- Diffusion
-
This article is about the generic concept of the time-dependent random process. For other uses, see Diffusion (disambiguation).
Diffusion describes the spread of particles through random motion from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. The time dependence of the statistical distribution in space is given by the diffusion equation. The concept of diffusion is tied to that of mass transfer driven by a concentration gradient. Diffusion is invoked in the social sciences to describe the spread of ideas.
Diffusion in physics
Diffusion is particles move/spread. In molecular diffusion, the moving entities are small molecules which are self propelled by thermal energy and do not require a concentration gradient to spread out through random motion. They move at random because they frequently collide. Diffusion is this thermal motion of all (liquid and gas) molecules at temperatures above absolute zero. Diffusion rate is a function of only temperature, and is not affected by concentration. Brownian motion is observed in molecules that are so large that they are not driven by their own thermal energy but by collisions with solvent particles.
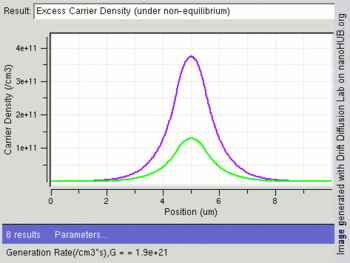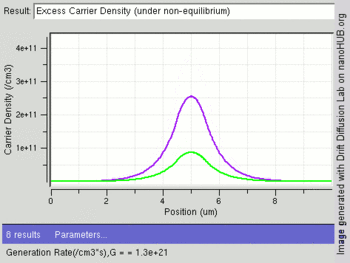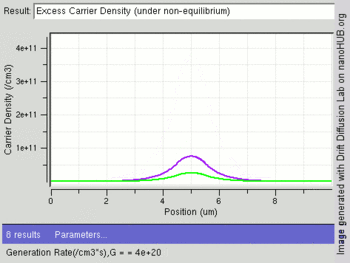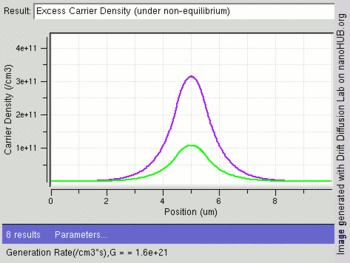 The following image shows change in excess carriers being generated (green:electrons and purple:holes) with increasing light intensity (Generation rate /cm3) at the center of an intrinsic semiconductor bar. Electrons have a higher diffusion constant than holes, leading to fewer excess electrons at the center as compared to holes.
The following image shows change in excess carriers being generated (green:electrons and purple:holes) with increasing light intensity (Generation rate /cm3) at the center of an intrinsic semiconductor bar. Electrons have a higher diffusion constant than holes, leading to fewer excess electrons at the center as compared to holes.
While Brownian motion of large molecules is observable under an electron-microscope, small-molecule diffusion can only be probed in carefully controlled experimental conditions. Under normal conditions, molecular diffusion is relevant only on length scales between nanometer and millimeter. On larger length scales, transport in liquids and gases is normally due to another transport phenomenon, convection.
Therefore, some often cited examples of diffusion are wrong: If cologne is sprayed in one place, it will soon be smelled in the entire room, but a simple calculation shows that this is due to diffusion. If ink is dropped in water, one usually observes an inhomogeneous evolution of the spatial distribution, which clearly indicates convection; diffusion dominates only in perfect thermal equilibrium.
In contrast, heat conduction through solid media is an everyday occurrence (e.g. a metal spoon partly immersed in a hot liquid). This explains why the diffusion of heat was explained mathematically before the diffusion of mass.
Other types of diffusion
- Anisotropic diffusion, also known as the Perona-Malik equation, enhances high gradients
- Anomalous diffusion,[1] in porous medium
- Atomic diffusion, in solids
- Eddy diffusion, in coarse-grained description of turbulent flow
- Effusion of a gas through small holes
- Electronic diffusion, resulting in an electric current called the diffusion current
- Facilitated diffusion, present in some organisms
- Gaseous diffusion, used for isotope separation
- Heat equation, diffusion of thermal energy
- Itō diffusion, mathematisation of Brownian motion, continuous stochastic process.
- Knudsen diffusion of gas in long pores with frequent wall collisions
- Momentum diffusion ex. the diffusion of the hydrodynamic velocity field
- Photon diffusion
- Random walk,[2] model for diffusion
- Reverse diffusion, against the concentration gradient, in phase separation
- Rotational diffusion, random reorientations of molecules
- Surface diffusion, diffusion of adparticles on a surface
- Turbulent diffusion, transport of mass, heat, or momentum within a turbulent fluid
References
- ^ D. Ben-Avraham and S. Havlin (2000). Diffusion and Reactions in Fractals and Disordered Systems. Cambridge University Press. http://havlin.biu.ac.il/Shlomo%20Havlin%20books_d_r.php.
- ^ Weiss, G. (1994). Aspects and Applications of the Random Walk. North-Holland.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.