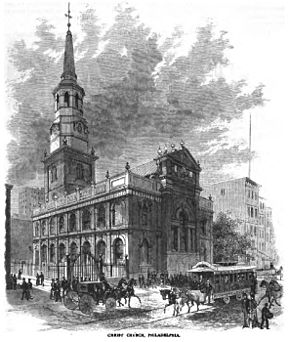- Christ Church (Philadelphia)
-
Christ Church
EpiscopalLocation: 22-26 North 2nd St.
Philadelphia, PennsylvaniaCoordinates: 39°57′2.60″N 75°8′37.90″W / 39.950722°N 75.143861°WCoordinates: 39°57′2.60″N 75°8′37.90″W / 39.950722°N 75.143861°W Built: 1727-1744 Architect: Unknown Architectural style: Georgian Governing body: Christ Church Philadelphia NRHP Reference#: 70000553[1] Added to NRHP: April 15, 1970 Christ Church is an Episcopal church located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1695 by members of the Church of England, who built a small wooden church on the site by the next year. When the congregation outgrew this structure some twenty years later, they decided to erect a new church, the most sumptuous in the colonies. The main body of the church was constructed between 1727 and 1744, and the steeple was added in 1754, making it the tallest building in North America, at 60 meters.[2] Christ Church is considered one of the nation's most beautiful surviving 18th-century structures, a monument to colonial craftsmanship and a handsome example of Georgian architecture. It features a symmetrical, classical façade with arched windows and a simple yet elegant interior with fluted columns and wooden pews. The baptismal font in which William Penn was baptized is still in use at Christ Church; it was sent to Philadelphia in 1697 from All Hallows by the Tower in London.
Contents
History
Christ Church's congregation included 15 signers of the Declaration of Independence. American Revolutionary War leaders who attended Christ Church include George Washington, Robert Morris, Benjamin Franklin and Betsy Ross (after she had been read out of the Quaker meeting house to which she belonged for marrying John Ross, son of an assistant rector at Christ Church). Brass plaques mark the pews where these individuals once sat. At the convening of the First Continental Congress in September 1774, Rector Jacob Duché was summoned to Carpenters' Hall to lead the opening prayers. During the war, the Reverend William White (1748–1836), rector of Christ Church, served as Chaplain to both the Continental Congress and the United States Senate.
As the first Protestant Episcopal church in the country, Christ Church is the birthplace of the American Episcopal Church in the United States. In September 1785, clerical and lay deputies from several states met in Christ Church and organized as a general convention, of which White was chosen president. He prepared a draft constitution for the church as well as an address to the archbishops and bishops of the Church of England, asking for the episcopate at their hands. White was also largely responsible for the liturgy and offices of the first American Book of Common Prayer (published 1789), which were to be submitted to Church of England authorities. At the convention of the Diocese of Pennsylvania in 1786, he was elected its first bishop and sailed for England with Dr. Samuel Provoost of New York, seeking consecration. After passage of a special enabling act by Parliament, White and Provoost were consecrated in early 1787 by the archbishops of Canterbury and York. Bishop White returned to Philadelphia that Easter Sunday. In 1789, under White's direction, the first meeting of the House of Bishops was held at Christ Church, marking the first true General Convention of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America. White was the first Episcopal Bishop of Pennsylvania and served the congregations of Christ Church and St. Peter's Church for decades. White is buried in the church's chancel.
Christ Church is a National Historic Landmark and a unique historic site that continues its original function as an Episcopal parish. More than 250,000 tourists visit the church each year.
Notable interments
Several notable people are buried in the church and adjacent churchyard, including:
- Jacob Broom (1752–1810), signer of the United States Constitution from Delaware[3]
- Pierce Butler (1744–1822), signer of the United States Constitution[3]
- Elizabeth Graeme Ferguson (1739–1801), poet, early American writer[3]
- General John Forbes (1710–1759), British commander during the French and Indian War[3]
- Andrew Hamilton (1676–1741), lawyer known as "The Philadelphia Lawyer"[3]
- Charles Lee (1731–1782), Revolutionary War Continental Major General[4]
- Robert Morris (1734–1806), signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, the Articles of Confederation, and the United States Constitution[3]
- John Penn (1729–1795), governor and proprietor of provincial Pennsylvania
- James Wilson (1742–1798), signer of the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution[3]
- Rev. William White (1748–1836), rector of Saint Peter Church and Christ Church, first Episcopal Bishop of Pennsylvania[3]
Many other notable people are buried at nearby associated Christ Church Burial Ground, including Benjamin Franklin and four other signers of the Declaration of Independence.
References
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 2007-01-23. http://nrhp.focus.nps.gov/natreg/docs/All_Data.html.
- ^ A historical account of Christ Church, Philadelphia, by Benjamin Dorr, Swords, Stanford & Co., N.Y., 1841.
- ^ a b c d e f g h The Graves, Christ Church, Philadelphia, official site
- ^ Gen. Charles Lee at Find A Grave
External links
- Christ Church tourism web site
- Christ Church parish web site
- Christ Church at the Historic American Buildings Survey
- Christ Church at Philadelphia Architects and Buildings
- Christ Episcopal Churchyard at Find-A-Grave
Christ Church (60 m) (1754) · Tenth Presbyterian Church (76 m) (1856) · North American Building (81 m) (1900) · Philadelphia City Hall (167 m) (1901) · One Liberty Place (288 m) (1987) · Comcast Center (297 m) (2008)
Timeline of tallest buildings in Pennsylvania Christ Church (60 m) (1754) · Tenth Presbyterian Church (76 m) (1856) · North American Building (81 m) (1900) · Philadelphia City Hall (167 m) (1901) · Gulf Tower (177 m) (1932) · U.S. Steel Tower (256 m) (1970) · One Liberty Place (288 m) (1987) · Comcast Center (297 m) (2008)
History of Christianity Centuries: 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 11th 12th 13th 14th 15th 16th 17th 18th 19th 20th 21st • Early • Roman • Medieval • Modern
Jesus and the Apostolic Age Background · Ministry · Good News · Crucifixion & Resurrection · Holy Spirit · Gospels · Acts · The 12 · Paul · Acts 15

Ante-Nicene Period Judaism split · Justin Martyr · Ignatius · Persecution · Fathers · Irenaeus · Marcionism · Canon · Tertullian · Montanism · Origen
Christian Empire Constantine the Great · Monasticism · Councils: Nicaea I · Creed · Athanasius · Arianism · Jerome · Augustine · Councils II · III · IV
Eastern Christianity Orthodoxy · Greece · Asia · Church of the East · Oriental Orthodoxy · Coptic · Nestorianism · Syria · Armenia · Ethiopia · Chrysostom · Iconoclasm · Bulgaria · Great Schism · Fall · Ottoman · Russia · America · 20th century
Middle Ages Pelagianism · Gregory I · Celtic · Germanic & Scandinavian · Kievan Rus' · Investiture · Anselm · Abelard · Bernard of Clairvaux · Crusades · Inquisition · Scholasticism · Dominic · Francis · Bonaventure · Aquinas · Wycliffe · Avignon · Papal Schism · Jan Hus · Conciliarism
Protestant
ReformationProtestantism · Erasmus · Five solas · Eucharist · Calvinist v. Arminian · Arminianism · Dort · Wars
Lutheranism · Martin Luther · 95 Theses · Diet of Worms · Melanchthon · Orthodoxy · Eucharist · Book of Concord
Reformed · Zwingli · Calvin · Calvinism history · Scotland · Knox · TULIP · Dort · Westminster
Anglicanism · Timeline · Henry VIII · Cranmer · Settlement · 39 Articles · Common Prayer · Puritans · Civil War
Anabaptism · Radical Reformation · Grebel · Swiss Brethren · Müntzer · Martyrs' Synod · Menno Simons · SmythCatholicism Primacy development · Papacy · Timeline · Lateran IV · Trent · Counter-Reformation · Thomas More · Leo X · Guadalupe · Jesuits · Jansenists · Xavier · Monastery dissolution · Wars · Teresa · Vatican I & II · Modernism
Modern Christianity
and RevivalismEnglish denominations · Baptists · Congregationalism · Great Awakening · Methodism · Millerism · Pietism · Neo- & Old Lutherans · Restoration Movement · Jehovah's Witnesses · Mormonism · Seventh-day Adventism
Industrial Age Age of Ideologies Timeline · Missions Timeline · Martyrs · Theology · Eastern Orthodoxy · Oriental Orthodoxy · Protestantism · Catholicism
Categories:- Churches in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
- National Register of Historic Places in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
- 1695 establishments
- Religious organizations established in the 1690s
- Religious buildings completed in 1727
- Episcopal churches in Pennsylvania
- Buildings of religious function on the National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania
- National Historic Landmarks in Pennsylvania
- Anglican congregations established in the 17th century
- Reportedly haunted locations in the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.