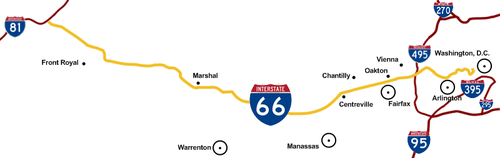
- Interstate 66
-
This article is about the current Interstate 66 in Virginia and the District of Columbia. For the proposed route in Kentucky and West Virginia, see Interstate 66 (west).
Interstate 66 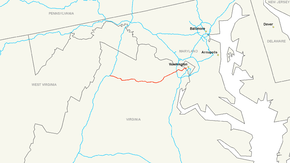
Route information Length: 76.28 mi[1] (122.76 km) Major junctions West end:  I-81 in Middletown, VA
I-81 in Middletown, VA
 US 340 / US 522 near Front Royal, VA
US 340 / US 522 near Front Royal, VA
 US 17 near Warrenton, VA
US 17 near Warrenton, VA
 US 15 in Haymarket, VA
US 15 in Haymarket, VA
 SR 234 in Bristow, VA
SR 234 in Bristow, VA
 US 50 near Fairfax, VA
US 50 near Fairfax, VA
 I-495 in Dunn Loring, VA
I-495 in Dunn Loring, VA
 SR 267 near Falls Church, VA
SR 267 near Falls Church, VAEast end:  US 29 in Washington, D.C.
US 29 in Washington, D.C.Highway system Main route of the Interstate Highway System
Main • Auxiliary • BusinessInterstate 66 (I-66) is an Interstate Highway in the eastern United States. As indicated by its even route number, it runs in an east–west direction. Its western terminus is at Middletown, Virginia, at an intersection with Interstate 81;[2] its eastern terminus is in Washington, D.C., at an intersection with U.S. Route 29.[3] Interstate 66 has no physical or historical connection to U.S. Route 66.
The E Street Expressway is a spur from Interstate 66 into the Foggy Bottom neighborhood of Washington, D.C.
Contents
Route description
Lengths mi km VA 75 121 DC 2 3 Total 77 124 Virginia
Because I-66 is the only Interstate Highway running west from Washington, D.C., into Northern Virginia, traffic on the road is often extremely heavy. For decades, there has been talk of widening I-66 from 2 to 3 lanes each way inside the Capital Beltway (Interstate 495) through Arlington, Virginia, although many Arlington residents are adamantly opposed to this plan.
In 2005, the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) studied the prospect of implementing a one-lane-plus-shoulder extension on westbound I-66 within the Beltway (in an attempt to reduce congestion for people commuting away from D.C.).[4]
In the summer of 2010, construction began on a third lane and a 12-foot shoulder lane between the Fairfax Drive ramp near the George Mason Drive entrance ramp to I-66 west and the Sycamore Street ramp, a 1.9 mile distance. The entrance ramp acceleration lane and the exit ramp deceleration lane are being lengthened until they meet to form a continuous lane between both ramps. The 12-foot shoulder lane will carry emergency vehicles and can be used in emergency situations. This project is scheduled for completion in December 2011.[5]
The Orange Line and the Silver Line (under construction) of the Washington Metro operate in the median of the highway in Fairfax and Arlington counties. Four stations (Vienna, Dunn Loring, West Falls Church, and East Falls Church) are located along this segment of I-66.
I-66 east has two exit ramps, one from each side of the highway, to the Inner Loop of I-495 heading northbound. One is a two lane right exit which merges down to one lane halfway along the ramp, while a second exit ramp is a left exit; the latter reserved for use by high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) traffic during morning rush hour, but open to all traffic excluding trucks at all other times. Both exit ramps for the Inner Loop merge prior to merging from the left with the Inner Loop. There is no access from the Outer Loop of I-495 to I-66 east; traffic wishing to make this movement must use State Route 267 east.
I-66 east also has two exits, one from each side of the highway, to the Outer Loop of I-495. One is a right exit, while one is a left exit; the latter shares a ramp with the exit to the Inner Loop of I-495.
I-66 is named the "Custis Memorial Parkway" east of the Capital Beltway in Virginia.[6] The name commemorates the Custis family, several of whose members (including Martha Dandridge Custis Washington, George Washington Parke Custis, Eleanor (Nellie) Parke Custis Lewis and Mary Anna Randolph Custis Lee) played prominent roles in Northern Virginia's history.
HOV designation and rules
Due to heavy commuter traffic, I-66 features a variety of high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) restrictions. Between US 29 in Gainesville, Virginia and the Capital Beltway, the left lane on eastbound I-66 is reserved for vehicles with two or more occupants (HOV-2 traffic) from 5:30 to 9:30 a.m., and the left lane on westbound I-66 is reserved for HOV-2 traffic from 3:00 to 7:00 p.m. The eastbound shoulder lane (far right lane) between US 50 in Fairfax, Virginia and the Beltway is open to all traffic from 5:30 to 11:00 a.m. The westbound shoulder lane (far right lane), also between the Capital Beltway and U.S. Route 50, is open to all traffic from 2:00 to 8:00 p.m.[7]
Between the Beltway and the Theodore Roosevelt Bridge, the entire eastbound (inbound) roadway is reserved for HOV-2 and Washington Dulles International Airport traffic from 6:30 to 9:00 a.m., and the entire westbound (outbound) roadway is reserved for HOV-2 and Dulles Airport traffic from 4:00 to 6:30 p.m. This is enforced by random police presence on the on- and off-ramps, because single-passenger vehicles are allowed to enter the highway inside the Beltway in the direction of rush-hour traffic when they intend to use the Dulles Access Road at exit 67. Police heavily monitor the three-mile stretch between the Dulles Access Road and the Beltway for violations, frequently having traffic slow down to visually inspect inside each vehicle.[8]
Both motorcycles and qualified "clean special fuel" vehicles are permitted to use HOV-2 facilities on I-66 during times when HOV regulations are in effect even without the required number of occupants. The "clean special fuel" designation is used primarily by hybrid vehicles, but is also available for vehicles using alternative fuels such as natural gas or electricity.[9] To qualify for the HOV exemption, a vehicle owner must specifically request the designation when registering the vehicle, pay the appropriate fees, and display a "clean special fuel" license plate. The clean-fuel exemption is scheduled to expire on June 30, 2012, although the Virginia General Assembly has extended the exemption every year, one year at a time, since it was originally designated to expire in 2006.[10] However, in 2011, the exemption was modified so it applies only to clean fuel vehicles registered before June 30, 2011. Clean-fuel vehicles registered after that date are not exempt from HOV regulations on I-66.[11]
As of January 28, 2011, penalties for HOV violators range from $125 on the first offense to $250 on the second offense, $500 on the third offense, and $1,000 on the fourth offense. Violators also receive three points on their driving record on the second and later offenses.[12]
District of Columbia
In Washington D.C., I-66 follows the West Leg of the Inner Loop freeway. After crossing the Potomac River on the Theodore Roosevelt Bridge concurrent with US 50, the route quickly turns north, separating from US 50. The highway interchanges with the E Street Expressway spur before passing beneath Virginia Avenue in a short tunnel. After an indirect interchange with the Rock Creek Parkway (via 27th Street), the highway terminates at a pair of ramps leading to the Whitehurst Freeway (US 29) and L Street.
This is the only 2 digit Interstate to enter the District of Columbia, other than the 100 yards (91 m) or so that I-95 passes through DC on the Woodrow Wilson Bridge (part of the Capital Beltway).
The eastern terminus of the E Street Expressway is at 20th Street NW. From there, traffic continues along E Street NW to 17th Street NW near the White House, the Old Executive Office Building, and the Corcoran Gallery of Art. Westbound traffic from 17th Street takes a one-block segment of New York Avenue to the expressway entrance at 20th and E Streets. The expressway and the connecting portions of E Street and New York Avenue are part of the National Highway System.
History
Virginia
 Interstate 66 in Fairfax County outside of the Capital Beltway, with the Metrorail Orange Line in the median. The left lane is HOV, and the right shoulder is used as a travel lane during rush hour.
Interstate 66 in Fairfax County outside of the Capital Beltway, with the Metrorail Orange Line in the median. The left lane is HOV, and the right shoulder is used as a travel lane during rush hour.
As with many urban Interstate Highway projects, I-66 has encountered opposition from local citizen groups.
Most notably for I-66 was the construction through Arlington, Virginia, proposed in 1956. After the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) (then known as the Virginia Department of Highways) acquired two sections of the former route of the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad to provide a right-of-way through Arlington for the new highway, the Arlington Coalition on Transportation (ACT) filed a lawsuit in Federal District Court in 1971 opposing the Arlington portion of the project. The group objected to that urban segment due to concerns over air quality, noise and community cohesion changes. In 1972 the U.S. Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals ruled in favor of ACT, technically blocking any construction. The U.S. Supreme Court upheld the ruling in favor of ACT later in 1972.[13]
The impasse was eventually broken when the parties agreed on experts to conduct air quality and noise studies for VDOT; the firm of ESL Inc., the expert hired originally by ACT, was agreed upon to be hired by VDOT. Then, U.S. Secretary of Transportation Coleman personally intervened in 1976 with negotiations to reach a compromise of a reduced highway width including a transit element.[14][15]
Less controversial was the portion of the highway's route immediately west of Arlington. There, VDOT decided to curve the highway to bypass the City of Falls Church, increasing the highway's length while sparing the city from the road's immediate environmental impacts.
In Gainesville, Virginia, the Gainesville Interchange Project is taking place at and near the interchange between US 29 and I-66, aiming to upgrade facilities for those and many other roads due to rapid development and accompanying heavy traffic in the Gainesville and Haymarket area. I-66's overpasses were reconstructed to accommodate nine lanes (six general purpose, two HOV, one collector-distributor eastbound) and lengthened for the expansion of US 29 to six lanes. These alterations were completed in June 2010. US 29 is also planned to be largely grade-separated in the area, including an interchange at its current intersection with SR 619 (Linton Hall Road); land for this has been acquired. The project overall began in 2004 and completion is slated for late 2014.[16]
District of Columbia
In Washington D.C., I-66 was planned to extend east of its current terminus along the North Leg of the Inner Loop freeway. I-66 would have also met the eastern terminus of a planned Interstate 266 at US 29, and the western terminus of the South Leg Freeway (I-695) at US 50; I-266 would have been a parallel route to I-66, providing more direct access to the North Leg from points west, while I-695 would have been an inner-city connector between I-66 and I-95.
The final plans for the North Leg Freeway, as published in 1971, outlined a 1.5-mile (2.4 km) six-lane tunnel beneath K Street, between I-266/US 29 and New York Avenue, where the North Leg would emerge from the tunnel and join with the Center Leg Freeway (formerly I-95, now I-395); the two routes would run concurrently for three-fourths of a mile before reaching the Union Station interchange, where I-66 was planned to terminate. Despite the plan to route the North Leg in a tunnel beneath K Street, the intense opposition to previous, scrapped alignments for the D.C. freeway network, which included previous alignments for the North Leg Freeway, led to the mass cancellation of all unbuilt D.C. freeways in 1977, resulting in the truncation of I-66 at US 29.
Exit list
County Location Mile # Destinations Notes Frederick Middletown 0.0 1  I-81 – Winchester, Roanoke
I-81 – Winchester, RoanokeWestbound exit and eastbound entrance, and signed as exits 1A (south, Roanoke) and 1B (north, Winchester) Warren Front Royal 6.4 6 
 US 340 / US 522 – Winchester, Front Royal
US 340 / US 522 – Winchester, Front Royal12.9 13 
 SR 79 to SR 55 – Linden
SR 79 to SR 55 – LindenFauquier 18.5 18  SR 688 – Markham
SR 688 – Markham23.3 23 
 US 17 north / SR 55 west – Delaplane, Paris
US 17 north / SR 55 west – Delaplane, ParisWest end of US 17/SR 55 overlap Marshall 27.0 27 
 SR 55 east / SR 647 – Marshall
SR 55 east / SR 647 – MarshallEast end of SR 55 overlap 28.3 28  US 17 south – Warrenton, Fredericksburg
US 17 south – Warrenton, FredericksburgEast end of US 17 overlap The Plains 31.3 31  SR 245 / Old Tavern Road
SR 245 / Old Tavern RoadPrince William Haymarket 40.5 40  US 15 – Leesburg, Haymarket
US 15 – Leesburg, HaymarketGainesville 43.1 43  US 29 – Gainesville, Charlottesville
US 29 – Gainesville, CharlottesvilleSigned as exits 43A (south, Gainesville) and 43B (north, Charlottesville) Manassas 44.5 44  SR 234 south (Prince William Parkway)
SR 234 south (Prince William Parkway)West end of SR 234 overlap 47.3 47 




 SR 234 north / SR 234 Bus. (Sudley Road) – Manassas
SR 234 north / SR 234 Bus. (Sudley Road) – ManassasEast end of SR 234 overlap; signed as exits 47A (Manassas) and 47B (Bussines) westbound Yorkshire 48.8 Rest Area At entrance to Prince William County from Fairfax County; both sides now reopened[17] Fairfax Centreville 52.1 52 
 US 29 to SR 28 south – Centreville
US 29 to SR 28 south – Centreville53.2 53  SR 28 (Sully Road) – Dulles Airport, Centreville
SR 28 (Sully Road) – Dulles Airport, CentrevilleNo eastbound exit to SR 28 south and westbound entrance from SR 28 north Fair Lakes 54.9  SR 645 (Stringfellow Road)
SR 645 (Stringfellow Road)Eastbound left entrance open only to HOV-2+ traffic weekdays from 5:30 to 9:30 a.m. Westbound left exit open all other times; exit restricted to HOV-2+ traffic weekdays from 3:00 to 7:00 p.m.[18] 55.9 55  SR 7100 (Fairfax County Parkway) – Springfield, Reston, Herndon
SR 7100 (Fairfax County Parkway) – Springfield, Reston, HerndonSigned as exits 55A (south, Springfield, Reston) and 55B (north, Herndon) Fairfax 57.1  SR 6751 (Monument Drive) – Fair Lakes, Fairfax
SR 6751 (Monument Drive) – Fair Lakes, FairfaxEastbound left entrance open only to HOV-2+ traffic weekdays from 5:30 to 9:30 a.m. Westbound left exit open all other times; exit restricted to HOV-2+ traffic weekdays from 3:00 to 7:00 p.m.[18] 58.1 57  US 50 – Winchester, Fairfax, Fair Oaks
US 50 – Winchester, Fairfax, Fair OaksSigned as exits 57A (east, Fair Oaks) and 57B (west, Fairfax, Winchester) 60.1 60  SR 123 – Fairfax, Vienna
SR 123 – Fairfax, ViennaVienna 62.5 62  SR 243 (Nutley Street) – Fairfax, Vienna
SR 243 (Nutley Street) – Fairfax, ViennaDunn Loring 65.1 64  I-495 (Capital Beltway) – Richmond, Baltimore
I-495 (Capital Beltway) – Richmond, BaltimoreLeft and right exit eastbound (left from HOV lane); no westbound exit to I-495 north and eastbound entrance from I-495 south; signed as exits 64A (south) and 64B (north) eastbound Tysons Corner 66.0 66  SR 7 (Leesburg Pike) – Falls Church
SR 7 (Leesburg Pike) – Falls ChurchSigned as exits 66A (east, Falls Church) and 66B (west) westbound Falls Church 66.6 67 
 SR 267 west to I-495 north / to Dulles Toll Road – Dulles Airport
SR 267 west to I-495 north / to Dulles Toll Road – Dulles AirportWestbound exit and eastbound entrance Arlington 67.8 68 Westmoreland Street Eastbound exit and westbound entrance 68.4 69 
 US 29 (Lee Highway) / SR 237 (Washington Boulevard) / Sycamore Street
US 29 (Lee Highway) / SR 237 (Washington Boulevard) / Sycamore Street70.5 71 
 SR 120 (Glebe Road) / SR 237 (Fairfax Drive)
SR 120 (Glebe Road) / SR 237 (Fairfax Drive)72.1 72  US 29 south (Lee Highway) / Spout Run Parkway
US 29 south (Lee Highway) / Spout Run ParkwayEastbound exit and westbound entrance 73.1 73  US 29 (Key Bridge) – Rosslyn
US 29 (Key Bridge) – RosslynNo eastbound exit to US 29 south and westbound entrance from US 29 north 74.2 75  SR 110 south – Pentagon, Alexandria, Pentagon City, Crystal City
SR 110 south – Pentagon, Alexandria, Pentagon City, Crystal CityEastbound exit and westbound entrance 74.5  US 50 west / Arlington Boulevard, George Washington Memorial Parkway
US 50 west / Arlington Boulevard, George Washington Memorial ParkwayWest end of US 50 overlap; westbound exit and eastbound entrance State line Washington 74.9 Independence Avenue 75.0  US 50 east / Constitution Avenue – Downtown
US 50 east / Constitution Avenue – DowntownEast end of US 50 overlap; eastbound exit and westbound entrance 75.2 E Street Expressway 75.0 Whitehurst Freeway 74.6 Rock Creek Parkway Eastbound exit and westbound entrance 75.7 Pennsylvania Avenue / L Street NW Eastbound exit and westbound entrance 75.8  US 29 south / Canal Road
US 29 south / Canal RoadWestbound exit and eastbound entrance 76.0 M street NW At-grade intersection 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi Auxiliary routes
Interstate 266 (I-266) was a proposed loop route of I-66 between Washington, D.C., and Arlington County, Virginia. District of Columbia officials proposed designating the route Interstate 66N, a move opposed by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials. In Virginia, Interstate 266 would have split off from Interstate 66 just east of the present Spout Run Parkway exit. From there, it would have followed an expanded Spout Run Parkway, crossed the George Washington Memorial Parkway, and crossed the Potomac River across a new bridge that would have been called the Three Sisters Bridge. Upon entering the District of Columbia, it would have followed Canal Road and an expanded Whitehurst Freeway to rejoin Interstate 66 at K Street. Interstate 266 was canceled in 1972 in the face of community opposition during Washington's "freeway revolts".[1][2]
References
- ^ Federal Highway Administration Route Log and Finder List, Main Routes of the Dwight D. Eisenhower National System Of Interstate and Defense Highways as of October 31, 2002
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – Interstate 66 (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?ll=38.999976,-78.298187&spn=0.470442,0.945854&hl=en. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ Google, Inc. Google Maps – Interstate 66 (Map). Cartography by Google, Inc. http://maps.google.com/maps?ll=38.894507,-77.054329&spn=0.014723,0.029558&hl=en. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ Shaffer, Ron (October 21, 2005). "Dr. Gridlock". Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/discussion/2005/10/21/DI2005102101155.html.
- ^ "I-66 Spot Improvements-Spot 1". VDOT. August 25, 2011. http://www.virginiadot.org/projects/northernvirginia/i-66_spot_improvements_-_spot_1.asp.
- ^ "Arlington Virginia List of State Roads". Environmental Services. Government of Arlington County, Virginia. 2009-07-14. http://www.arlingtonva.us/Departments/EnvironmentalServices/cpe/row/EnvironmentalServicesState.aspx. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ^ "HOV Lanes - Northern Virginia HOV Operating Hours". VDOT Travel Center. http://www.virginiadot.org/travel/hov-novasched.asp. Retrieved December 4, 2008.
- ^ Weiss, Eric M (16 June 2008). "When 'Airport Business' Is a Ticket to Less Traffic; Loophole Gives Drivers Shortcut Through Dulles for Access Road Commute". The Washington Post. p. A1. http://pqasb.pqarchiver.com/washingtonpost/access/1495283241.html?dids=1495283241:1495283241&FMT=ABS&FMTS=ABS:FT&date=Jun+16%2C+2008&author=Eric+M+Weiss+-+Washington+Post+Staff+Writer&pub=The+Washington+Post&edition=&startpage=A.1&desc=When+%27Airport+Business%27+Is+a+Ticket+to+Less+Traffic%3B+Loophole+Gives+Drivers+Shortcut+Through+Dulles+for+Access+Road+Commute. Archived 16 August 2008.
- ^ Virginia DMV: Clean Special Fuel Vehicles/Plates Retrieved on May 21, 2009
- ^ Thomson, Robert (6 March 2011). "Hybrids stay in Virginia HOV lanes". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2011/03/04/AR2011030407175.html. Accessed 14 May 2011.
- ^ HOV Exemption for Hybrid Vehicles Extended to June 30, 2012 Signed by Gov. McDonnell March, 2011 Retrieved April 15, 2010
- ^ http://www.virginiadot.org/travel/hov-rulesfaq.asp
- ^ Jay Mathews, High Court Backs Delay Of Rte. 66, The Washington Post, Times Herald, Washington, D.C., Nov 7, 1972
- ^ "An Abridged I-66 Chronology". The Arlington Coalition for Sensible Transportation. http://www.acstnet.org/66part6.htm. Retrieved February 5, 2006.
- ^ Hogan, C. M. and Harry Seidman, Air Quality and Acoustics Analysis of Proposed I-66 through Arlington, Virginia, ESL Inc. Technical Document T1026, Sunnyvale, Calif. (1971)
- ^ "Gainesville Interchange Project". 2011. http://www.nvta.org/content.asp?sl=459&contentid=1889. Retrieved 2011-07-04.
- ^ "Eight Additional Rest Areas Now Open". The Appomatox News. 2010-03-17. http://www.appomattoxnews.com/2010/eight-additional-rest-areas-now-open.html. Retrieved 2010-03-21.
- ^ a b I-66 West HOV Ramps Now Open Off-Peak and Weekends. 2011-02-28. Retrieved 2011-02-28.
External links
- HOV schedule in Northern Virginia, from Virginia Dept. of Transportation
- December 22, 1982 Completion of I-66, from AASHTO
- This Day In Interstate Highway System History, from AASHTO
- Roads to the Future: Washington D.C. Interstates and Freeways
Main Interstate Highways (major interstates highlighted)
4 5 8 10 12 15 16 17 19 20 22 24 25 26 27 29 30 35 37 39 40 43 44 45 49 55 57 59 64 65 66 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 (W) 76 (E) 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 (W) 84 (E) 85 86 (W) 86 (E) 87 88 (W) 88 (E) 89 90 91 93 94 95 96 97 99 H-1 H-2 H-3 Unsigned A-1 A-2 A-3 A-4 PRI-1 PRI-2 PRI-3 Lists Primary Main - Intrastate - Suffixed - Temporary - Future - Gaps Auxiliary Main - Future - Unsigned Other Standards - Business - Bypassed - Tolled Browse numbered routes ←  SR 65
SR 65VA SR 67  →
→←  US 50
US 50DC I-95  →Categories:
→Categories:- Interstate Highway System
- Interstate Highways in the District of Columbia
- Interstate Highways in Virginia
- Northern Virginia
- Transportation in Frederick County, Virginia
- Transportation in Warren County, Virginia
- Transportation in Fauquier County, Virginia
- Transportation in Prince William County, Virginia
- Roads in Fairfax County, Virginia
- Transportation in Arlington County, Virginia
- Cancelled highway projects in the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.