-70 and I-76) north of Bedford, where the road continues south as U.S. Route 220 (US 220). The northern terminus is at I-80 near Bellefonte. I-99 passes through Altoona and State College–the latter home to Pennsylvania State University–and is entirely concurrent to US 220. Long-term plans call for I-99 to be extended southward along the US 220 corridor to an interchange with I-68 in Cumberland, Maryland, and northward along the US 220 and US 15 corridors to an interchange with I-86 west of Corning, New York.
Unlike most Interstate Highway numbers, which were assigned by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) to fit into a grid, I-99's number was written into Section 332 of the National Highway Designation Act of 1995 by Bud Shuster, then-chair of the U.S. House Committee on Transportation and Infrastructure, the bill's sponsor, and the representative of the district through which the highway runs. I-99 violates the AASHTO numbering convention associated with Interstate Highways, since it lies east of I-79 but west of I-81.
Contents
Route description
I-99 begins at an indirect interchange with US 220 and the Pennsylvania Turnpike (designated as I-70 and I-76) north of Bedford. It begins concurrent with US 220, which continues south from the interchange toward the Maryland state line as a two-lane highway known as the Appalachian Thruway. The interchange with the Turnpike requires drivers to use a short segment of US 220 Business to access the Turnpike at exit 146. North of the Turnpike junction, the limited-access highway becomes the Bud Shuster Highway as it heads through a rural portion of Bedford County. It connects to Pennsylvania Route 56 (PA 56) just west of the Bedford County Airport at exit 3 and PA 869 at exit 7 before crossing into Blair County. Here, it meets PA 164 north of East Freedom at exit 23 prior to entering the Altoona area.[2]
In Hollidaysburg, a borough south of the city, I-99 and US 220 connect to US 22 at exit 28, a large modified trumpet interchange. This junction allows travelers to head west towards Ebensburg, Johnstown, and Pittsburgh. The freeway continues to Altoona itself, where it indirectly connects to PA 36 via exit 32. Unlike the original routing of US 220 which goes through the city center, I-99 and US 220 mostly bypass it to the east, connecting to the city via streets leading eastward from the downtown district. At the northern edge of Altoona, PA 764 joins the old alignment of US 220 and parallels I-99 north for 3 miles (5 km) toward Bellwood. PA 764 leaves old US 220 about 2 miles (3.2 km) south of Bellwood, however, and terminates at I-99 exit 39. Bellwood itself is served by exit 41, which leads to PA 865.[2]
The highway veers northeastward from Bellwood to serve the borough of Tyrone, located at the junction of old US 220 and PA 453. Access to the borough is made by way of exit 48, which serves PA 453. Past Tyrone, I-99 and US 220 head through sparsely populated areas of Blair and Centre Counties. For this reason, only three exits exist between Tyrone and State College: exit 52, serving PA 350 and the small community of Bald Eagle, and exits 61 and 62, which connect to US 322 and the borough of Port Matilda. Here, US 322 joins I-99 and US 220 and follows them eastward to the State College area.[2]
At exit 68 (US 322 Business), I-99 merges into the Mount Nittany Expressway, an older, northerly bypass of State College. I-99, US 220, and US 322 follow the expressway to the Mount Nittany Interchange, a directional T interchange located on the northern fringe of the Pennsylvania State University campus. US 322 continues east through the interchange to follow the Mount Nittany Expressway while I-99 and US 220 split from US 322 and head northeastward toward Pleasant Gap, which I-99 connects to via exit 81 and PA 26. At this point, PA 26 joins the freeway and follows it to Bellefonte, served by exit 83 and PA 550. I-99 ends about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) later at an interchange with I-80, where PA 26 continues north and US 220 joins I-80 east.[2]
History
Origins
 2002 photo of the I-99 excavation, looking south from Julian at the area where acidic rock was exposed on Bald Eagle Mountain
2002 photo of the I-99 excavation, looking south from Julian at the area where acidic rock was exposed on Bald Eagle Mountain
Corridor O of the Appalachian Development Highway System was assigned in 1925,[citation needed] running from Cumberland, Maryland (Corridor E, now I-68) to Bellefonte (I-80) along US 220.[3] The portion in Pennsylvania, from Bedford north to Bald Eagle, was upgraded to a freeway in stages from the 1960s to the 1990s. The first section, from US 30 in Bedford to PA 56 near Cessna, opened in the latter half of the 1960s.[4][5] Two more sections—from PA 56 north to modern exit 15 in Blair County and from Charlottsville (exit 45) to Bald Eagle—were completed in the 1970s.[5][6] The portion between exit 15 and Altoona (exit 33) was finished in the 1980s[6][7] while the segment between modern exits 33 and 45 was opened by 1997.[8]
In 1991, the Intermodal Surface Transportation Efficiency Act (ISTEA) was signed into law.[citation needed] It included a number of High Priority Corridors, one of which—Corridor 9—ran along US 220 from Bedford to Williamsport, and then north on US 15 to Corning, New York.[citation needed] The National Highway Designation Act of 1995 amended ISTEA; among these amendments were that "the portion of the route referred to in subsection (c)(9) [Corridor 9] is designated as Interstate Route I-99."[citation needed] This was the first Interstate Highway number to be written into law rather than to be assigned by AASHTO. The number was specificated by Representative Bud Shuster, who said that the standard spur numbering was not "catchy"; instead, I-99 was named after a street car, No. 99, that took people from Shuster's hometown of Glassport to McKeesport. I-99 violates the AASHTO numbering convention associated with Interstate Highways, since it lies east of I-79 but west of I-81.[9]
Designation and Bald Eagle Ridge
On November 6, 1998, AASHTO formally approved the I-99 designation, which initially extended 51.2 miles (82.4 km) from the Pennsylvania Turnpike in Bedford to PA 350 in Bald Eagle.[1] In 2002, plans were set in motion to extend I-99 northeast from Bald Eagle to State College via Port Matilda.[10] The extension was fraught with issues, however. The proposed alignment for the highway north to Port Matilda proved to be controversial: while environmentalists called for I-99 to be constructed in the valley below Bald Eagle Ridge, the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT) and valley residents favored a routing that took the freeway above the valley and along the side of the ridge.[11] Farther north, the widening of Skytop, the mountain cut that US 322 uses to traverse Bald Eagle Ridge, resulted in the exposure of acidic pyrite rock in 2003.[10]
Work on the segment ceased one year later[10] as PennDOT attempted to stop the flow of acidic runoff from the site. The state remedied the situation by removing 1,000,000 cubic yards (760,000 m3) of pyrite and replacing it with a mix of limestone and fill, a process that took two years and cost $83 million.[9] With the environmental issues settled, construction resumed on the portion of the freeway south of Skytop Mountain. The section from Bald Eagle to Port Matilda was opened to traffic on December 17, 2007,[12] while the remaining section between Port Matilda and the west end of the Mount Nittany Expressway near State College was completely opened on November 17, 2008.[10] In all, the Bald Eagle – State College section of I-99 cost $631 million to construct.[9]
I-99 was extended northeastward to meet I-80 northeast of Bellefonte following the completion of the Bald Eagle – State College segment. The connection was made by way of the pre-existing Mount Nittany Expressway and another, unnamed limited-access highway connecting the State College bypass to the Bellefonte area.[9] The portion of the latter highway north of the PA 26 interchange was originally built in the 1970s as a two-lane freeway connecting Pleasant Gap to I-80. At the time, it was designated solely as PA 26.[5][6] It was widened to four lanes in 1997.[citation needed] The piece connecting the PA 26 freeway to the Mount Nittany Expressway was completed in 2002.[citation needed] US 220 was rerouted via US 322 and the new road, and the old alignment of US 220 north of US 322 was designated US 220 Alternate on May 30, 2003.[13]
Future
Long-term plans for I-99 call for the freeway to be extended northeastward along US 220 from Bellefonte to Williamsport and northward along US 15 from Williamsport to I-86 in Corning, New York.[citation needed] Signs have been placed along the present US 220 and US 15 between Bellefonte and Corning—much of which are built to Interstate Highway standards—marking the route as the "Future I-99 Corridor".[citation needed] The entirety of US 15 north of Williamsport is a limited-access highway save for a 4.5-mile (7.2 km) segment in New York between Lindley and Presho. Construction on the missing piece is underway and is expected to be completed in 2012.[14]
Exit list
County Location Mile[15] Exit Destinations Notes Bedford Bedford Township 0.00 1 

 I-70 / I-76 / Penna. Tpk. – Pittsburgh, Harrisburg
I-70 / I-76 / Penna. Tpk. – Pittsburgh, HarrisburgIndirect connection via US 220 Business 2.93 3  PA 56 (US 220 Bus. south) – Johnstown, Cessna
PA 56 (US 220 Bus. south) – Johnstown, CessnaEast St. Clair Township 6.65 7  PA 869 – St. Clairsville, Osterburg
PA 869 – St. Clairsville, OsterburgLow clearance at exit King Township 10.13 10 Blue Knob State Park Blair Greenfield Township 14.92 15 Claysburg, King (US 220 Bus. north) Freedom Township 22.88 23 

 PA 36 / PA 164 to US 22 east – Roaring Spring, Portage, Hollidaysburg
PA 36 / PA 164 to US 22 east – Roaring Spring, Portage, HollidaysburgAllegheny Township 28.12 28  US 22 – Ebensburg, Hollidaysburg
US 22 – Ebensburg, HollidaysburgLogan Township 30.60 31 Plank Road (US 220 Bus.) 31.88 32  To PA 36 (Frankstown Road)
To PA 36 (Frankstown Road)33.24 33 17th Street Antis Township 38.62 39  PA 764 south – Pinecroft
PA 764 south – Pinecroft41.30 41  PA 865 north – Bellwood
PA 865 north – Bellwood45.41 45 Tipton, Grazierville Tyrone 47.89 48  PA 453 – Tyrone
PA 453 – TyroneSnyder Township 51.84 52  PA 350 (US 220 Bus. south) – Bald Eagle
PA 350 (US 220 Bus. south) – Bald EagleCentre Worth Township 61 Port Matilda (US 220 Alt. north) 62  US 322 west – Philipsburg
US 322 west – PhilipsburgSouth end of US 322 overlap; southbound exit and northbound entrance; northbound exit is via exit 61 Patton Township 68 Gray's Woods, Waddle 69 


 US 322 Bus. east (Atherton Street)
US 322 Bus. east (Atherton Street)Northbound exit and southbound entrance 69 Valley Vista Drive – Park Forest Southbound exit and northbound entrance 71 Toftrees, Woodycrest College Township 73  US 322 east – State College, Lewistown
US 322 east – State College, LewistownNorth end of US 322 overlap 74 Innovation Park, Penn State University Northbound exit is part of exit 73 Benner Township 76 Shiloh Road 78  PA 150 – Bellefonte
PA 150 – BellefonteSigned as exits 78A (south) and 78B (north) Spring Township 80 Harrison Road Northbound exit and southbound entrance 81 
 PA 26 south to PA 64 – Pleasant Gap
PA 26 south to PA 64 – Pleasant GapSouth end of PA 26 overlap 83  PA 550 – Bellefonte, Zion
PA 550 – Bellefonte, ZionNorth end of freeway 
 I-80 / US 220 north (US 220 Alt. south) – Williamsport, Dubois
I-80 / US 220 north (US 220 Alt. south) – Williamsport, Dubois1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi References
- ^ a b "Report of the Special Committee on U.S. Route Numbering to the Standing Committee on Highways". American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. November 7, 1998. http://cms.transportation.org/sites/route/docs/1998-USRN_Cmte.pdf. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e Google, Inc. Google Maps – overview map of I-99 (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&source=s_d&saddr=40.057583,-78.517853&daddr=I-99+N%2FPA-26+N&geocode=%3BFSy6cAIdQABe-w&hl=en&mra=mi&mrsp=0&sz=16&sll=40.057069,-78.513815&sspn=0.012055,0.027831&ie=UTF8&z=16. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ "Status of the Appalachian Development Highway System as of September 30, 2009". Appalachian Regional Commission. December 2009. http://www.arc.gov/images/programs/transp/adhs_status_report_2009/ADHS2009StatusReportGeneralReport.pdf. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ Sun Oil Company (1964) (PDF). Pennsylvania (Map). Cartography by H. M. Gousha Company (1964–65 ed.).
- ^ a b c Pennsylvania Department of Highways (1970) (PDF). Official Map of Pennsylvania (Map). ftp://ftp.dot.state.pa.us/public/pdf/BPR_pdf_files/Maps/Statewide/Historic_OTMs/1970fr.pdf. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ a b c Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (1980) (PDF). Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Official Transportation Map (Map). ftp://ftp.dot.state.pa.us/public/pdf/BPR_pdf_files/Maps/Statewide/Historic_OTMs/1980fr.pdf. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (1989) (PDF). Pennsylvania Official Transportation Map (Map). ftp://ftp.dot.state.pa.us/public/pdf/BPR_pdf_files/Maps/Statewide/Historic_OTMs/1989fr.pdf. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ Rand McNally and Company (1997). Easy-to-Read Travel Atlas: United States – Canada – Mexico (Map). p. 44. ISBN 0-528-81575-X.
- ^ a b c d Hamill, Sean D. (December 27, 2008). "Road Stirs Up Debate, Even on Its Name". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/12/28/us/28highway.html.
- ^ a b c d Bock, Greg (November 25, 2008). "Long road for I-99 comes to end". Altoona Mirror. http://www.altoonamirror.com/page/content.detail/id/513588.html. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ Gibb, Tom (December 7, 2002). "I-99 segment gets environmental OK". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. http://www.post-gazette.com/healthscience/20021207highway2.asp. Retrieved July 19, 2010.
- ^ Bock, Greg (December 18, 2007). "Long-awaited I-99 stretch opens". Altoona Mirror. http://www.altoonamirror.com/page/content.detail/id/502818.html. Retrieved July 19, 2010.
- ^ "Report of the Special Committee on U.S. Route Numbering to the Standing Committee on Highways". American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. May 31, 2003. http://cms.transportation.org/sites/route/docs/2003-USRN_Cmte.pdf. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ Clarke, Cheryl R. (September 22, 2009). "Groundbreaking held for last section of '15' north". Williamsport Sun-Gazette. http://www.sungazette.com/page/content.detail/id/532742.html?nav=5011. Retrieved January 17, 2010.
- ^ DeLorme (2007). Street Atlas USA (Map).
External links
Main Interstate Highways (major interstates highlighted)
4 5 8 10 12 15 16 17 19 20 22 24 25 26 27 29 30 35 37 39 40 43 44 45 49 55 57 59 64 65 66 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 (W) 76 (E) 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 (W) 84 (E) 85 86 (W) 86 (E) 87 88 (W) 88 (E) 89 90 91 93 94 95 96 97 99 H-1 H-2 H-3 Unsigned A-1 A-2 A-3 A-4 PRI-1 PRI-2 PRI-3 Lists Primary Main - Intrastate - Suffixed - Temporary - Future - Gaps Auxiliary Main - Future - Unsigned Other Standards - Business - Bypassed - Tolled Interstate Highways in Pennsylvania Current Unbuilt 695 • 895Former Future State College in Centre County, Pennsylvania Infrastructure Alpha Fire Company · Mount Nittany Medical Center · University Park Airport · Centre Area Transportation Authority · Nittany MallMajor roads Education Newspapers TV/Radio Broadcast television in West-Central Pennsylvania, including Johnstown, Altoona and State College Local stations WPSU (3.1 PBS, 3.2 Create, 3.3 PBS World) - WJAC (6.1 NBC, 6.2 Me-TV) - WWCP (8.1 Fox, 8.2 WATM) - WTAJ (10.1 CBS) - WSCP-CA (13 Ind) - WPCW (19.1 CW) - WATM (23.1 ABC HD, 23.2 WWCP HD, 23.3 This TV) - WHVL-LP (29.1 MNTV, 29.2 A1) - W36BE-D (16.1 ABC, 16.2 Antenna TV) - W41CF (41 Ind) - WKBS (47.1 COR) - WLLS-LP (49 A1)
Local cable
channelsIUP-TV (Ind)
Adjacent locals Pennsylvania Broadcast television: Binghamton, NY • Buffalo, NY • Elmira, NY • Erie • Johnstown/Altoona/State College • New York City • Philadelphia • Pittsburgh • Scranton/Wilkes-Barre • Susquehanna Valley (Harrisburg) • Washington, DC • Youngstown, OH
Radio stations in the State College, Pennsylvania market By FM frequency By AM frequency By callsign Defunct WQWK · WJOWPennsylvania radio markets: Allentown-Bethlehem • Altoona • Bradford-Coudersport • Chambersburg-Waynesboro • Erie • Harrisburg-Lebanon-Carlisle • Lancaster • Montrose • New Castle • Philadelphia • Pittsburgh • Reading • State College • Sunbury-Selinsgrove-Lewisburg • Wilkes Barre-Scranton • Sayre-Towanda-Mansfield-Wellsboro • Williamsport • York
Other Pennsylvania radio regions: Bedford • Indiana • Johnstown • Lewistown-Mifflintown • Meadville-Franklin • Punxsutawney-DuBois • St. Marys-Emporium-Kane • Stroudsburg • Warren
Website: www.statecollegepa.usAttractions Downtown · Horseshoe Curve · Lakemont Park (Leap-The-Dips) · Mishler Theatre · Logan Valley Mall · Penn Alto Building · Railroaders Memorial Museum · Allegheny Portage RailroadTransportation Altoona Transportation Center · Altoona-Blair County Airport · AMTRAN · I-99 · U.S. Route 22 · U.S. Route 220 · PA 36-18th Street · PA 764Religion Education Industry Sports Newspapers Altoona MirrorTV/Radio Broadcast television in West-Central Pennsylvania, including Johnstown, Altoona and State College Local stations WPSU (3.1 PBS, 3.2 Create, 3.3 PBS World) - WJAC (6.1 NBC, 6.2 Me-TV) - WWCP (8.1 Fox, 8.2 WATM) - WTAJ (10.1 CBS) - WSCP-CA (13 Ind) - WPCW (19.1 CW) - WATM (23.1 ABC HD, 23.2 WWCP HD, 23.3 This TV) - WHVL-LP (29.1 MNTV, 29.2 A1) - W36BE-D (16.1 ABC, 16.2 Antenna TV) - W41CF (41 Ind) - WKBS (47.1 COR) - WLLS-LP (49 A1)
Local cable
channelsIUP-TV (Ind)
Adjacent locals Pennsylvania Broadcast television: Binghamton, NY • Buffalo, NY • Elmira, NY • Erie • Johnstown/Altoona/State College • New York City • Philadelphia • Pittsburgh • Scranton/Wilkes-Barre • Susquehanna Valley (Harrisburg) • Washington, DC • Youngstown, OH
Radio stations in the Altoona, Pennsylvania market By FM frequency By AM frequency By callsign Pennsylvania radio markets: Allentown-Bethlehem • Altoona • Bradford-Coudersport • Chambersburg-Waynesboro • Erie • Harrisburg-Lebanon-Carlisle • Lancaster • Montrose • New Castle • Philadelphia • Pittsburgh • Reading • State College • Sunbury-Selinsgrove-Lewisburg • Wilkes Barre-Scranton • Sayre-Towanda-Mansfield-Wellsboro • Williamsport • York
Other Pennsylvania radio regions: Bedford • Indiana • Johnstown • Lewistown-Mifflintown • Meadville-Franklin • Punxsutawney-DuBois • St. Marys-Emporium-Kane • Stroudsburg • Warren
Categories:- Interstate Highway System
- Interstate Highways in Pennsylvania
- Bald Eagle Valley
- Nittany Valley
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.