- Che Guevara
-
"Che" redirects here. For other uses, see Che (disambiguation).
Che Guevara 
"Guerrillero Heroico"
Che Guevara at the La Coubre memorial service.
Taken by Alberto Korda on March 5, 1960.Born Ernesto Guevara
June 14, 1928 [1]
Rosario, Santa Fe, ArgentinaDied October 9, 1967 (aged 39)
La Higuera, Vallegrande, BoliviaCause of death Executed Resting place Che Guevara Mausoleum
Santa Clara, CubaOrganization 26th of July Movement, United Party of the Cuban Socialist Revolution,[2] National Liberation Army (Bolivia) Religion None (Marxist humanist)[3][4][5] Spouse Hilda Gadea (1955–1959)
Aleida March (1959-1967, his death)Children Hilda (1956–1995), Aleida (b. 1960), Camilo (b. 1962), Celia (b. 1963), Ernesto (b. 1965) Signature 
Ernesto "Che" Guevara (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈtʃe geˈβaɾa];[6] June 14,[1] 1928 – October 9, 1967), commonly known as el Che or simply Che, was an Argentine Marxist revolutionary, physician, author, intellectual, guerrilla leader, diplomat and military theorist. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia within popular culture.[7]
As a young medical student, Guevara traveled throughout Latin America and was radically transformed by the endemic poverty and alienation he witnessed.[8] His experiences and observations during these trips led him to conclude that the region's ingrained economic inequalities were an intrinsic result of capitalism, monopolism, neocolonialism, and imperialism, with the only remedy being world revolution.[9] This belief prompted his involvement in Guatemala's social reforms under President Jacobo Arbenz, whose eventual CIA-assisted overthrow solidified Guevara's political ideology. Later, while living in Mexico City, he met Raúl and Fidel Castro, joined their 26th of July Movement, and sailed to Cuba aboard the yacht, Granma, with the intention of overthrowing U.S.-backed Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista.[10] Guevara soon rose to prominence among the insurgents, was promoted to second-in-command, and played a pivotal role in the victorious two year guerrilla campaign that deposed the Batista regime.[11]
Following the Cuban Revolution, Guevara performed a number of key roles in the new government. These included reviewing the appeals and firing squads for those convicted as war criminals during the revolutionary tribunals,[12] instituting agrarian reform as minister of industries, helping spearhead a successful nationwide literacy campaign, serving as both national bank president and instructional director for Cuba’s armed forces, and traversing the globe as a diplomat on behalf of Cuban socialism. Such positions also allowed him to play a central role in training the militia forces who repelled the Bay of Pigs Invasion[13] and bringing the Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles to Cuba which precipitated the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis.[14] Additionally, he was a prolific writer and diarist, composing a seminal manual on guerrilla warfare, along with a best-selling memoir about his youthful motorcycle journey across South America. Guevara left Cuba in 1965 to foment revolution abroad, first unsuccessfully in Congo-Kinshasa and later in Bolivia, where he was captured by CIA-assisted Bolivian forces and executed.[15]
Guevara remains both a revered and reviled historical figure, polarized in the collective imagination in a multitude of biographies, memoirs, essays, documentaries, songs, and films. As a result of his perceived martyrdom, poetic invocations for class struggle, and desire to create the consciousness of a "new man" driven by moral rather than material incentives; he has evolved into a quintessential icon of various leftist-inspired movements. Time magazine named him one of the 100 most influential people of the 20th century,[16] while an Alberto Korda photograph of him entitled Guerrillero Heroico (shown), was declared "the most famous photograph in the world".[17]
Contents
Early life
Ernesto Guevara was born to Celia de la Serna y Llosa and Ernesto Guevara Lynch on June 14, 1928[1] in Rosario, Argentina, the eldest of five children in an Argentine family of Spanish, Basque and Irish descent.[18] In lieu of his parents' surnames, his legal name (Ernesto Guevara) will sometimes appear with de la Serna, or Lynch accompanying it. In reference to Che's "restless" nature, his father declared "the first thing to note is that in my son's veins flowed the blood of the Irish rebels."[19] Very early on in life Ernestito (as he was then called) developed an "affinity for the poor."[20] Growing up in a family with leftist leanings, Guevara was introduced to a wide spectrum of political perspectives even as a boy.[21] His father, a staunch supporter of Republicans from the Spanish Civil War, often hosted many veterans from the conflict in the Guevara home.[22]
Though suffering crippling bouts of acute asthma that were to afflict him throughout his life, he excelled as an athlete, enjoying swimming, football, golf, and shooting; while also becoming an "untiring" cyclist.[23][24] He was an avid rugby union player,[25] and played at fly-half for Club Universitario de Buenos Aires.[26] His rugby playing earned him the nickname "Fuser"—a contraction of El Furibundo (raging) and his mother's surname, de la Serna—for his aggressive style of play.[27]
Guevara learned chess from his father and began participating in local tournaments by age 12. During adolescence and throughout his life he was passionate about poetry, especially that of Pablo Neruda, John Keats, Antonio Machado, Federico García Lorca, Gabriela Mistral, César Vallejo, and Walt Whitman.[28] He could also recite Rudyard Kipling's "If—" and José Hernández's "Martín Fierro" from memory.[28] The Guevara home contained more than 3,000 books, which allowed Guevara to be an enthusiastic and eclectic reader, with interests including Karl Marx, William Faulkner, André Gide, Emilio Salgari and Jules Verne.[29] Additionally, he enjoyed the works of Jawaharlal Nehru, Franz Kafka, Albert Camus, Vladimir Lenin, and Jean-Paul Sartre; as well as Anatole France, Friedrich Engels, H. G. Wells, and Robert Frost.[30]
As he grew older, he developed an interest in the Latin American writers Horacio Quiroga, Ciro Alegría, Jorge Icaza, Rubén Darío, and Miguel Asturias.[30] Many of these authors' ideas he cataloged in his own handwritten notebooks of concepts, definitions, and philosophies of influential intellectuals. These included composing analytical sketches of Buddha and Aristotle, along with examining Bertrand Russell on love and patriotism, Jack London on society, and Nietzsche on the idea of death. Sigmund Freud's ideas fascinated him as he quoted him on a variety of topics from dreams and libido to narcissism and the oedipus complex.[30] His favorite subjects in school included philosophy, mathematics, engineering, political science, sociology, history and archaeology.[31][32]
Years later, a February 13, 1958, declassified CIA 'biographical and personality report' would make note of Guevara’s wide range of academic interests and intellect, describing him as "quite well read" while adding that "Che is fairly intellectual for a Latino."[33]
Motorcycle journey
Main articles: The Motorcycle Diaries (book) and The Motorcycle Diaries (film)In 1948, Guevara entered the University of Buenos Aires to study medicine. His "hunger to explore the world"[34] led him to intersperse his collegiate pursuits with two long introspective journeys that would fundamentally change the way he viewed himself and the contemporary economic conditions in Latin America. The first expedition in 1950 was a 4,500 kilometer (2,800 mi) solo trip through the rural provinces of northern Argentina on a bicycle on which he installed a small motor.[35] This was followed in 1951 by a nine month 8,000 kilometer (5,000 mi) continental motorcycle trek through most of South America. For the latter, he took a year off from studies to embark with his friend Alberto Granado, with the final goal of spending a few weeks volunteering at the San Pablo Leper colony in Peru, on the banks of the Amazon River.
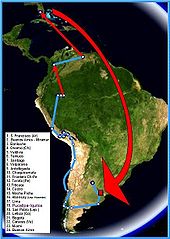 A map of Guevara's 1952 trip with Alberto Granado. The red arrows correspond to air travel.
A map of Guevara's 1952 trip with Alberto Granado. The red arrows correspond to air travel.
 Guevara (right) with Alberto Granado (left) aboard their "Mambo-Tango" wooden raft on the Amazon River in June of 1952. The raft was a gift from the lepers whom they had treated.[36]
Guevara (right) with Alberto Granado (left) aboard their "Mambo-Tango" wooden raft on the Amazon River in June of 1952. The raft was a gift from the lepers whom they had treated.[36]
In Chile, Guevara found himself enraged by the working conditions of the miners in Anaconda's Chuquicamata copper mine; and moved by his overnight encounter in the Atacama Desert with a persecuted communist couple who didn't even own a blanket, describing them as "the shivering flesh-and-blood victims of capitalist exploitation."[37] Additionally, on the way to Machu Picchu high in the Andes, he was struck by the crushing poverty of the remote rural areas, where peasant farmers worked small plots of land owned by wealthy landlords.[38] Later on his journey, Guevara was especially impressed by the camaraderie among those living in a Leper Colony, stating "The highest forms of human solidarity and loyalty arise among such lonely and desperate people."[38] Guevara used notes taken during this trip to write an account entitled The Motorcycle Diaries, which later became a New York Times best-seller,[39] and was adapted into a 2004 award-winning film of the same name.
In total, the journey took Guevara through Argentina, Chile, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Panama, and to Miami, before returning home to Buenos Aires. By trip's end, he came to view Latin America not as collection of separate nations, but as a single entity requiring a continent-wide liberation strategy. His conception of a borderless, united Hispanic America sharing a common 'Latino' heritage was a theme that prominently recurred during his later revolutionary activities. Upon returning to Argentina, he completed his studies and received his medical degree in June 1953, making him officially "Dr. Ernesto Guevara."[40][41]
"A motorcycle journey the length of South America awakened him to the injustice of U.S. domination in the hemisphere, and to the suffering colonialism brought to its original inhabitants."
— George Galloway, British politician [42]Guevara later remarked that through his travels of Latin America, he came in "close contact with poverty, hunger and disease" along with the "inability to treat a child because of lack of money" and "stupefaction provoked by the continual hunger and punishment" that leads a father to "accept the loss of a son as an unimportant accident." It was these experiences which Guevara cites as convincing him that in order to "help these people", he needed to leave the realm of medicine, and consider the political arena of armed struggle.[8]
Guatemala, Arbenz and United Fruit
Main article: 1954 Guatemalan coup d'état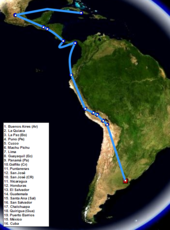 A map of Che Guevara's travels between 1953 and 1956, including his journey aboard the Granma
A map of Che Guevara's travels between 1953 and 1956, including his journey aboard the Granma
On July 7, 1953, Guevara set out again, this time to Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras and El Salvador. On December 10, 1953, before leaving for Guatemala, Guevara sent an update to his Aunt Beatriz from San José, Costa Rica. In the letter Guevara speaks of traversing through the "dominions" of the United Fruit Company, which convinced him "how terrible" the "Capitalist octopuses" were.[43] This affirmed indignation carried the "head hunting tone" that he adopted in order to frighten his more Conservative relatives, and ends with Guevara swearing on an image of the then recently deceased Joseph Stalin, not to rest until these "octopuses have been vanquished."[44] Later that month, Guevara arrived in Guatemala where President Jacobo Arbenz Guzmán headed a democratically elected government that, through land reform and other initiatives, was attempting to end the latifundia system. To accomplish this, President Arbenz had enacted a major land reform program, where all uncultivated portions of large land holdings were to be expropriated and redistributed to landless peasants. The biggest land owner, and one most affected by the reforms, was the United Fruit Company, from which the Arbenz government had already taken more than 225,000 acres (910 km2) of uncultivated land.[45] Pleased with the road the nation was heading down, Guevara decided to settle down in Guatemala so as to "perfect himself and accomplish whatever may be necessary in order to become a true revolutionary."[46]
In Guatemala City, Guevara sought out Hilda Gadea Acosta, a Peruvian economist who was well-connected politically as a member of the left-leaning Alianza Popular Revolucionaria Americana (APRA, American Popular Revolutionary Alliance). She introduced Guevara to a number of high-level officials in the Arbenz government. Guevara then established contact with a group of Cuban exiles linked to Fidel Castro through the July 26, 1953 attack on the Moncada Barracks in Santiago de Cuba. During this period he acquired his famous nickname, due to his frequent use of the Argentine diminutive interjection che, a vocative casual speech filler used to call attention or ascertain comprehension, similarly to both "bro" or the Canadian phrase "eh".[47]
Guevara's attempts to obtain a medical internship were unsuccessful and his economic situation was often precarious. On May 15, 1954, a shipment of Škoda infantry and light artillery weapons was sent from Communist Czechoslovakia for the Arbenz Government and arrived in Puerto Barrios.[48] As a result, the U.S. CIA sponsored an army which invaded the country and installed the right-wing dictatorship of Carlos Castillo Armas.[46] Guevara was eager to fight on behalf of Arbenz and joined an armed militia organized by the Communist Youth for that purpose, but frustrated with the group's inaction, he soon returned to medical duties. Following the coup, he again volunteered to fight, but soon after, Arbenz took refuge in the Mexican Embassy and told his foreign supporters to leave the country. Guevara’s repeated calls to resist were noted by supporters of the coup, and he was marked for murder.[49] After Hilda Gadea was arrested, Guevara sought protection inside the Argentine consulate, where he remained until he received a safe-conduct pass some weeks later and made his way to Mexico.[50] He married Gadea in Mexico in September 1955.[51]
The overthrow of the Arbenz regime cemented Guevara's view of the United States as an imperialist power that would oppose and attempt to destroy any government that sought to redress the socioeconomic inequality endemic to Latin America and other developing countries. In speaking about the coup Guevara stated:
"The last Latin American revolutionary democracy – that of Jacobo Arbenz – failed as a result of the cold premeditated aggression carried out by the U.S.A. Its visible head was the Secretary of State John Foster Dulles, a man who, through a rare coincidence, was also a stockholder and attorney for the United Fruit Company."[49]Guevara's conviction that Marxism achieved through armed struggle and defended by an armed populace was the only way to rectify such conditions was thus strengthened.[52] Gadea wrote later, "It was Guatemala which finally convinced him of the necessity for armed struggle and for taking the initiative against imperialism. By the time he left, he was sure of this."[53]
Mexico City and preparation
 Guevara with Hilda Gadea at Chichén Itzá on their honeymoon trip
Guevara with Hilda Gadea at Chichén Itzá on their honeymoon trip
Guevara arrived in Mexico City in early September 1954, and worked in the allergy section of the General Hospital. In addition he gave lectures on medicine at the National Autonomous University of Mexico and worked as a news photographer for Latina News Agency.[54] His first wife Hilda notes in her memoir My Life with Che, that for a while, Guevara considered going to work as a doctor in Africa and that he continued to be deeply troubled by the poverty around him.[55] In one instance, Hilda describes Guevara's obsession with an elderly washerwoman whom he was treating, remarking that he saw her as "representative of the most forgotten and exploited class." Hilda later found a poem that Che had dedicated to the old woman, containing "a promise to fight for a better world, for a better life for all the poor and exploited."[55]
During this time he renewed his friendship with Ñico López and the other Cuban exiles whom he had met in Guatemala. In June 1955, López introduced him to Raúl Castro who subsequently introduced him to his older brother, Fidel Castro, the revolutionary leader who had formed the 26th of July Movement and was now plotting to overthrow the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista. During a long conversation with Fidel on the night of their first meeting, Guevara concluded that the Cuban's cause was the one for which he had been searching and before daybreak he had signed up as a member of the July 26 Movement.[56] Despite their "contrasting personalities", from this point on Che and Fidel began to foster what dual biographer Simon Reid-Henry deems a "revolutionary friendship that would change the world", as a result of their coinciding commitment to anti-imperialism.[57]
By this point in Guevara’s life, he deemed that U.S.-controlled conglomerates installed and supported repressive regimes around the world. In this vein, he considered Batista a "U.S. puppet whose strings needed cutting."[58] Although he planned to be the group's combat medic, Guevara participated in the military training with the members of the Movement. The key portion of training involved learning hit and run tactics of guerrilla warfare. Guevara and the others underwent arduous 15-hour marches over mountains, across rivers, and through the dense undergrowth, learning and perfecting the procedures of ambush and quick retreat. From the start Guevara was Alberto Bayo's "prize student" among those in training, scoring the highest on all of the tests given.[59] At the end of the course, he was called "the best guerrilla of them all" by their instructor, General Bayo.[60]
Cuban Revolution
Invasion, warfare and Santa Clara
 Guevara atop a mule in Las Villas province, Cuba, November 1958
Guevara atop a mule in Las Villas province, Cuba, November 1958
The first step in Castro's revolutionary plan was an assault on Cuba from Mexico via the Granma, an old, leaky cabin cruiser. They set out for Cuba on November 25, 1956. Attacked by Batista's military soon after landing, many of the 82 men were either killed in the attack or executed upon capture; only 22 found each other afterwards.[61] Guevara wrote that it was during this bloody confrontation that he laid down his medical supplies and picked up a box of ammunition dropped by a fleeing comrade, finalizing his symbolic transition from physician to combatant.
Only a small band of revolutionaries survived to re-group as a bedraggled fighting force deep in the Sierra Maestra mountains, where they received support from the urban guerrilla network of Frank País, the 26th of July Movement, and local campesinos. With the group withdrawn to the Sierra, the world wondered whether Castro was alive or dead until early 1957 when the interview by Herbert Matthews appeared in The New York Times. The article presented a lasting, almost mythical image for Castro and the guerrillas. Guevara was not present for the interview, but in the coming months he began to realize the importance of the media in their struggle. Meanwhile, as supplies and morale diminished, and with an allergy to mosquito bites which resulted in agonizing walnut-sized cysts on his body,[62] Guevara considered these "the most painful days of the war."[63]
During Guevara’s time living hidden among the poor subsistence farmers of the Sierra Maestra mountains, he discovered that there were no schools, no electricity, minimal access to healthcare, and more than 40 percent of the adults were illiterate.[64] As the war continued, Guevara became an integral part of the rebel army and "convinced Castro with competence, diplomacy and patience."[11] Guevara set up factories to make grenades, built ovens to bake bread, taught new recruits about tactics, and organized schools to teach illiterate campesinos to read and write.[11] Moreover, Guevara established health clinics, workshops to teach military tactics, and a newspaper to disseminate information.[65] The man who three years later would be dubbed by Time Magazine: "Castro's brain", at this point was promoted by Fidel Castro to Comandante (commander) of a second army column.[11]
As the only other ranked Comandante besides Fidel Castro, Guevara was a harsh disciplinarian who sometimes shot defectors. Deserters were punished as traitors, and Guevara was known to send squads to track those seeking to go AWOL.[66] As a result, Guevara became feared for his brutality and ruthlessness.[67] During the guerrilla campaign, Guevara was also responsible for the sometimes summary execution of a number of men accused of being informers, deserters or spies.[68] In his diaries, Guevara described the first such execution of Eutimio Guerra, a peasant army guide who admitted treason when it was discovered he accepted the promise of ten thousand pesos for repeatedly giving away the rebel's position for attack by the Cuban air force.[69] Such information also allowed Batista's army to burn the homes of rebel-friendly peasants.[69] Upon Guerra's request that they "end his life quickly",[69] Che stepped forward and shot him in the head, writing "The situation was uncomfortable for the people and for Eutimio so I ended the problem giving him a shot with a .32 pistol in the right side of the brain, with exit orifice in the right temporal [lobe]."[70] His scientific notations and matter-of-fact description, suggested to one biographer a "remarkable detachment to violence" by that point in the war.[70] Later, Guevara published a literary account of the incident entitled "Death of a Traitor", where he transfigured Eutimio's betrayal and pre-execution request that the revolution "take care of his children", into a "revolutionary parable about redemption through sacrifice."[70]
 Smoking a pipe at his guerrilla base in the Escambray Mountains.
Smoking a pipe at his guerrilla base in the Escambray Mountains.
Although he maintained a demanding and harsh disposition, Guevara also viewed his role of commander as one of a teacher, entertaining his men during breaks between engagements with readings from the likes of Robert Louis Stevenson, Cervantes, and Spanish lyric poets.[71] Together with this role, and inspired by José Martí's principle of "literacy without borders", Guevara further ensured that his rebel fighters made daily time to teach the uneducated campesinos with whom they lived and fought to read and write, in what Guevara termed the "battle against ignorance."[64]
His commanding officer Fidel Castro has described Guevara as intelligent, daring, and an exemplary leader who "had great moral authority over his troops."[72] Castro further remarked that Guevara took too many risks, even having a "tendency toward foolhardiness."[73] Guevara's teenage lieutenant, Joel Iglesias, recounts such actions in his diary, noting that Guevara's behavior in combat even brought admiration from the enemy. On one occasion Iglesias recounts the time he had been wounded in battle, stating "Che ran out to me, defying the bullets, threw me over his shoulder, and got me out of there. The guards didn't dare fire at him ... later they told me he made a great impression on them when they saw him run out with his pistol stuck in his belt, ignoring the danger, they didn't dare shoot."[74]
Guevara was instrumental in creating the clandestine radio station Radio Rebelde (Rebel Radio) in February 1958, which broadcast news to the Cuban people with statements by the 26th of July movement, and provided radiotelephone communication between the growing number of rebel columns across the island. Guevara had apparently been inspired to create the station by observing the effectiveness of CIA supplied radio in Guatemala in ousting the government of Jacobo Arbenz Guzmán.[75]
In late July 1958, Guevara played a critical role in the Battle of Las Mercedes by using his column to halt a force of 1,500 men called up by Batista's General Cantillo in a plan to encircle and destroy Castro's forces. Years later, Major Larry Bockman of the United States Marine Corps would analyze and describe Che's tactical appreciation of this battle as "brilliant."[76] During this time Guevara also became an "expert" at leading hit and run tactics against Batista’s army, and then fading back into the countryside before the army could counterattack.[77]
As the war extended, Guevara led a new column of fighters dispatched westward for the final push towards Havana. Travelling by foot, Guevara embarked on a difficult 7 week march only travelling at night to avoid ambush, and often not eating for several days.[78] In the closing days of December 1958, Guevara’s task was to cut the island in half by taking Las Villas province. In a matter of days he executed a series of "brilliant tactical victories" that gave him control of all but the province’s capital city of Santa Clara.[78] Guevara then directed his "suicide squad" in the attack on Santa Clara, that became the final decisive military victory of the revolution.[79][80] In the six weeks leading up to the Battle of Santa Clara there were times when his men were completely surrounded, outgunned, and overrun. Che's eventual victory despite being outnumbered 10:1, remains in the view of some observers a "remarkable tour de force in modern warfare."[81]
 After the battle of Santa Clara, January 1, 1959
After the battle of Santa Clara, January 1, 1959
Radio Rebelde broadcast the first reports that Guevara's column had taken Santa Clara on New Year's Eve 1958. This contradicted reports by the heavily controlled national news media, which had at one stage reported Guevara's death during the fighting. At 3 am on January 1, 1959, upon learning that his generals were negotiating a separate peace with Guevara, Fulgencio Batista boarded a plane in Havana and fled for the Dominican Republic, along with an amassed "fortune of more than $ 300,000,000 through graft and payoffs."[82] The following day on January 2, Guevara entered Havana to take final control of the capital.[83] Fidel Castro took 6 more days to arrive, as he stopped to rally support in several large cities on his way to rolling victoriously into Havana on January 8, 1959. In mid-January 1959, Guevara went to live at a summer villa in Tarara to recover from a violent asthma attack.[84] While there he started the Tarara Group, a group that debated and formed the new plans for Cuba's social, political, and economic development.[85] In addition, Che began to write his book Guerrilla Warfare while resting at Tarara.[85]
In February, the revolutionary government proclaimed Guevara "a Cuban citizen by birth" in recognition of his role in the triumph.[86] When Hilda Gadea arrived in Cuba in late January, Guevara told her that he was involved with another woman, and the two agreed on a divorce,[87] which was finalized on May 22.[88] On June 2, 1959, he married Aleida March, a Cuban-born member of the 26th of July movement with whom he had been living since late 1958. Guevara returned to the seaside village of Tarara in June for his honeymoon with Aleida.[89] Guevara had children from both his marriages, and one illegitimate child, as follows: With Hilda Gadea (married August 18, 1955; divorced May 22, 1959), Hilda Beatriz Guevara Gadea, born February 15, 1956 in Mexico City; died August 21, 1995 in Havana, Cuba; with Aleida March (married June 2, 1959), Aleida Guevara March, born November 24, 1960 in Havana, Cuba, Camilo Guevara March, born May 20, 1962 in Havana, Cuba, Celia Guevara March, born June 14, 1963 in Havana, Cuba, and Ernesto Guevara March, born February 24, 1965 in Havana, Cuba; and with Lilia Rosa López (extramarital), Omar Pérez, born March 19, 1964 in Havana, Cuba.[90]
La Cabaña, land reform, and literacy
 (right to left) Rebel leader Camilo Cienfuegos, Cuban President Manuel Urrutia, and Guevara (January 1959)
(right to left) Rebel leader Camilo Cienfuegos, Cuban President Manuel Urrutia, and Guevara (January 1959)
The first major political crisis arose over what to do with the captured Batista officials who had been responsible for the worst of the repression.[91] During the rebellion against Batista's dictatorship, the general command of the rebel army, led by Fidel Castro, introduced into the liberated territories the 19th century penal law commonly known as the Ley de la Sierra (Law of the Sierra).[92] This law included the death penalty for extremely serious crimes, whether perpetrated by the Batista regime or by supporters of the revolution. In 1959, the revolutionary government extended its application to the whole of the republic and to those it considered war criminals, captured and tried after the revolution. According to the Cuban Ministry of Justice, this latter extension was supported by the majority of the population, and followed the same procedure as those in the Nuremberg Trials held by the Allies after World War II.[93]
To implement a portion of this plan, Castro named Guevara commander of the La Cabaña Fortress prison, for a five-month tenure (January 2 through June 12, 1959).[94] Guevara was charged with purging the Batista army and consolidating victory by exacting "revolutionary justice" against those considered to be traitors, chivatos (informants) or war criminals.[95] Serving in the post as commander of La Cabaña, Guevara reviewed the appeals of those convicted during the revolutionary tribunal process.[12] On some occasions the penalty delivered by the tribunal was death by firing squad.[96] Raúl Gómez Treto, senior legal advisor to the Cuban Ministry of Justice, has argued that the death penalty was justified in order to prevent citizens themselves from taking justice into their own hands, as happened twenty years earlier in the anti-Machado rebellion.[97] Biographers note that in January 1959, the Cuban public was in a "lynching mood",[98] and point to a survey at the time showing 93% public approval for the tribunal process.[12] Moreover, a January 22, 1959, Universal Newsreel broadcast in the U.S. and narrated by Ed Herlihy, featured Fidel Castro asking an estimated one million Cubans whether they approved of the executions, and was met with a roaring "¡Si!" (yes).[99] With 20,000 Cubans estimated to have been killed at the hands of Batista's collaborators,[100] and many of the war criminals sentenced to death accused of torture and physical atrocities,[12] the newly empowered government carried out executions, punctuated by cries from the crowds of "¡paredón!" (to the wall),[91] which biographer Jorge Castañeda describes as "without respect for due process."[101]
"I have yet to find a single credible source pointing to a case where Che executed 'an innocent'. Those persons executed by Guevara or on his orders were condemned for the usual crimes punishable by death at times of war or in its aftermath: desertion, treason or crimes such as rape, torture or murder. I should add that my research spanned five years, and included anti-Castro Cubans among the Cuban-American exile community in Miami and elsewhere."
Although there are differences between different accounts, it is estimated that several hundred people were executed nationwide during this time, with estimates for Guevara's jurisdictional death total at La Cabaña ranging from 55 to 164.[103] Conflicting views exist of Guevara's attitude towards the executions at La Cabaña. Some exiled opposition biographers report that he relished the rituals of the firing squad, and organized them with gusto, while others relate that Guevara pardoned as many prisoners as he could.[101] What is acknowledged by all sides is that Guevara had become a "hardened" man, who had no qualms about the death penalty or summary and collective trials. If the only way to "defend the revolution was to execute its enemies, he would not be swayed by humanitarian or political arguments."[101] This is further confirmed by a February 5, 1959, letter to Luis Paredes López in Buenos Aires where Guevara states unequivocally "The executions by firing squads are not only a necessity for the people of Cuba, but also an imposition of the people."[104]
Along with ensuring "revolutionary justice", the other key early platform of Guevara's was establishing agrarian land reform. Almost immediately after the success of the revolution on January 27, 1959, Guevara made one of his most significant speeches where he talked about "the social ideas of the rebel army." During this speech, he declared that the main concern of the new Cuban government was "the social justice that land redistribution brings about."[105] A few months later on May 17, 1959, the Agrarian Reform Law crafted by Guevara went into effect, limiting the size of all farms to 1,000 acres (4.0 km2). Any holdings over these limits were expropriated by the government and either redistributed to peasants in 67-acre (270,000 m2) parcels or held as state run communes.[106] The law also stipulated that sugar plantations could not be owned by foreigners.[107]
 Guevara in his trademark olive-green military fatigues and beret.
Guevara in his trademark olive-green military fatigues and beret.
On June 12, 1959, Castro sent Guevara out on a three-month tour of 14 mostly Bandung Pact countries (Morocco, Sudan, Egypt, Syria, Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka, Burma, Thailand, Indonesia, Japan, Yugoslavia, Greece) and the cities of Singapore and Hong Kong.[108] Sending Guevara away from Havana allowed Castro to appear to be distancing himself from Guevara and his Marxist sympathies, which troubled both the United States and some of Castro's July 26 Movement members.[109] Guevara spent 12 days in Japan (July 15–27), participating in negotiations aimed at expanding Cuba's trade relations with that nation. During the visit, he refused to visit and lay a wreath at Japan's Tomb of the Unknown Soldier commemorating soldiers lost during World War II, remarking that the Japanese "imperialists" had "killed millions of Asians."[110] In its place, Guevara stated that he would instead visit Hiroshima, where the American military had detonated an atom-bomb 14 years earlier.[110] Despite his denunciation of Imperial Japan, Guevara also considered President Truman a "macabre clown" for the bombings,[111] and after visiting Hiroshima and its Peace Memorial Museum, he sent back a postcard to Cuba stating "In order to fight better for peace, one must look at Hiroshima."[112]
Upon Guevara's return to Cuba in September 1959, it was evident that Castro now had more political power. The government had begun land seizures included in the agrarian reform law, but was hedging on compensation offers to landowners, instead offering low interest "bonds", a step which put the U.S. on alert. At this point the affected wealthy cattlemen of Camagüey mounted a campaign against the land redistributions, and enlisted the newly disaffected rebel leader Huber Matos, who along with the anti-Communist wing of the 26th of July Movement, joined them in denouncing the "Communist encroachment."[113] During this time Dominican dictator Rafael Trujillo was offering assistance to the "Anti-Communist Legion of the Caribbean" which was training in the Dominican Republic. This multi-national force, composed mostly of Spaniards and Cubans, but also of Croatians, Germans, Greeks, and right-wing mercenaries, was plotting to topple Castro's new regime.[113]
Such threats were heightened when, on March 4, 1960, two massive explosions ripped through the French freighter La Coubre, which was carrying Belgian munitions from the port of Antwerp, and was docked in Havana Harbor. The blasts killed at least 76 people and injured several hundred, with Guevara personally providing first aid to some of the victims. Cuban leader Fidel Castro immediately accused the CIA of "an act of terrorism" and held a state funeral the following day for the victims of the blast.[114] It was at the memorial service that Alberto Korda took the famous photograph of Guevara, now known as Guerrillero Heroico.[115]
These perceived threats prompted Castro to further eliminate "counter-revolutionaries", and to utilize Guevara to drastically increase the speed of land reform. To implement this plan, a new government agency, the National Institute of Agrarian Reform (INRA), was established to administer the new Agrarian Reform law. INRA quickly became the most important governing body in the nation, with Guevara serving as its head in his capacity as minister of industries.[107] Under Guevara's command, INRA established its own 100,000 person militia, used first to help the government seize control of the expropriated land and supervise its distribution, and later to set up cooperative farms. The land confiscated included 480,000 acres (1,900 km2) owned by U.S. corporations.[107] Months later, as retaliation, U.S President Dwight D. Eisenhower sharply reduced U.S. imports of Cuban sugar (Cuba’s main cash crop), thus leading Guevara on July 10, 1960, to address over 100,000 workers in front of the Presidential Palace at a rally called to denounce U.S. "economic aggression."[116]
Along with land reform, one of the primary areas that Guevara stressed needed national improvement was in the area of literacy. Before 1959 the official literacy rate for Cuba was between 60–76%, with educational access in rural areas and a lack of instructors the main determining factors.[117] As a result, the Cuban government at Guevara's behest dubbed 1961 the "year of education", and mobilized over 100,000 volunteers into "literacy brigades", who were then sent out into the countryside to construct schools, train new educators, and teach the predominately illiterate Guajiros (peasants) to read and write.[64][117] Unlike many of Guevara's later economic initiatives, this campaign was "a remarkable success."[117] By the completion of the Cuban Literacy Campaign, 707,212 adults had been taught to read and write, raising the national literacy rate to 96%.[117]
"Guevara was like a father to me ... he educated me. He taught me to think. He taught me the most beautiful thing which is to be human."
— Urbano (aka Leonardo Tamayo),
fought with Guevara in Cuba and Bolivia [118]Accompanying literacy, Guevara was also concerned with establishing universal access to higher education. To accomplish this, the new regime introduced affirmative action to the universities.[119] While announcing this new commitment, Guevara told the gathered faculty and students at the University of Las Villas that the days when education was "a privilege of the white middle class" had ended. "The University" he said, "must paint itself black, mulatto, worker, and peasant." If it didn’t, he warned, the people would break down its doors "and paint the University the colors they like."[119]
The "New Man", Bay of Pigs and Missile Crisis
Main articles: Bay of Pigs Invasion and Cuban Missile Crisis"Man truly achieves his full human condition when he produces without being compelled by the physical necessity of selling himself as a commodity."— Che Guevara, Man and Socialism in Cuba [120]At this stage, Guevara acquired the additional position of Finance Minister, as well as President of the National Bank. These appointments, combined with his existing position as Minister of Industries, placed Guevara at the zenith of his power, as the "virtual czar" of the Cuban economy.[116] As a consequence of his position at the head of the central bank, it was now Guevara's duty to sign the Cuban currency, which per custom would bear his signature. Instead of using his full name, he signed the bills solely "Che."[121] It was through this symbolic act, which horrified many in the Cuban financial sector, that Guevara signaled his distaste for money and the class distinctions it brought about.[121] Guevara's long time friend Ricardo Rojo later remarked that "the day he signed Che on the bills, (he) literally knocked the props from under the widespread belief that money was sacred."[122]
 Meeting with French existentialist philosophers Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir in March 1960. In addition to Spanish, Guevara was fluent in French.[123]
Meeting with French existentialist philosophers Jean-Paul Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir in March 1960. In addition to Spanish, Guevara was fluent in French.[123]
Guevara's first desired economic goal, which coincided with his aversion for wealth, was to see a nation-wide elimination of material incentives in favor of moral ones. He viewed capitalism as a "contest among wolves" where "one can only win at the cost of others," and thus desired to see the creation of a "new man and woman."[124] Guevara continually stressed that a socialist economy in itself is not "worth the effort, sacrifice, and risks of war and destruction" if it ends up encouraging "greed and individual ambition at the expense of collective spirit."[125] A primary goal of Guevara's thus became to reform "individual consciousness" and values to produce better workers and citizens.[125] In his view, Cuba's "new man" would be able to overcome the "egotism" and "selfishness" that he loathed and discerned was uniquely characteristic of individuals in capitalist societies.[125] In describing this new method of "development", Guevara stated:
"There is a great difference between free-enterprise development and revolutionary development. In one of them, wealth is concentrated in the hands of a fortunate few, the friends of the government, the best wheeler-dealers. In the other, wealth is the people’s patrimony."[126]A further integral part of fostering a sense of "unity between the individual and the mass", Guevara believed, was volunteer work and will. To display this, Guevara "led by example", working "endlessly at his ministry job, in construction, and even cutting sugar cane" on his day off.[127] He was known for working 36 hours at a stretch, calling meetings after midnight, and eating on the run.[125] Such behavior was emblematic of Guevara's new program of moral incentives, where each worker was now required to meet a quota and produce a certain quantity of goods. As a replacement for the pay increases abolished by Guevara, workers who exceeded their quota now only received a certificate of commendation, while workers who failed to meet their quotas were given a pay cut.[125] Guevara unapologetically defended his personal philosophy towards motivation and work, stating:
 Guevara fishing off the coast of Havana, on May 15, 1960. Along with Castro, Guevara competed with expatriate author Ernest Hemingway at what was known as the "Hemingway Fishing Contest".
Guevara fishing off the coast of Havana, on May 15, 1960. Along with Castro, Guevara competed with expatriate author Ernest Hemingway at what was known as the "Hemingway Fishing Contest". "This is not a matter of how many pounds of meat one might be able to eat, or how many times a year someone can go to the beach, or how many ornaments from abroad one might be able to buy with his current salary. What really matters is that the individual feels more complete, with much more internal richness and much more responsibility."[128]
"This is not a matter of how many pounds of meat one might be able to eat, or how many times a year someone can go to the beach, or how many ornaments from abroad one might be able to buy with his current salary. What really matters is that the individual feels more complete, with much more internal richness and much more responsibility."[128]In the face of a loss of commercial connections with Western states, Guevara tried to replace them with closer commercial relationships with Eastern Bloc states, visiting a number of Marxist states and signing trade agreements with them. At the end of 1960 he visited Czechoslovakia, the U.S.S.R., North Korea, Hungary and East Germany and signed, for instance, a trade agreement in East Berlin on December 17, 1960.[129] Such agreements helped Cuba's economy to a certain degree but also had the disadvantage of a growing economic dependency on the Eastern Bloc. It was also in East Germany where Guevara met Tamara Bunke (later known as "Tania"), who was assigned as his interpreter, and who would years later join him and be killed with him in Bolivia.
Whatever the merits or demerits of Guevara’s economic principles, his programs were unsuccessful.[130] Guevara's program of "moral incentives" for workers caused a rapid drop in productivity and a rapid rise in absenteeism.[131] In reference to the collective failings of Guevara's vision, reporter I.F. Stone who interviewed Guevara twice during this time, remarked that he was "Galahad not Robespierre", while opining that "in a sense he was, like some early saint, taking refuge in the desert. Only there could the purity of the faith be safeguarded from the unregenerate revisionism of human nature."[132]
On April 17, 1961, 1,400 U.S.-trained Cuban exiles invaded Cuba during the Bay of Pigs Invasion. Guevara did not play a key role in the fighting, as one day before the invasion a warship carrying Marines faked an invasion off the West Coast of Pinar del Río and drew forces commanded by Guevara to that region. However, historians give him a share of credit for the victory as he was director of instruction for Cuba’s armed forces at the time.[13] Author Tad Szulc in his explanation of the Cuban victory, assigns Guevara partial credit, stating: "The revolutionaries won because Che Guevara, as the head of the Instruction Department of the Revolutionary Armed Forces in charge of the militia training program, had done so well in preparing 200,000 men and women for war."[13] It was also during this deployment that he suffered a bullet grazing to the cheek when his pistol fell out of its holster and accidentally discharged.[133]
 Guevara (left) and Fidel Castro, photographed by Alberto Korda in 1961
Guevara (left) and Fidel Castro, photographed by Alberto Korda in 1961
In August 1961, during an economic conference of the Organization of American States in Punta del Este, Uruguay, Che Guevara sent a note of "gratitude" to U.S. President John F. Kennedy through Richard N. Goodwin, a young secretary of the White House. It read "Thanks for Playa Girón (Bay of Pigs). Before the invasion, the revolution was shaky. Now it's stronger than ever."[134] In response to U.S. Treasury Secretary Douglas Dillon presenting the Alliance for Progress for ratification by the meeting, Guevara antagonistically attacked the United States claim of being a "democracy", stating that such a system was not compatible with "financial oligarchy, discrimination against blacks, and outrages by the Ku Klux Klan."[135] Guevara continued, speaking out against the "persecution" that in his view "drove scientists like Oppenheimer from their posts, deprived the world for years of the marvelous voice of Paul Robeson, and sent the Rosenbergs to their deaths against the protests of a shocked world."[135] Guevara ended his remarks by insinuating that the United States was not interested in real reforms, sardonically quipping that "U.S. experts never talk about agrarian reform; they prefer a safe subject, like a better water supply. In short they seem to prepare the revolution of the toilets."[30]
Guevara, who was practically the architect of the Soviet-Cuban relationship,[136] then played a key role in bringing to Cuba the Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles that precipitated the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962 and brought the world to the brink of nuclear war.[137] A few weeks after the crisis, during an interview with the British communist newspaper the Daily Worker, Guevara was still fuming over the perceived Soviet betrayal and told correspondent Sam Russell that, if the missiles had been under Cuban control, they would have fired them off.[138] While expounding on the incident later, Guevara reiterated that the cause of socialist liberation against global "imperialist aggression", would ultimately have been worth the possibility of "millions of atomic war victims."[139] The missile crisis further convinced Guevara that the two World's superpowers (U.S. & U.S.S.R.) used Cuba as a pawn in their own global strategies. Afterward he denounced the Soviets almost as frequently as he denounced the Americans.[140]
International diplomacy
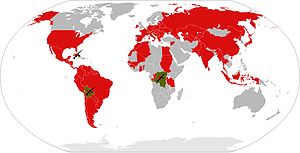 A world map displaying those countries lived in or visited by Che Guevara in red. The three nations where he engaged in armed revolution are signified in green.
A world map displaying those countries lived in or visited by Che Guevara in red. The three nations where he engaged in armed revolution are signified in green.
By December 1964, Che Guevara had emerged as a "revolutionary statesman of world stature" and thus traveled to New York City as head of the Cuban delegation to speak at the United Nations.[122] During his impassioned address, he criticized the United Nations inability to confront the "brutal policy of apartheid" in South Africa, proclaiming "can the United Nations do nothing to stop this?"[141] Guevara then denounced the United States policy towards their black population, stating:
"Those who kill their own children and discriminate daily against them because of the color of their skin; those who let the murderers of blacks remain free, protecting them, and furthermore punishing the black population because they demand their legitimate rights as free men—how can those who do this consider themselves guardians of freedom?"[141]An indignant Guevara ended his speech by reciting the Second Declaration of Havana, decreeing Latin America a "family of 200 million brothers who suffer the same miseries."[141] This "epic", Guevara declared, would be written by the "hungry Indian masses, peasants without land, exploited workers, and progressive masses." To Guevara the conflict was a struggle of mass and ideas, which would be carried forth by those "mistreated and scorned by imperialism" who were previously considered "a weak and submissive flock." With this "flock", Guevara now asserted, "Yankee monopoly capitalism" now terrifyingly saw their "gravediggers."[141] It would be during this "hour of vindication" Guevara pronounced, that the "anonymous mass" would begin to write its own history "with its own blood", and reclaim those "rights that were laughed at by one and all for 500 years." Guevara ended his remarks to the United Nations general assembly by hypothesizing that this "wave of anger” would "sweep the lands of Latin America", and that the labor masses who "turn the wheel of history", for the first time were "awakening from the long, brutalizing sleep to which they had been subjected.[141]
Guevara later learned that there were two failed attempts on his life by Cuban exiles during his stop at the U.N. complex.[142] The first from Molly Gonzales who tried to break through barricades upon his arrival with a seven-inch hunting knife, and later during his address by Guillermo Novo with a timer-initiated bazooka that was fired off target from a boat in the East River at the United Nations Headquarters.[142][143] Afterwards, Guevara commented on both incidents stating that "it is better to be killed by a woman with a knife than by a man with a gun", while adding with a languid wave of his cigar that the explosion had "given the whole thing more flavor."[142]
While in New York City, Guevara also appeared on the CBS Sunday news program Face the Nation and met with a range of people, from U.S. Senator Eugene McCarthy[144] to associates of Malcolm X. Malcolm X expressed his admiration, declaring Guevara "one of the most revolutionary men in this country right now" while reading a statement from him to a crowd at the Audubon Ballroom.[145]
 Walking through Red Square in Moscow, November 1964
Walking through Red Square in Moscow, November 1964
On December 17, Guevara left for Paris and embarked on a three-month tour that included the People's Republic of China, the United Arab Republic (Egypt), Algeria, Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Dahomey, Congo-Brazzaville and Tanzania, with stops in Ireland and Prague. While in Ireland, Guevara embraced his own Irish heritage, celebrating Saint Patrick's Day in Limerick City.[146] He wrote to his father on this visit, humorously stating "I am in this green Ireland of your ancestors. When they found out, the television [station] came to ask me about the Lynch genealogy, but in case they were horse thieves or something like that, I didn't say much."[147]
During this voyage, he wrote a letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of a Uruguayan weekly, which was later re-titled Socialism and Man in Cuba.[124] Outlined in the treatise was Guevara's summons for the creation of a new consciousness, status of work, and role of the individual. He also laid out the reasoning behind his anti-capitalist sentiments, stating:
"The laws of capitalism, blind and invisible to the majority, act upon the individual without his thinking about it. He sees only the vastness of a seemingly infinite horizon before him. That is how it is painted by capitalist propagandists, who purport to draw a lesson from the example of Rockefeller—whether or not it is true—about the possibilities of success. The amount of poverty and suffering required for the emergence of a Rockefeller, and the amount of depravity that the accumulation of a fortune of such magnitude entails, are left out of the picture, and it is not always possible to make the people in general see this."[124]Guevara ended the essay by declaring that "the true revolutionary is guided by a great feeling of love" and beckoning on all revolutionaries to "strive every day so that this love of living humanity will be transformed into acts that serve as examples", thus becoming "a moving force."[124] The genesis for Guevara's assertions relied on the fact that he believed the example of the Cuban Revolution was "something spiritual that would transcend all borders."[30]
Algiers, the Soviets and China
In Algiers, Algeria on February 24, 1965, Guevara made what turned out to be his last public appearance on the international stage when he delivered a speech at an economic seminar on Afro-Asian solidarity.[148] He specified the moral duty of the socialist countries, accusing them of tacit complicity with the exploiting Western countries. He proceeded to outline a number of measures which he said the communist-bloc countries must implement in order to accomplish the defeat of imperialism.[149] Having criticized the Soviet Union (the primary financial backer of Cuba) in such a public manner, he returned to Cuba on March 14 to a solemn reception by Fidel and Raúl Castro, Osvaldo Dorticós and Carlos Rafael Rodríguez at the Havana airport.
As revealed in his last public speech in Algiers, Guevara had come to view the Northern Hemisphere, led by the U.S. in the West and the Soviet Union in the East, as the exploiter of the Southern Hemisphere. He strongly supported Communist North Vietnam in the Vietnam War, and urged the peoples of other developing countries to take up arms and create "many Vietnams."[150]
Moreover, the coincidence of Guevara's views with those expounded by the Chinese Communist leadership under Mao Zedong was increasingly problematic for Cuba as the nation's economy became more and more dependent on the Soviet Union. Since the early days of the Cuban revolution, Guevara had been considered by many an advocate of Maoist strategy in Latin America and the originator of a plan for the rapid industrialization of Cuba which was frequently compared to China's "Great Leap Forward." Castro became weary of Guevara's opposition to Soviet conditions and recommendations; measures that Castro saw as necessary, but which Guevara described as corrupt and "pre-monopolist."[151]
"Marx characterized the psychological or philosophical manifestation of capitalist social relations as alienation and antagonism; the result of the commodification of labor and the operation of the law of value. For Guevara, the challenge was to replace the individuals' alienation from the productive process, and the antagonism generated by class relations, with integration and solidarity, developing a collective attitude to production and the concept of work as a social duty."
— Helen Yaffe, author of Che Guevara: The Economics of Revolution [152]In Guevara's private writings from this time (since released), he displays his growing criticism of the Soviet political economy, believing that they had "forgotten Marx".[152] This led Guevara to denounce a range of Soviet practices including what he saw as their attempt to "air-brush the inherent violence of class struggle integral to the transition from capitalism to socialism", their "dangerous" policy of peaceful co-existence with the United States, their failure to push for a "change in consciousness" towards the idea of work, and their attempt to "liberalise" the socialist economy.[152] It was Guevara's desire to see the complete elimination of money, interest, commodity production, the market economy, and "mercantile relationships"; all conditions that the Soviets argued would only disappear when world communism was achieved.[152] Disagreeing with this incrementalist approach, Guevara's critique of the Soviet Manual of Political Economy was encapsulated with him correctly predicting that since the Soviets were not willing to abolish the law of value (as Guevara desired), they would eventually return to capitalism.[152]
Two weeks after his Algiers speech, Guevara dropped out of public life and then vanished altogether. His whereabouts were a great mystery in Cuba, as he was generally regarded as second in power to Castro himself. His disappearance was variously attributed to the failure of the industrialization scheme he had advocated while minister of industry, to pressure exerted on Castro by Soviet officials disapproving of Guevara's pro-Chinese Communist stance on the Sino-Soviet split, and to serious differences between Guevara and the pragmatic Castro regarding Cuba's economic development and ideological line. Pressed by international speculation regarding Guevara's fate, Castro stated on June 16, 1965 that the people would be informed when Guevara himself wished to let them know. Still, rumors spread both inside and outside Cuba. On October 3, Castro revealed an undated letter purportedly written to him by Guevara some months earlier: in it, Guevara reaffirmed his enduring solidarity with the Cuban Revolution, but declared his intention to leave Cuba to fight for the revolutionary cause abroad. Additionally, he resigned from all his positions in the government and party, and renounced his honorary Cuban citizenship.[153]
Congo
In early 1965, Guevara went to Africa to offer his knowledge and experience as a guerrilla to the ongoing conflict in the Congo. According to Algerian President Ahmed Ben Bella, Guevara thought that Africa was imperialism's weak link and therefore had enormous revolutionary potential.[154] Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had fraternal relations with Che dating back to his 1959 visit, saw Guevara's plans to fight in the Congo as "unwise" and warned that he would become a "Tarzan" figure, doomed to failure.[155] Despite the warning, Guevara traveled to the Congo while using the alias Ramón Benítez.[156] Guevara led the Cuban operation in support of the Marxist Simba movement, which had emerged from the ongoing Congo Crisis. Guevara, his second-in-command Victor Dreke, and 12 other Cuban expeditionaries arrived in the Congo on April 24, 1965 and a contingent of approximately 100 Afro-Cubans joined them soon afterward.[157][158] They collaborated for a time with guerrilla leader Laurent-Désiré Kabila, who had previously helped supporters of the overthrown Patrice Lumumba lead an unsuccessful revolt months earlier. As an admirer of the late Lumumba, Guevara declared that his "murder should be a lesson for all of us."[159] Guevara, with limited knowledge of Swahili and the local languages was assigned a teenage interpreter Freddy Ilanga. Over the course of seven months Ilanga grew to "admire the hard-working Guevara", who according to Mr. Ilanga, "showed the same respect to black people as he did to whites."[160] However, Guevara soon became disillusioned with the discipline of Kabila's troops and later dismissed him, stating "nothing leads me to believe he is the man of the hour."[161]
As an additional obstacle, white South African mercenaries, led by Mike Hoare in concert with Cuban exiles and the CIA, worked with the Congo National Army to thwart Guevara in the mountains near the village of Fizi on Lake Tanganyika. They were able to monitor his communications, and so pre-empted his attacks and interdicted his supply lines. Despite the fact that Guevara sought to conceal his presence in the Congo, the U.S. government was aware of his location and activities: The National Security Agency was intercepting all of his incoming and outgoing transmissions via equipment aboard the USNS Private Jose F. Valdez (T-AG-169), a floating listening post that continuously cruised the Indian Ocean off Dar es Salaam for that purpose.[162]
 Listening to a Zenith Trans-Oceanic shortwave receiver are (seated from the left) Rogelio Oliva, José María Martínez Tamayo (known as "Mbili" in the Congo and "Ricardo" in Bolivia), and Guevara. Standing behind them is Roberto Sánchez ("Lawton" in Cuba and "Changa" in the Congo).
Listening to a Zenith Trans-Oceanic shortwave receiver are (seated from the left) Rogelio Oliva, José María Martínez Tamayo (known as "Mbili" in the Congo and "Ricardo" in Bolivia), and Guevara. Standing behind them is Roberto Sánchez ("Lawton" in Cuba and "Changa" in the Congo).
Guevara's aim was to export the revolution by instructing local anti-Mobutu Simba fighters in Marxist ideology and foco theory strategies of guerrilla warfare. In his Congo Diary, he cites the incompetence, intransigence and infighting of the local Congolese forces as key reasons for the revolt's failure.[163] Later that year on November 20, 1965, in ill health with dysentery, suffering from acute asthma, and disheartened after seven months of frustrations, Guevara left the Congo with the Cuban survivors (Six members of his 12-man column had died). At one point Guevara considered sending the wounded back to Cuba, and fighting in Congo alone until his death, as a revolutionary example; after being urged by his comrades and pressed by two emissaries sent by Castro, at the last moment he reluctantly agreed to leave Africa. In speaking about his experience in the Congo months later, Guevara concluded that he left rather than fight to the death because: "The human element failed. There is no will to fight. The leaders are corrupt. In a word... there was nothing to do."[164] Guevara also declared that "we can't liberate by ourselves a country that does not want to fight."[165] A few weeks later, when writing the preface to the diary he kept during the Congo venture, he began: "This is the history of a failure."[166]
Guevara was reluctant to return to Cuba, because Castro had made public Guevara's "farewell letter"—a letter intended to only be revealed in the case of his death—wherein he severed all ties in order to devote himself to revolution throughout the world.[167] As a result, Guevara spent the next six months living clandestinely in Dar es Salaam and Prague.[168] During this time he compiled his memoirs of the Congo experience, and wrote drafts of two more books, one on philosophy and the other on economics. He then visited several Western European countries to test his new false identity papers, created by Cuban Intelligence for his later travels to South America. As Guevara prepared for Bolivia, he secretly traveled back to Cuba to visit Castro, as well as to see his wife and to write a last letter to his five children to be read upon his death, which ended with him instructing them:
"Above all, always be capable of feeling deeply any injustice committed against anyone, anywhere in the world. This is the most beautiful quality in a revolutionary."[169]Bolivia
Main article: Ñancahuazú GuerrillaIn late 1966, Guevara's location was still not public knowledge, although representatives of Mozambique's independence movement, the FRELIMO, reported that they met with Guevara in late 1966 or early 1967 in Dar es Salaam regarding his offer to aid in their revolutionary project, which they ultimately rejected.[170] In a speech at the 1967 International Workers' Day rally in Havana, the Acting Minister of the armed forces, Major Juan Almeida, announced that Guevara was "serving the revolution somewhere in Latin America".
Before he departed for Bolivia, Guevara altered his appearance by shaving off his beard and part of the top of his head as well as dyeing it grey so he would be unrecognizable as Che Guevara.[171] On November 3, 1966, Guevara secretly arrived in La Paz, Bolivia on a flight from Montevideo, Uruguay under the false name Adolfo Mena González, and posed as a Uruguayan businessman working for the Organization of American States.[172]
 In rural Bolivia shortly before his death (1967)
In rural Bolivia shortly before his death (1967)
Guevara's first base camp was located in the montane dry forest in the remote Ñancahuazú region. Training at the camp in the Ñancahuazú valley proved to be hazardous and little was accomplished in the way of building a guerrilla army. Former Stasi operative Haydée Tamara Bunke Bider, better known by her nom de guerre "Tania", who had been installed as his primary agent in La Paz, was reportedly also working for the KGB and in several Western sources she is inferred to have unwittingly served Soviet interests by leading Bolivian authorities to Guevara's trail.[173][174]
Guevara's guerrilla force, numbering about 50[175] and operating as the ELN (Ejército de Liberación Nacional de Bolivia; "National Liberation Army of Bolivia"), was well equipped and scored a number of early successes against Bolivian army regulars in the difficult terrain of the mountainous Camiri region. As a result of Guevara’s units winning several skirmishes against Bolivian troops in the spring and summer of 1967, the Bolivian government began to overestimate the true size of the guerrilla force.[176] But in September, the Army managed to eliminate two guerrilla groups in a violent battle, reportedly killing one of the leaders.
 Location of Vallegrande in Bolivia
Location of Vallegrande in Bolivia
Researchers hypothesize that Guevara's plan for fomenting revolution in Bolivia failed, for an array of reasons:
- He had expected to deal only with the Bolivian military, who were poorly trained and equipped, and was unaware that the U.S. government had sent a team of the CIA's Special Activities Division commandos and other operatives into Bolivia to aid the anti-insurrection effort. The Bolivian Army would also be trained, advised, and supplied by U.S. Army Special Forces including a recently organized elite battalion of Rangers trained in jungle warfare that set up camp in La Esperanza, a small settlement close to the location of Guevara's guerrillas.[177]
- Guevara had expected assistance and cooperation from the local dissidents which he did not receive, nor did he receive support from Bolivia's Communist Party, under the leadership of Mario Monje, which was oriented toward Moscow rather than Havana. In Guevara's own diary captured after his death, he wrote about the Communist Party of Bolivia, which he characterized as "distrustful, disloyal and stupid."[178]
- He had expected to remain in radio contact with Havana. The two shortwave transmitters provided to him by Cuba were faulty; thus the guerrillas were unable to communicate with and be resupplied, leaving them isolated and stranded.
In addition, Guevara's known preference for confrontation rather than compromise, which had previously surfaced during his guerrilla warfare campaign in Cuba, contributed to his inability to develop successful working relationships with local leaders in Bolivia, just as it had in the Congo.[179] This tendency had existed in Cuba, but had been kept in check by the timely interventions and guidance of Fidel Castro.[180]
The end result was that Guevara was unable to attract inhabitants of the local area to join his militia during the 11 months he attempted recruitment. Near the end of the venture Guevara wrote in his diary that "the peasants do not give us any help, and are turning into informers."[181]
Capture and execution
"There was no person more feared by the company (CIA) than Che Guevara because he had the capacity and charisma necessary to direct the struggle against the political repression of the traditional hierarchies in power in the countries of Latin America."
— Philip Agee, CIA agent, later defected to Cuba [182]Félix Rodríguez, a Cuban exile turned CIA Special Activities Division operative, advised Bolivian troops during the hunt for Guevara in Bolivia.[183] In addition, the 2007 documentary My Enemy's Enemy, directed by Kevin Macdonald, alleges that Nazi war criminal Klaus Barbie aka "The Butcher of Lyon", advised and possibly helped the CIA orchestrate Guevara's eventual capture.[184]
On October 7, 1967, an informant apprised the Bolivian Special Forces of the location of Guevara's guerrilla encampment in the Yuro ravine.[185] On October 8, they encircled the area with 1,800 soldiers, and Guevara was wounded and taken prisoner while leading a detachment with Simeón Cuba Sarabia. Che biographer Jon Lee Anderson reports Bolivian Sergeant Bernardino Huanca's account: that a twice wounded Guevara, his gun rendered useless, shouted "Do not shoot! I am Che Guevara and worth more to you alive than dead."[186]
 Monument to Guevara in La Higuera
Monument to Guevara in La Higuera
Guevara was tied up and taken to a dilapidated mud schoolhouse in the nearby village of La Higuera on the night of October 8. For the next half day, Guevara refused to be interrogated by Bolivian officers and would only speak quietly to Bolivian soldiers. One of those Bolivian soldiers, helicopter pilot Jaime Nino de Guzman, describes Che as looking "dreadful". According to Guzman, Guevara was shot through the right calf, his hair was matted with dirt, his clothes were shredded, and his feet were covered in rough leather sheaths. Despite his haggard appearance, he recounts that "Che held his head high, looked everyone straight in the eyes and asked only for something to smoke." De Guzman states that he "took pity" and gave him a small bag of tobacco for his pipe, with Guevara then smiling and thanking him.[187] Later on the night of October 8, Guevara, despite having his hands tied, kicked Bolivian Officer Espinosa into the wall, after the officer entered the schoolhouse in order to snatch Guevara's pipe from his mouth as a souvenir.[188] In another instance of defiance, Guevara spat in the face of Bolivian Rear Admiral Ugarteche shortly before his execution.[188]
The following morning on October 9, Guevara asked to see the "maestra" (school teacher) of the village, 22-year-old Julia Cortez. Cortez would later state that she found Guevara to be an "agreeable looking man with a soft and ironic glance" and that during their conversation she found herself "unable to look him in the eye", because his "gaze was unbearable, piercing, and so tranquil."[188] During their short conversation, Guevara pointed out to Cortez the poor condition of the schoolhouse, stating that it was "anti-pedagogical" to expect campesino students to be educated there, while "government officials drive Mercedes cars" ... declaring "that's what we are fighting against."[188]
Later that morning on October 9, Bolivian President René Barrientos ordered that Guevara be killed. The order was relayed by Félix Rodríguez despite the U.S. government’s desire that Guevara be taken to Panama for further interrogation.[189] The executioner was Mario Terán, a half-drunken sergeant in the Bolivian army who had requested to shoot Che on the basis of the fact that three of his friends from B Company, all named "Mario", had been killed in an earlier firefight with Guevara's band of guerrillas.[12] To make the bullet wounds appear consistent with the story the government planned to release to the public, Félix Rodríguez ordered Terán to aim carefully to make it appear that Guevara had been killed in action during a clash with the Bolivian army.[190] Gary Prado, the Bolivian captain in command of the army company that captured Guevara, said that the reasons Barrientos ordered the immediate execution of Guevara is so there would be no possibility that Guevara would escape from prison, and also so there would be no drama in regard to a trial.[191]
Moments before Guevara was executed he was asked by a Bolivian soldier if he was thinking about his own immortality. "No", he replied, "I'm thinking about the immortality of the revolution."[192] When Sergeant Terán entered the hut, Che Guevara then told his executioner, "I know you've come to kill me. Shoot, coward! You are only going to kill a man!"[193] Terán hesitated, then opened fire with his semiautomatic rifle, hitting Guevara in the arms and legs. Guevara writhed on the ground, apparently biting one of his wrists to avoid crying out. Terán then fired several times again, wounding him fatally in the chest at 1:10 pm, according to Rodríguez.[193] In all, Guevara was shot nine times. This included five times in the legs, once in the right shoulder and arm, once in the chest, and finally in the throat.[188]
Months earlier, during his last public declaration to the Tricontinental Conference,[150] Guevara wrote his own epitaph, stating "Wherever death may surprise us, let it be welcome, provided that this our battle cry may have reached some receptive ear and another hand may be extended to wield our weapons."[194]
Post-execution, remains and memorial
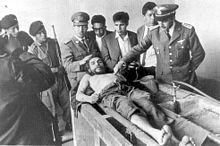 The day after his execution on October 10, 1967, Guevara's corpse was displayed to the world press in the laundry house of the Vallegrande hospital. (photo by Freddy Alborta)
The day after his execution on October 10, 1967, Guevara's corpse was displayed to the world press in the laundry house of the Vallegrande hospital. (photo by Freddy Alborta)
 Face Side angle ShoesMain article: Che Guevara Mausoleum
Face Side angle ShoesMain article: Che Guevara MausoleumAfter his execution, Guevara's body was lashed to the landing skids of a helicopter and flown to nearby Vallegrande, where photographs were taken of him lying on a concrete slab in the laundry room of the Nuestra Señora de Malta.[195] Several witnesses were called to confirm that it was Guevara, key amongst them British journalist Richard Gott, the only witness to have met Guevara when he was alive.
Put on public show, as hundreds of local residents filed past the body, many of them considered Guevara's corpse to represent a "Christ-like" visage, with some of them even surreptitiously clipping locks of his hair as divine relics.[196] Such comparisons were further extended when two weeks later upon seeing the post-mortem photographs, English art critic John Berger observed that they resembled two famous paintings: Rembrandt's The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp and Andrea Mantegna's Lamentation over the Dead Christ.[197] There were also four correspondents present when Guevara's body arrived in Vallegrande, including Bjorn Kumm of the Swedish Aftonbladet, who described the scene in an November 11, 1967, exclusive for The New Republic.[198]
A declassified memorandum dated October 11, 1967 to United States President Lyndon B. Johnson from his National Security Advisor, Walt Whitman Rostow, called the decision to kill Guevara "stupid" but "understandable from a Bolivian standpoint."[199] After the execution, Rodríguez took several of Guevara's personal items, including a Rolex GMT Master wristwatch[200] which he continued to wear many years later, often showing them to reporters during the ensuing years.[201] Today, some of these belongings, including his flashlight, are on display at the CIA.[202] After a military doctor amputated his hands, Bolivian army officers transferred Guevara's body to an undisclosed location and refused to reveal whether his remains had been buried or cremated. The hands were preserved in formaldehyde to be sent to Buenos Aires for fingerprint identification. (His fingerprints were on file with the Argentine police.) They were later sent to Cuba.
 Plaza de la Revolución, in Havana, Cuba. Aside the Ministry of the Interior building where Guevara once worked, is a 5 story steel outline of his face. Under the image is Guevara's motto, the Spanish phrase: "Hasta la Victoria Siempre" (English: Until the Everlasting Victory Always).
Plaza de la Revolución, in Havana, Cuba. Aside the Ministry of the Interior building where Guevara once worked, is a 5 story steel outline of his face. Under the image is Guevara's motto, the Spanish phrase: "Hasta la Victoria Siempre" (English: Until the Everlasting Victory Always).
On October 15, Fidel Castro acknowledged that Guevara was dead and proclaimed three days of public mourning throughout the island.[203] On October 18, Castro addressed a crowd of one million mourners in Havana's Plaza de la Revolución and spoke about Guevara's character as a revolutionary.[204] Fidel Castro closed his impassioned eulogy thusly:
"If we wish to express what we want the men of future generations to be, we must say: Let them be like Che! If we wish to say how we want our children to be educated, we must say without hesitation: We want them to be educated in Che’s spirit! If we want the model of a man, who does not belong to our times but to the future, I say from the depths of my heart that such a model, without a single stain on his conduct, without a single stain on his action, is Che!"[205]French intellectual Régis Debray, who was captured in April 1967 while with Guevara in Bolivia, gave an interview from prison, in August 1968, where he enlarged on the circumstances of Guevara's capture. Debray, who had lived with Guevara's band of guerrillas for a short time, said that in his view they were "victims of the forest" and thus "eaten by the jungle."[206] Debray described a destitute situation where Guevara's men suffered malnutrition, lack of water, absence of shoes, and only possessed six blankets for 22 men. Debray recounts that Guevara and the others had been suffering an "illness" which caused their hands and feet to swell into "mounds of flesh" to the point where you could not discern the fingers on their hands.[206] Despite the futile situation, Debray described Guevara as "optimistic about the future of Latin America" and remarked that Guevara was "resigned to die in the knowledge that his death would be a sort of renaissance", noting that Guevara perceived death "as a promise of rebirth" and "ritual of renewal."[206]
In late 1995, retired Bolivian General Mario Vargas revealed to Jon Lee Anderson, author of Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life, that Guevara's body was located near a Vallegrande airstrip. The result was a multi-national search for the remains, which would last more than a year. In July 1997, a team of Cuban geologists and Argentine forensic anthropologists discovered the remnants of seven bodies in two mass graves, including one man with amputated hands (like Guevara). Bolivian government officials with the Ministry of Interior later identified the body as Guevara when the excavated teeth "perfectly matched" a plaster mold of Che's teeth, made in Cuba prior to his Congolese expedition. The "clincher" then arrived when Argentine forensic anthropologist Alejandro Inchaurregui inspected the inside hidden pocket of a blue jacket dug up next to the handless cadaver and found a small bag of pipe tobacco. Nino de Guzman, the Bolivian helicopter pilot who had given Che a small bag of tobacco, later remarked that he "had serious doubts" at first and "thought the Cubans would just find any old bones and call it Che"; he stated "after hearing about the tobacco pouch, I have no doubts."[187] On October 17, 1997, Guevara's remains, with those of six of his fellow combatants, were laid to rest with military honors in a specially built mausoleum in the Cuban city of Santa Clara, where he had commanded over the decisive military victory of the Cuban Revolution.[207]
Removed when Guevara was captured were his 30,000-word, hand-written diary, a collection of his personal poetry, and a short story he authored about a young Communist guerrilla who learns to overcome his fears.[208] His diary documented events of the guerrilla campaign in Bolivia[209] with the first entry on November 7, 1966 shortly after his arrival at the farm in Ñancahuazú, and the last dated October 7, 1967, the day before his capture. The diary tells how the guerrillas were forced to begin operations prematurely because of discovery by the Bolivian Army, explains Guevara's decision to divide the column into two units that were subsequently unable to re-establish contact, and describes their overall unsuccessful venture. It also records the rift between Guevara and the Communist Party of Bolivia that resulted in Guevara having significantly fewer soldiers than originally expected and shows that Guevara had a great deal of difficulty recruiting from the local populace, partly because of the fact that the guerrilla group had learned Quechua, unaware that the local language was actually a Tupí–Guaraní language.[210] As the campaign drew to an unexpected close, Guevara became increasingly ill. He suffered from ever-worsening bouts of asthma, and most of his last offensives were carried out in an attempt to obtain medicine.[211]
The Bolivian Diary was quickly and crudely translated by Ramparts magazine and circulated around the world.[212] There are at least four additional diaries in existence—those of Israel Reyes Zayas (Alias "Braulio"), Harry Villegas Tamayo ("Pombo"), Eliseo Reyes Rodriguez ("Rolando")[173] and Dariel Alarcón Ramírez ("Benigno")[213]—each of which reveals additional aspects of the events. In July 2008, the Bolivian government of Evo Morales unveiled Guevara's formerly sealed diaries composed in two frayed notebooks, along with a logbook and several black-and-white photographs. At this event, Bolivia's vice minister of culture, Pablo Groux, expressed that there were plans to publish photographs of every handwritten page later in the year.[214] Meanwhile, in August 2009, anthropologists working for Bolivia's Justice Ministry discovered and unearthed five of Guevara's fellow guerrillas near the Bolivian town of Teoponte.[215]
Legacy
Main articles: Legacy of Che Guevara and Che Guevara in popular culture"The discovery of Che’s remains metonymically activated a series of interlinked associations – rebel, martyr, rogue figure from a picaresque adventure, savior, renegade, extremist – in which there was no fixed divide among them. The current court of opinion places Che on a continuum that teeters between viewing him as a misguided rebel, a coruscatingly brilliant guerrilla philosopher, a poet-warrior jousting at windmills, a brazen warrior who threw down the gauntlet to the bourgeoisie, the object of fervent paeans to his sainthood, or a mass murderer clothed in the guise of an avenging angel whose every action is imbricated in violence – the archetypal Fanatical Terrorist."
— Dr. Peter McLaren, author of Che Guevara, Paulo Freire, and the Pedagogy of Revolution [216]
Over forty years after his execution, Che's life and legacy still remain a contentious issue. The contradictions of his ethos at various points in his life have created a complex character of unending duality.
An array of notable individuals have lauded Guevara as a hero;[217] for example, Nelson Mandela referred to him as "an inspiration for every human being who loves freedom"[182] while Jean-Paul Sartre described him as "not only an intellectual but also the most complete human being of our age."[218] Others who expressed their admiration include authors Graham Greene who remarked that Che "represented the idea of gallantry, chivalry, and adventure",[219] and Susan Sontag who expounded that "(Che's) goal was nothing less than the cause of humanity itself."[220] In the black community, philosopher Frantz Fanon professed Guevara to be "the world symbol of the possibilities of one man",[221] while Black Panther Party head Stokely Carmichael eulogized that "Che Guevara is not dead, his ideas are with us."[222] Praise has been reflected throughout the political spectrum, with the anarcho-capitalist / libertarian theorist Murray Rothbard extolling Guevara as a "heroic figure", lamenting after his death that "more than any man of our epoch or even of our century, (Che) was the living embodiment of the principle of revolution",[223] while journalist Christopher Hitchens commented that "[Che's] death meant a lot to me and countless like me at the time, he was a role model, albeit an impossible one for us bourgeois romantics insofar as he went and did what revolutionaries were meant to do—fought and died for his beliefs."[224] Guevara remains a beloved national hero to many in Cuba, where his image adorns the $3 Cuban Peso and school children begin each morning by pledging "We will be like Che."[225] In his homeland of Argentina, where high schools bear his name,[226] numerous Che museums dot the country, which in 2008 unveiled a 12-foot (3.7 m) bronze statue of him in his birth city of Rosario.[227] Additionally, Guevara has been sanctified by some Bolivian campesinos[228] as "Saint Ernesto", to whom they pray for assistance.[229]
Conversely, Jacobo Machover, an exiled opposition author, dismisses the hero-worshipping and portrays him as a ruthless executioner.[230] Detractors have theorized that in much of Latin America, Che-inspired revolutions had the practical result of reinforcing brutal militarism and internecine conflict for many years.[231] In an assessment of Guevara, British historian Hugh Thomas opines that Che was a "brave, sincere and determined man who was also obstinate, narrow, and dogmatic."[232] At the end of his life, according to Thomas, "he seems to have become convinced of the virtues of violence for its own sake", while "his influence over Castro for good or evil" grew after his death, as Fidel took up many of his views. In Thomas' assessment "as in the case of Martí, or Lawrence of Arabia, failure has brightened, not dimmed the legend."[232] Alvaro Vargas Llosa of The Independent Institute has hypothesized that Guevara’s contemporary followers "delude themselves by clinging to a myth", while describing Guevara as "Marxist Puritan" who employed his rigid power to suppress dissent, while also operating as a "cold-blooded killing machine".[231] Llosa has also accused Guevara's "fanatical disposition" as being the linchpin of the "Sovietization" of the Cuban revolution, speculating that he possessed a "total subordination of reality to blind ideological orthodoxy."[231] Guevara remains a hated figure amongst many in the Cuban exile and Cuban-American community of the United States, who view him with animosity as "the butcher of La Cabaña."[233]
Despite his polarized status, a high-contrast monochrome graphic of his face, created in 1968 by Irish artist Jim Fitzpatrick, has become one of the world's most universally merchandized and objectified images,[234][235] found on an endless array of items, including t-shirts, hats, posters, tattoos, and bikinis,[236] ironically contributing to the consumer culture Guevara despised. Yet, he still remains a transcendent figure both in specifically political contexts[237] and as a wide-ranging popular icon of youthful rebellion.[238]
Timeline
Che Guevara timelineArchival media
Video footage
- Guevara interviewed in 1964 on a visit to Dublin, Ireland, (2:53), English translation, from RTÉ Libraries and Archives, Video Clip
- Guevara reciting a poem, (1:00), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, Video Clip
- Guevara showing support for Fidel Castro, (0:22), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, Video Clip
- Guevara speaking about labor, (0:28), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, Video Clip
- Guevara speaking about the Bay of Pigs, (0:17), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, Video Clip
- Guevara speaking against imperialism, (1:20), English subtitles, from El Che: Investigating a Legend – Kultur Video 2001, Video Clip
Audio recording
- Guevara interviewed on ABC's Issues and Answers, (23:53), English translation, narrated by Lisa Howard, March 24, 1964, Audio clip
List of works
Main article: Bibliography of Che GuevaraOriginally written in Spanish by Ernesto "Che" Guevara, later translated into English
- A New Society: Reflections for Today's World, Ocean Press, 1996, ISBN 1-875284-06-0
- Back on the Road: A Journey Through Latin America, Grove Press, 2002, ISBN 0-8021-3942-6
- Che Guevara, Cuba, and the Road to Socialism, Pathfinder Press, 1991, ISBN 0-87348-643-9
- Che Guevara on Global Justice, Ocean Press (AU), 2002, ISBN 1-876175-45-1
- Che Guevara: Radical Writings on Guerrilla Warfare, Politics and Revolution, Filiquarian Publishing, 2006, ISBN 1-59986-999-3
- Che Guevara Reader: Writings on Politics & Revolution, Ocean Press, 2003, ISBN 1-876175-69-9
- Che Guevara Speaks: Selected Speeches and Writings, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1980, ISBN 0-87348-602-1
- Che Guevara Talks to Young People, Pathfinder, 2000, ISBN 0-87348-911-X
- Che: The Diaries of Ernesto Che Guevara, Ocean Press (AU), 2008, ISBN 1-920888-93-4
- Colonialism is Doomed, Ministry of External Relations: Republic of Cuba, 1964, ASIN B0010AAN1K
- Critical Notes on Political Economy: A Revolutionary Humanist Approach to Marxist Economics, Ocean Press, 2008, ISBN 1-876175-55-9
- Episodes of the Cuban Revolutionary War, 1956–58, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1996, ISBN 0-87348-824-5
- Guerrilla Warfare: Authorized Edition, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-920888-28-4
- Latin America: Awakening of a Continent, Ocean Press, 2005, ISBN 1-876175-73-7
- Marx & Engels: An Introduction, Ocean Press, 2007, ISBN 1-920888-92-6
- Our America And Theirs: Kennedy And The Alliance For Progress, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-876175-81-8
- Reminiscences of the Cuban Revolutionary War: Authorized Edition, Ocean Press, 2005, ISBN 1-920888-33-0
- Self Portrait Che Guevara, Ocean Press (AU), 2004, ISBN 1-876175-82-6
- Socialism and Man in Cuba, Pathfinder Press (NY), 1989, ISBN 0-87348-577-7
- The African Dream: The Diaries of the Revolutionary War in the Congo, Grove Press, 2001, ISBN 0-8021-3834-9
- The Argentine, Ocean Press (AU), 2008, ISBN 1-920888-93-4
- The Bolivian Diary of Ernesto Che Guevara, Pathfinder Press, 1994, ISBN 0-87348-766-4
- The Great Debate on Political Economy, Ocean Press, 2006, ISBN 1-876175-54-0
- The Motorcycle Diaries: A Journey Around South America, London: Verso, 1996, ISBN 1-85702-399-4
- The Secret Papers of a Revolutionary: The Diary of Che Guevara, American Reprint Co, 1975, ASIN B0007GW08W
- To Speak the Truth: Why Washington's "Cold War" Against Cuba Doesn't End, Pathfinder, 1993, ISBN 0-87348-633-1
See also
Notes
- ^ a b c The date of birth recorded on his birth certificate was June 14, 1928, although one tertiary source, (Julia Constenla, quoted by Jon Lee Anderson), asserts that he was actually born on May 14 of that year. Constenla alleges that she was told by an unidentified astrologer that his mother, Celia de la Serna, was already pregnant when she and Ernesto Guevara Lynch were married and that the date on the birth certificate of their son was forged to make it appear that he was born a month later than the actual date to avoid scandal. (Anderson 1997, pp. 3, 769.)
- ^ Partido Unido de la Revolución Socialista de Cuba, aka PURSC.
- ^ The Spark That Does Not Die by Michael Löwy, International Viewpoint, July 1997
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 78.
- ^ Embodiment and Agency, by Sue Campbell & Letitia Meynell, Penn State Press, 2009, ISBN 0271035226, p. 243
- ^ The various sound clips on this site of international Spanish speakers all use the phoneme that the IPA denotes as "g" in the name "Guevara": Forvo.com
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 128.
- ^ a b On Revolutionary Medicine Speech by Che Guevara to the Cuban Militia on August 19, 1960.
- ^ At the Afro-Asian Conference in Algeria A speech by Che Guevara to the Second Economic Seminar of Afro-Asian Solidarity in Algiers, Algeria on February 24, 1965.
- ^ Beaubien, NPR Audio Report, 2009, 00:09–00:13.
- ^ a b c d "Castro's Brain" 1960.
- ^ a b c d e Taibo 1999, p. 267.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, pp. 69–70.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 526–530.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 4.
- ^ Dorfman 1999.
- ^ Maryland Institute of Art, referenced at BBC News May 26, 2001.
- ^ Che's last name "Guevara" derives from the Castilianized form of the Basque "Gebara", a habitational name from the province of Álava. Through his grandmother, Ana Lynch, he was a descendant of Patrick Lynch, an emigrant from Galway, Ireland in the 1740s.
- ^ Lavretsky 1976.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 23.
- ^ Argentina: Che's Red Mother Time Magazine, July 14, 1961.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 22–23.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 8.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 24.
- ^ Argentine Rugby Inspired by Che Guevara by Brendan Gallagher, The Daily Telegraph, October 5, 2007
- ^ Cain, Nick & Growden, Greg "Chapter 21: Ten Peculiar Facts about Rugby" in Rugby Union for Dummies (2nd Edition), John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 9780470035375, p. 293.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 28.
- ^ a b Hart 2004, p. 98.
- ^ Haney 2005, p. 164.
- ^ a b c d e (Anderson 1997, pp. 37–38).
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 10.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 26.
- ^ Ratner 1997, p. 25.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 64.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 59-64.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 89.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 75-76.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 27.
- ^ NYT bestseller list: #38 Paperback Nonfiction on 2005-02-20, #9 Nonfiction on 2004-10-07 and on more occasions.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 98.
- ^ A copy of Guevara's University transcripts showing conferral of his medical diploma can be found on p. 75 of Becoming Che: Guevara's Second and Final Trip through Latin America, by Carlos 'Calica' Ferrer (Translated from the Spanish by Sarah L. Smith), Marea Editorial, 2006, ISBN 987-1307-07-1. Ferrer was a longtime childhood friend of Che, and when Guevara passed the last of his 12 exams in 1953, he gave him a copy to prove to Ferrer, who had been telling Guevara that he would never finish, that he had finally completed his studies.
- ^ A Very Modern Icon by George Galloway, New Statesman, June 12, 2006
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 126.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 31.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 31.
- ^ a b Guevara Lynch 2000, p. 26.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 172.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 144.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 32.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 39.
- ^ Snow, Anita. "'My Life With Che' by Hilda Gadea." Associated Press at WJXX-TV. August 16, 2008. Retrieved on February 23, 2009.
- ^ Che Guevara 1960–67 by Frank E. Smitha.
- ^ Sinclair, Andrew (1970). Che Guevara. The Viking Press. p. 12.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 33.
- ^ a b Rebel Wife, A Review of My Life With Che: The Making of a Revolutionary by Hilda Gadea by Tom Gjelten, The Washington Post, October 12, 2008.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 55.
- ^ Fidel and Che: A Revolutionary Friendship by Simon Reid-Henry audio slideshow by The Guardian, January 9, 2009
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 28.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 37.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 194.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 213.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 32.
- ^ DePalma 2006, pp. 110–111.
- ^ a b c Latin lessons: What can we Learn from the World’s most Ambitious Literacy Campaign? by The Independent, November 7, 2010
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 45.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 269–270.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, pp. 105, 119.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 237–238, 269–270, 277–278.
- ^ a b c Luther 2001, pp. 97–99.
- ^ a b c Anderson 1997, 237.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 35.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 177.
- ^ Ignacio 2007, p. 193.
- ^ Poster Boy of The Revolution by Saul Landau, The Washington Post, October 19, 1997, p. X01.
- ^ Moore, Don. "Revolution! Clandestine Radio and the Rise of Fidel Castro". Patepluma Radio. http://www.pateplumaradio.com/central/cuba/rebel1.html.
- ^ Bockman 1984.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 40.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 47.
- ^ Castro 1972, pp. 439–442.
- ^ Dorschner 1980, pp. 41–47, 81–87.
- ^ Sandison 1996, p. 39.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 48.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 13.
- ^ Castañeda, pp. 145–146.
- ^ a b Castañeda, p. 146.
- ^ Anderson 1997, 397.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 400–401.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 424.
- ^ Castañeda, p. 159.
- ^ (Castañeda 1998, pp. 264–265).
- ^ a b Skidmore 2008, pp. 273.
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, p. 115. "The Penal Law of the War of Independence (July 28, 1896) was reinforced by Rule 1 of the Penal Regulations of the Rebel Army, approved in the Sierra Maestra February 21, 1958, and published in the army's official bulletin (Ley penal de Cuba en armas, 1959)" (Gómez Treto 1991, p. 123).
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, pp. 115–116.
- ^ Anderson 1997, pp. 372, 425.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 376.
- ^ Niess 2007, p. 60.
- ^ Gómez Treto 1991, p. 116.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 388.
- ^ Rally For Castro: One Million Roar "Si" To Cuba Executions – Video Clip by Universal-International News, narrated by Ed Herlihy, from January 22, 1959
- ^ Niess 2007, p. 61.
- ^ a b c Castañeda 1998, pp. 143–144.
- ^ The Legacy of Che Guevara – a PBS online forum with author Jon Lee Anderson, November 20, 1997
- ^ Different sources cite differing numbers of executions attributable to Guevara, with some of the discrepancy resulting from the question of which deaths to attribute directly to Guevara and which to the regime as a whole. Anderson (1997) gives the number specifically at La Cabaña prison as 55 (p. 387.), while also stating that "several hundred people were officially tried and executed across Cuba" as a whole (p. 387). (Castañeda 1998) notes that historians differ on the total number killed, with different studies placing it as anywhere from 200 to 700 nationwide (p. 143), although he notes that "after a certain date most of the executions occurred outside of Che's jurisdiction" (p. 143). These numbers are supported by Armando Lago and the opposition-based Free Society Project / Cuba Archive, which gives the figure as 216 executions ordered by Guevara across Cuba in three years (1957–1960) and 164 "victims" specifically at La Cabaña, which were according to Lago, "all carried out without affording the victims due process of law." Of further note, much of the discrepancy in the estimates as between 55 versus 164 executed at La Cabaña revolves around whether to include instances where Guevara had denied an appeal and signed off on a death warrant, but where the sentence was carried out after he relinquished his command of La Cabaña fortress on June 12, 1959.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 375.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 54.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 57.
- ^ a b c Kellner 1989, p. 58.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 282-285.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 423.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 431.
- ^ Taibo 1999, p. 300.
- ^ Che Guevara's Daughter Visits Bomb Memorial in Hiroshima by The Japan Times, May 16, 2008
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 435.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 25.
- ^ Casey 2009, pp. 25–50.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 55.
- ^ a b c d Kellner 1989, p. 61.
- ^ Latin America's New Look at Che by Daniel Schweimler, BBC News, October 9, 2007.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, pp. 449
- ^ Man and Socialism in Cuba by Che Guevara
- ^ a b Crompton 2009, p. 71.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 60.
- ^ Dumur 1964 a 1964 video interview of Che Guevara speaking French (with English subtitles).
- ^ a b c d "Socialism and Man in Cuba" A letter to Carlos Quijano, editor of Marcha, a weekly published in Montevideo, Uruguay; published as "From Algiers, for Marcha: The Cuban Revolution Today" by Che Guevara on March 12, 1965.
- ^ a b c d e Kellner 1989, p. 62.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 59.
- ^ PBS: Che Guevara, Popular but Ineffective.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 75.
- ^ Latin America Report. Foreign Broadcast Information Service (FBIS). 1984–03–23. p. 24. http://www.dtic.mil/cgi-bin/GetTRDoc?Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf&AD=ADA351284. Retrieved 2010-10-30.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 63.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 74.
- ^ The Spirit of Che Guevara by I.F. Stone, New Statesman, October 20, 1967.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 507.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 509.
- ^ a b "Economics Cannot be Separated from Politics" speech by Che Guevara to the ministerial meeting of the Inter-American Economic and Social Council (CIES), in Punta del Este, Uruguay on August 8, 1961.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 492.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 530.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 545.
- ^ Guevara 1997, pp 304
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 73.
- ^ a b c d e "Colonialism is Doomed" speech to the 19th General Assembly of the United Nations in New York City by Cuban representative Che Guevara on December 11, 1964.
- ^ a b c Bazooka Fired at U.N. as Cuban Speaks by Homer Bigart, The New York Times, December 12, 1964 – p. 1.
- ^ Guillermo Novo Biography by Spartacus Educational Encyclopedia.
- ^ Hart 2004, p. 271.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 618.
- ^ "Che Guevara: Father Of Revolution, Son Of Galway". Fantompowa.net. http://www.fantompowa.net/Flame/che_guevara_irish_roots.htm. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
- ^ Gerry Adams Featured in New Che Guevara Documentary by Kenneth Haynes, Irish Central, September 8, 2009
- ^ Guevara 1969, p. 350.
- ^ Guevara 1969, pp. 352–59.
- ^ a b Message to the Tricontinental A letter sent by Che Guevara from his jungle camp in Bolivia, to the Tricontinental Solidarity Organisation in Havana, Cuba, in the Spring of 1967.
- ^ Che Guevara's Final Verdict on the Soviet Economy by John Riddell, Centre for Research on Globalization, June 13, 2008.
- ^ a b c d e Ernesto 'Che' Guevara: A Rebel Against Soviet Political Economy by Helen Yaffe (author of Che Guevara: The Economics of Revolution), 2006
- ^ Guevara 1965.
- ^ Ben Bella 1997.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 624.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 629.
- ^ Gálvez 1999, p. 62.
- ^ Gott 2004 p. 219.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 86.
- ^ DR Congo's Rebel-Turned-Brain Surgeon by Mark Doyle, BBC World Affairs', December 13, 2005.
- ^ BBC News January 17, 2001.
- ^ "The intercept operators knew that Dar-es-Salaam was serving as a communications center for the fighters, receiving messages from Castro in Cuba and relaying them on to the guerrillas deep in the bush (Bamford 2002, p. 181).
- ^ Ireland's Own 2000.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 87.
- ^ From Cuba to Congo, Dream to Disaster for Che Guevara by The Guardian, August 12, 2000
- ^ Guevara 2000, p. 1.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, p. 316.
- ^ Che Guevara’s Central Bohemian Hideaway article and audio by Ian Willoughby, Český rozhlas, June 27, 2010
- ^ Guevara 2009, p. 167.
- ^ Mittleman 1981, p. 38.
- ^ Jacobson, Sid and Ernie Colón. Che: A Graphic Biography. Hill and Wang, 2009. 96–97.
- ^ Jacobson, Sid and Ernie Colón. Che: A Graphic Biography. Hill and Wang, 2009. 98.
- ^ a b Selvage 1985.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 693.
- ^ Members of Che Guevara's Guerrilla Movement in Bolivia by the Latin American Studies Organization
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 97.
- ^ U.S. Army 1967 and Ryan 1998, pp. 82–102, inter alia. "U.S. military personnel in Bolivia never exceeded 53 advisers, including a sixteen-man Mobile Training Team (MTT) from the 8th Special Forces Group based at Fort Gulick, Panama Canal Zone" (Selvage 1985).
- ^ "Bidding for Che", Time Magazine, Dec. 15, 1967.
- ^ Guevara 1972.
- ^ Castañeda 1998, pp. 107–112; 131–132.
- ^ Wright 2000, p. 86.
- ^ a b Guevara 2009, p. II.
- ^ Shadow Warrior: The CIA Hero of 100 Unknown Battles, Felix Rodriguez and John Weisman, Simon & Schuster, October 1989.
- ^ Barbie "Boasted of Hunting Down Che" by David Smith, The Observer, December 23, 2007.
- ^ Green Beret Behind the Capture of Che Guevara by Richard Gott, The Age, September 8, 2010
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 733.
- ^ a b "The Man Who Buried Che" by Juan O. Tamayo, Miami Herald, September 19, 1997.
- ^ a b c d e Ray, Michèle (March 1968). "In Cold Blood: The Execution of Che by the CIA". Ramparts Magazine: 33.
- ^ Grant 2007
- ^ Grant 2007. René Barrientos has never revealed his motives for ordering the summary execution of Guevara.
- ^ Almudevar, Lola. "Bolivia marks capture, execution of 'Che' Guevara 40 years ago." San Francisco Chronicle. Tuesday October 9, 2007. Retrieved on November 7, 2009.
- ^ Time magazine 1970.
- ^ a b Anderson 1997, p. 739.
- ^ Obituary: Che Guevara, Marxist Architect of Revolution by Richard Bourne, The Guardian, October 11, 1967
- ^ Almudevar 2007 and Gott 2005.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 179.
- ^ Casey 2009, p. 183.
- ^ The Death of Che Guevara by Bjorn Kumm, The New Republic, Originally published on November 11, 1967.
- ^ Lacey 2007a.
- ^ Watch blog image of Guevara's GMT Master.
- ^ Felix Rodríguez entry from Spartacus Schoolnet Encyclopedia.
- ^ Kornbluh 1997.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 740.
- ^ Anderson 1997, p. 741.
- ^ Kellner 1989, p. 101.
- ^ a b c Nadle, Marlene (August 24, 1968). "Régis Debray Speaks from Prison". Ramparts Magazine: 42.
- ^ Cuba salutes 'Che' Guevara: Revolutionary Icon Finally Laid to Rest CNN, October 17, 1997
- ^ "Bidding for Che", Time Magazine, Dec. 15, 1967.
- ^ Guevara 1967b.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 45.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 104.
- ^ Ryan 1998, p. 148.
- ^ Ramírez 1997.
- ^ Bolivia unveils original Che Guevara diary by Eduardo Garcia, Reuters, July 7, 2008.
- ^ Slain Che Guevara Soldiers Found? video report by National Geographic, August 21, 2009.
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 7.
- ^ Che's Second Coming? by David Rieff, November 20, 2005, New York Times.
- ^ Moynihan 2006.
- ^ Sinclair 1968 / 2006, p. 80.
- ^ Sinclair 1968 / 2006, p. 127.
- ^ McLaren 2000, p. 3.
- ^ Sinclair 1968 / 2006, p. 67.
- ^ Ernesto Che Guevara R.I.P. by Murray Rothbard, Left and Right: A Journal of Libertarian Thought, Volume 3, Number 3 (Spring-Autumn 1967).
- ^ Just a Pretty Face? by Sean O'Hagan, The Observer, July 11, 2004.
- ^ People's Weekly 2004.
- ^ Argentina pays belated homage to "Che" Guevara by Helen Popper, Reuters, June 14, 2008.
- ^ Statue for Che's '80th birthday' by Daniel Schweimler, BBC News, June 15, 2008.
- ^ On a tourist trail in Bolivia's hills, Che's fame lives on By Hector Tobar, Los Angeles Times, October 17, 2004.
- ^ Schipani 2007.
- ^ Behind Che Guevara’s mask, the cold executioner Times Online, September 16, 2007.
- ^ a b c Vargas Llosa 2005.
- ^ a b Kellner 1989, p. 106.
- ^ Casey 2009, pp. 325 & 235.
- ^ BBC News May 26, 2001.
- ^ see also Che Guevara (photo).
- ^ Lacey 2007b.
- ^ BBC News 2007.
- ^ O'Hagan 2004.
References
- Almudevar, Lola (October 9, 2007). "Bolivia marks capture, execution of 'Che' Guevara 40 years ago". San Francisco Chronicle.
- Anderson, Jon Lee (1997). Che Guevara: A Revolutionary Life. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 0-8021-1600-0.
- Bamford, James (2002). Body of Secrets: Anatomy of the Ultra-Secret National Security Agency (Reprint edition). New York: Anchor Books. ISBN 0-385-49908-6.
- BBC News (January 17, 2001). "Profile: Laurent Kabila". Accessed April 10, 2008.
- BBC News (May 26, 2001). Che Guevara photographer dies. Accessed January 4, 2006.
- BBC News (October 9, 2007). "Cuba pays tribute to Che Guevara". BBC News, International version.
- Beaubien, Jason (2009). Cuba Marks 50 Years Since 'Triumphant Revolution'. NPR: All Things Considered, Audio Report. http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=98937598.
- Ben Bella, Ahmed (October 1997). "Che as I knew him". Le Monde diplomatique. mondediplo.com. Accessed February 28, 2008.
- Bockman, USMC Major Larry James (April 1, 1984). The Spirit of Moncada: Fidel Castro's Rise to Power 1953–1959. United States: Marine Corps Command and Staff College.
- Casey, Michael (2009). Che's Afterlife: The Legacy of an Image. Vintage. ISBN 0307279308.
- Castañeda, Jorge G (1998). Che Guevara: Compañero. New York: Random House. ISBN 0-679-75940-9.
- Castro, Fidel (editors Bonachea, Rolando E. and Nelson P. Valdés; 1972). Revolutionary Struggle 1947–1958. Cambridge, Massachusetts and London: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-02065-3.
- Crompton, Samuel (2009). Che Guevara: The Making of a Revolutionary. Gareth Stevens. ISBN 143390053X.
- DePalma, Anthony (2006). The Man Who Invented Fidel: Castro, Cuba, and Herbert L. Matthews of the New York Times. New York: Public Affairs. ISBN 1-58648-332-3.
- Dorfman, Ariel (June 14, 1999). Time 100: Che Guevara. Time magazine.
- Dorschner, John and Roberto Fabricio (1980). The Winds of December: The Cuban Revolution of 1958. New York: Coward, McCann & Geoghegen. ISBN 0-698-10993-7.
- Dumur, Jean (interviewer) (1964). L'interview de Che Guevara (Video clip; 9:43; with English subtitles).
- Gálvez, William (1999). Che in Africa: Che Guevara's Congo Diary. Melbourne: Ocean Press, 1999. ISBN 1-876175-08-7.
- Gómez Treto, Raúl (Spring 1991). "Thirty Years of Cuban Revolutionary Penal Law". Latin American Perspectives 18(2), Cuban Views on the Revolution. 114–125.
- Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A New History. Yale University Press. ISBN 0300104111.
- Gott, Richard (August 11, 2005). "Bolivia on the Day of the Death of Che Guevara". Le Monde diplomatique. Accessed February 26, 2006.
- Grant, Will (October 8, 2007). "CIA man recounts Che Guevara's death". BBC News. Accessed February 29, 2008.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (1995). Motorcycle Diaries. London: Verso Books.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (editor Waters, Mary Alice) (1996). Episodes of the Cuban Revolutionary War 1956–1958. New York: Pathfinder. ISBN 0-87348-824-5.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (1965). "Che Guevara's Farewell Letter".
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (1967a). "English Translation of Complete Text of his Message to the Tricontinental"
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (1967b). "Diario (Bolivia)". Written 1966–1967.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (editors Bonachea, Rolando E. and Nelson P. Valdés; 1969). Che: Selected Works of Ernesto Guevara, Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-52016-8
- Guevara, Ernesto (2009). Che: The Diaries of Ernesto Che Guevara. Ocean Press. ISBN 1920888934.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (1972). Pasajes de la guerra revolucionaria.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (translated from the Spanish by Patrick Camiller; 2000). The African Dream. New York: Grove Publishers. ISBN 0-8021-3834-9.
- Guevara, Ernesto "Che" (2005). "Socialism and man in Cuba" (First published March 12, 1965 as "From Algiers, for Marcha. The Cuban Revolution Today"). Che Guevara Reader. (1997). Ocean Press. ISBN 1-875284-93-1
- Guevara, Ernesto; Deutschmann, David (1997). Che Guevara Reader: Writings by Ernesto Che Guevara on Guerrilla Strategy, Politics & Revolution. Ocean Press. ISBN 1875284931.
- Guevara Lynch, Ernesto (2000). Aquí va un soldado de América. Barcelona: Plaza y Janés Editores, S.A. ISBN 84-01-01327-5.
- Hall, Kevin (2004). "In Bolivia, Push for Che Tourism Follows Locals' Reverence". Common Dreams. commondreams.org. Accessed November 15, 2008.
- Haney, Rich (2005). Celia Sánchez: The Legend of Cuba's Revolutionary Heart. New York: Algora Pub. ISBN 0-87586-395-7.
- Hari, Johann (October 6, 2007). "Johann Hari: Should Che be an icon? No". The Independent.
- Hart, Joseph (2004). Che: The Life, Death, and Afterlife of a Revolutionary. New York: Thunder's Mouth Press. ISBN 1-56025-519-6.
- Ireland's Own (August 12, 2000). From Cuba to Congo, Dream to Disaster for Che Guevara. Accessed January 11, 2006.
- Kellner, Douglas (1989). Ernesto "Che" Guevara (World Leaders Past & Present). Chelsea House Publishers (Library Binding edition). p. 112. ISBN 1555468357.
- Kornbluh, Peter (1997). Electronic Briefing Book No. 5. National Security Archive. Accessed March 25, 2007.
- Lacey, Mark (October 26, 2007). "Lone Bidder Buys Strands of Che's Hair at U.S. Auction". New York Times.
- Lacey, Mark (October 9, 2007). "A Revolutionary Icon, and Now, a Bikini". The New York Times.
- Lago, Armando M (September 2005). "216 Documented Victims of Che Guevara in Cuba: 1957 to 1959PDF (24.8 KB)". Cuba: the Human Cost of Social Revolution. (Manuscript pending publication.) Summit, New Jersey: Free Society Project.
- Lavretsky, Iosif (1976). Ernesto Che Guevara. translated by A. B. Eklof. Moscow: Progress. p. 5. ASIN B000B9V7AW. OCLC 22746662.
- Luther, Eric (2001). Che Guevara (Critical Lives). Penguin Group (USA). p. 276. ISBN 002864199X.
- McLaren, Peter (2000). Che Guevara, Paulo Freire, and the Pedagogy of Revolution. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0847695336.
- Mittleman, James H (1981). Underdevelopment and the Transition to Socialism – Mozambique and Tanzania. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-500660-8
- Moynihan, Michael. "Neutering Sartre at Dagens Nyheter". Stockholm Spectator. Accessed February 26, 2006.
- Murray, Edmundo (November–December 2005). "Guevara, Ernesto [Che] (1928–1967)". Irish Migration Studies in Latin America (www.irlandeses.org).
- Che Guevara, by Frank Niess, Haus Publishers Ltd, 2007, ISBN 1-904341-99-3.
- O'Hagan, Sean (July 11, 2004). "Just a pretty face?". The Guardian. Accessed October 25, 2006.
- Ramírez, Dariel Alarcón (1997). Le Che en Bolivie. Paris: Éditions du Rocher. ISBN 2-268-02437-7.
- Ramonez, Ignacio (2007). Translated by Andrew Hurley. Fidel Castro: My Life London: Penguin Books. ISBN 9780141026268
- Ratner, Michael (1997). Che Guevara and the FBI: The U.S. Political Police Dossier on the Latin American Revolutionary. Ocean Press. ISBN 1875284761.
- Rodriguez, Félix I. and John Weisman (1989). Shadow Warrior/the CIA Hero of a Hundred Unknown Battles. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-66721-1.
- Ryan, Henry Butterfield (1998). The Fall of Che Guevara: A Story of Soldiers, Spies, and Diplomats. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-511879-0.
- Sanati, Kimia (October 3, 2007). "Islamist, Socialist Revolutions Don't Mix". IPS News. (Reporting from Tehran, Iran). Accessed October 13, 2010.
- Sandison, David (1996). The Life & Times of Che Guevara. Paragon. ISBN 0752517767.
- Schipani, Andres (September 23, 2007). "The Final Triumph of Saint Che". The Observer. (Reporting from La Higuera.)
- Selvage, Major Donald R. – USMC (April 1, 1985). Che Guevara in Bolivia. Globalsecurity.org. Accessed January 5, 2006.
- Sinclair, Andrew (1968 / re-released in 2006). Viva Che!: The Strange Death and Life of Che Guevara. Sutton publishing. ISBN 0750943106.
- Skidmore, Thomas E.; Peter H. Smith (2008). Modern Latin America. Oxford University Press. p. 436. ISBN 0195055330.
- Taibo II, Paco Ignacio (1999). Guevara, Also Known as Che. St Martin's Griffin. 2nd edition. p. 691. ISBN 0312206526.
- Time Magazine (October 12, 1970). "Che: A Myth Embalmed in a Matrix of Ignorance".
- Time Magazine cover story (August 8, 1960). "Castro's Brain".
- U.S. Army (April 28, 1967). Memorandum of Understanding Concerning the Activation, Organization and Training of the 2d Ranger Battalion – Bolivian Army. Accessed June 19, 2006.
- Vargas Llosa, Alvaro (July 11, 2005). "The Killing Machine: Che Guevara, from Communist Firebrand to Capitalist Brand". The Independent Institute. Accessed November 10, 2006.
- "World Combined Sources" (October 2, 2004). "Che Guevara remains a hero to Cubans". People's Weekly World.
- Wright, Thomas C. (2000 Revised edition). Latin America in the Era of the Cuban Revolution. Praeger. ISBN 0275967069.
External links
Che Guevara Events 
People Alberto Granado · Hilda Gadea · Aleida March · Aleida Guevara · Raúl Castro · Fidel Castro · Camilo Cienfuegos · "Tania" · "Willy" · "Pombo" · Régis Debray · Félix Rodríguez · Orlando Borrego · Mario TeránTheory Books Film Icon Famous photo · His legacy · In popular culture · In fashion · Korda · Feltrinelli · Jim Fitzpatrick · Sartre · La Higuera · MausoleumAuthors Socialism Currents Marxist Socialism · Christian Socialism · Islamic Socialism · Scientific socialism · Democratic socialism · Libertarian socialism · Mutualism · Market socialism · State socialism · Utopian socialism · Communism · Socialist anarchism · Syndicalism · Social democracy · Revolutionary socialism · Green socialism · Guild socialism · Socialism of the 21st century · Agrarian socialism · BolivarianismKey topics and issues Concepts Economic planning · Free association · Equality of opportunity · Direct democracy · Adhocracy · Technocracy · Self-management · Industrial democracy · Economic democracy · Public ownership · Common ownership · Social dividend · Basic income · Production for use · Calculation in kind · Labour voucherPeople Charles Hall · Henri de Saint-Simon · Robert Owen · Charles Fourier · William Thompson · Pierre Joseph Proudhon · Thomas Hodgskin · Louis Blanc · Moses Hess · Mikhail Bakunin · Karl Marx · Friedrich Engels · Ferdinand Lassalle · William Morris · Mary Harris Jones · Peter Kropotkin · Eduard Bernstein · Daniel De Leon · Eugene V. Debs · Jean Jaurès · John Dewey · Enrico Barone · Ben Tillett · Vladimir Lenin · Karl Liebknecht · Bertrand Russell · Rosa Luxemburg · Joseph Stalin · Leon Trotsky · Clement Attlee · Joseph Schumpeter · Lev Kamenev · Amadeo Bordiga · Jawaharlal Nehru · Josip Broz Tito · Mao Zedong · Subhas Chandra Bose · Tommy Douglas · Leonid Brezhnev · Kwame Nkrumah · Edvard Kardelj · Howard Zinn · Frantz Fanon · Robin Hahnel · Michael Albert · Hugo ChavezOrganizations First International (International Workingmen's Association) · Second International · Third International (Comintern) · Fourth International · Fifth International · Socialist International · World Federation of Democratic Youth (WFDY) · International Union of Socialist Youth (IUSY) · World Socialist Movement · International League of Religious SocialistsReligious socialism Regional socialism Related topics Criticism of capitalism · Class struggle · Democracy · Dictatorship of the proletariat · Egalitarianism · Equality of outcome · Impossibilism · Internationalism · State-owned enterprise · Left-wing politics · Marxism · Mixed economy · Nationalisation · Socialisation of production · Planned economy · Proletarian revolution · Reformism · Socialism in One Country · Socialist market economy · Post-capitalism · Trade union · Mode of production Communism
Communism 
Basic concepts Aspects Communist state · Communist party · Communist revolution · Communist symbolism · Communism and religion · History of communismVariants Marxism · Leninism · Trotskyism · Maoism · Luxemburgism · Titoism · Stalinism · Castroism · Guevarism · Hoxhaism · Juche · Left communism · Council communism · Anarchist communism · Religious communism · Christian communism · Eurocommunism · World communism · Stateless communism · National communism · Primitive communism · Scientific communism · List of communist partiesInternationals Figures Gracchus Babeuf · Karl Marx · Friedrich Engels · Peter Kropotkin · Rosa Luxemburg · Karl Liebknecht · Antonio Gramsci · Vladimir Lenin · Leon Trotsky · Joseph Stalin · Kim Il-sung · Mao Zedong · Ho Chi Minh · Josip Broz Tito · Che GuevaraRelated topics Categories:- 1928 births
- 1967 deaths
- Che Guevara
- Anti-fascists
- Anti-imperialism
- Argentine academics
- Argentine activists
- Argentine atheists
- Argentine communists
- Anti-Revisionists
- Argentine diplomats
- Argentine educators
- Argentine essayists
- Argentine expatriates
- Argentine guerrillas
- Argentine non-fiction writers
- Argentine people of Basque descent
- Argentine people of Irish descent
- Argentine people of Spanish descent
- Argentine physicians
- Argentine poets
- Argentine political scientists
- Argentine political writers
- Argentine rugby union players
- Argentine travel writers
- Deaths by firearm in Bolivia
- Executed revolutionaries
- Guerrilla warfare theorists
- Guerrillas killed in action
- Indigenous activists
- Marxist theorists
- Marxist writers
- Motorcycling writers
- National liberation movements
- People from Rosario, Santa Fe
- Revolutionaries
- Revolution theorists
- University of Buenos Aires alumni
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.







