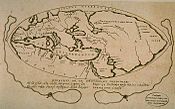
- World map
-
This article is about maps of the Earth. For other uses, see World map (disambiguation).
A world map is a map of the surface of the Earth, which may be made using any of a number of different map projections. A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane.
Maps of the world are often either 'political' or 'physical'. The most important purpose of the political map is to show territorial borders; the purpose of the physical map is to show features of geography such as mountains, soil type or land use. Geological maps show not only the physical surface, but characteristics of the underlying rock, fault lines, and subsurface structures.
Contents
Projections
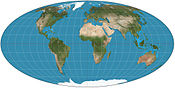
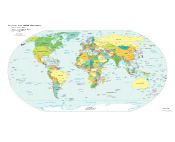
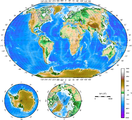
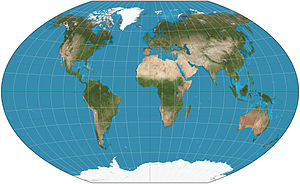 A world map on the Winkel tripel projection, a low-error map projection[1] adopted by the National Geographic Society for reference maps.
A world map on the Winkel tripel projection, a low-error map projection[1] adopted by the National Geographic Society for reference maps. Main article: Map projection
Main article: Map projectionMaps that depict the surface of the Earth use a projection, a way of translating the three-dimensional real surface of the geoid to a two-dimensional picture. Perhaps the best-known world-map projection is the Mercator Projection, originally designed as a form of nautical chart.
Aeroplane pilots use aeronautical charts based on a Lambert conformal conic projection, in which a cone is laid over the section of the earth to be mapped. The cone intersects the sphere (the earth) at one or two parallels which are chosen as standard lines. This allows the pilots to plot a great circle (shortest distance) route approximation on a flat, two-dimensional chart.
Thematic
Further information: thematic map-
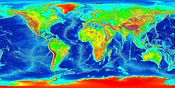
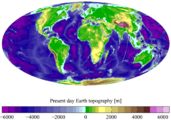
Elevation map
-
Present day Earth altimetry and bathymetry (Mollweide projection)
Historical
Further information: Early world maps-
Tabula Rogeriana world map by Muhammad al-Idrisi in 1154. Note that north is to the bottom
See also
- Ancient world maps
- Clickable world map
- Continental drift
- Blank maps of the world for historical use
- European Digital Archive on Soil Maps of the World
- International Map of the World
- List of World Map changes
- Mappa mundi
- OneGeology
- Time zone
- World Map at Lake Klejtrup
- Global Map
Projections
Main article: List of map projections- Albers projection
- Azimuthal conformal projection: see Stereographic projection
- Azimuthal equidistant projection
- Behrmann projection
- Bonne projection
- Bottomley projection
- Cahill octahedral Butterfly projection: see Bernard J.S. Cahill
- Craig retroazimuthal projection
- Dymaxion projection
- Equirectangular projection
- Gall–Peters projection
- Gnomonic projection
- Goode homolosine projection
- Hammer projection
- Hobo–Dyer projection
- Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection
- Lambert conformal conic projection
- Lambert cylindrical equal-area projection
- Littrow projection
- Mercator projection
- Miller cylindrical projection
- Mollweide projection
- Peters projection
- Plate carrée projection
- Polyconic projection
- Robinson projection
- Sinusoidal projection
- Stereographic projection
- Transverse Mercator projection
- Waterman butterfly projection
- Werner projection
- Winkel Tripel projection
References
- ^ Large-Scale Distortions in Map Projections, 2007, David M. Goldberg & J. Richard Gott III, 2007, V42 N4.
External links
- World map at WikiMapia
- World maps from the CIA World Factbook
- An interactive JAVA applet to study deformations (area, distance, angle) of world maps
- World maps in PDF format
- United Nations Map Library
- University of Texas Map Collection
- Java world map allowing different projections and orientations
- (European Digital Archive on the Soil Maps of the World - EuDASM)
- Brief History of Maps and Cartography
- GinkgoMaps - Free Digital World Maps published under the CC-by Licence
- American Geographical Society Library Digital Map Collection
Categories:- Map types
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.