- Robinson projection
-
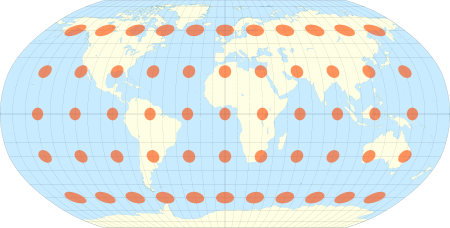 The Robinson projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation
The Robinson projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation
The Robinson projection is a map projection of a world map, which shows the entire world at once. It was specifically created in an attempt to find a good compromise to the problem of readily showing the whole globe as a flat image.
The Robinson projection is an accomplishment of Arthur H. Robinson in 1961, and has been in use by Rand McNally since the 1960s and was used by the National Geographic Society between 1988 and 1998. Since 1998, the National Geographic Society has used the Winkel tripel projection.
Contents
Strengths and weaknesses
The Robinson projection is neither equal-area nor conformal, abandoning both for a compromise. The creator felt this produced a better overall view than could be achieved by adhering to either. The meridians curve gently, avoiding extremes, but thereby stretch the poles into long lines instead of leaving them as points.
Hence, distortion close to the poles is severe, but quickly declines to moderate levels moving away from them. The straight parallels imply severe angular distortion at the high latitudes toward the outer edges of the map, a fault inherent in any pseudocylindrical projection. However, at the time it was developed, the projection effectively met Rand McNally's goal to produce appealing depictions of the entire world.
I decided to go about it backwards. … I started with a kind of artistic approach. I visualized the best-looking shapes and sizes. I worked with the variables until it got to the point where, if I changed one of them, it didn't get any better. Then I figured out the mathematical formula to produce that effect. Most mapmakers start with the mathematics.—1988 NY Times articleSpecification
The projection is defined by the table:
Latitude PLEN PDFE 00 1.0000 0.0000 05 0.9986 0.0620 10 0.9954 0.1240 15 0.9900 0.1860 20 0.9822 0.2480 25 0.9730 0.3100 30 0.9600 0.3720 35 0.9427 0.4340 40 0.9216 0.4958 45 0.8962 0.5571 50 0.8679 0.6176 55 0.8350 0.6769 60 0.7986 0.7346 65 0.7597 0.7903 70 0.7186 0.8435 75 0.6732 0.8936 80 0.6213 0.9394 85 0.5722 0.9761 90 0.5322 1.0000 The table is indexed by latitude, using interpolation. The PLEN column is the length of the parallel of latitude, and the PDFE column is multiplied by 0.5072 to obtain the distance of that parallel from the equator. Meridians of longitude are equally spaced on each parallel of latitude.
See also
- Winkel Tripel — projection currently used by the National Geographic.
Further reading
- Arthur H. Robinson (1974). "A New Map Projection: Its Development and Characteristics". In: International Yearbook of Cartography. Vol 14, 1974, pp. 145–155.
- John B. Garver Jr. (1988). "New Perspective on the World". In: National Geographic, December 1988, pp. 911–913.
- John P. Snyder (1993). Flattening The Earth—2000 Years of Map Projections, The University of Chicago Press. pp. 214–216.
External links
- Table of examples and properties of all common projections, from radicalcartography.net
- An interactive Java Applet to study the metric deformations of the Robinson Projection.
- Numerical evaluation of the Robinson projection, from Cartography and Geographic Information Science, April, 2004 by Cengizhan Ipbuker
Categories:- Cartographic projections
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

