- Texas Department of Transportation
-
Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) 
Agency overview Formed 1991 Preceding agencies Texas Highway Department
Texas Department of Highways and Public TransportationJurisdiction Texas Headquarters 125 East 11th Street, Austin, Texas Agency executive Phil Wilson[1], Executive Director Parent agency State of Texas Website http://www.txdot.gov/ The Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT, pronounced "tex-dot") is a governmental agency in the U.S. state of Texas. Its stated mission is to "work cooperatively to provide safe, effective and efficient movement of people and goods"[2] throughout the state. Though the public face of the agency is generally associated with the construction and maintenance of the state's immense highway system, the agency is also responsible for overseeing aviation,[3] rail[4] and public transportation[5] systems in the state.
At one time TxDOT also administered vehicle registration;[6] however this function transferred to the Texas Department of Motor Vehicles, a newly created state agency which began operations in November 2009.[7]
The agency has been headquartered in the Dewitt C. Greer Building at 125 East 11th Street in Downtown Austin, Texas, since 1933.[8]
Contents
History
The Texas Legislature created the Texas Highway Department in 1917 to administer federal highway construction and maintenance. In 1975, its responsibilities increased when the agency merged with the Texas Mass Transportation Commission, to form the State Department of Highways and Public Transportation.
In 1986 the department started using "Don't Mess with Texas" as its slogan to reduce littering on Texas roadways, as part of a statewide advertising campaign. The phrase was prominently shown on road signs on major highways, as well as in television, radio and print advertisements. The slogan is still in use and remains very popular.
In 1991, the Legislature combined the State Department of Highways and Public Transportation, the Department of Aviation and the Texas Motor Vehicle Commission to create the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT).
In 1997 the pre-existing Texas Turnpike Authority (TTA) was divided into two successor agencies: the North Texas Tollway Authority took responsibility for TTA assets in four north Texas counties, while the Turnpike Authority Division of Texas DOT was given jurisdiction over toll facilities in the rest of the state.[9]
Administration
The executive director (currently Phil Wilson) is assisted by one deputy director (position is currently vacant), and four assistant executive directors. The department is organized into 25 geographical districts, 21 topical divisions, and 5 offices.
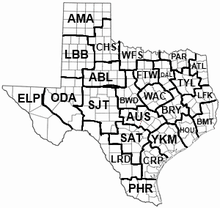
Districts
TxDOT is one of the state's largest departments in terms of the number of subordinate offices – it maintains 25 geographical districts throughout the state. The large number of departments is needed due to the large size of the state, the widely varying climate and soil conditions affecting public roads, and the differing needs of the local populace (urban vs. suburban vs. rural). In 2010 TxDOT was reorganized into four Regions, North, South, East and West. The regions are designated as Regional Support Centers or RCE's. The number of districts remained the same. Each district, managed by a district engineer, is responsible for the design, location, construction and maintenance of its area transportation systems. Local field offices within districts are known as area offices, and many districts also have separate maintenance offices, usually on a county-by-county basis. Functional divisions and offices headquartered in Austin provide administrative and technical support to the districts.
Divisions
- Aviation
- Bridge
- Construction
- Design
- Environmental
- Finance
- General Services
- Government & Public Affairs
- Human Resources
- Technology Services
- Maintenance
- Motor Carrier
- Motor Vehicle
- Occupational Safety
- Public Transportation
- Right of Way
- Traffic Operations
- Transportation Planning & Programming
- Travel
- Turnpike Authority Division
- Vehicle Titles & Registration
Offices
- Business Opportunity Program
- Civil Rights
- General Counsel
- International Relations
- Research and Technology Implementation
Publications
Every month, TxDOT publishes Texas Highways, a magazine aimed at showcasing various aspects of the state, often by providing interesting travel information on a specific stretch of highway (or highways) in the state. TxDOT also publishes the annual Texas Travel Guide, which offers points of interests for all regions of Texas.
Horizon is a quarterly journal focusing on transportation policy issues and financing in particular.
TxDOT has also produced a weekly podcast focusing on transportation planning and the Trans-Texas Corridor hosted by public information officer Larry Krantz since December 2007.
Gallery
-
Dewitt C. Greer Building, the headquarters of the Texas Department of Transportation, is a National Registered Historic Place[10]
References
- ^ "Phil Wilson Selected to Lead Texas Department of Transportation". http://www.txdot.gov/news/039-2011.htm. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ "Mission and Vision". TxDOT. http://www.txdot.gov/about_us/mission.htm. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ "Aviation Division". Texas Department of Transportation. http://www.txdot.gov/business/aviation/default.htm. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Rail Safety Inspection Program". TxDOT. http://www.txdot.gov/services/transportation_planning_and_programming/rail_inspection.htm. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ "Public Transportation Division". TxDOT. http://www.txdot.gov/services/public_transportation/default.htm. Retrieved 28 April 2007.
- ^ Vehicle Registration
- ^ "About the Texas Department of Motor Vehicles." Texas Department of Motor Vehicles. Retrieved on December 26, 2009.
- ^ http://www.txdot.gov/contact_us/
- ^ Linda M. Spock & Sally Diane Liff, Tolling Practices for Highway Facilities (Transportation Research Board, 1998), ISBN 9780309068161, p.12 (excerpt available at Google Books).
- ^ National Register Information System[dead link], National Register of Historic Places, National Park Service. Retrieved March 6, 2009.
External links
State and insular area departments of transportation in the United States Alabama · Alaska · Arizona · Arkansas · California · Colorado · Connecticut · Delaware · District of Columbia · Florida · Georgia · Hawaii · Idaho · Illinois · Indiana · Iowa · Kansas · Kentucky · Louisiana · Maine · Maryland · Massachusetts · Michigan · Minnesota · Mississippi · Missouri · Montana · Nebraska · Nevada · New Hampshire · New Jersey · New Mexico · New York · North Carolina · North Dakota · Ohio · Oklahoma · Oregon · Pennsylvania · Puerto Rico · Rhode Island · South Carolina · South Dakota · Tennessee · Texas · Utah · Vermont · Virginia · Washington · West Virginia · Wisconsin · WyomingCategories:- NRHP articles with dead external links
- State agencies of Texas
- State departments of transportation of the United States
- United States railroad regulation
- Motor vehicle registration agencies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.