- Finnish military ranks
-
Finnish military ranks form a system that incorporates features from Swedish, German, and Russian armed forces. In addition, the system has some typically Finnish characteristics that are mostly due to the personnel structure of the Finnish Defence Forces. The ranks have official names in Finnish and Swedish languages and official English translations. The Swedish forms are used in all Swedish-languages communications in Finland, e.g. in Swedish-speaking units of Finnish Defence Force. The system of ranks in the Swedish Armed Forces is slightly different.
Finland practices universal conscription of men (ca. 80% of each age cohort), and maintains only a cadre of paid personnel for training and maintaining military readiness. Most of lower ranks are conscripts, and leave service as sotamies (Private) or korpraali (Private 1st Class). Junior leaders, about 20% of age cohort, serve 12 months and leave service as alikersantti (Corporal) or kersantti (Sergeant). 10% of conscripts are trained as reserve officers, serving 12 months, and leave service usually as vänrikki (2nd Lieutenant) or in the Navy as aliluutnantti (Ensign). In principle, there should be no distinction between reserve and active ranks, and NCOs and reserve officers can be promoted in reserve, up to everstiluutnantti (Lieutenant Colonel). During peace time, reserve officers are inactive, i.e. they do not receive pay or have a position in the chain of command. Reservists are in duty only when mobilized during a crisis or when attending mandatory or voluntary refresher exercises. Nevertheless, reserve NCO or officer ranks are respected within the Finnish society and are an entrance requirement to a military or border guard career.
Rank and file and non-commissioned officers are promoted to their ranks by the commander of a brigade or equivalent, with the exception of the highest NCO ranks of ylivääpeli (Master Sergeant) and sotilasmestari (Sergeant Major). All officers from vänrikki (2nd Lieutenant) and higher are promoted to their ranks and commissioned to their offices by the President of Finland.[1] Professional officers are trained at the Finnish National Defence University. Career officers graduate first as sotatieteen kandidaatti (Bachelor of Military Science), which enables promotion to luutnantti (Lieutenant) then continue after 3–4 years temporary work to sotatieteen maisteri (Master of Military Science), which enables promotion to yliluutnantti (1st Lieutenant) and a commission to an office.
Contents
Table of ranks
The ranks currently used by the Finnish Defence Forces are (Finnish name above, and Swedish name below):
Army and Air Force ranks
Officers Translation Collar Insignia Sleeve Insignia Kenraali
GeneralGeneral 

Kenraaliluutnantti
GenerallöjtnantLieutenant General 

Kenraalimajuri
GeneralmajorMajor General 
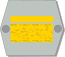
Prikaatikenraali
BrigadgeneralBrigadier General 
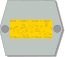
Eversti
ÖversteColonel 

Everstiluutnantti
ÖverstelöjtnantLieutenant Colonel 

Majuri
MajorMajor 
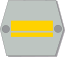
Kapteeni
KaptenCaptain 
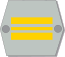
Yliluutnantti
Premiärlöjtnant1st Lieutenant 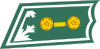
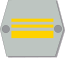
Luutnantti
LöjtnantLieutenant 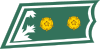

Vänrikki
Fänrik2nd Lieutenant 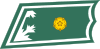
Non-commissioned officers Sotilasmestari
MilitärmästareSergeant Major 

Ylivääpeli
ÖverfältväbelMaster Sergeant 

Vääpeli
FältväbelSergeant 1st Class 

Ylikersantti
ÖversergeantStaff Sergeant 

Upseerikokelas
OfficersaspirantOfficer Candidate 

Kersantti
SergeantSergeant 

Upseerioppilas
OfficerselevOfficer Student 

Alikersantti
UndersergeantCorporal 

Rank-and-file Korpraali
KorpralPrivate 1st Class 

Aliupseerioppilas
UnderofficerselevNCO Student 
(Sotamies)
(Soldat)Private 

Officers Translation Shoulder Insignia Sleeve Insignia Amiraali
AmiralAdmiral 

Vara-amiraali
ViceamiralVice-Admiral 

Kontra-amiraali
KonteramiralRear Admiral 

Lippueamiraali
FlottiljamiralCommodore 

Kommodori
KommodorCaptain 

Komentaja
KommendörCommander 

Komentajakapteeni
KommendörkaptenLieutenant Commander 

Kapteeniluutnantti
KaptenlöjtnantLieutenant Sr. Grade 

Yliluutnantti
PremiärlöjtnantLieutenant 

Luutnantti
LöjtnantLieutenant Jr. Grade 

Aliluutnantti
UnderlöjtnantEnsign 

Petty Officers Sotilasmestari
MilitärmästareMaster Chief Petty Officer — 
Ylipursimies
ÖverbåtsmanSenior Chief Petty Officer — 
Pursimies
BåtsmanChief Petty Officer — 
Ylikersantti
ÖversergeantPetty Officer 1st Class — 
Upseerikokelas
OfficersaspirantOfficer Candidate — 
Kersantti
SergeantPetty Officer 2nd Class — 
Upseerioppilas
OfficerselevOfficer Student — 
Alikersantti
UndersergeantPetty Officer 3rd Class — 
Rank-and-file Ylimatruusi
ÖvermatrosSeaman — 
Aliupseerioppilas
UnderofficerselevNCO Student — 
Matruusi
MatrosSeaman Apprentice — 
Soldiers in the rank of a Private have branch-specific titles such as tykkimies "gunner"; the general rank of sotamies is no longer in use (see below).
The insignia is different from other European systems by some features. Stars are not used in the insignia. Large roses, instead of oak leaves, denote ranks from major to colonel. Generals wear lions (Lion of Finland), not stars. The qualifiers yli "Senior" and ali "Junior" are used in the names of some ranks; for example, kersantti is "Sergeant", while alikersantti is "Junior Sergeant" (Corporal).
In the army the insignia are placed in the collar in parade and service uniforms M/58 and M/83 and in field uniforms M/62 and M/91. The airforce places the M/58 insignia on the sleeve instead of the collar. In the navy where they have different parade dress they place the ranks on the sleeve and they also have the M/83 insignia on the shoulders. If the insignia are placed on the arm or on the sleeve, sleeve insignia are used. In the modern field uniform M/05, the collar insignia are placed on the chest. The colours of the background and the lining on the Army and Airforce collar patches indicate branch of specialization. In field uniforms, the collar patches do not carry branch colours, borders or corner accents. The national flag is carried in all uniforms and the unit insignia on background of the serviceman's branch colour is carried on the arm in battledress M/91 and M/05. In the table above, the army insignia for ranks from Private to Major are depicted on infantry collar patches, with the exception of Officer Student, which features Reserve Officer School collar patches. General officers' collar patches are most often gold on red. However, in some cases, the background of the collar patch retains the original colour of his branch of service.
In the Navy uniform, officers wear the Lion of Finland on the top of their insignia, while Warrant officers use the special insignia of their duty branch. In field uniforms, these emblems are dropped. Specialist officers always wear their specialist insignia in addition to their rank insignia on the collar patches. On sleeve and shoulder insignia, the specialty is denoted by coloured insignia background.
The NCO students do not wear any collar insignia. Their sole rank insignia consists of a silver line worn on the shoulder or arm of all uniforms, except in M/05 where the silver line is worn on the chest.
Exceptions
General officers
The ranks of Field Marshal (sotamarsalkka) and Marshal of Finland (Suomen marsalkka) were bestowed on Carl Gustaf Emil Mannerheim in 1933 and 1942, respectively. These are officially not military ranks but honorific titles, but were used like military ranks senior to the rank of General. The rank of General may, as a sign of special recognition, include a service branch: those historically used were General of Infantry (jalkaväenkenraali), General of Cavalry (ratsuväenkenraali) and General of Artillery (tykistökenraali). These additions do not affect seniority. There are no living general officers with such recognition, the last one being General of Infantry Adolf Ehrnrooth (1905–2004).
All generals from Brigadier General to General are addressed as Mr./Mrs. General (herra/rouva kenraali), and similarly for Admirals.
Military civil servants and specialist officers
Personnel serving in technical duties belonging to the officers without officer training hold the position of military civil servant (sotilasvirkamies). Their rank is comparable to either Senior Lieutenant, Lieutenant and Staff Sergeant, depending on the level of the civilian education required to serve in this position. The lowest class is reserved for non-salaried military civil servants. Usually the military civil servants are an exception as their positions are likely to be filled by special officers, who have received officer training and hold commissions in addition to civilian academic education. The most typical specialties are engineering and medicine.
Reservists may be promoted up to the rank of Major both in special and normal officer ranks, if they show extraordinary commitment to national defence. In rare cases, reservists have been promoted to the rank of Lieutenant Colonel.
Chaplains serve in the ranks of Chaplain (sotilaspastori), Senior Chaplain (kenttärovasti, literally, Field Dean), and Chaplain General (kenttäpiispa, literally, Field Bishop), corresponding to the ranks of Captain, Lieutenant Colonel, and Brigadier General, respectively. In addition, they have a personal rank into which they revert at the end of their clerical service in the Finnish Defence Force. Conscript chaplains and deacons serve in their personal rank.
Officer training
Conscripts who have passed a reserve officer course, serve as Officer Candidate (upseerikokelas) and are considered NCOs ranking as sergeants, although usually senior to conscript sergeants (they are promoted at least one day before any Corporal of the same induction year is promoted to Sergeant). They are addressed rouva/herra kokelas or rouva/herra upseerikokelas. At the end of their service period, they are promoted to 2nd Lieutenants. Cadets (kadetti) are career military, attending their professional officer education in the National Defence College. Cadets are senior to 2nd Lieutenants. In addition, the cadets may hold a cadet NCO rank which pertains to the seniority inside the Cadet Corps but does not affect their ranks in relation to other military personnel.
NCO ranks
The NCO ranks in the Finnish Defence Force are filled by conscripts, career NCOs and contractual military personnel. The basic NCO rank is Enlistee (sotilasammattihenkilö), which is a rank and file position reserved for career NCOs who have not received reserve NCO training. Its relation to other rank and file ranks is unspecified. Career NCOs usually serve in the ranks of Sergeant Major, Master Sergeant, Sergeant 1st Class, Staff Sergeant and Sergeant, the rank of Enlistee being reserved for career NCOs without conscript NCO training.
The contractual military personnel (sopimussotilaat) serve in their reserve ranks. Until 2007, reserve officers served in the rank of Staff Sergeant. This practice has now been abolished and nowadays reserve officers use their reserve rank of 2nd Lieutenant. As both conscript and career NCOs may serve in the rank of Sergeant, career Sergeants use a small sword insignia in conjunction of the chevrons to distinguish them from conscripts.
After discharge from the military, both career NCOs and contractual military personnel revert to their personal reserve ranks. The conscripts may hold the NCO ranks of Officer Cadet, Sergeant, Officer Student, or Corporal. Reserve personnel may hold any NCO rank.
Special positions
There are some positions, which resemble military ranks in their name, but are not. The position of the "Sergeant Major of a company" (or other unit such as battery in artillery) is called komppanian vääpeli "Sergeant 1st Class of the company". In past times it just to be position of the units most senior career NCO, but in now days the post in training units is held often by a Senior Lieutenant, and in mobilized units, a conscript NCO (alikersantti, kersantti etc.). Another example is komendantti, which is not a rank but a security/executive officer position in a brigade. While the rank of komentaja is found in the Navy, in general use it refers to a commander of a battalion or a larger unit.
Privates
Sotamies is the generic rank for Private, however the word sotamies is no longer used in any service branch apart from the air-force private, lentosotamies and land-force transports, car private, autosotamies. The rank is always given the name specific to the service branch:
- Jaeger (jääkäri) in infantry (including mortar personnel, who may be subordinated to artillery units)
- Signalist (viestimies) in signals corps
- Armourman (panssarimies) in tank units and Armour Jaeger (panssarijääkäri) in mechanised infantry
- Driver (autosotamies) in transport corps
- Gunner (tykkimies) in anti-aircraft corps, field artillery and coastal units of the Navy
- NBC private (suojelumies) in NBC defence units
- Engineer (pioneeri) in engineers
- Border Jaeger (rajajääkäri) in the Border Guard (Conscript rank, enlisted Border Guard personnel are NCOs in ranks of Border Guard (nuorempi rajavartija), Senior Border Guard (vanhempi rajavartija), Border Guard Sergeant (ylirajavartija) and Border Guard Master Sergeant (rajavartiomestari).)
- Special Border Jaeger (erikoisrajajääkäri) in Special Border Jaeger company of Border and Coast Guard School (Raja- ja merivartiokoulu).
- Airman (lentosotamies) in the Air Force
- Seaman (matruusi) in the Navy
- Coastal Jaeger (rannikkojääkäri) in certain units of Uusimaa Brigade (Uudenmaan prikaati)
- Dragoon (rakuuna) in the Dragoon troop of Army Warfare School (Rakuunaeskadroona/Maasotakoulu)
- Cavalryman (ratsumies) in the Häme Regiment (Hämeen rykmentti)
- Guard Jaeger (kaartinjääkäri) in Guard Jaeger Regiment (Kaartin jääkärirykmentti)
- Paratroop Jaeger (laskuvarjojääkäri) in Utti Jaeger Regiment (Utin jääkärirykmentti)
NCO students hold either the permanent rank of Private or Lance Corporal and rank accordingly. The rank of alokas is used to denote privates in basic training. The recruite, alokas is a new private, who has not been trained enough to have given a military oath or military guarantee. After having given an oath or such guarantee, the private soldier is not called anymore alokas, but he or she will be addressed as private or corresponding private level military rank.
See also
- Finnish Army Insignia of Rank (in Finnish)
- Finnish Navy Insignia of Rank (in Finnish)
- Finnish Air Force Insignia of Rank (in Finnish)
- Finnish Special Ranks' Insignia (in Finnish)
- Finnish Branch colors used with ranks' (in Finnish)
- Yleinen Palvelusohjesääntö (General Regulations, in Finnish)
- Conscript 2011
References
- ^ Laki puolustusvoimista 11.5.2007/551, 38 §, 40 §
Military ranks and insignia by country Africa Egypt (Army · Air Force · Navy) · South Africa · Tanzania
Americas Asia Burma · People's Republic of China (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Republic of China · India (Army · Air Force · Navy) · Indonesia · Iran (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Iraq · Israel · Japan · Jordan · Korea · Lebanon · Pakistan · Saudi Arabia · Singapore · Sri Lanka (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Thailand · Vietnam
Former: Imperial Japan (Army · Navy)Europe Albania · Austria · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Denmark (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Estonia · Finland · France (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland (Land Forces · Coast Guard) · Ireland (Army · Naval Service · Air Corps) · Italy (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Macedonia · Monaco · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Serbia · Slovenia · Spain (Army · Navy · Air Force) · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey · Ukraine · United Kingdom (Navy · Army · Air Force) · Vatican
Former: Austria–Hungary · East Germany · Nazi Germany (Volkssturm · SA · SS) · Kingdom of Greece (Army · Navy) · Soviet Union · Yugoslavia · Serbia and MontenegroOceania Categories:- Military ranks of Finland
- Military insignia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
