- Uniforms of the United States Navy
-
This article examines dress uniforms, daily service uniforms, working uniforms, special situations, and the history of uniforms of the United States Navy. For simplicity in this article, "Officers" refers to both commissioned officers and warrant officers.
Contents
Dress Uniforms
The United States Navy has three categories of dress uniforms, from least to most formal: service, full, and dinner dress.
Service Dress
Service dress uniforms are worn for official functions not rising to the level of full or dinner dress. They are also commonly worn when traveling in official capacity, or when reporting to a command. They are seasonal, with the white uniform worn in summer and the blue in winter. Service Dress Blue may be worn year round for travel only. The civilian equivalent is a business suit. Ribbons are worn over the left breast pocket in all variations of the service dress uniform. The All-Weather Coat, Overcoat, or Reefer may be worn with Service Dress uniforms in cold or inclement weather.
Officers and Chief Petty Officers
- Service Dress Blue
The Service Dress Blue uniform consists of a navy blue suit coat, trousers, white shirt, and four-in-hand necktie (women substitute a neck tab). The material is generally wool or a wool blend, depending on the vendor. The men's jacket is double breasted with six gold-colored buttons, and the women's jacket has a single row of four gold-colored buttons. Rank insignia is the gold sleeve stripes for commissioned officers, while rating badges and service stripes are worn on the left sleeve by Chief Petty Officers (CPOs). The prescribed headgear is the white combination cap, although a navy blue garrison cap is optional, unless stated otherwise by the prescribing authority in some situations when the jacket is not worn.
- Service Dress Khaki
The Service Dress Khaki uniform, announced in 2006, is authorized for wear for commissioned officers and CPOs. [1] The uniform reintroduces a khaki service coat worn with a black necktie and shoulder boards. Widely seen during World War II through the Vietnam War years, this uniform was dropped in 1975 by then-Chief of Naval Operations, Admiral Elmo Zumwalt, in order to reduce the number of items in the officer's seabag. It was reintroduced to provide a more practical alternative to the Service Dress Whites. Some commentators, including the periodical Navy Times, have spoken of this uniform as having a "throwback" look.[2] The prescribed headgear is a combination cap with khaki cover.
- Service Dress White
The Service Dress White uniform is very different for the men's and women's variations. Men wear a high stand-collared white tunic, with black shoulder boards for officers or the metal anchor collar devices for CPOs, white trousers, and white shoes. This uniform is informally called "chokers" due to the standing collar. The material is a weave of polyester known as "Certified Navy Twill". Women wear a uniform similar to the service dress blue but with a white coat and skirt or trousers. The white combination cap is the prescribed headgear. A noticeable difference between the male uniforms and the female uniforms is the placement of the women officer's rank insignia on the sleeves (in the same manner as that on the blue uniform) and the placement of women CPO rank insignia (the fouled anchor with USN monogram and five-pointed cocked "line" stars) on the lapels of the jacket.
Junior Enlisted
Service Dress Blue for enlisted personnel are based on the standard Navy jumper in navy blue, colloquially referred to as "crackerjacks" because of the Navy-uniformed figure that adorns the Cracker Jack snack box. They consist of navy blue wool with three rows of white piping on the collar and cuffs and white stars at the corners of the "tar flap." A traditional white "Dixie cup" sailor cap is also issued with the uniform, as well as black leather shoes. The trousers for the blue uniform are flared toward the cuff and are sometimes erroneously called "bell bottoms" (bell bottoms were an unauthorized modification sometimes seen in the early to mid-20th Century in which the legs were tailored tightly and the cuff end of the trousers were flared to an extreme). The trousers have a flap opening with thirteen buttons (which, contrary to popular belief, do not represent the original Thirteen Colonies of the early United States). Female enlisted Sailors' Service Dress Blue is similar to the Chief Petty Officer Service Dress Blue with the exception that silver-colored buttons, rather than gold, are worn on the jacket.
Service Dress White consists of white straight-leg or bell-bottom trousers with a fly front, black leather shoes, a white jumper with plain "tar flap" collar, a black polyester neckerchief and a white sailor cap (nicknamed the "Dixie cup" after the paper cups) for males or combination cover for females with a silver eagle emblem and the letters "USN." The Service Dress White jumper is actually derived from the pre-1974 Undress White, with its wide cuffless sleeves and no piping.
Ribbons are worn with these uniforms over the top left pocket opening (the jumper pockets do not have flaps), along with warfare insignia. If these uniforms are to be assigned as the Uniform of the Day, a Plan of the Day/Plan of the Week will state either "Service Dress White" or "Service Dress Blue." Either the All-Weather Coat or Peacoat may be worn with this uniform in cold or inclement weather. The color of the enlisted rank insignia is either gold or red based upon the U.S. Navy Good Conduct Variation.
Full Dress
Full Dress uniforms are worn for ceremonies such as changes of command, retirements, commissionings and decommissionings, funerals, weddings, or when otherwise appropriate. Full Dress is similar to Service Dress, but ribbons are replaced with full-size medals above the left breast pocket, with ribbons worn on the opposite side for decorations without corresponding medals. Swords or cutlasses are authorized for wear by officers and Chief Petty Officers,[3] and may be required for Lt. Commander and above. For the U.S. Navy Ceremonial Guard in Washington, D.C., the enlisted (E6 and below) Full Dress uniforms are further modified with the wearing of a white pistol belt, ascot, and dress aiguilette (the latter two are white for Summer and navy blue for Winter), and white canvas leggings. Other honor guards are only authorized leggings and white pistol belt.
Dinner Dress
The dinner dress uniforms of the United States Navy are the most formal and have the most variations. For officers, there are Dinner Dress Blue and Dinner Dress White, Dinner Dress Blue Jacket and Dinner Dress White Jacket, and Formal Dress. Although trousers are authorized, women frequently wear the appropriate color skirt. Dinner Dress Blue and White are identical to their Service Dress versions, but worn with miniature medals and badges with no ribbons. Dinner Dress Blue is additionally worn with a dress shirt and black bow tie. These variants are commonly worn by many junior officers and enlisted personnel as substitutes for the more formal Dinner Dress Jacket variant which is only prescribable for Lieutenant Commander and above and optional for Lieutenant and below. The Dinner Dress Blue/White Jacket uniforms feature a short jacket with three buttons on either side, worn open with a black bow tie and cummerbund (women substitute a neck tab for the bow tie). Male officers show rank stripes on the sleeves of the jacket for the blue version and on shoulder boards for the white version, while women officers only wear sleeve stripes. This uniform is equivalent to black tie in usage.
The Formal Dress variation is the most formal, and is identical to the Dinner Dress Blue Jacket uniform but worn with a white waistcoat with gold buttons in place of the cummerbund, a white bow tie, and matching mother-of-pearl studs and cuff links. Though rarely used, men can also substitute a tailcoat for the standard dinner dress jacket with this uniform. The female version is substantially the same as Dinner Dress Blue Jacket, but substitutes the mother-of-pearl studs and cuff links for gold. This uniform is equivalent to white tie in usage. Additionally, this uniform is only prescribed for chiefs and officers.
Headgear is not required for dinner dress uniforms unless an outer jacket is worn.
Those holding the rank of Lieutenant and below have the option of using the Dinner Dress uniform when Dinner Dress Jacket is prescribed. The enlisted sailors who are Chief Petty Officer and above wear a uniform similar to the officers, but with rank insignia and service stripes on the left sleeve. While enlisted who are Petty Officer First Class and below have Dinner Dress Jacket uniforms similar to the officers and chiefs, they may also wear their Service Dress uniform, the traditional sailor suit, with miniature medals.
Service Uniforms
Service Uniforms are the Navy's daily wear uniforms, and exist in several variations. They are intended for use in office environments, in positions that interact with the public, and in watch situations. Skirts are authorized for women in all service uniforms.
Officers and chief petty officers
- Service Khaki
The Service Khaki uniform is the sole province of commissioned officers in grades O-1 through O-10, chief warrant officers in grades W-2 through W-5 (the W-1 grade is not currently in use in the U.S. Navy) and chief petty officers (also known as CPOs) in grades E-7 through E-9. It is a khaki button-up shirt and trousers, worn with a gold belt buckle. The shirt features two front flap pockets and a pointed collar. Ribbons are worn above the left pocket of the shirt, with the warfare insignia above them. A nametag may be worn above the right pocket, and rank insignia is worn on the collar. The regulations for ribbons state the highest three awards, or all ribbons can be worn at once. There are actually three kinds of headgear authorized. Frequently, a khaki garrison cap is worn, but a khaki combination cover is also authorized.[4] Currently black and brown oxford shoes are authorized for all officers and CPOs.[5] Females are authorized to wear the same overblouse as junior enlisted.
- Summer White Service
The Summer White Service uniform (nicknamed the "milkman" and "Good Humor") consists of a short-sleeved white button-up shirt worn open-collared, white trousers and belt, and white dress shoes. Authorized headwear is the combination cap. Officers wear shoulder boards with this uniform, while chiefs wear metal collar insignia. The women's shirt for all ranks has shoulder straps, but carry nothing except for shoulder boards worn by officers. Like Service Khakis, Summer Whites are available in several materials (poly/cotton and Certified Navy Twill). When assigned as the Uniform of the Day, a Plan of the Day/Plan of the week will state "Summer White." Either the All-Weather Coat, Blue jacket, or Peacoat may be worn with this uniform. While once authorized for junior enlisted, it is now restricted to officers and chiefs.
Junior Enlisted
- Navy Service Uniform
The Navy underwent a comprehensive review of every uniform from 2006 through 2007, intending to replace the different seasonal service uniforms with a single year-round service uniform for personnel E-1 through E-6. Accordingly, the Navy Service Uniform has replaced the Winter Blue Uniform and Summer White Uniform (both discussed below), which were phased out on December 31, 2010 when the rollout of the New Service Uniform was completed. Enlisted personnel now have a single Service Uniform. Navy JROTC units also received this new uniform, which phased out the Winter Blue and Summer Blue service uniforms.
The Navy Service Uniform is a year-round service uniform to withstand day-to-day classroom and office-like environments where the service uniform is typically worn. It consists of a short-sleeve khaki shirt for males and a khaki weskit-style blouse for females, made from a wash and wear 75% polyester, 25% wool blend, with permanent military creases, black trousers for males with beltless slacks for females and optional beltless skirt, and a black unisex garrison cap. Silver anodized-metal rank insignia is worn on shirt/blouse collars and cap. The service uniform also includes a black relaxed-fit Eisenhower-style jacket with a knit stand-up collar and epaulets, on which petty officers wear large, silver anodized-metal rate insignia. Those entitled to wear gold chevrons continue to wear gold chevrons on the large metal rate insignia on the jacket.
Working Uniforms
Working uniforms are worn when other uniforms may become unduly soiled or are otherwise inappropriate for the task. These are worn at sea, and in industrial environments ashore. In July, 2010, the new Navy Working Uniform and coveralls became the only authorized working uniforms.
The Navy Working Uniform (NWU) is the latest working uniform to be introduced by the United States Navy.
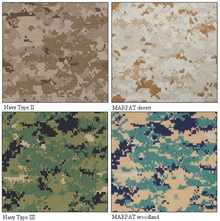
Based on the Marine Corps MARPAT Marine Corps Combat Utility Uniform, with multiple pockets on the shirt and trousers, it uses a multi-color digital print pattern similar to those introduced by other services. However, the NWU will also be made in three variants: predominately blue, with some gray, for the majority of sailors and shipboard use in addition to a woodland digital pattern and a desert digital pattern for sailors serving in units requiring those types of uniforms. Woodland and desert variants may be tailored differently than the blue-pattern uniform.
The overall blue color reflects the Navy's heritage and connection to seaborne operations.[6] The pixelated pattern is also used to hide wear and stains, something unavoidable with the utilities and working khakis used previously.[7] The colors were also chosen to match the most commonly used paint colors aboard ship, extending the lifetime of the uniform on long deployments where uniforms often come into contact with freshly painted surfaces. As of 2009, the uniform is authorized for wear outside of military installations.[8]
The uniform is primarily composed of a 50/50 nylon and cotton blend, which eliminates the need for a "starch and press" appearance and reduces the possibility of snags and tears from sharp objects (thus making the garment last longer). Accessories include a navy blue cotton t-shirt, an eight-point utility cover (similar to that worn by Marines), and a web belt with closed buckle. All-weather garments will include a unisex pullover sweater, a fleece jacket, and a parka, all of which will be available in matching camouflage patterns.[9]
The uniform is worn with rank insignia on both collar points and on the front panel of the 8-sided camouflage cover, with sew-on name and "U.S. NAVY" tapes, also on the new digital background pattern, having gold-colored lettering for officers and CPOs and silver-colored lettering for all lower ranks. An embroidered Anchor, USS Constitution, and Eagle (ACE) is on the left breast pocket on all NWUs.
Black safety boots, identical to those worn by United States Coast Guard personnel with their new Operational Dress Uniform, are worn with the new NWUs. Boots will come in two versions: black smooth leather boots, and black suede no-shine boots for optional wear while assigned to non-shipboard commands.
Like the previous working uniforms, the new NWU was designed to allow personnel to stay warm and dry in inclement weather, thus they were designed to be slightly larger for the wearing of sweaters underneath, along with meeting shipboard fire safety standards. The NWU, unlike its predecessors, was also designed to be longer-lasting and does not need to be ironed like previous uniforms. The uniform also has more pockets than its predecessors, with four on the shirt including the two pockets on the sleeves of the uniform, and six on the trousers. The NWUs are currently in production and were phased into service beginning in January 2009.[10]
In January 2010, the Navy began considering new Navy Working Uniform patterns modified from MARPAT, named Type II and Type III, desert and woodland, respectively.[11] These patterns are overall darker than their respective MARPAT progenitors, modified with different color shades,[12] and addressed the fact that the blue and grey Type I pattern was not meant for a tactical environment (the Battle Dress Uniform and Desert Camouflage Uniform are still used for this purpose).[13] Backlash from Marines, including an objection from Commandant Conway, led to restrictions when NAVADMIN 374/09 was released:[14] the Type II to Naval Special Warfare personnel, while Type III is restricted to Navy ground units.[15]
Coveralls
Simple blue coveralls are a working uniform at sea and in dirty, laborious environments ashore. Coveralls are not authorized for wear outside a naval installation, and typical local regulations dictate that coveralls are not authorized off of the pier, or outside the confines of an assigned workcenter ashore. Naval Officers' and Chief Petty Officers' coveralls are worn with gold insignia, khaki belt and a gold buckle, whereas sailors in paygrades E-6 and below wear coveralls with silver insignia, black belt and a silver buckle. "U.S. Navy" on the left and the wearer's surname on the right are worn embroidered. Rank insignia is worn on the collar. This uniform is worn with black boots. All Weather Coat, Utility Jacket or Peacoat can be worn. Coveralls are certified to be fire resistant. When assigned as the Uniform of the Day, a Plan of the Day/Plan of the week will state "Coveralls." This uniform was recently changed, and a navy blue undershirt is now worn with the uniform.
The Navy Working Uniform, discussed above, is intended to replace the use of coveralls in the aforementioned environments ashore. Shipboard commands have the latitude to determine whether they will wear the NWU or coveralls.[citation needed]
Coats
All Enlisted personnel may wear the Navy Blue Peacoat with a rank insignia for Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) and up on the left sleeve, a Navy Blue All Weather Coat with rank insignia worn on the collar, or a Navy Blue Working Uniform Jacket with rank insignia worn on the collar.
Officers and Chiefs may wear the reefer, with rank insignia worn on the shoulder epaulets, or the all weather coat, with rank insignia also worn on the shoulder or collar, depending on rank. Additionally, a khaki windbreaker may be worn the service khaki uniform.
Naval Aviators, Naval Flight Officers, Naval Flight Surgeons, Naval Aviation Physiologists, and Naval Aircrewman are authorized to wear G-1 seal-brown goatskin-leather flight jackets, with warfare insignia listed on a name tag (rank optional) over the left breast pocket, either permanently stitched to the leather or attached with a Velcro hook-and-loop fastener. These jackets were previously adorned with various "mission patches," which indicate places the wearer has served. Today, patches on the G-1 are limited to a maximum of three in addition to the nametag, i.e., a unit insignia on the right breast, an aircraft type insignia on the right sleeve and an aircraft type insignia or embroidered U.S. flag on the left sleeve.
Also, the Navy issues foul-weather or cold-weather jackets as appropriate for the environment, which are generally olive or Navy blue in color. These jackets are considered "Organizational Clothing". They do not belong to the sailor, and are not allowed for wear off of the ship unless working in the near vicinity of the ship.
Special Uniform Situations
In certain duty stations, Navy personnel are issued woodland or desert utility uniforms. These are similar to the other military services' utility uniforms.
As the Marines do not have medical personnel and chaplains, the Navy provides them. (The Chief of Naval Operations and Commandant of the Marine Corps are heads of separate branches – the connections between the Navy and Marines include that they report to the Secretary of the Navy and they share common legal institutions like Naval Criminal Investigative Service and JAG.) The officers and enlisted include doctors, dentists, nurses, hospital corpsmen, chaplains, Naval Gunfire Liaison Officers and religious program specialists. There are also specialized ratings that will be attached to Marine commands such as Navy Divers for example. Because of this relationship, these personnel are authorized to wear U.S. Marine Corps utility (desert/woodland) uniforms with Navy rank insignia replacing the Marine insignia for enlisted personnel (Navy and Marine officer rank insignia are identical) and with a "U.S. Navy" patch replacing the "U.S. Marines" one. They wear the 8-point utility cover, but it lacks the Marine Corps emblem. Additionally, Navy personnel attached to Marine units can elect to wear Marine service uniforms, with Navy insignia. Those opting to wear Marine Corps service uniforms must meet Marine Corps grooming and physical appearance standards, which are more stringent than Navy standards. This does not apply to the MARPAT uniforms, as this uniform is required for wear in the field when attached to Marine units, regardless of adherence to Marine Corps grooming standards. Navy personnel are not authorized to wear the Marine Corps Dress Blue Uniform; instead Navy Dress Blue and White uniforms are worn.[16][dead link]
Other wear of Combat Utilities
In addition to Marine Corps detachments, combat utilities are also worn by Navy SEAL teams, along with SWCC crews who conduct clandestine maritime operations including supporting SEAL platoons and SOF cells. The Combat Utility Uniform (CUU) is authorized for those in the Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) and Fleet Diver communities. Combat utilities are also authorized for those attached to the Naval Construction Force (NCF) (Seabee), Navy's Expeditionary Logistics Group, or the Navy's Expeditionary Combat Command (NECC). Also, Navy personnel assigned to some joint headquarters units, like Central Command in Qatar and Iraq wear Desert Utility Uniforms (DUU). Navy personnel such as Individual Augmentees, Combat Camera Groups, Detainee OPS, and some in the special warfare community have been wearing the Army's ACU (Army Combat Uniform) when working closely with or attached to Army commands.
Pilots, Naval Flight Officers, and Naval Aircrewman are authorized to wear green or desert flight suits (made of nomex for fire protection), with rank insignia for officers stitched on the shoulders, and a name tag/warfare insignia on the left breast pocket. Either a Command/Navy ballcap or a Khaki Garrison Cap (for Commissioned Officers and CPOs) are worn with this uniform.
Coveralls are authorized to be worn with either the all weather coat or utility jacket (Petty Officers only).
Due to the extreme noise on the flightdeck of an aircraft carrier, personnel handling the aircraft have specific-colored flightdeck jerseys which by sight describes that person's function and is also the basis for referring to these personnel as "Skittles". Due to the inevitable wear, lubricant stains and short service life, flight deck personnel often wear a variety of trousers (BDUs, utilities, etc.) with the jerseys on deck.[17]:
- Purple – Aviation Fuel Handlers (also known as "grapes")
- Blue – Plane Handlers, Tractor Drivers, Elevator Operators
- Yellow – Flight Deck Officers and Plane Directors
- Green – Operations Personnel, Catapult and Arresting Gear Personnel, Ground Support Equipment Maintenance Personnel, Squadron Maintenance Personnel, Cargo handling personnel, Hook runners, Landing Signalmen Enlisted (LSE), and Photographers
- White – Safety Observers, Squadron Final Checkers (F/C), Landing Signal Officers (LSO), Corpsmen, LOX Handlers, Air Transfer Officers, and visitors
- Red – Ordnance Handlers, EOD Personnel, Crash and Salvage Crews
- Brown – Plane Captains (Crew Chiefs and Mechanics)
USS Constitution
The ship USS Constitution is the oldest commissioned ship in the U.S. Navy, the only one of the six original United States frigates still in existence. Constitution is presented to the public as she appeared during the War of 1812, and personnel stationed aboard the Constitution still wear uniforms according to regulations posted in 1815. These uniforms are worn on ceremonial occasions, such as the annual turn-around cruise in Boston every Independence Day.[18]
Obsolete uniforms
Following a comprehensive review of all uniforms, the Navy ceased issuing the following uniforms in 2009, though as long as the discontinued uniforms remain in stock they may be purchased. All Naval personnel must replace the below listed uniforms by December 31, 2010.
- Service Dress Blue Yankee
The rarely seen Service Dress Blue Yankee uniform replaced the dark trousers and black shoes of the service dress blue with white trousers and shoes from the white uniform. This uniform made the wearer resemble the commodore of a yacht club or similar social organization, and was most commonly prescribed for enlisted sailors serving as stewards, at official functions, or at officers' messes.[19]
- Winter Blue
The Winter Blue uniform was authorized for all ranks. Due to its near-black color, it was called the "Johnny Cash" uniform (a reference to the song/album Man in Black by the singer of the same name)[20][21] It was a long sleeve black button-up shirt and black belt and trousers (optional skirt for females), with the headgear either the combination cover, white hat, or an optional black garrison cap.
As a service uniform, ribbons and badges were worn, and officers and Chief Petty Officers wore metal collar insignia, while enlisted E-6 and below wore just the rating badge on the left arm. All men wore ties, females necktabs, with an optional silver clip for Petty Officers First Class and below, others a gold clip.
Winter Working Blue was similar to the Winter Blue Service Uniform. The main difference was that the ribbons and necktie were omitted.
- Working Khaki
The Working Khaki uniform was worn by Officers and Chief Petty Officers, primarily aboard ship or in selected working areas at bases ashore. Similar to, but less formal than, the Service Khaki, it consisted of a short or long-sleeve khaki uniform shirt, with warfare insignia and badges (i.e. command pins, nametags, etc., but no ribbons) worn on the top of the left pocket, and pin-on metal rank devices located on the collar. It also came with a set of khaki trousers, a khaki belt with a gold belt buckle, a command or "US Navy" ballcap, and black or brown low quarter shoes, black or brown boots, or black leather safety shoes. It was often referred to as the "Wash Khaki" uniform, because it was a 100% cotton uniform that required pressing, differentiating it from the Summer Khaki made of Certified Navy Twill (CNT) or a poly-wool blend that was considered acceptable for wear ashore and off base.
;Aviation Working Green A winter working green uniform for commissioned officers and Chief Petty Officers in the Naval Aviation community was used from 1917 to January 2011. In its final version, it was somewhat similar to the Navy's revived Service Dress Khaki uniform in cut and design and bore additional similarities to the Marine Corps' Service Dress "Alpha" green uniform. It consisted of a green wool coat and green wool trousers with bronze buttons and a long-sleeve khaki shirt with black tie. Rank insignia consisted of black embroidery on sleeves in a style similar to the gold sleeve braid for officers, or rating marks and service "hash" marks for Chief Petty Officers, on Service Dress Blue uniforms. Metal rank insignia was worn concurrently on the collar points of the khaki shirt by line officers and CPOs. For staff corps officers, rank insignia was worn on the right collar point and staff corps insignia on the left collar point (typically Medical Corps for Naval Flight Surgeons, etc.) of the shirt. Warfare insignia and, if applicable, Command at Sea and/or Command Ashore insignia, were worn on the jacket and optionally on the shirt. Either black or brown shoes were worn, but brown was the most common. Authorized headgear included a combination cover in green, or a green garrison cover.
During World War II and the Korean War, ribbons were also authorized with this uniform, making it a de facto "liberty uniform" authorized for wear off base, but by the early 1960s, it had become a "working uniform" for use on base or aboard ship only. It was infrequently worn, primarily due its expense and its 100% wool fabric that typically made it practical only during cold weather.
The AWG uniform was phased out on January 1, 2011 and replaced with the Naval Working Uniform.
- Tropical Uniforms
The rarely seen tropical white uniform was similar to the Summer White Service uniform, except white knee shorts and knee socks were worn. It was colloquially known as the "Captain Steubing" uniform, after the character on The Love Boat TV show. Exceptionally rarely worn, though authorized with this uniform, was a pith helmet, with a Naval Officer's insignia at the front, above the brim.
Tropical working uniforms existed, but were variations on the working khaki and utility uniforms. Knee shorts and black knee socks are worn, along with short sleeved button-up shirts.
- Utilities
The enlisted utilities uniform was worn by junior enlisted sailors from the early 1990s until 2010, when they were phased out in favor of the NWU. Utilities consisted of dark blue chino cloth trousers with a polyester–cotton blend shirt, and were considered an updated version of the dungarees uniform. Utilities were meant to be worn in a working environment and were rarely, if ever, authorized to be worn outside military installations.
Usually sailors wore the command ball cap with this uniform, although a black watch cap was allowed in cold weather. Cloth name tapes were worn similar to that used on utility uniforms of the other services. In 1995 a tape with the words "U.S. NAVY" was included above the left breast pocket with embroidered enlisted warfare insignia authorized above it, and an embroidered rating badge. The footwear for this uniform was full black, round-toed boots (referred to as boondockers), preferably with steel toes. The blue utility jacket was authorized in climates not cold enough as to warrant wearing the black All-Weather Coat.
- Dungarees
Dungarees were the working uniform worn from the 1950s through the 1990s. Like the utility uniform, dungarees were not allowed to be worn outside of military installations.
Dungarees consisted of a short or long-sleeve blue chambray shirt, white t-shirt, and boot-cut denim jeans. Head gear was the white "dixie cup" cover for men and an early form of the black garrison cap or a black beret for women. During cold weather a black watch cap was allowed. The command ball cap was optional. Names were hand-stencilled and the rating badge was "iron on." Only petty officers wore a rating badge on this uniform, on the left arm. The sailor's last name was affixed in white on the pants just above the back pocket on the right side. The name was also affixed in black on the shirt just above the right breast pocket. An iron-on surface warfare or submarine warfare insignia iron-on was authorized to be placed over the left breast pocket.
Low black leather boots called "boondockers" were worn with the dungaree uniform.
See also
- Badges of the United States Navy
- United States Navy officer rank insignia
- List of United States Navy staff corps (insignia)
- List of United States Navy ratings
- United States Navy enlisted rate insignia
- List of camouflage patterns#North America N-Z
- Uniforms of the United States Military
- Uniforms of the United States Marine Corps
References
- ^ MSNBC article
- ^ United States Navy Uniform Regulations NAVPERS 15665
- ^ "Military Photos: The New Navy Work Uniform". Strategy Page. StrategyWorld.com. May 4, 2006. Archived from the original on October 19, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5keQKUtX1. Retrieved October 19, 2009. "The color pattern of the NWU (navy blue, deck gray, haze gray and black)"
- ^ "Navy Uniform Frequently Asked Questions". New-Navy-Uniform.com. Archived from the original on October 19, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5keQwZoeu. Retrieved October 19, 2009.
- ^ http://www.navy.mil/search/display.asp?story_id=46524
- ^ Foutch, Michael (March 2, 2006). "New Navy Working Uniform and Service Uniform Concepts Approved". NNS. Archived from the original on November 5, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5l4J8K0Ho. Retrieved November 5, 2009.
- ^ Faram, Mark D (October 30, 2008). "Blue cammies coming soon". Army Times Publishing Company. Archived from the original on November 5, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5l4JWITfv. Retrieved November 5, 2009.
- ^ "Two New Navy Working Uniforms Announced". United States Navy. January 8, 2010. http://www.navy.mil/search/display.asp?story_id=50454. Retrieved 6 May 2010.
- ^ McCullough, Amy (January 20, 2010). "Your thoughts: Navy may try Corps-like camo". Marine Corps Times. http://www.marinecorpstimes.com/news/2010/01/marine_uniform_011810w/. Retrieved 6 May 2010.
- ^ "Navy Working Uniform (NWU) Concepts Frequently Asked Questions". Task Force Uniform Public Affairs. United States Navy. January 13, 2005. http://www.navy.mil/search/display.asp?story_id=16603. Retrieved 6 May 2010.
- ^ "NAVADMIN 374/09: Navy Working Uniform Type II and III". Chief of Naval Operations. CDR Salamander. January 4, 2010. http://cdrsalamander.blogspot.com/2010/01/nwu-unending-nightmare.html. Retrieved 6 May 2010.
- ^ "Sailor Outcry over Desert Camo Denial". Navy Times staff (Marine Corps Times). February 22, 2010.
- ^ U.S. Navy Uniform Regulations, Chapter 2 - Grooming Standards
- ^ "Rainbow Wardrobe". U.S. Navy Office of Information. http://www.navy.mil/navydata/ships/carriers/rainbow.asp. Retrieved 2007-05-16.
- ^ http://www.history.navy.mil/ussconstitution/capn_crew.html
- ^ Service Dress Blue Yankee for male and for female officers
- ^ Faram, Mark D (March 28, 2005). "New duds for everyone?". NavyTimes (Army Times Publishing Company). Archived from the original on October 16, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5kYlNj5gL. Retrieved October 16, 2009. "They include service khakis, clearly the most used of the trio; summer whites, featuring white pants and shirts and shoulder boards for officers; and the less-visible winter blues, commonly known as the "Johnny Cash" uniform."
- ^ Van Avery, Chris (October 4, 2004). "The good, bad and ugly of proposed uniforms". NavyTimes (Army Times Publishing Company). Archived from the original on October 16, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5kYllpN7C. Retrieved October 16, 2009. "Combining a short- or long-sleeved white shirt with the blue trousers already in sailors' seabags eliminates the trouble of keeping summer white trousers white and Johnny Cash shirts unburned by a temperamental iron."
External links
- US Navy BUPERS site including pictures and descriptions for all naval uniforms including item by item descriptions.
- Flash-powered 360° view of the new Navy uniforms, due fiscal 2008
- Official Navy Uniforms Site
- New Uniform Photos showing the Service Uniform, Working Uniform, and PT Uniform.
Leadership - Commander-in-chief: President of the United States
- Secretary of Defense
- Deputy Secretary of Defense
- Joint Chiefs of Staff (Chairman)
- United States Congress: Committees on Armed Services:
- Active duty four-star officers
- Highest ranking officers in history
- National Security Act of 1947
- Goldwater–Nichols Act
Organization BranchesReserve componentsStructure - United States Code
- The Pentagon
- Installations
- Budget
- Units:
- Logistics
- Media
Operations and history - Current deployments
- Conflicts
- Wars
- Timeline
- History:
- Colonial
- WWII
- Civil affairs
- African Americans
- Asian Americans
- Jewish Americans
- Sikh Americans
- Historiography:
- Art:
- A
- AF
Personnel TrainingOther- Oath:
- Creeds & Codes:
- Service numbers:
- A
- MC
- N
- AF
- CG
- Military Occupational Specialty/Rating/Air Force Specialty Code
- Pay
- Uniform Code of Military Justice
- Judge Advocate General's Corps
- Military Health System/TRICARE
- Separation
- Veterans Affairs
- Conscription
- Chiefs of Chaplains:
Equipment LandSeaAirOtherLegend: A = Army, MC = Marine Corps, N = Navy, AF = Air Force, CG = Coast Guard, PHS = Public Health Service, NOAA = National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, MSC = Military Sealift CommandCategories:- Equipment of the United States Navy
- American military uniforms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.