- Williamsburg, Virginia
-
Williamsburg, Virginia — City — 
SealLocation in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Coordinates: 37°16′15″N 76°42′25″W / 37.27083°N 76.70694°WCoordinates: 37°16′15″N 76°42′25″W / 37.27083°N 76.70694°W Country United States State Virginia Counties Independent city Government - Mayor Clyde Haulman Area - Total 8.7 sq mi (22.5 km2) - Land 8.5 sq mi (22.1 km2) - Water 0.1 sq mi (0.3 km2) Elevation 82 ft (15 m) Population (2010) - Total 14,068 - Density 1,648.5/sq mi (636.5/km2) Time zone EST (UTC-5) - Summer (DST) EDT (UTC-4) ZIP codes 23185-23188 Area code(s) 757 FIPS code 51-86160[1] GNIS feature ID 1498551[2] Website http://www.williamsburgva.gov/ Williamsburg is an independent city located on the Virginia Peninsula in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area of Virginia, USA. As of the 2010 Census, the city had an estimated population of 14,068.[3] It is bordered by James City County[4] and York County, and is an independent city. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the city of Williamsburg with James City County for statistical purposes.
Originally Middle Plantation, a 1632 fortified settlement located on high ground on the Peninsula between the James and York rivers, it was renamed Williamsburg after the capital of the Virginia Colony was moved there from Jamestown in 1698. The town received a royal charter as a city in 1722, and was the center of political events in Virginia leading to the American Revolution.
Williamsburg is well-known for Colonial Williamsburg, the restored Historic Area of the city, and for the adjacent College of William & Mary, established in 1693, the second-oldest university in the United States. Nearby, and established in 1770, the predecessor of the current Eastern State Hospital is considered to have been the earliest mental hospital in the United States.
The Historic Triangle of Virginia, which also includes Jamestown and Yorktown, is among the most popular tourist destinations in the world, with Williamsburg located in the center. The three are linked by the National Park Service's Colonial Parkway, a 23-mile (37 km)-long National Scenic Byway which is carefully shielded from views of commercial development. The toll-free Jamestown Ferry is located at the southern end of the Colonial Parkway. State Route 5, another scenic byway, links Williamsburg and Richmond at a driving distance of approximately 54 miles (87 km).
Most highway travelers reach Williamsburg via nearby Interstate 64, U.S. Route 60, and State Route 143, each major east-west highways. Commercial airline service is available at Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport (20 miles), and at Richmond and Norfolk airports (both 55 miles (89 km) away). All are located along I-64 and offer limousine service to Williamsburg, as well as rental cars. Williamsburg also offers public transportation alternatives for visitors and citizens. The intermodal Williamsburg Transportation Center is located in a restored Chesapeake and Ohio Railway station near the Historic Area, downtown, and the College. It offers Amtrak and Greyhound services, taxicabs, and rental cars. There, many visitors transfer to the community's local transit bus system, Williamsburg Area Transport, which operates accessible equipment for the mobility-impaired with bicycle racks on buses as well.
Contents
History
Prior to the arrival of the English colonists at Jamestown in the Colony of Virginia in 1607, the area which became Williamsburg was largely wooded. It was well within the territory of the Native American group known as the Powhatan Confederacy. In the early colonial period, the navigable rivers were the equivalent of modern highways. For ease of travel, and security from conflicts with the Native Americans, early colonial settlements were established close by the rivers.
By the 1630s, English settlements had grown to dominate the lower (eastern) portion of the Virginia Peninsula, and the Natives had abandoned their villages nearby such as Kiskiack (also spelled "Chiskiack"), shifting to more remote locations, but attacking intermittently. To offer protection for the farming and fishing communities lower on the Peninsula, the colonists built a stockade across the peninsula to provide some security from attacks by the natives.
Lying along the center-line of the Virginia Peninsula, the location which became Williamsburg was some distance from both the James River and the York River, the ground sloping down to the shore of each. Near Williamsburg, College Creek and Queen's Creek each fed into one of the two rivers. Between these two creeks the land area was only about 6 miles (9.7 km) wide, much less than at other points.
The area which became Williamsburg was settled in 1638 and named Middle Plantation, after its location on the high ground about half-way across the Peninsula. The cross-peninsula defensive palisade completed in 1634 was an integral part of the creation of Middle Plantation, though its exact route is long gone. Remnants have recently been discovered by archaeologists on the Bruton Heights School property adjacent to the site of the house of Governor John Page while working on a Colonial Williamsburg archaeological research project.[5]
Jamestown was the original capital of Virginia Colony, but was burned down during the events of Bacon's Rebellion in 1676. As soon as Governor William Berkeley regained control, temporary headquarters for the government to function were established about 12 miles (19 km) away on the high ground at Middle Plantation, whilst the Statehouse at Jamestown was rebuilt. The members of the House of Burgesses discovered that the 'temporary' location was both safer and more pleasant environmentally than Jamestown, which was humid and plagued with mosquitoes.
A school of higher education had long been an aspiration of the colonists. An early attempt at Henricus failed after the Indian Massacre of 1622. The location at the outskirts of the developed part of the colony had left it more vulnerable to the attack. In the 1690s, the colonists tried again to establish a school. They commissioned Reverend James Blair, who spent several years in England lobbying, and finally obtained a royal charter for the desired new school. It was to be named the College of William and Mary in honor of the monarchs of the time. When Reverend Blair returned to Virginia, the new school was founded in a safe place, Middle Plantation in 1693. Classes began in temporary quarters in 1694, and the College Building, a precursor to the Wren Building, was soon under construction.
Williamsburg as capital
Four years later, in 1698, the rebuilt Statehouse in Jamestown burned down again, this time accidentally. The government again relocated 'temporarily' to Middle Plantation, and in addition to the better climate now also enjoyed use of the College's facilities. The College students made a presentation to the House of Burgesses, and it was agreed in 1699 that the colonial capital should be permanently moved to Middle Plantation. A village was laid out and Middle Plantation was renamed Williamsburg in honor of King William III of England, befitting the town's newly elevated status.
Following its designation as the Capital of the Colony, immediate provision was made for construction of a capitol building and for plotting out the new city according to the survey of Theodorick Bland. His design utilized the extant sites of the College and the almost-new brick Bruton Parish Church as focal points, and placed the new Capitol building opposite the College, with Duke of Gloucester Street connecting them.
Alexander Spotswood, who arrived in Virginia as lieutenant governor in 1710, had several ravines filled and streets levelled, and assisted in erecting additional College buildings, a church, and a magazine for the storage of arms. In 1722, the town of Williamsburg was granted a royal charter as a city, (now believed to be the oldest charter in the United States).
Middle Plantation was included in James City Shire when it was established in 1634, as the Colony reached a total population of approximately 5,000. (James City and the other shires in Virginia changed their names a few years later; James City Shire then became known as James City County). However, the middle ground ridge line was essentially the dividing line with Charles River Shire, which was renamed York County after King Charles I fell out of favor with the citizens of England. As Middle Plantation, and later Williamsburg developed, the boundaries were adjusted slightly. For most of the colonial period, the border between the two counties ran down the center of Duke of Gloucester Street. During this time, and for almost 100 years after formation of the Commonwealth of Virginia and the United States, despite practical complications, the town remained divided between the two counties.
Williamsburg was the site of the first attempted canal in the United States. In 1771, Lord Dunmore, who would turn out to be Virginia's last Royal Governor, announced plans to connect Archer's Creek, which leads to the James River with Queen's Creek, leading to the York River. It would have formed a water route across the Virginia Peninsula, but was not completed. Remains of this canal are visible at the rear of the grounds behind the Governor's Palace in Colonial Williamsburg.[6]
The first purpose-built psychiatric hospital in the United States was founded in the city in the 1770s: 'Public Hospital for Persons of Insane and Disordered Minds'. Known in modern times as Eastern State Hospital, it was established by Act of the Virginia colonial legislature on June 4, 1770. The Act to 'Make Provision for the Support and Maintenance of Ideots, Lunaticks, and other Persons of unsound Minds' authorized the House of Burgesses to appoint a fifteen-man Court Of Directors to oversee the future hospital’s operations and admissions. In 1771, contractor Benjamin Powell constructed a two-story building on Francis Street near the College, capable of housing twenty-four patients. The design of the grounds included 'yards for patients to walk and take the Air in' as well as provisions for a fence to keep the patients out of the nearby town.
The Gunpowder Incident began in April 1775 as a dispute between Governor Dunmore and Virginia colonists over gunpowder stored in the Williamsburg magazine. Dunmore, fearing rebellion, ordered royal marines to seize gunpowder from the magazine. Virginia militia led by Patrick Henry responded to the 'theft' and marched on Williamsburg. A standoff ensued, with Dunmore threatening to destroy the city if attacked by the militia. The dispute was resolved when payment for the powder was arranged. This was an important precursor in the run-up to the American Revolution
Following the Declaration of Independence from Britain, the American Revolutionary War broke out in 1776. During the War, the capital of Virginia was moved again, in 1780, this time to Richmond at the urging of then-Governor Thomas Jefferson, who feared Williamsburg's location made it vulnerable to a British attack. However, during the Revolutionary War Williamsburg retained its status as a venue for many important conventions.
Decline and the Civil War
Having lost the Capitol from 1780, Williamsburg was reduced in prominence, although not to the degree Jamestown had previously experienced. Another factor was travel: 18th and early 19th century transportation in the Colony was largely by canals and navigable rivers. As it had been built on 'high ground' Williamsburg was not sited on a major water route, unlike many early communities in the United States. The railroads which began to be built from the 1830s also did not come through the city.
Despite the loss of the business activity involved in Government, the Williamsburg College continued and expanded, as did the Public Hospital for Persons of Insane and Disordered Minds, with the latter becoming known as Eastern State Hospital.
At the outset of the American Civil War (1861–1865), enlistments in the Confederate Army depleted the student body of the College of William and Mary and on May 10, 1861 the faculty voted to close the College for the duration of the conflict. The College Building was used as a Confederate barracks and later as a hospital, first by Confederate and later by Union forces.[citation needed]
The Williamsburg area saw combat in the spring of 1862 during the Peninsula Campaign, an effort to take Richmond from the east from a base at Fort Monroe. Throughout late 1861 and early 1862, the small contingent of Confederate defenders was known as the Army of the Peninsula, and led by General John B. Magruder. He successfully created ruses which fooled the invaders as to the size and strength of his forces, and deterred their attack. Their subsequent slow movement up the peninsula gained valuable time for defenses to be constructed at the Confederate capital at Richmond.[citation needed]
In early May 1862, after holding the Union troops off for over a month, the defenders withdrew quietly from the Warwick Line (stretching across the Peninsula between Yorktown and Mulberry Island). As General George McClellan's Union forces crept up the Peninsula to pursue the retreating Confederate forces, a rear guard force led by General James Longstreet and supported by General J.E.B. Stuart's cavalry blocked their westward progression at the Williamsburg Line. This was a series of 14 redoubts east of town, with earthen Fort Magruder (also known as Redoubt # 6) at the crucial junction of the two major roads leading to Williamsburg from the east. The design and construction had been overseen by Benjamin S. Ewell, the President of the College of William and Mary. He owned a farm in James City County, and had been commissioned as an officer in the Confederate Army after the College closed in 1861.[citation needed]
At the Battle of Williamsburg on May 5, 1862, the defenders succeeded in delaying the Union forces long enough for the retreating Confederates to reach the outer defenses of Richmond.
A siege of Richmond ensued, culminating in the Seven Days Battles. McClellan's campaign failed, and as a result, the War dragged on for almost three years at great cost to lives and finances for both sides before its conclusion in April 1865.[citation needed] Meanwhile, on May 6, 1862 Williamsburg had fallen to the Union. The Brafferton building of the College was used for a time as quarters for the commanding officer of the Union garrison occupying the town. On September 9 that year, drunken soldiers of the 5th Pennsylvania Cavalry set fire to the College Building,[7] allegedly to prevent Confederate snipers from using it for cover. Much damage was done to Williamsburg during the Union occupation, which lasted until September 1865.[citation needed]
Late 19th century
 Williamsburg Transportation Center is an intermodal facility located in a restored Chesapeake and Ohio Railway station located within walking distance of Colonial Williamsburg's Historic Area, the College of William and Mary, and the downtown area.
Williamsburg Transportation Center is an intermodal facility located in a restored Chesapeake and Ohio Railway station located within walking distance of Colonial Williamsburg's Historic Area, the College of William and Mary, and the downtown area.
About 20 years later, in 1881, Collis P. Huntington's Chesapeake and Ohio Railroad (C&O) built its Peninsula Extension through the area, eventually establishing six stations in Williamsburg and the surrounding area. The Peninsula Extension was good news for the farmers and merchants of the Virginia Peninsula, and they generally welcomed the railroad, which aided passenger travel and shipping. Williamsburg allowed tracks to be placed down the main street of town, Duke of Gloucester Street, and even directly through the ruins of the historic capitol building. (They were later relocated, and Collis Huntington's real estate arm, Old Dominion Land Company, eventually donated the historic site to the forerunner of the Association for the Preservation of Virginia Antiquities.)
However, the main business purpose for the new railroad was unquestionably shipping eastbound West Virginia bituminous coal to Newport News. Using the new coal piers, it was loaded aboard large colliers in the harbor of Hampton Roads for shipment to New England and export destinations world wide.[8]
Due in no small part to the tireless efforts of its president, Benjamin Stoddert Ewell, education continued at the College of William and Mary, although teaching was temporarily suspended for financial reasons from 1882 until 1886. Ewell's efforts to restore the historic school and its programs during and after Reconstruction became legendary in Williamsburg and at the College and were ultimately successful, with funding from both the U.S. Congress and the Commonwealth of Virginia. After 1886, the College became a state school. Benjamin Ewell remained in Williamsburg as President Emeritus of the College until his death in 1894.[9]
Beginning in the 1890s, C&O land agent Carl M. Bergh, a Norwegian-American who had earlier farmed in the mid-western states, realized that the gentler climate of eastern Virginia and depressed post-Civil War land prices would be attractive to his fellow Scandinavians who were farming in other northern parts of the country. He began sending out notices, and selling land. Soon there was a substantial concentration of relocated Americans of Norwegian, Swedish, and Danish descent in the area. The location earlier known as Vaiden's Siding on the railroad just west of Williamsburg in James City County, was renamed Norge. These citizens and their descendants found the area conditions favorable as described by Bergh, and many became leading merchants, tradespersons, and farmers in the community. These transplanted Americans brought some new blood and enthusiasm to the old colonial capitol area.
Revival
Williamsburg was still a sleepy little town in the early 20th century. Some newer structures were interspersed with colonial-era buildings, but the town was much less progressive than other busier communities of similar size in Virginia. Some local lore indicates that the residents were satisfied with it that way, and longtime Virginia Peninsula journalist, author and historian Parke S. Rouse Jr. has pointed this out in his published work. On June 26, 1912, the Richmond Times-Dispatch newspaper ran an editorial which dubbed the town 'Lotusburg' for "Tuesday was election day in Williamsburg but nobody remembered it. The clerk forgot to wake the electoral board, the electoral board could not arouse itself long enough to have the ballots printed, the candidates forgot they were running, the voters forgot they were alive."[10]
However, even if such complacency existed, a dream of one Episcopalian priest was to expand and change Williamsburg's future thus providing it a new major purpose, turning much of it into a massive living museum. In the early 20th century, one of the largest historic restorations ever undertaken in the US was championed by the Reverend Dr W.A.R. Goodwin of Williamsburg's Bruton Parish Church. Initially, Dr Goodwin had just aimed to save his historic church building. This he accomplished by 1907, in time for the 300th anniversary of the founding of the Episcopal Church in Virginia. However, upon returning to Williamsburg in 1923 after serving a number of years in upstate New York, he realized that many of the other colonial-era buildings which remained were also in deteriorating condition: their survival was at stake.
Goodwin dreamed of a much larger restoration along the lines of what he had accomplished with his historic church. A cleric of modest means, he sought support and financing from a number of sources before successfully attracting the interest and major financial support of Standard Oil heir and philanthropist John D. Rockefeller, Jr. and his wife Abby Aldrich Rockefeller. Their combined efforts created Colonial Williamsburg, involving restoration of much of the downtown Williamsburg area and the creation of a 301-acre (1.22 km2) Historic Area, celebrating the patriots and the early history of America.
Today, Colonial Williamsburg is Virginia's largest tourist attraction (based upon attendance) and is the cornerstone of the Historic Triangle with Jamestown and Yorktown joined by the Colonial Parkway. In the 21st century, Williamsburg has continued to update and refine its attractions. There are more features designed to attract modern children and to offer better and additional interpretation of the African-American experience in the town. A century after Dr. Goodwin's work began, this masterpiece of Virginia and United States history remains a remarkable work-in-progress.
In addition to the Historic Area of Colonial Williamsburg, the city's railroad station was restored to become an intermodal passenger facility (see Transportation section below). Nearby in James City County, the old ca. 1908 C&O Railway combination passenger and freight station at Norge was preserved and with a donation from CSX Transportation was relocated in 2006 to a site at the Croaker Branch of the Williamsburg Regional Library. Other landmarks outside the historic area include Carter's Grove and Gunston Hall.
Recent history
The third of three debates between Republican President Gerald Ford and Democratic challenger Jimmy Carter was held at Phi Beta Kappa Memorial Hall at The College of William & Mary on October 22, 1976. Perhaps in tribute to the debate’s historic venue, as well as to the United States Bicentennial celebration, both candidates spoke of a "new spirit" in America.
The 9th G7 Summit was held in Williamsburg in 1983. The summit participants discussed the growing debt crisis, arms control and greater co-operation between the Soviet Union and the G7 (now the G8). At the end of the meeting, Secretary of State George P. Shultz read to the press a statement confirming the deployment of American Pershing II-nuclear rockets in West Germany later in 1983.[11]
On May 3, 2007 England's Queen Elizabeth II visited Jamestown and Williamsburg, Va. Her last visit to Williamsburg was in 1957.
On February 5, 2009, President Barack Obama took his first trip aboard Air Force One to a House Democrats retreat in the city to attend and address their “Issues Conference.”[12][13]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 8.7 square miles (23 km2), of which 8.5 square miles (22 km2) is land and 0.1 square miles (0.26 km2) is water.
Williamsburg is spread upon a ridge on the peninsula between the James and York Rivers. Queen's Creek and College Creek (called in early days Archer's Hope Creek) partly encircle the city.
The city is located on the I-64 corridor on the Virginia Peninsula, 45 miles (72 km) southeast of Richmond and approximately 37 miles (60 km) northwest of Norfolk. It is in the northwest corner of the greater Hampton Roads area, (officially known as the Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News, VA-NC MSA), which is the 34th largest in the United States, with a total population of 1,576,370. The area includes the Virginia cities of Norfolk, Virginia Beach, Chesapeake, Hampton, Newport News, Poquoson, Portsmouth, Suffolk, Williamsburg, and the counties of Gloucester, Isle of Wight, James City, Mathews, Surry, and York, as well as the North Carolina county of Currituck. While Virginia Beach is the most populated city within Hampton Roads, it currently functions more as a suburb. The city of Norfolk is recognized as the central business district, while the Virginia Beach seaside resort district and Williamsburg are primarily centers of tourism.
Climate
Williamsburg is located in the humid subtropical climate zone, allowing outdoor activities to be enjoyed year round. Summers are hot and humid with cool evenings. The mean annual temperature is 60 °F (16 °C), with an average annual snowfall of 6 inches (150 mm) and an average annual rainfall of 47 inches (1,200 mm). No measurable snow fell in 1999. The wettest seasons are the spring and summer, although rainfall is fairly constant all year round. The highest recorded temperature was 107.0 °F (41.7 °C) on July 7, July 24, and July 25, 2010. The lowest recorded temperature was −7 °F (−21.7 °C) on January 21, 1985.
Adjacent counties
- York County, Virginia - north and east
- James City County, Virginia - south and west
National protected area
Demographics
As of the census[1] of 2010, there are 14,068 people, 3,619 households, and 1,787 families residing in the city. The population density is 1,404.1 people per square mile (542.4/km²). There are 3,880 housing units at an average density of 454.1 per square mile (175.4/km²). The racial makeup of the city is 74.0% White, 14.0% Black or African American, 0.3% Native American, 5.7% Asian, 0.0% Pacific Islander, 2.5% from other races, and 3.5% from two or more races. 6.7% of the population are Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There are 3,619 households out of which 16.5% have children under the age of 18 living with them, 37.2% are married couples living together, 9.6% have a female householder with no husband present, and 50.6% are non-families. 35.9% of all households are made up of individuals and 11.4% have someone living alone who is 65 years of age or older. The average household size is 2.07 and the average family size is 2.66.
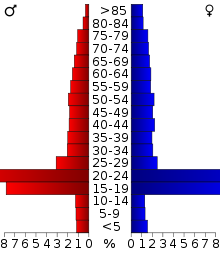
The age distribution, which is heavily influenced by the College of William and Mary, is: 9.6% under the age of 18, 46.0% from 18 to 24, 17.7% from 25 to 44, 15.0% from 45 to 64, and 11.7% who are 65 years of age or older. The median age is 23 years. For every 100 females there are 81.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there are 80.8 males.
The median income for a household in the city is $37,093, and the median income for a family is $52,358. Males have a median income of $28,625 versus $26,840 for females. The per capita income for the city is $18,483. 18.3% of the population and 9.3% of families are below the poverty line. Out of the total population, 29.7% of those under the age of 18 and 5.5% of those 65 and older are living below the poverty line.
Williamsburg is notable for the fact that a high proportion of city residents derive a significant percentage of their annual income from investment sources, either in addition to or in lieu of income from work. This is because many retirees relocate to Williamsburg, who typically draw income from investments such as 401(k) plans and the like (see also retirement community).
Economy
Entrance to Busch Gardens Europe, featuring the countries' flags
The tourist volume of Colonial Williamsburg has attracted many other related businesses to the area. Notable among these was Anheuser-Busch, which established large operations in James City County and York County just outside the city. The company operates a large brewery there, and a subsidiary of the company operates two of its theme parks near the brewery, Busch Gardens Europe, and Water Country USA. Anheuser-Busch's subsidiary Busch Properties also operates a commerce park, McLaw's Circle, and Kingsmill on the James a gated residential neighborhood that contains a resort of the same name.
Culture
As with most of Virginia (the Northern Virginia/Washington D.C. metro area being the notable exception), Williamsburg is most often associated with the larger American South. People who have grown up in the Hampton Roads area have a unique Tidewater accent which sounds different from a stereotypical Southern accent. Vowels have a longer pronunciation than in a regular southern accent. For example, "house" is pronounced "hoose" in the Tidewater accent.[14]
 View of Duke of Gloucester Street in Colonial Williamsburg.
View of Duke of Gloucester Street in Colonial Williamsburg.
Williamsburg is perhaps best known for its tourist and historical points of interest, the centerpiece of which is Colonial Williamsburg, which is essentially a living history museum, depicting the lifestyles and culture of the 18th century colonial period in American history. Major points of interest in this historic district include the Virginia's first capitol building, the Governor's Palace, Bruton Parish Church (the oldest continually-operating church in the United States), and the College of William and Mary.
Other highlights in the city include The Williamsburg Winery (Virginia's largest winery), the Williamsburg Botanical Garden, and the National Center for State Courts. Also located in Williamsburg are two major theme parks, Busch Gardens Europe and Water Country USA, as well as Go-Karts Plus action park and 2 miniature golf courses. The 200-acre (0.81 km2) Williamsburg Pottery Factory shopping complex visited by 3 million people annually is located at nearby Lightfoot, Virginia. "Artistic" and ornamental items are sold at the Market Square shops adjacent to the colonial area, and at many stores on Richmond Road. President's Park is a new educational attraction displaying outdoor statue heads of all 43 Presidents, each one accompanied by a descriptive biographical plaque.[15][16] It should be noted that the President's Park caused a stir in the local community when debate erupted over the "tastefulness" of the display.[citation needed]
Media
The dominant[citation needed] newspaper in Williamsburg is The Virginia Gazette. The Gazette is a bi-weekly, published in Williamsburg, and was the first newspaper to be published south of the Potomac River, starting in 1736.[citation needed] Its publisher was William Parks, who had similar ventures in Maryland.[17][18]
The Daily Press, published in nearby Newport News, covers local, regional and national news. The College of William & Mary has two student newspapers; the student-fee-supported campus newspaper is The Flat Hat while the independent campus newspaper is The Virginia Informer.[19] William & Mary students produce many other publications and run their own radio station, WCWM. Hampton Roads Magazine serves as a bi-monthly regional magazine for Williamsburg and the Hampton Roads area.[20] Williamsburg is served by a variety of radio stations on the AM and FM dials, with towers located around the Hampton Roads area.[21]
Williamsburg is served by the Norfolk-Portsmouth-Newport News designated market area (DMA), which is the forty-second largest in the U.S. with 712,790 homes (0.64% of the total U.S.).[22]
Government
Federally, Williamsburg is part of Virginia's 1st congressional district, represented by Republican Rob Wittman, elected in 2007.
The "city" which Williamsburg became in 1722 had portions located in both James City and York County. In 1870, the Virginia General Assembly changed the boundaries so that it was entirely within James City County. The new state constitution which took effect that year also created the political entity known as an independent city, which is not located in any county. Williamsburg subsequently met the requirements and changed to that status, continuing to share a joint court system. The city also operates a joint school division with James City County, under voluntary agreement which leaders revisit at planned intervals.
Williamsburg, as an independent city, has operated under the council-manager form of government since 1932. The governing body is composed of public-spirited citizens serving on a part-time basis to decide major policy issues. The Mayor is elected by the city council, and presides over council meetings and served as the Chief Elected Official for the city. The city council consists of five members that serve staggered, four-year terms. A city manager is hired by the city council, and is comparable to a corporation's chief executive officer. This person is usually a professionally-trained public administrator, who is charged with implementing the policies and directives of the city council, and has broad administrative authority with strict rules prohibiting political interference in administrative matters.[23]
As of 2010, the current Mayor of the city of Williamsburg is Clyde Haulman, and the Vice Mayor is Paul Freiling. Other members of the city council are Scott Foster (the first William and Mary student elected to city council), Douglas Pons, and Judith Knudson. The current city manager is Jackson C. Tuttle.[24]
The city shares constitutional officers, courts, and the Williamsburg-James City County Public Schools system (WJCC) with adjacent James City County, and is the county seat.[25]
As a college town, Williamsburg's large student population has also resulted in a few conflicts with the local city government. For example, in addressing concerns of property values and noise complaints near the campus, the council has undertaken initiatives to reduce student off-campus residential presence in the city by instituting a maximum occupancy rule of three-unrelated persons for single-family dwellings,[26] as well as a plan to buy rental houses with taxpayer dollars and resell them with the stipulation that the new owners must occupy them.[27] Prior to July 1, 2007, the voting registrar, David Andrews, had interpreted Virginia law to exclude a high percentage of students.[citation needed] He argued that students should be registered where their parents live.[citation needed] The new voter registrar, Win Sowder, said she is registering students as she would "any other resident of the city. If they're living in the dorms for eight months out of the year, and have an address located within the city limits on a Virginia driver's license, they're entitled to register to vote."[28]
Education
Main articles: Williamsburg-James City County Public Schools and The College of William & MaryThe public school system is jointly operated by the city of Williamsburg and James City County. The Williamsburg-James City County Public Schools system (known informally as "WJCC") consists approximately 9,000 students in 14 schools—8 elementary schools, 3 middle schools, and 3 high schools. Within the county's boundaries, the two established high schools, Lafayette, and Jamestown, are considered above average institutions. A third high school, Warhill, opened in the Lightfoot area in August 2007. An eighth elementary school, named Matoaka Elementary School, also opened at that time.[29][30]
James River Elementary School, located in the Grove Community in the county's southeastern end, is a magnet school. It offers the International Baccalaureate Primary Years Programme, one of only five such schools Virginia to do so.[31]
For the 2001–2002 academic year, the public school system was ranked among the top five school systems in the Commonwealth of Virginia and in the top 15% nationwide by Expansion Management Magazine. There are also two regional Governor's Schools in the area that serve gifted and talented students.
The city has also been the home to The College of William & Mary since its founding in 1693, making it America's second oldest college (behind Harvard University). Technically a university, William & Mary was also the first U.S. institution to have a Royal Charter, and the only one to have coat-of-arms from the College of Arms in London. The College campus closely adjoins the Historic District, and the Wren Building of the College at the head of Duke of Gloucester Street was one of the earliest restored by the efforts of Reverend Dr. W.A.R. Goodwin and the family of John D. Rockefeller Jr. as they began creating what is now commonly known as Colonial Williamsburg. Over 70% of the students of the College either work part-time or serve as volunteers in the community. Students contribute over 300,000 hours of volunteer service to the Williamsburg community annually.[32]
Six other universities are located within a one-hour drive of the city, including Christopher Newport University (Newport News), Old Dominion University and Norfolk State University (Norfolk), Hampton University (Hampton), Virginia Commonwealth University (Richmond), the University of Richmond (Richmond) and Virginia Union University (Richmond).[33][34][35][36][37][38]
There are also three community colleges, offering associate degrees and college transfer programs, within a twenty-five mile radius of Williamsburg: Thomas Nelson Community College, Paul D. Camp Community College, and Rappahannock Community College. A branch of Thomas Nelson Community College is located just east of the city limits in James City County.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Main articles: Transportation in Williamsburg, Virginia and Williamsburg (Amtrak station)The primary airport for the Virginia Peninsula is the Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport in Newport News, a twenty-minute drive from Williamsburg.[39] Norfolk International Airport and Richmond International Airport also serve passengers from the city.
Amtrak serves Williamsburg with three trains a day stopping at the Amtrak Station. The line runs west along the Virginia Peninsula to Richmond and points beyond. A high speed rail connection at Richmond to both the Northeast Corridor and the Southeast High Speed Rail Corridor are also under study.[40]
Williamsburg is located adjacent to Interstate 64 which parallels U.S. Route 60 and runs east-west in the area. State Route 199, officially named the Humelsine Parkway (after former Colonial Williamsburg President Carl Humelsine), surrounds the city in a semicircle. State Route 5 links the city with the James River Plantations along the north shore of the James River, Interstate 295 and Richmond. State Route 31 links the city to Jamestown and the toll-free Jamestown Ferry.
The Colonial Parkway provides a bucolic low-speed link between the points of the Historic Triangle which in addition to Colonial Williamsburg, includes Jamestown and Yorktown. It passes under the "Restored Area" in a tunnel. With the exception of buses, commercial vehicles are not allowed on the Parkway.[41]
In the "restored" or Historic Area, motorized traffic is not allowed on Duke of Gloucester Street, helping visitors to gain a perspective of what life was really like transportation-wise in the colonial days (before the invention of the automobile). There are bus stops and some parking areas located conveniently nearby, however. The only exceptions to this are for residents living in the historic area, and members of Bruton Parish Church, who have limited access and parking on Sundays.[42]
Intercity bus service is provided by Greyhound Lines (Carolina Trailways) and Hampton Roads Transit (HRT).
 Greyhound Bus loading at Williamsburg's Transportation Center.
Greyhound Bus loading at Williamsburg's Transportation Center.
The center also offers several modes of local transportation. Williamsburg Area Transport (WAT) uses the center as a transfer hub for its network of handicapped accessible transit bus routes serving the city, James City County, and most portions of York County adjacent to the Williamsburg area, with hourly service 6 days a week during daytime and evening hours.[43]
The community's public bus system, Williamsburg Area Transport (WAT), has its central hub at the transportation center. Various color-coded routes, with buses accessible to disabled persons, serve many hotels and motels, restaurants, stores, and non-CW attractions in the City of Williamsburg and much of neighboring James City County and part of York County. The system also provides paratransit services and operates replica trolley buses at the Yorktown Riverfront attraction.[44]
WAT connects with the much larger Hampton Roads Transit (HRT) (Route 116) bus system at Lee Hall in northwestern Newport News and at the Williamsburg Transportation Center (HRT Route 121). HRT routes connect to many other cities to the east in Hampton Roads and Greyhound Lines bus routes serve a nationwide network.[45]
WAT also operates a bus line for the College of William and Mary and its students, faculty, and staff, connecting the central university campus with points in the city of Williamsburg and James City County, the law school campus, and various outlying dormitories and auxiliary buildings owned or operated by the university that are not contiguous with the main campus.[46]
Utilities
The Newport News Waterworks was begun as a project of Collis P. Huntington as part of the development of the lower peninsula with the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway, the coal piers on the harbor of Hampton Roads, and massive shipyard which were the major sources of industrial growth which helped found nearby Newport News as a new independent city in 1896. It included initially an impingement of the Warwick River. Later expansions included more reservoirs, including one at Skiffe's Creek and another near Walker's Dam on the Chickahominy River.
A regional water provider, in modern times it is owned and operated by the City of Newport News, and serves over 400,000 people in the cities of Hampton, Newport News, Poquoson, and portions of York County and James City County.[47]
The City provides wastewater services for residents and transports wastewater to the regional Hampton Roads Sanitation District treatment plants.[48]
See also
- Colonial Williamsburg
- Hampton Roads
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Williamsburg, Virginia
- The Williamsburg Winery
- The Wren Building
- Virginia Peninsula
References
- ^ a b "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. http://geonames.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ [1]. Weldon Cooper Center 2010 Census Count Retrieved January 26, 2011
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Counties/Pages/FindACounty.aspx. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ^ David F. Muraca (1998). "The John Page Site:Excavation of a Major House Site on the Bruton Heights Property". Colonial Williamsburg. http://research.history.org/Archaeological_Research/Research_Articles/ThemeVirginia/JohnPage.cfm. Retrieved 2006-05-31.
- ^ Charles A. Grymes (1998). "Second-Worst Decision of the State of Virginia?". http://www.virginiaplaces.org/transportation/secondworst.html. Retrieved 2007-02-20.
- ^ "Historical Facts (1850–1899)". The College of William and Mary. http://www.wm.edu/vitalfacts/nineteenth2.php. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ^ Chesapeake and Ohio Historical Society
- ^ Benjamin Stoddert Ewell (1810 - 1894) - Find A Grave Memorial
- ^ WPA_Guide: Colonial Williamsburg: The Corporate Town-Before
- ^ Obama invited here next month
- ^ Obama taking first Air Force One trip as president
- ^ Obama Goes Airborne Today For First Time As President
- ^ "Virginia’s Many Voices". Fairfax County Public Library. http://www.fairfaxcounty.gov/library/niceandcurious/manyvoices.htm. Retrieved 2008-03-07.[dead link]
- ^ Williamsburg Pottery
- ^ Williamsburg Winery
- ^ the Daily Press (Newport News, Virginia)
- ^ History of the Virginia Gazette
- ^ "Hampton Roads News Links". abyznewslinks.com. http://www.abyznewslinks.com/unitevawl.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-06.
- ^ "Hampton Roads Magazine". Hampton Roads Magazine. http://www.hrmag.com. Retrieved 2007-08-06.
- ^ "Hampton Roads Radio Links". ontheradio.net. http://www.ontheradio.net/metro/Norfolk_VA.aspx. Retrieved 2007-08-06.
- ^ Holmes, Gary. "Nielsen Reports 1.1% increase in U.S. Television Households for the 2006–2007 Season." Nielsen Media Research. August 23, 2006. Retrieved on February 20, 2007.
- ^ Williamsburg City Manager
- ^ City of Williamsburg: City Council
- ^ Williamsburg-James City Courthouse
- ^ Evans, James (November 5, 2004). "Three's a Crowd, Four is Illegal". DoG Street Journal. http://www.dogstreetjournal.com/story/1016. Retrieved 2006-05-30.
- ^ Damon, James (March 17, 2006). "City Council Votes to Purchase House". The Flat Hat. http://flathat.wm.edu/2006-03-17/story.php?type=1&aid=1. Retrieved 2006-05-30.
- ^ Day,Shawn (September 26, 2007). "Registrar gives nod to students". Daily Press. http://www.dailypress.com/news/local/williamsburg/dp-news_wmvotes_0926sep26,0,4648843.story.
- ^ "Quick Facts" (PDF). http://www.wjcc.k12.va.us/content/admin/superintendent/quickfacts/quickfactsbrochure.pdf. Retrieved 2008-04-05.
- ^ "New ES". http://www.wjcc.k12.va.us/bs/New%20ES.html. Retrieved 2007-12-12.
- ^ "About James River." James River Elementary School. Retrieved on February 24, 2007.
- ^ Whitson, Brian (April 27, 2006). "Community contributions: Students invest more than 300,000 hours". William and Mary News. http://www.wm.edu/news/?id=5786. Retrieved 2006-05-31.
- ^ Christopher Newport University
- ^ University of Richmond
- ^ Old Dominion University
- ^ Norfolk State University
- ^ Hampton University
- ^ Virginia Union University
- ^ "Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport: Location and Directions". Newport News/Williamsburg International Airport. http://www.nnwairport.com/airport-information/location-a-directionshttp://www.nnwairport.com/. Retrieved 2011-02-18.
- ^ "Southeast High Speed Rail". Southeast High Speed Rail. http://www.sehsr.org/. Retrieved 2007-10-15.
- ^ Colonial National Historical Park website
- ^ Duke of Gloucester Street
- ^ Williamsburg Transportation Center
- ^ Williamsburg Area Transport
- ^ Route 121 Hampton Roads Transit
- ^ Green/Gold Lines Williamsburg Area Transport
- ^ Waterworks — City of Newport News
- ^ "Hampton Roads Sanitation District". Hampton Roads Sanitation District. http://www.hrsd.state.va.us/. Retrieved 2008-03-08.
- McCartney, Martha W. (1977) James City County: Keystone of the Commonwealth; James City County, Virginia; Donning and Company; ISBN 0-89865-999-X
External links
- Official City Government Website
- Colonial Williamsburg Official Website
- Convention & Visitors' Bureau (CVB)
- Williamsburg Weekends (the CVB's Weekend Events Guide)

York County 
James City County 
York County  Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg, Virginia 

James City County Colonial Williamsburg HISTORYBattle of Williamsburg • Colonial Williamsburg History • Historic Triangle • Middle Plantation • Rich Neck Plantation
STRUCTURESAbby Aldrich Rockefeller Folk Art Museum • Alexander Craig House • Bassett Hall • Bruton Parish Church • Capitol • Charlton House • Courthouse • DeWitt Wallace Decorative Arts Museum • Governor's Palace • James Semple House • John Crump House • Nicolson Store • Palmer House • Peyton Randolph House • Raleigh Tavern • St. George Tucker House • Wetherburn's Tavern • Wren Building • Wythe House
GEOGRAPHYWilliamsburg • Hampton Roads • Virginia
City of Williamsburg, Virginia Topics 
Attractions Colonial Williamsburg • Busch Gardens Europe • Water Country USA • Williamsburg Winery • Williamsburg Botanical Garden • Colonial Parkway • Bruton Parish Church • Colonial Capitol • DeWitt Wallace Decorative Arts Museum • Go-Karts Plus • Governor's Palace • Raleigh Tavern • Sunken Garden • Williamsburg Botanical Garden • Williamsburg Pottery FactoryMilitary Hampton Roads Metropolitan Area • Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News, VA-NC MSA • Virginia • United States Hampton Roads Virginia Beach-Norfolk-Newport News Metropolitan Area Major Cities Chesapeake · Hampton · Newport News · Norfolk · Portsmouth · Suffolk · Virginia Beach
Counties Currituck · Gloucester · Isle of Wight · James City · Mathews · Surry · York
Other cities Towns Claremont · Dendron · Smithfield · Surry · Windsor
Sub-regions Topics Transportation · People · History · Battle of Hampton Roads ·
Note: Italic indicates independent city not part of any county  Commonwealth of Virginia
Commonwealth of VirginiaRichmond (capital) Topics Climate · Colleges and universities · Colony · Congressional Districts · Culture · Delegations · Demographics · Economy · Education · Environment · Furniture · Geography · Government · Governors · History · Historic Landmarks · Magisterial Districts · Homes · Music · People · Police · Politics · Rights · Rivers · School divisions · Scouting · Slogan · Sports teams · State Fair · State parks · Symbols · Towns · Transportation · Tribes · Visitor Attractions
Regions Allegheny Mountains · Atlantic Coastal Plain · Blue Ridge · Chesapeake Bay · Cumberland Mountains · Delmarva Peninsula · Eastern Shore · Hampton Roads · Middle Peninsula · Northern Neck · Northern Virginia · Piedmont · Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians · Shenandoah Valley · South Hampton Roads · Southside · Southwest Virginia · Tennessee Valley · Tidewater · Tri-Cities · Virginia Peninsula
Metro areas Blacksburg-Christiansburg-Radford · Bluefield · Bristol · Charlottesville · Culpeper · Danville · Fredericksburg · Harrisonburg · Lynchburg · Martinsville · Richmond · Roanoke · Staunton · Hampton Roads · Washington-Arlington-Alexandria · Waynesboro · Winchester
Counties Accomack · Albemarle · Alleghany · Amelia · Amherst · Appomattox · Arlington · Augusta · Bath · Bedford · Bland · Botetourt · Brunswick · Buchanan · Buckingham · Campbell · Caroline · Carroll · Charles City · Charlotte · Chesterfield · Clarke · Craig · Culpeper · Cumberland · Dickenson · Dinwiddie · Essex · Fairfax · Fauquier · Floyd · Fluvanna · Franklin · Frederick · Giles · Gloucester · Goochland · Grayson · Greene · Greensville · Halifax · Hanover · Henrico · Henry · Highland · Isle of Wight · James City · King and Queen · King George · King William · Lancaster · Lee · Loudoun · Louisa · Lunenburg · Madison · Mathews · Mecklenburg · Middlesex · Montgomery · Nelson · New Kent · Northampton · Northumberland · Nottoway · Orange · Page · Patrick · Pittsylvania · Powhatan · Prince Edward · Prince George · Prince William · Pulaski · Rappahannock · Richmond · Roanoke · Rockbridge · Rockingham · Russell · Scott · Shenandoah · Smyth · Southampton · Spotsylvania · Stafford · Surry · Sussex · Tazewell · Warren · Washington · Westmoreland · Wise · Wythe · York
Independent
citiesAlexandria · Bedford · Bristol · Buena Vista · Charlottesville · Chesapeake · Colonial Heights · Covington · Danville · Emporia · Fairfax · Falls Church · Franklin · Fredericksburg · Galax · Hampton · Harrisonburg · Hopewell · Lexington · Lynchburg · Manassas · Manassas Park · Martinsville · Newport News · Norfolk · Norton · Petersburg · Poquoson · Portsmouth · Radford · Richmond · Roanoke · Salem · Staunton · Suffolk · Virginia Beach · Waynesboro · Williamsburg · Winchester
Categories:- Cities in Virginia
- Williamsburg, Virginia
- Rockefeller family
- County seats in Virginia
- Hampton Roads
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.