- United States Navy officer rank insignia
-
Contents
In the United States Navy, officers have various ranks, called rates in the USN. Equivalency between services is by pay grade.
Rank categories
In the U.S. Navy, pay grades for officers are:
- W-2 to W-5 for Chief Warrant Officers. Chief Warrant Officers (CWO2-CWO5) are Commissioned Officers; a Warrant Officer (W-1) is not a commissioned officer. Warrant officers are "appointed" to their grade and have a probationary period assigned. The Army and Marine Corps currently appoint Warrant Officers to this pay grade.
- O-1 to O-10 for Unrestricted Line, Restricted Line, or Staff Corps Officers:
- O-1 through O-4 are junior officers - Ensign, Lieutenant (junior grade), Lieutenant, and Lieutenant Commander
- O-5 and O-6 are senior officers - Commander and Captain
- O-7 through O-10 are flag officers - Rear Admiral (lower half) (one star), Rear Admiral (two star), Vice Admiral (three star), and Admiral (four star).[1][2]
- O-11 is the additional flag officer is the rank of Fleet Admiral (five star). It is a wartime rank only and since 1945, there have been no additional Fleet Admirals appointed in the U.S. Navy. However, the rank of Fleet Admiral still remains listed on official rank insignia precedence charts and, if needed, this rank could be reestablished at the discretion of Congress and the President. All five-star officers are, technically, unable to retire from active duty. The last living Fleet Admiral in the U.S. Navy, FADM Chester W. Nimitz, died in 1966.[3]
Rank and promotion system
In the event that officers demonstrate superior performance and prove themselves capable of performing at the next higher pay grade, they are given an increase in pay grade. The official Navy term for this process is a promotion. Above the rank of Admiral is the rank of Fleet Admiral. The rank was held by four officers during World War II and not been held by any officer since. It is reserved for wartime use. The rank of Admiral of the Navy was an earlier equivalent to Fleet Admiral. It was awarded to only one person in the history of the U.S. Navy, that being, George Dewey in 1899. Efforts to resurrect the rank in the 20th century (as an O-12 grade outranking Fleet Admirals) failed, making it very unlikely that it will ever be used again.
Commissioned officers originate from the United States Naval Academy, Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps (NROTC), Officer Candidate School (OCS), and a host of other commissioning programs such as the Seaman to Admiral-21 program and the Limited Duty Officer/Chief Warrant Officer (LDO/CWO) Selection Program. There are also a small number of Direct Commissioned Officers (DCO), primarily staff corps officers in the medical, dental, nurse, chaplain and judge advocate general career fields.
Commissioned officers can generally be divided into line officers and staff corps:
- Line officers (or officers of the line) derive their name from the 18th-century British tactic of employing warships in a line of battle to take advantage of cannon on each side of the ship. These vessels were dubbed ships of the line and those who commanded them were likewise called "line officers." Today, all United States Navy unrestricted line and restricted line officers denote their status with a star located above their rank devices on the shoulder boards and sleeves of their white, blue and aviation winter working green uniforms, metal rank insignia on both collarpoints of khaki shirts/blouses, and cloth equivalents on both collarpoints of utility uniforms. Officers of the Staff Corps replace the star (or the left collarpoint on applicable shirts/blouses) with different insignias to indicate their field of specialty.[4] Line officers can be categorized into unrestricted and restricted communities.
- Unrestricted Line Officers are the most visible and well-known, due to their role as the Navy's war-fighting command element. They receive training in tactics, strategy, command and control, and actual combat and are considered unrestricted because they are authorized to command ships, aviation squadrons, and special operations units at sea or combat aviation squadrons or special operations units deployed ashore.
- Restricted Line Officers concentrate on non-combat related fields, which include marine engineering, aeronautical engineering, ship and aircraft maintenance, meteorology and oceanography, and naval intelligence. They are not qualified to command combat units, but can command organizations in their respective specialized career fields. In certain shipboard environments, many unrestricted line officers fill what might be considered restricted line duties, such as the officers in a ship's engineering department. Because they maintain their general shipboard duties, instead of completely specializing in one career area, they maintain their unrestricted line command career path.
- Staff corps officers are specialists in fields that are themselves professional careers and not exclusive to the military, for example health care, law, civil engineering and religion. There are eight staff corps: Medical Corps, Dental Corps, Nurse Corps, Medical Service Corps, Chaplain Corps, Navy Supply Corps, Judge Advocate General's Corps, and Civil Engineer Corps. They exist to augment the line communities and are able to be assigned to both line and staff commands. (The exception to this is the case of Civil Engineer Corps officers, who serve as the officers for Seabee units. This requires them to serve in a command capacity for ground combatants when the Seabees are deployed to combat areas.)
See also Commodore (United States) - today a title for selected Captains (O-6), and formerly a rank (O-7).
A "tombstone promotion" was a means of promoting combat-decorated officers to the next higher rank at the time of retirement. The advancement in grade resulted in no increase in retired pay. This practice was in use from at least 1920, but was discontinued in December 1959.[5]
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned Officer Rank Structure of the United States Navy Pay grade O-11 O-10 O-9 O-8 O-7 O-6 O-5 O-4 O-3 O-2 O-1 Insignia 










Title Fleet Admiral Admiral Vice Admiral Rear Admiral [6][7] Rear Admiral
(lower half)Captain Commander Lieutenant
CommanderLieutenant Lieutenant
(junior grade) [6][7]Ensign Abbreviation FADM ADM VADM RADM RDML CAPT CDR LCDR LT LTJG ENS NATO Code OF-10 OF-9 OF-8 OF-7 OF-6 OF-5 OF-4 OF-3 OF-2 OF-1 OF-1 - ¹Awarded only in times of Congressionally declared war (inactive).
Commissioned Warrant Officer Ranks
Commissioned Warrant Officer Rank Structure of the United States Navy Pay grade W-5 W-4 W-3 W-2 Insignia 



Title Chief Warrant Officer Five Chief Warrant Officer Four Chief Warrant Officer Three Chief Warrant Officer Two Abbreviation CWO-5 CWO-4 CWO-3 CWO-2 Officer Corps
Navy Officers serve either as a line officer (with a star above the stripes on the sleeve or shoulderboards), or in one of the staff corps:
Staff Corps Medical Corps Dental Corps Nurse Corps Medical Service Corps Judge Advocate General's Corps Insignia 




Designator1 210X 220X 290X 230X 250X Staff Corps Chaplain Corps
(Christian Faith)Chaplain Corps
(Jewish Faith)Chaplain Corps
(Muslim Faith)Chaplain Corps
(Buddhist Faith)Supply Corps Civil Engineer Corps Insignia 





Designator1 410X 410X 410X 410X 310X 510X
1An officer designator describes their general community or profession. The final (fourth) digit (X) denotes whether the officer has a Regular (0), Reserve (5), or Full Time Support (7) commission.
The staff corps devices are also worn on the left collar of uniforms.
See also
- Staff (military)
- List of Naval Officer Designators
- List of United States Navy staff corps
- Uniforms of the United States Navy
- Badges of the United States Navy
- U.S. Navy Midshipman rank insignia can be found in the Midshipman article.
- U.S. Navy Warrant officer rank insignia can be found in the Warrant Officer (United States) article.
- United States Navy enlisted rate insignia
- Naval officer ranks - comparison to other countries and explanation of NATO rank codes
- Navy Enlisted Classification
References
- ^ http://www.defenselink.mil/prhome/poprep2000/html/chapter4/chapter4_2.htm
- ^ http://www.defenselink.mil/specials/insignias/officers.html
- ^ Fleet Admiral (United States)
- ^ "Specialty Insignia - Staff Corps".
- ^ United States Navy Regulations, 1920 with changes up to and including No. 19 1938 Article 1668(3)
- ^ a b [1] 10 USC 5501. Navy: grades above chief warrant officer, W–5
- ^ a b [2] 37 USC 201. Pay grades: assignment to; general rules
External links
- Info on becoming a Navy Officer
- Chapter 4, Section 1: OFFICER RANK INSIGNIA of the Bureau of Personnel Uniform Regulations
- Department of Defense Rank Insignias — Officers Rank
United States Uniformed Services rank and rate insigniaOfficer Army · Marine Corps · Navy (midshipman) · Air Force · Coast Guard · PHS Commissioned Corps · NOAA Commissioned Corps • WarrantEnlisted Leadership Commander-in-chief: President of the United States · Secretary of Defense · Deputy Secretary of Defense · Joint Chiefs of Staff (Chairman) · United States Congress: Committees on Armed Services: (Senate · House) · Active duty four-star officers · Highest ranking officers in history · National Security Act of 1947 · Goldwater–Nichols Act
Organization BranchesReserve componentsNorthern · Central · European · Pacific · Southern · Africa · Special Operations · Strategic · Transportation
Structure United States Code (Title 10 · Title 14 · Title 32) · The Pentagon · Installations (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Budget · Units: (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Logistics · Media
Operations and history Current deployments · Conflicts · Wars · Timeline · History: (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Colonial · WWII · Civil affairs · African Americans · Asian Americans · Jewish Americans · Sikh Americans · Historiography: (A: 1/2 · MC · N · AF) · Art: (A · AF)
Personnel TrainingOtherOath: (Enlistment · Office) · Creeds & Codes: (Code of Conduct · NCO · A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Service numbers: (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Military Occupational Specialty/Rating/Air Force Specialty Code · Pay · Uniform Code of Military Justice · Judge Advocate General's Corps · Military Health System/TRICARE · Separation · Veterans Affairs · Conscription · Chiefs of Chaplains: (A · MC · N · AF · CG)
Equipment LandSeaAirAircraft (WWI · active) · Aircraft designation · Missiles · Helicopter arms
OtherLegend: A = Army, MC = Marine Corps, N = Navy, AF = Air Force, CG = Coast Guard, PHS = Public Health Service, NOAA = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, MSC = Military Sealift CommandUnited States commissioned officer and officer candidate ranks Pay Grade / Branch of Service Officer
CandidateO-1 O-2 O-3 O-4 O-5 O-6 O-7 O-8 O-9 O-10 Special Special Approximate insignia (no universal insignia) 




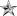
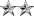
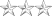


 or
or 
Air Force CDT / OT 2d Lt 1st Lt Capt Maj Lt Col Col Brig Gen Maj Gen Lt Gen Gen GAF[1] [3] Army CDT / OC 2LT 1LT CPT MAJ LTC COL BG MG LTG GEN GA[1] General of the Armies[1] Marine Corps Midn / Cand 2ndLt 1stLt Capt Maj LtCol Col BGen MajGen LtGen Gen [3] [3] Navy MIDN / OC ENS LTJG LT LCDR CDR CAPT RDML RADM VADM ADM FADM[1] Admiral of the Navy[1] Coast Guard CDT / OC ENS LTJG LT LCDR CDR CAPT RDML RADM VADM ADM [1] [1] Public Health Service [3] ENS LTJG LT LCDR CDR CAPT RADM RADM VADM ADM [3] [3] National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration[3] ENS LTJG LT LCDR CDR CAPT RDML RADM VADM[1] [2] [3] [3] Grade inactive; requires Congressional approval for re-activation [1]
Grade is authorized for use by U.S. Code but has not been created [2]
Grade never created or authorized [3]United States warrant officer ranks W-1 W-2 W-3 W-4 W-5 Air Force WO1[1] CWO2[1] CWO3[1] CWO4[1] CWO5[1] Army WO1 CW2 CW3 CW4 CW5 Marine Corps WO1 CWO2 CWO3 CWO4 CWO5 Navy WO1[1] CWO2 CWO3 CWO4 CWO5 Coast Guard WO1[1] CWO2 CWO3 CWO4 [2] Public Health Service [2] [2] [2] [2] [3] National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration[3] [3] [3] [3] [3] Grade inactive [1]
Grade is authorized for use by U.S. Code but has not been created [2]
Grade never created or authorized [3]Military ranks and insignia by country Africa Egypt (Army · Air Force · Navy) · South Africa · Tanzania
Americas Asia Burma · People's Republic of China (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Republic of China · India (Army · Air Force · Navy) · Indonesia · Iran (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Iraq · Israel · Japan · Jordan · Korea · Lebanon · Pakistan · Saudi Arabia · Singapore · Sri Lanka (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Thailand · Vietnam
Former: Imperial Japan (Army · Navy)Europe Albania · Austria · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Denmark (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Estonia · Finland · France (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland (Land Forces · Coast Guard) · Ireland (Army · Naval Service · Air Corps) · Italy (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Macedonia · Monaco · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Serbia · Slovenia · Spain (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey · Ukraine · United Kingdom (Navy · Army · Air Force) · Vatican
Former: Austria–Hungary · East Germany · Nazi Germany (Volkssturm · SA · SS) · Kingdom of Greece (Army · Navy) · Soviet Union · Yugoslavia · Serbia and MontenegroOceania Categories:- United States Navy lists
- Military insignia
- Military ranks of the United States Navy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


