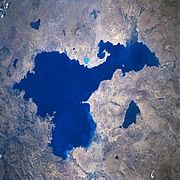
- Endorheic basin
-
An endorheic basin [1] (from the Greek: ἔνδον, éndon, "within" and ῥεῖν, rheîn, "to flow"; also terminal or closed basin) is a closed drainage basin that retains water and allows no outflow to other bodies of water such as rivers or oceans. Normally, water that has accrued in a drainage basin eventually flows out through rivers or streams on Earth's surface or by underground diffusion through permeable rock, ultimately ending up in the oceans. However, in an endorheic basin, rain (or other precipitation) that falls within it does not flow out but may only leave the drainage system by evaporation and seepage. The bottom of such a basin is typically occupied by a salt lake or salt pan. Endorheic basins are also called internal drainage systems.
Endorheic regions, in contrast to exorheic regions which flow to the ocean in geologically defined patterns, are closed hydrologic systems. Their surface waters drain to inland terminal locations where the water evaporates or seeps into the ground, having no access to discharge into the sea.[2] Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Aral Sea and the Caspian Sea, the world’s largest saline body of water cut off from the ocean.[3]
Contents
Endorheic lakes
Endorheic lakes are bodies of water that do not flow into the sea. Most of the water falling on earth finds its way to the oceans through a network of rivers, lakes and wetlands. However, there is a class of water bodies that are located in closed or endorheic watersheds where the topography prevents their drainage to the oceans. These endorheic watersheds (containing water in rivers or lakes that form a balance of surface inflows, evaporation and seepage) are often called terminal lakes or sink lakes.[4]
Endorheic lakes are usually in the interior of a body mass, far from an ocean. Their watersheds are often confined by natural geologic land formations such as a mountain range, cutting off water access to the ocean. The inland water flows into dry watersheds where the water evaporates, leaving a high concentration of minerals and other inflow erosion products. Over time this input of erosion products can cause the endorheic lake to become relatively saline (a "salt lake"). Since the main outflow pathways of these lakes are chiefly through evaporation and seepage, endorheic lakes are usually more sensitive to environmental pollutants inputs than water bodies that have access to oceans.[3]
Occurrence
Endorheic regions can occur in any climate but are most commonly found in hot desert locations. In areas where rainfall is higher, riparian erosion will generally carve drainage channels (particularly in times of flood), or cause the water level in the terminal lake to rise until it finds an outlet, breaking the enclosed endorheic hydrological system’s geographical barrier and opening it to the surrounding terrain. The Black Sea was likely such a lake, having once been an independent hydrological system before the Mediterranean Sea broke through the terrain separating the two.
Endorheic regions tend to be far inland with their boundaries defined by mountains or other geological features that block their access to oceans. Since the inflowing water can evacuate only through seepage or evaporation, dried minerals or other products collect in the basin, eventually making the water saline and also making the basin vulnerable to pollution.[3] Continents vary in their concentration of endorheic regions due to conditions of geography and climate. Australia has the highest percentage of endorheic regions at 21 percent while North America has the least at 5 percent.[5] Approximately 18 percent of the earth’s land drains to endorheic lakes or seas, the largest of these land areas being the interior of Asia.
In deserts, water inflow is low and loss to solar evaporation high, drastically reducing the formation of complete drainage systems. Closed water flow areas often lead to the concentration of salts and other minerals in the basin. Minerals leached from the surrounding rocks are deposited in the basin, and left behind when the water evaporates. Thus endorheic basins often contain extensive salt pans (also called salt flats, salt lakes, alkali flats, dry lake beds or playas). These areas tend to be large, flat hardened surfaces and are sometimes used for aviation runways or land speed record attempts, because of their extensive areas of perfectly level terrain.
Both permanent and seasonal endorheic lakes can form in endorheic basins. Some endorheic basins are essentially stable, climate change having reduced precipitation to the degree that a lake no longer forms. Even most permanent endorheic lakes change size and shape dramatically over time, often becoming much smaller or breaking into several smaller parts during the dry season. As humans have expanded into previously uninhabitable desert areas, the river systems that feed many endorheic lakes have been altered by the construction of dams and aqueducts. As a result many endorheic lakes in developed or developing countries have contracted dramatically, resulting in increased salinity, higher concentrations of pollutants, and the disruption of ecosystems.
Even within exorheic basins, there can be "non-contributing", low-lying areas that trap runoff and prevent it from contributing to flows downstream during years of average or below-average runoff. In flat river basins, non-contributing areas can be a large fraction of the driver basin. (E.g. Lake Winnipeg's basin.[6])
Notable endorheic basins and lakes
Antarctica
Endorheic lakes in Antarctica are located in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, Antarctica, the largest ice-free area in Antarctica.
- Don Juan Pond in Wright Valley is fed by groundwater from a rock glacier and remains unfrozen throughout the year.
- Lake Vanda in Wright Valley has a perennial ice cover, the edges of which melt in the summer allowing flow from the longest river in Antarctica, the Onyx River. The lake is over 70 m deep and is hypersaline.
- Lake Bonney is in Taylor Valley and has a perennial ice cover and two lobes separated by the Bonney Riegel. The lake is fed by glacial melt and discharge from Blood Falls. Its unique glacial history has resulted in a hypersaline brine in the bottom waters and fresh water at the surface.
- Lake Hoare, in Taylor Valley, is the freshest of the Dry Valley lakes receiving its melt almost exclusively from the Canada Glacier. The lake has an ice cover and forms a moat during the Austral summer.
- Lake Fryxell, is adjacent to the Ross Sea in Taylor Valley. The lake has an ice cover and receives its water from numerous glacial meltwater streams for approximately 6 weeks out of the year. Its salinity increases with depth.
Asia
Much of western and Central Asia is a giant endorheic region made up of a number of contiguous closed basins. The region contains several basins and terminal lakes, including:
- The Caspian Sea, the largest lake on Earth. A large part of Eastern Europe, drained by the Volga River, is part of the Caspian's basin.
- The Aral Sea, whose tributary rivers have been diverted, leading to a dramatic shrinkage of the lake. The resulting ecological disaster has brought the plight faced by internal drainage basins to public attention.
- Lake Balkhash, in Kazakhstan.
- Issyk-Kul Lake, Son-Kul Lake, and Chatyr-Kul Lake in Kyrgyzstan.
- Lop Lake, in the Tarim Basin of China's Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region.
- The Central Asian Internal Drainage Basin, in southern and western Mongolia, contains a series of closed drainage basins, such as the Khyargas Nuur basin, the Uvs Nuur basin, and the Pu-Lun-To River Basin.[7]
- Qaidam Basin, in Qinghai Province, China.
- Sistan Basin covering areas of Iran and Afghanistan
Other endorheic lakes and basins in Asia include:
- The Dead Sea, the lowest surface point on Earth and one of its saltiest bodies of water, lies between Israel and Jordan.
- Sambhar Lake, in Rajasthan, north-western India, is also the terminal point of an endorheic basin.
- Lake Van, in Turkey, is one of the world's largest endorheic lakes.
- Sabkhat al-Jabbul, extensive salt flats and a 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi) lake in Syria.
- Solar Lake, Sinai, near the Israeli-Egypt border.
Australia
Australia, being very dry and having exceedingly low runoff ratios due to its ancient soils, has many endorheic drainages. The most important are:
- Lake Eyre Basin, which drains into the highly variable Lake Eyre and includes Lake Frome.
- Lake Torrens, to the west of the Flinders Ranges in South Australia.
- Lake Corangamite, a highly saline crater lake in western Victoria.
- Lake George, formerly connected to the Murray-Darling Basin
Africa
Large endorheic regions in Africa are located in the Sahara Desert, the Kalahari Desert, and the Great Rift Valley:
- Chad Basin, in the northern center of Africa. It covers an area of approximately 2.434 million km².
- Qattara Depression, in Egypt.
- Chott Melrhir, in Algeria.
- Chott el Djerid, in Tunisia.
- The Okavango River, in the Kalahari Desert, is part of an endorheic basin region which also includes the Okavango Delta, Lake Ngami, the Nata River, and a number of salt pans such as Makgadikgadi Pan.
- Etosha pan in Namibia’s Etosha National Park.
- Lake Turkana, in Kenya, whose basin includes the Omo River of Ethiopia.
- Lake Chilwa, in Malawi.
- Afar Depression, in Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Djibouti.
- Some Rift Valley lakes, such as Lake Abijatta, Lake Chew Bahir, Lake Shala, Lake Chamo, and Lake Awasa.
- Lake Mweru Wantipa, in Zambia.
North and Central America
- The Valley of Mexico. In Pre-Columbian times, the Valley was substantially covered with five lakes, including Lake Texcoco, Lake Xochimilco, and Lake Chalco.
- Guzmán Basin, in northern Mexico and the southwestern United States.
- Lago de Atitlán, in the highlands of Guatemala.
- Bolsón de Mapimí, in northern Mexico.
- The Great Basin,[8] which covers much of Nevada and Utah, is a large region of contiguous closed basins, including:
- Great Salt Lake, in Utah, the largest terminal lake in the Western Hemisphere.
- The Black Rock Desert in Nevada, location of the Thrust2 and ThrustSSC landspeed record runs, and the annual home to the Burning Man festival.
- Death Valley, the lowest land point in the United States. During the Holocene epoch, Lake Manly filled the Death Valley basin of Inyo County, California. Later, Death Valley had a system of tributary basins:
- Rogers Dry Lake, at Edwards Air Force Base in California.
- Owens Lake and the Owens River basin.
- Mono Lake in California.
- Groom Dry Lake in Nevada, location of Area 51.
- Salton Sea in California, a lake accidentally recreated in 1905 when irrigation canals ruptured, filling a desert endorheic basin and recreating an ancient saline sea.
- Sevier Lake, in Utah.
- Pyramid Lake in Nevada, whose drainage basin includes Lake Tahoe.
- Humboldt Sink and the Humboldt River basin in Nevada.
- Carson Sink and the Carson River basin in Nevada.
- Walker Lake and the Walker River in Nevada.
- Tulare Lake at the southern end of the San Joaquin Valley fed by the Kaweah, Kern and Tule Rivers plus southern distributaries of the Kings; however, agricultural development and irrigation diversions have left the lake dry.
- Crater Lake, in Oregon.
- The Great Divide Basin in Wyoming, a small endorheic basin that straddles the Continental Divide of the Americas.
- Devils Lake, in North Dakota.
- Devil's Lake, in Wisconsin.
- Little Manitou Lake in Saskatchewan.
- Old Wives Lake, on the Laurentian Divide in Saskatchewan.
- Pakowki Lake, on the Laurentian Divide in Alberta.
- New Mexico has a number of desert endorheic basins including:
- The Tularosa Basin, a rift valley.
- Zuni Salt Lake, a maar.
- The Mimbres River Basin, in Grant County.
Many small lakes and ponds in North Dakota and Manitoba are endorheic; some of them have salt encrustations along their shores.
Europe
- Lake Neusiedl, in Austria and Hungary.
- Lake Trasimeno, in Italy.
- Lake Velence, in Hungary.
- Lake Prespa, between Albania, Greece and the Republic of Macedonia.
- Rahasane turlough, the largest turlough in Ireland.
- Laacher See, in Germany.
All these lakes are drained, however, either through manmade canals or via karstic phenomena. Minor additional endorheic lakes exist throughout the Mediterranean countries Spain (e.g. Laguna de Gallocanta), Italy, Cyprus (Larnaca and Akrotiri salt lakes) and Greece.
South America
 MODIS image from November 4, 2001 showing Lake Titicaca, the Salar de Uyuni, and the Salar de Coipasa. These are all parts of the Altiplano
MODIS image from November 4, 2001 showing Lake Titicaca, the Salar de Uyuni, and the Salar de Coipasa. These are all parts of the Altiplano
- Laguna del Carbón, in Gran Bajo de San Julián, Argentina - the lowest point in the Western and Southern hemispheres
- The Altiplano includes a number of closed basins such as Poopó Lake.
- Lake Valencia, in Venezuela.
- Salar de Atacama, in the Atacama Desert, Chile.
Ancient
Some of the Earth’s ancient endorheic systems include:
- The Black Sea, until its merger with the Mediterranean.
- The Mediterranean Sea itself and all its tributary basins, during its Messinian desiccation (5 m.y. BP approx.) as it became disconnected from the Atlantic Ocean.
- Lake Lahontan in North America.
- Lake Bonneville in North America.
- Ebro and Duero basins, draining most of northern Spain during the Neogene and perhaps Pliocene.
See also
References
- ^ This term is little-used among North American geoscientists.
- ^ "Drainage systems". Encyclopedia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/eb/topic-187043/endorheic-system. Retrieved 2008-02-11.
- ^ a b c "Endorheic Lakes: Waterbodies That Don't Flow to the Sea". United Nations Environment Programme. http://www.unep.or.jp/ietc/publications/short_series/lakereservoirs-2/10.asp. Retrieved 2008-02-11.
- ^ "What is a watershed and why should I care?". university of delaware. http://www.wr.udel.edu/cb/whatwhycare.html. Retrieved 2008-02-11.
- ^ Saline Lake Ecosystems of the World. Springer. 1986-04-30. ISBN 9789061935353. http://books.google.com/?id=NOdvPFm6SyoC&pg=PA18&lpg=PA18&dq=endorheic. Retrieved 2007-07-31.
- ^ http://www.gov.mb.ca/waterstewardship/water_quality/state_lk_winnipeg_report/pdf/state_of_lake_winnipeg_rpt_technical_high_resolution.pdf, p 2.
- ^ "Basins". Mongolian River Resources. http://www.mongolianriverresources.mn/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=81&pid=366. Retrieved 21 November 2010.
- ^ Houghton, Samuel G. (1994). A trace of desert waters: the Great Basin story. Reno: University of Nevada Press.
External links
- Primer on endorheic lakes
- The Silk Roads and Eurasian Geography
- The role of climate during high plateau formation. Insights from numerical experiments
Categories:- Endorheic basins
- Drainage basins
- Hydrology
- Endorheic lakes
- Lakes
- Fluvial landforms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.