- United States Department of the Navy
-
Department of the Navy
DON
Seal of the Department of the Navy Agency overview Formed 1798 Headquarters Pentagon Agency executive Ray Mabus (SECNAV) Parent agency Department of Defense The Department of the Navy of the United States of America (DON) was established by an Act of Congress on 30 April 1798, to provide a government organizational structure to the United States Navy and, from 1834 onwards, for the United States Marine Corps, and when directed by the President, of the United States Coast Guard as a service within the Navy. The Department of the Navy was an Executive Department and the Secretary of the Navy was a member of the President's cabinet until 1949, when amendments to the National Security Act of 1947 changed the name of the National Military Establishment to the Department of Defense and made it an Executive Department. The Department of the Navy then became, along with the Department of the Army and Department of the Air Force, a Military Department within the Department of Defense: subject to the authority, direction and control of the Secretary of Defense.
Contents
Leadership
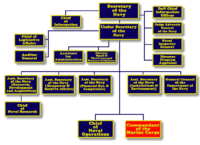
The Department of the Navy is headed by the Secretary of the Navy, also known as the SECNAV in naval jargon, who has the authority to conduct all of the affairs of the Department: subject to lawful authority, the Secretary of Defense, and the President. The Secretary of the Navy is appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate.[1] The Secretary is assisted by an Under Secretary of the Navy, four Assistant Secretaries of the Navy and a General Counsel of the Department of the Navy, who are also appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate.
The highest ranking military officers in the Department of the Navy are the Chief of Naval Operations and the Commandant of the Marine Corps, who are the principal military advisors to the Secretary of the Navy. They supervise their respective military services of the Department of the Navy, and in a separate capacity serves as members of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. They are assisted by a Vice Chief of Naval Operations and an Assistant Commandant of the Marine Corps.
Composition
Unlike its Army and Air Force counterparts, the Department of the Navy comprises two uniformed services, also called the Naval Services, the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. The Department of the Navy consists of all elements of the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. The Term "Navy Department", according to Navy Regulations Section 0204-2, refers only to the executive offices at the Seat of Government.
The Department of the Navy is composed of the following:[2]
- Office of the Secretary of the Navy, also known as the Secretariat.
- Office of the Chief of Naval Operations.
- Headquarters Marine Corps.
- The entire operating forces, including naval aviation, of the Navy and of the Marine Corps, and the reserve components of those operating forces.
- All field activities, headquarters, forces, bases, installations, activities, and functions under the control or supervision of the Secretary of the Navy.
- The Coast Guard when it is operating as a service in the Navy.
In H.R. 1585, the Fiscal Year 2008 National Defense Authorization Bill (NDAA) for 2008, the Department of the Navy was to be renamed the Department of the Navy and Marine Corps. The Bill passed in the on 17 May 2007.[3]
The proposed renaming encountered opposition among members of the DOD civilian leadership and among senior Navy admirals and Marine Corps generals. In the U.S. Senate, the House Bill was replaced by SA2011, an amendment in the nature of a substitute, removing the renaming provision along with other changes. The amendment was sponsored by Senator Carl Levin, Democrat of Michigan, introduced on 9 July 2007, and agreed to by unanimous consent on 1 October 2007.[4]
The House version including the provision was withdrawn in conference committee.
References
- United States Navy Regulations, Accessed on 2011-03-23.
- ^ 10 USC §5013, Accessed on 2011-03-23.
- ^ 10 USC §5061, Accessed on 2011-03-23
- ^ "H.R. 1585: National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2008". Legislation: 2007-2008 (110th Congress). GovTrack.us. http://www.govtrack.us/congress/bill.xpd?bill=h110-1585. Retrieved 2007.
- ^ "S.Amdt. 2011: In the nature of a substitute.". Legislation: 2007-2008 (110th Congress). GovTrack.us. http://www.govtrack.us/congress/amendment.xpd?session=110&amdt=s2011. Retrieved 24 December 2007.
External links
- Department of the Navy website
- US Marine Corps official website
- US Navy official website
- Department of Defense website
- History of the Department of the Navy Seal used on US Naval Dinnerware from late 1800s through the 1970s
- Proposed and finalized federal regulations from the United States Department of the Navy
United States federal executive departments United States Department of the Navy leadershipSecretaries Stoddert • Smith • Hamilton • Jones • Crowninshield • S Thompson • Southard • Branch • L. Woodbury • Dickerson • Paulding • Badger • Upshur • Henshaw • Gilmer • Mason • Bancroft • Mason • Preston • Graham • Kennedy • Dobbin • Toucey • Welles • Borie • Robeson • R Thompson • Goff • Hunt • Chandler • Whitney • Tracy • Herbert • Long • Moody • Morton • Bonaparte • Metcalf • Newberry • Meyer • Daniels • Denby • Wilbur • Adams • Swanson • Edison • Knox • Forrestal


Under
SecretariesAssistant
SecretariesPre-1954Fox • Faxon • Soley • McAdoo • T. Roosevelt Sr. • Allen • Hackett • Darling • Newberry • Satterlee • Winthrop • F. Roosevelt • G. Woodbury • T. Roosevelt Jr. • Robinson • Jahncke • H. Roosevelt • Edison • Compton • Bard • Hensel • Kenney • Andrews • Koehler • Askins • FoglerPost-1954Financial Management and Comptroller • Installations and Environment • Manpower and Reserve Affairs • Research, Development and Acquisitions • General Counsel of the Navy • defunct: (Air · Installations and Logistics · Material · Research and Development · Research, Engineering and Systems · Shipbuilding and Logistics)Categories:- Former United States Executive Departments
- United States Department of Defense
- United States Navy organization
- 1798 establishments in the United States
- 1949 disestablishments
- 1949 establishments
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.