- United States Secretary of Defense
-
United States Secretary of Defense 
Seal of the Department of Defense
Flag of the Secretary of DefenseFormation September 19, 1947 First holder James Forrestal Succession Sixth
(in the presidential line of succession)Deputy The Deputy Secretary of Defense Salary Executive Schedule, Level 1
(5 U.S.C. § 5312)Website www.defense.gov The Secretary of Defense (SecDef) is the head and chief executive officer of the Department of Defense of the United States of America. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a Defense Minister in other countries. Under the direction of the President, the Secretary of Defense has per federal law (10 U.S.C. § 113) "authority, direction and control over the Department of Defense", and is further designated by statute as "the principal assistant to the President in all matters relating to the Department of Defense".[1]
The Secretary of Defense is in the chain of command and exercises command and control, subject only to the orders of the President, over all Department of Defense forces – i.e. Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps – for both operational and administrative purposes.[2][3][4][5] Only the Secretary of Defense or the President can authorize the transfer of forces from one Combatant Command to another.[6] The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is the principal military adviser to the Secretary of Defense and the President, and while the Chairman may assist them in their command functions, the Chairman is not in the chain of command.[7]
The Secretary of Defense is appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate, and is by custom a member of the Cabinet, and by law a member of the National Security Council. An individual may not be appointed as Secretary of Defense within seven years after relief from active duty as a commissioned officer of a regular component of an armed force.[8]
Along with the Secretary of State, the Attorney General and the Secretary of the Treasury, the Secretary of Defense is generally regarded as one of the Big Four important cabinet officials. Secretary of Defense is a Level I position of the Executive Schedule and thus earns a salary of $199,700 per year. The current Secretary is Leon Panetta who assumed office July 1, 2011.
Contents
History
The Army, Navy, and Marine Corps were established in 1775, in concurrence with the American Revolution. The War Department, headed by the Secretary of War, was created by Act of Congress in 1789 and was responsible for both the Army and Navy until the founding of a separate Department of the Navy in 1798.
Based on the experiences of World War II, proposals were soon made on how to more effectively manage the large combined military establishment over which only the President had direct line authority. The Army generally favored centralization while the Navy had institutional preferences for decentralization and the status quo. The resulting National Security Act of 1947 was largely a compromise between these divergent viewpoints. The Act split the War Department into the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force, each with their own Secretary, and created a sui generis National Military Establishment led by a Secretary of Defense. At first, each of the service secretaries maintained quasi-cabinet status The first Secretary of Defense, James Forrestal, who as Secretary of the Navy had opposed creation of the new position, found it difficult to exercise authority over them with the limited powers his office had. To address this and other problems, the Act was amended in 1949 to further consolidate the national defense structure in order to reduce interservice rivalry, directly subordinate the Secretaries of the Army, the Navy and the Air Force to the Secretary of Defense in the chain of command, and rename the National Military Establishment to the Department of Defense. The position of the Deputy Secretary of Defense, the number two position in the department, was also created at this time.
The general trend since 1949 has been to further centralize management in the Department of Defense, elevating the status and authorities of civilian OSD appointees and defense-wide organizations at the expense of the military departments and the services within them. The last major revision of the statutory framework concerning the position was done in the Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1986. In particular, it elevated the status of joint service for commissioned officers, making it in practice a requirement before appointments to general officer and flag officer grades could be made.
Powers and Functions
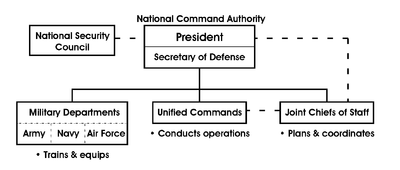
In the U.S. Armed Forces, the Secretary of Defense is often referred to as SecDef or SD. The Secretary of Defense and the President together constitute the National Command Authorities (NCA),[9] which has sole authority to launch strategic nuclear weapons. All nuclear weapons are governed by this dual-authority – both must concur before a strategic nuclear strike may be ordered.
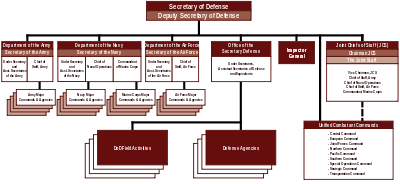
The Secretary's staff element is called the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) and is composed of a Deputy Secretary of Defense (DEPSECDEF) and five Under Secretaries of Defense in the fields of Acquisition, Technology & Logistics; Comptroller/Chief Financial Officer; Intelligence; Personnel & Readiness; and Policy.
The Secretary of Defense by statute also exercises "authority, direction and control" over the three Secretaries of the military departments (Secretary of the Army, Secretary of the Navy, and Secretary of the Air Force), the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, the other members of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Army Chief of Staff, Commandant of the Marine Corps, Chief of Naval Operations, and Air Force Chief of Staff), the Combatant Commanders of the Unified Combatant Commands, the Directors of the Defense Agencies (for example the Director of the National Security Agency) and of the DoD Field Activities. All of these high-ranking positions require Senate confirmation.
The Secretary is one of few civilians[10] who is authorized to act as convening authority in the military justice system for General Courts-Martial (10 U.S.C. § 822: article 22, UCMJ), Special Courts-Martial (10 U.S.C. § 823: article 23, UCMJ), and Summary Courts-Martial (10 U.S.C. § 824: article 24 UCMJ).
List of Secretaries of Defense
The longest-serving Secretary of Defense is the late Robert McNamara, who served for a total of 2,595 days.
- Parties
- Status
Denotes acting Secretary of DefenseNo. Portrait Name State of Residence Took Office Left Office Days served President(s) 1 
James Vincent Forrestal New York September 19, 1947 March 19, 1949 558 Harry S. Truman 2 
Louis Arthur Johnson West Virginia March 28, 1949 September 19, 1950 540 3 George Catlett Marshall, Jr. Virginia September 19, 1950 September 19, 1951 365 4 
Robert Abercrombie Lovett New York September 19, 1951 January 20, 1953 491 5 
Charles Erwin Wilson Indiana January 20, 1953 October 8, 1957 1,722 Dwight D. Eisenhower 6 
Neil Hosler McElroy Ohio October 9, 1957 December 1, 1959 783 7 
Thomas Sovereign Gates, Jr. Pennsylvania December 2, 1959 January 20, 1961 415 8 
Robert Strange McNamara Michigan January 21, 1961 February 29, 1968 2,595 John F. Kennedy Lyndon B. Johnson 9 
Clark McAdams Clifford Kansas March 1, 1968 January 20, 1969 326 10 Melvin Robert Laird Wisconsin January 22, 1969 January 29, 1973 1,469 Richard Nixon 11 
Elliot Lee Richardson Massachusetts January 30, 1973 May 24, 1973 114 – 
William Perry Clements, Jr. Texas May 24, 1973 July 2, 1973 39 12 
James Rodney Schlesinger Virginia July 2, 1973 November 19, 1975 870 Gerald Ford 13 
Donald Henry Rumsfeld Illinois November 20, 1975 January 20, 1977 427 14 
Harold Brown New York January 21, 1977 January 20, 1981 1,460 Jimmy Carter 15 
Caspar Willard Weinberger California January 21, 1981 November 23, 1987 2,497 Ronald Reagan 16 
Frank Charles Carlucci III Pennsylvania November 23, 1987 January 20, 1989 424 – William Howard Taft IV Ohio January 20, 1989 March 20, 1989 59 George H. W. Bush 17 
Richard Bruce Cheney Wyoming March 21, 1989 January 20, 1993 1,402 18 
Leslie Aspin, Jr. Wisconsin January 21, 1993 February 3, 1994 378 Bill Clinton 19 
William James Perry Pennsylvania February 3, 1994 January 24, 1997 1,085 20 
William Sebastian Cohen Maine January 24, 1997 January 20, 2001 1,457 21 
Donald Henry Rumsfeld Illinois January 20, 2001 December 18, 2006 2,158 George W. Bush 22 
Robert Michael Gates Texas December 18, 2006 July 1, 2011[11] 1,643 Barack Obama 23 
Leon Edward Panetta California July 1, 2011 Incumbent 135 Succession
Presidential succession
The Secretary of Defense is sixth in the presidential line of succession, following the Secretary of the Treasury and preceding the Attorney General.
Secretary of Defense succession
In Executive Order 13533 of March 1, 2010, President Barack Obama modified the line of succession regarding who would act as Secretary of Defense in the event of a vacancy or incapacitation, thus reversing the changes made by President George W. Bush in Executive Order 13394 as to the relative positions of the Secretaries of the Military Departments. All of the officials in the line of succession are civilians appointed by the President with the advice and consent of the Senate:
Executive Order 13533 (March 1, 2010—Present)
# Office Secretary of Defense 1 Deputy Secretary of Defense 2 Secretary of the Army 3 Secretary of the Navy 4 Secretary of the Air Force 5 Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology, and Logistics 6 Under Secretary of Defense for Policy 7 Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller) 8 Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness 9 Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence 10 Deputy Chief Management Officer of the Department of Defense 11 Principal Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology, and Logistics 12 Principal Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Policy 13 Principal Deputy Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller) 14 Principal Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness 15 Principal Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence 16 Director of Defense Research and Engineering 17 General Counsel of the Department of Defense
Assistant Secretaries of Defense
Assistant to the Secretary of Defense for Nuclear and Chemical and Biological Defense Programs
Director of Operational Test and Evaluation
Director of Operational Energy Plans and Programs
and the Director of Cost Assessment and Program Evaluation18 Under Secretary of the Army
Under Secretary of the Navy
and the Under Secretary of the Air Force19 Assistant Secretaries of the Army
Assistant Secretaries of the Navy
Assistant Secretaries of the Air Force
General Counsel of the Army
General Counsel of the Navy
and the General Counsel of the Air Force.Executive Order 13394 (December 22, 2005—March 1, 2010)
# Office Secretary of Defense 1 Deputy Secretary of Defense 2 Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence 3 Under Secretary of Defense for Policy 4 Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology, and Logistics 5 Secretary of the Army 6 Secretary of the Air Force 7 Secretary of the Navy 8 Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness
and the Under Secretary of Defense (Comptroller)9 Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Technology
Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Policy
and the Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Personnel and Readiness10 General Counsel of the Department of Defense
Assistant Secretaries of Defense
and the Director of Operational Test and Evaluation11 Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Logistics and Material Readiness
and the Director of Defense Research and Engineering12 Under Secretary of the Army
Under Secretary of the Navy
and the Under Secretary of the Air Force13 Assistant Secretaries of the Army
Assistant Secretaries of the Navy
Assistant Secretaries of the Air Force
General Counsel of the Army
General Counsel of the Navy
and the General Counsel of the Air Force.Living former Secretaries of Defense
- 10th – Melvin Robert Laird
- 12th – James Rodney Schlesinger
- 13th and 21st – Donald Henry Rumsfeld
- 14th – Harold Brown
- 16th – Frank Charles Carlucci III
- 17th – Richard Bruce Cheney
- 19th – William James Perry
- 20th – William Sebastian Cohen
- 22nd – Robert Michael Gates
See also
- List of United States Secretaries of Defense by time in office
References
Federal law
Directives and doctrine
- Gates, Robert M. (2010-12-21). [[1] Department of Defense Directive 5100.1: Functions of the Department of Defense and Its Major Components]. Department of Defense Directive. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. [2].
- Mullen, Michael G. (2009-03-20). [[3] Joint Publication 1 – Doctrine for the Armed Forces of the United States]. Joint Publications. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Defense. [4].
Print sources
- Trask, Roger R.; Goldberg, Alfred (1997). [[5] The Department of Defense 1997-1947: Organization and Leaders]. Washington, D.C.: Historical Office, Office of the Secretary of Defense/U.S. Government Printing Office. ISBN 0160491630. [6].
Online sources
- "Histories of the Secretaries of Defense". U.S. Department of Defense. http://www.defenselink.mil/specials/secdef_histories/. Retrieved September 3, 2002.
- "The Department of Defense Organizational Structure". U.S. Department of Defense. http://www.dod.mil/odam/omp/pubs/GuideBook/DoD.htm#Secretary%20of%20Defense. Retrieved November 13, 2006.
Footnotes
- ^ Title 10 of the United States Code §113
- ^ Title 10 of the United States Code §162(b)
- ^ >Title 10 of the United States Code §3011
- ^ Title 10 of the United States Code §5011
- ^ Title 10 of the United States Code §8011
- ^ Title 10 of the United States Code §162(a)
- ^ Title 10 of the United States Code §152(c)
- ^ The National Security Act of 1947 originally required an interval of ten years after relief from active duty, which was reduced to seven years by Sec. 903(a) of the 2008 National Defense Authorization Act. In 1950 Congress passed special legislation (Pub. Law 81-788) to allow George C. Marshall to serve as Secretary of Defense while remaining a commissioned officer on the active list of the Army (Army regulations kept all five-star generals on active duty for life), but warned:
It is hereby expressed as the intent of the Congress that the authority granted by this Act is not to be construed as approval by the Congress of continuing appointments of military men to the office of Secretary of Defense in the future. It is hereby expressed as the sense of the Congress that after General Marshall leaves the office of Secretary of Defense, no additional appointments of military men to that office shall be approved.
See Defenselink bio, retrieved 8/2/2010; and Marshall Foundation bio, retrieved 8/2/2010.
- ^ http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1O63-NationalCommandAuthoritis.html
- ^ Others include the President, the Secretaries of the Military Departments, and the Secretary of Homeland Security (when the Coast Guard is not under DoD)
- ^ http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/43591679/ns/politics-more_politics/
External links
- The Reinvention of Robert Gates by Michael Crowley, The New Republic, November 9, 2009
- "Top Civilian and Military Leaders". U.S. Department of Defense. http://www.defenselink.mil/osd/topleaders.aspx. Retrieved October 13, 2007.[dead link] – Includes the Secretary of Defense
- More information on each position and biographies of the current Deputy Secretary (DepSecDef) and Under Secretaries (USDs)
United States presidential line of succession Preceded by
Secretary of the Treasury6th in line Succeeded by
Attorney GeneralSecretaries of Defense of the United States of America

Senior Officials in the United States Department of Defense Secretary of Defense: Leon Panetta
Deputy Secretary of Defense: Ashton Carter
Secretaries of the Military Departments:
Secretary of the Army: John McHugh • Secretary of the Navy: Ray Mabus • Secretary of the Air Force: Michael DonleyChairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff: Martin Dempsey, USA
Under Secretaries of Defense:
Acquisition, Technology and Logistics: Frank Kendall III (Acting) • Policy: Michèle Flournoy • Comptroller/Chief Financial Officer: Robert Hale • Personnel and Readiness: Clifford Stanley • Intelligence: Michael VickersVice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff: James Winnefeld, USN
Chiefs of the Military Services:
Chief of Staff of the Army: Raymond Odierno • Commandant of the Marine Corps: James Amos • Chief of Naval Operations: Jonathan Greenert • Chief of Staff of the Air Force: Norton Schwartz
Leadership Commander-in-chief: President of the United States · Secretary of Defense · Deputy Secretary of Defense · Joint Chiefs of Staff (Chairman) · United States Congress: Committees on Armed Services: (Senate · House) · Active duty four-star officers · Highest ranking officers in history · National Security Act of 1947 · Goldwater–Nichols Act
Organization Department of Defense (Secretary): Army (Secretary) · Navy (Secretary) · Air Force (Secretary)
Department of Homeland Security (Secretary): Coast GuardBranchesReserve componentsNorthern · Central · European · Pacific · Southern · Africa · Special Operations · Strategic · Transportation
Structure United States Code (Title 10 · Title 14 · Title 32) · The Pentagon · Installations (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Budget · Units: (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Logistics · Media
Operations and history Current deployments · Conflicts · Wars · Timeline · History: (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Colonial · WWII · Civil affairs · African Americans · Asian Americans · Jewish Americans · Sikh Americans · Historiography: (A: 1/2 · MC · N · AF) · Art: (A · AF)
Personnel TrainingOtherOath: (Enlistment · Office) · Creeds & Codes: (Code of Conduct · NCO · A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Service numbers: (A · MC · N · AF · CG) · Military Occupational Specialty/Rating/Air Force Specialty Code · Pay · Uniform Code of Military Justice · Judge Advocate General's Corps · Military Health System/TRICARE · Separation · Veterans Affairs · Conscription · Chiefs of Chaplains: (A · MC · N · AF · CG)
Equipment LandSeaAirAircraft (WWI · active) · Aircraft designation · Missiles · Helicopter arms
OtherLegend: A = Army, MC = Marine Corps, N = Navy, AF = Air Force, CG = Coast Guard, PHS = Public Health Service, NOAA = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, MSC = Military Sealift Command Leaders of the United States federal executive departments Agriculture • Commerce • Defense • Education • Energy • Health and Human Services • Homeland Security • Housing and Urban Development • Interior • Justice • Labor • State • Transportation • Treasury • Veterans Affairs
Past department leaders: Commerce and Labor • Health, Education, and Welfare • Navy • Post Office • WarCategories:- Lists of government ministers
- United States Executive Cabinet
- United States Secretaries of Defense
- 1947 establishments in the United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.