- Yom Kippur War
-
"Battle of Syria" redirects here. For the World War II campaign against the Vichy French in Syria, see Syria-Lebanon Campaign.
Yom Kippur War/October War Part of the Arab-Israeli conflict 
Egyptian forces crossing the Suez Canal on October 7Date October 6 – October 25, 1973 Location Both banks of the Suez Canal, Golan Heights and surrounding regions Result - Israeli tactical victory[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] and a UN cease-fire after UNSCR 338, 339 and 340, leading to the Geneva Conference and the Sinai Interim Agreement.
- Political and strategic gains for Egypt and Israel
- See long-term effects
Belligerents  Egypt
Egypt
 Syria
Syria
Major Arab Expeditionary Forces:
 Iraq
Iraq
 Jordan
Jordan Israel
IsraelCommanders and leaders  Ahmad Ismail Ali
Ahmad Ismail Ali
 Mustafa Tlass
Mustafa Tlass
 Saad El Shazly
Saad El Shazly
 Yusuf Shakkour
Yusuf Shakkour
 Abdel Ghani el-Gammasy
Abdel Ghani el-Gammasy
 Ali Aslan
Ali Aslan Moshe Dayan
Moshe Dayan
 David Elazar
David Elazar
 Israel Tal
Israel Tal
 Shmuel Gonen
Shmuel Gonen
 Yitzhak Hofi
Yitzhak Hofi
 Binyamin Peled
Binyamin Peled
 Haim Bar-Lev
Haim Bar-LevStrength Egypt: 650,000[8]–800,000[9] troops, 1,700 tanks (1,020 crossed),[10] 2,400 armored carriers, 1,120 artillery units,[11] 400 combat aircraft, 140 helicopters,[12] 104 Navy vessels, 150 surface to air missile batteries (62 in the front line)[13]
Syria: 150,000[8] troops, 1,200 tanks, 800–900 armored carriers, 600 artillery units,[11][14][15]
Expeditionary Forces*: 100,000 troops,[8] 500-670 tanks,[16][17] 700 armored carriers[16]375,000[8]–415,000 troops,
1,700 tanks,[18]
3,000 armored carriers,
945 artillery units,[11]
440 combat aircraftCasualties and losses 8,000[19]–18,500[20] dead
18,000[19]–35,000[21] wounded
8,783 captured
2,250[22]–2,300[23] tanks destroyed or captured
341[19]–514[24] aircraft destroyed
19 naval vessels sunk[25]2,521[26]–2,800[19] dead
7,250[27]–8,800[19] wounded
293 captured
400 tanks destroyed[28]
102 aircraft destroyed[29]* Not all participated in combat operations Yom Kippur WarSyrian front
- 1st Hermon
- Valley of Tears
- Model 5
- Latakia
- 2nd Hermon
- Syrian GHQ Raid
- Gown
- al-Mazzah Airport Raid
- 3rd Hermon
Egyptian front
- Badr
- Budapest
- Lahtzanit
- Ofira
- Romani
- Marsa Talamat
- Tagar
- Baltim
- Sinai
- Mansoura
- Chinese Farm
- Egyptian Missile Bases Raid
- 25th Brigade ambush
- Ismailia
- Scud missile attack
- Suez
International front
The Yom Kippur War, Ramadan War or October War (Hebrew: מלחמת יום הכיפורים Milẖemet Yom HaKipurim or מלחמת יום כיפור Milẖemet Yom Kipur; Arabic: حرب أكتوبر ḥarb ʾUktōbar or حرب تشرين ḥarb Tišrīn), also known as the 1973 Arab-Israeli War and the Fourth Arab-Israeli War, was fought from October 6 to 25, 1973, between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria. The war began when the coalition launched a joint surprise attack on Israel on Yom Kippur, the holiest day in Judaism, which coincided with the Muslim holy month of Ramadan. Egyptian and Syrian forces crossed ceasefire lines to enter the Israeli-held Sinai Peninsula and Golan Heights respectively, which had been captured and occupied since the 1967 Six-Day War. Both the United States and the Soviet Union, initiated massive resupply efforts to their respective allies during the war, and this led to a near-confrontation between the two nuclear superpowers.[30]
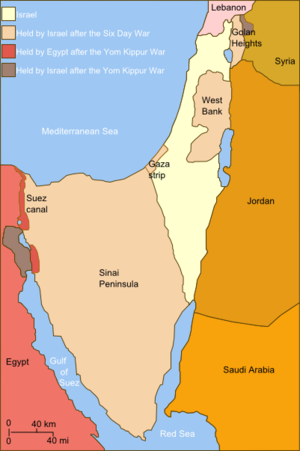
The war began with a massive and successful Egyptian crossing of the Suez Canal during the first three days, after which they dug in, settling into a stalemate. The Syrians coordinated their attack on the Golan Heights to coincide with the Egyptian offensive and initially made threatening gains against the greatly outnumbered Israelis. Within a week, Israel recovered and launched a four-day counter-offensive, driving deep into Syria. To relieve this pressure, the Egyptians went back on the offensive, but were decisively defeated; the Israelis then counterattacked at the seam between two Egyptian armies, crossed the Suez Canal, and advanced southward and westward in over a week of heavy fighting. On October 22 a United Nations-brokered ceasefire quickly unraveled, with each side blaming the other for the breach. By 24 October, the Israelis had improved their positions considerably and completed their encirclement of Egypt's Third Army. This development led to tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union. As a result, a second ceasefire was imposed cooperatively on October 25 to end the war. At the conclusion of hostilities, Israeli forces were 40 kilometres (25 mi) from Damascus and 101 kilometres (63 mi) from Cairo.
The war had far-reaching implications. The Arab World, which had been humiliated by the lopsided rout of the Egyptian-Syrian-Jordanian alliance in the Six-Day War, felt psychologically vindicated by early successes in the conflict. In Israel, despite impressive operational and tactical achievements on the battlefield, the war effectively ended its sense of invincibility and complacency. The war also challenged many American assumptions; the United States initiated new efforts at mediation and peacemaking. These changes paved the way for the subsequent peace process. The Camp David Accords that followed led to the return of the Sinai to Egypt and normalized relations—the first peaceful recognition of Israel by an Arab country. Egypt continued its drift away from the Soviet Union and left the Soviet sphere of influence entirely.
Contents
Background
The war was part of the Arab-Israeli conflict, an ongoing dispute which included many battles and wars since 1948, when the state of Israel was formed. During the Six-Day War of 1967, the Israelis captured Egypt's Sinai Peninsula all the way to the Suez Canal, which became the cease-fire line, and roughly half of Syria's Golan Heights.
According to Chaim Herzog:
On June 19, 1967, the National Unity Government of Israel voted unanimously to return the Sinai to Egypt and the Golan Heights to Syria in return for peace agreements. The Golan would have to be demilitarized and special arrangement would be negotiated for the Straits of Tiran. The government also resolved to open negotiations with King Hussein of Jordan regarding the Eastern border.[31]
The Israeli decision was to be conveyed to the Arab states by the U.S. government. The U.S. was informed of the decision, but not that it was to transmit it. There is no evidence it was conveyed to Egypt or Syria. The decision was kept a closely guarded secret within Israeli government circles and the offer was withdrawn in October 1967.[32]
Egypt and Syria both desired a return of the land lost in the Six-Day War. In September 1967, the Khartoum Arab Summit issued the "three no's", resolving that there would be "no peace, no recognition and no negotiation with Israel". In the years following the war, Israel erected lines of fortification in both the Sinai and the Golan Heights. In 1971, Israel spent $500 million fortifying its positions on the Suez Canal, a chain of fortifications and gigantic earthworks known as the Bar Lev Line, named after Israeli General Chaim Bar-Lev.
President Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt died in September 1970. He was succeeded by Anwar Sadat, who resolved to win back the lost territory. In 1971, Sadat, in response to an initiative by UN intermediary Gunnar Jarring, declared that if Israel committed itself to "withdrawal of its armed forces from Sinai and the Gaza Strip", to "[a]chievement of a just settlement for the refugee problem", to "the withdrawal of the Israeli armed forces from all the territories occupied since 5 June 1967", and to implementation of other provisions of UN Security Council Resolution 242 as requested by Jarring, Egypt would then "be ready to enter into a peace agreement with Israel." Israel responded that it would not withdraw to the pre-June 5, 1967 lines.[33]
Sadat hoped that by inflicting even a limited defeat on the Israelis, the status quo could be altered. Hafez al-Assad, the leader of Syria, had a different view. He had little interest in negotiation and felt the retaking of the Golan Heights would be a purely military option. After the Six-Day War, Assad had launched a massive military buildup and hoped to make Syria the dominant military power of the Arab states. With the aid of Egypt, Assad felt that his new army could win convincingly against Israel and thus secure Syria's role in the region. Assad only saw negotiations beginning once the Golan Heights had been retaken by force, which would induce Israel to give up the West Bank and Gaza, and make other concessions.
Sadat also had important domestic concerns in wanting war. "The three years since Sadat had taken office... were the most demoralized in Egyptian history.... A desiccated economy added to the nation's despondency. War was a desperate option."[34] In his biography of Sadat, Raphael Israeli argued that Sadat felt the root of the problem was in the great shame over the Six-Day War, and before any reforms could be introduced he felt that shame had to be overcome. Egypt's economy was in shambles, but Sadat knew that the deep reforms that he felt were needed would be deeply unpopular among parts of the population. A military victory would give him the popularity he needed to make changes. A portion of the Egyptian population, most prominently university students who launched wide protests, strongly desired a war to reclaim the Sinai and was highly upset that Sadat had not launched one in his first three years in office.
The other Arab states showed much more reluctance to fully commit to a new war. King Hussein of Jordan feared another major loss of territory as had occurred in the Six-Day War, in which Jordan lost all of the West Bank, territory it had conquered and annexed in 1948-49 which had doubled its population. Sadat was also backing the claim of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) to the West Bank and Gaza and in the event of a victory promised Yasser Arafat that he would be given control of them. Hussein still saw the West Bank as part of Jordan and wanted it restored to his kingdom. Moreover, during the Black September crisis of 1970, a near civil war had broken out between the PLO and the Jordanian government. In that war, Syria had intervened militarily on the side of the PLO, estranging Hussein.
Iraq and Syria also had strained relations, and the Iraqis refused to join the initial offensive. Lebanon, which shared a border with Israel, was not expected to join the Arab war effort because of its small army and already evident instability. The months before the war saw Sadat engage in a diplomatic offensive to try to win support for the war. By the fall of 1973, he claimed the backing of more than a hundred states. These were most of the countries of the Arab League, Non-Aligned Movement, and Organization of African Unity. Sadat had also worked to curry favour in Europe and had some success before the war. Britain and France for the first time sided with the Arab powers against Israel on the United Nations Security Council.
Events leading up to the war
Following Israel's rejection of Sadat's peace initiative, which had proposed a full Israeli withdrawal to the pre-67 borders in exchange for a non-belligerency pact,[35] Sadat declared that Egypt was prepared to "sacrifice a million Egyptian soldiers" to recover its lost territory.[36] From the end of 1972, Egypt began a concentrated effort to build up its forces, receiving MiG-21 jet fighters, SA-2, SA-3, SA-6 and SA-7 antiaircraft missiles, T-55 and T-62 tanks, RPG-7 antitank weapons, and the AT-3 Sagger anti-tank guided missile from the Soviet Union and improving its military tactics, based on Soviet battlefield doctrines. Political generals, who had in large part been responsible for the rout in 1967, were replaced with competent ones.[37]
The role of the superpowers, too, was a major factor in the outcome of the two wars. The policy of the Soviet Union was one of the causes of Egypt's military weakness. President Nasser was only able to obtain the material for an anti-aircraft missile defense wall after visiting Moscow and pleading with Kremlin leaders. He said that if supplies were not given, he would have to return to Egypt and tell the Egyptian people Moscow had abandoned them, and then relinquish power to one of his peers who would be able to deal with the Americans. The Americans would then have the upper hand in the region, which Moscow could not permit.
One of Egypt's undeclared objectives of the War of Attrition was to force the Soviet Union to supply Egypt with more advanced arms and materiel. Egypt felt the only way to convince the Soviet leaders of the deficiencies of most of the aircraft and air defense weaponry supplied to Egypt following 1967 was to put the Soviet weapons to the test against the advanced weaponry the United States had supplied to Israel.
Nasser's policy following the 1967 defeat conflicted with that of the Soviet Union. The Soviets sought to avoid a new conflagration between the Arabs and Israelis so as not to be drawn into a confrontation with the United States. The reality of the situation became apparent when the superpowers met in Oslo and agreed to maintain the status quo. This was unacceptable to Egyptian leaders, and when it was discovered that the Egyptian preparations for crossing the canal were being leaked, it became imperative to expel the Soviets from Egypt. In July 1972, Sadat expelled almost all of the 20,000 Soviet military advisers in the country and reoriented the country's foreign policy to be more favorable to the United States. The Syrians remained close to the Soviet Union.
The Soviets thought little of Sadat's chances in any war. They warned that any attempt to cross the heavily fortified Suez Canal would incur massive losses. Both the Soviets and the Americans were then pursuing détente, and had no interest in seeing the Middle East destabilized. In a June 1973 meeting with U.S. President Richard Nixon, Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev had proposed Israel pull back to its 1967 border. Brezhnev said that if Israel did not, "we will have difficulty keeping the military situation from flaring up"—an indication that the Soviet Union had been unable to restrain Sadat's plans.[38]
In an interview published in Newsweek (April 9, 1973), President Sadat again threatened war with Israel. Several times during 1973, Arab forces conducted large-scale exercises that put the Israeli military on the highest level of alert, only to be recalled a few days later. The Israeli leadership already believed that if an attack took place, the Israeli Air Force (IAF) could repel it.
Almost a full year before the war, in an October 24, 1972 meeting with his Supreme Council of the Armed Forces, Sadat declared his intention to go to war with Israel even without proper Soviet support.[39] Planning had begun in 1971 and was conducted in absolute secrecy—even the upper-echelon commanders were not told of war plans until less than a week prior to the attack, and the soldiers were not told until a few hours beforehand. The plan to attack Israel in concert with Syria was code-named Operation Badr (Arabic for "full moon"), after the Battle of Badr, in which Muslims under Muhammad defeated the Quraish tribe of Mecca.
Lead-up to the surprise attack
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) Directorate of Military Intelligence's (abbreviated as "Aman") Research Department was responsible for formulating Israel's intelligence estimate. Their assessments on the likelihood of war were based on several assumptions. First, it was assumed correctly that Syria would not go to war with Israel unless Egypt did so as well. Second, the department learned from a high-level Egyptian informant, Ashraf Marwan, that Egypt wanted to regain all of the Sinai, but would not go to war until they were supplied MiG-23 fighter-bombers to neutralize the Israeli Air Force, and Scud missiles to be used against Israeli cities as a deterrent against Israeli attacks on Egyptian infrastructure. Since they had not received MiG-23s, and Scud missiles had only arrived in Egypt from Bulgaria in late August and it would take four months to train the Egyptian ground crews, Aman predicted war with Egypt was not imminent. This assumption about Egypt's strategic plans, known as "the concept", strongly prejudiced the department's thinking and led it to dismiss other war warnings.
The Egyptians did much to further this misconception. Both the Israelis and the Americans felt that the expulsion of the Soviet military observers had severely reduced the effectiveness of the Egyptian army. The Egyptians ensured that there was a continual stream of false information on maintenance problems and a lack of personnel to operate the most advanced equipment. The Egyptians made repeated misleading reports about lack of spare parts that also made their way to the Israelis. Sadat had so long engaged in brinkmanship that his frequent war threats were being ignored by the world. In May and August 1973, the Egyptian army conducted military exercises near the border, and the Israeli army mobilized in response both times at considerable cost.
For the week leading up to Yom Kippur, the Egyptian army staged a week-long training exercise adjacent to the Suez Canal. Israeli intelligence, detecting large troop movements towards the canal, dismissed these movements as mere training exercises. Movements of Syrian troops towards the border were puzzling, but not a threat because, Aman believed, they would not attack without Egypt and Egypt would not attack until the weaponry they wanted arrived.
On September 27 and 30, two batches of reservists were called up by the Egyptian army to participate in these exercises. Two days before the outbreak of the war, on October 4, the Egyptian command publicly announced the demobilization of part of the reservists called up during September 27 to lull suspicion on the Israeli side. Around 20,000 troops were demobilized, and subsequently some of these men were given leave to perform the Umrah (pilgrimage) to Mecca.[40][41]
The obvious reason for choosing the Jewish holiday of Yom Kippur to stage a surprise attack on Israel was that on this specific holiday (unlike any other) the country comes to a complete standstill. Yom Kippur is the holiest day in the Jewish calendar; both religiously observant Jews and most of the secular majority fast[citation needed], abstain from any use of fire, electricity, engines, communications, etc., and all road traffic ceases. Many soldiers also go home from military facilities for the holiday, and Israel is more vulnerable with much of its military on leave. The war coincided that year with the Muslim month of Ramadan, when many Arab Muslim soldiers also fast. Other analysts believe that the attack on Yom Kippur actually helped Israel to more easily marshal reserves from their homes and synagogues, because the nature of the holiday meant that roads and communication were largely open and this eased mobilizing and transporting the military.
Despite refusing to participate, King Hussein of Jordan "had met with Sadat and [Syrian President] Assad in Alexandria two weeks before. Given the mutual suspicions prevailing among the Arab leaders, it was unlikely that he had been told any specific war plans. But it was probable that Sadat and Assad had raised the prospect of war against Israel in more general terms to feel out the likelihood of Jordan joining in."[42]
On the night of September 25, Hussein secretly flew to Tel Aviv to warn Israeli Prime Minister Golda Meir of an impending Syrian attack. "Are they going to war without the Egyptians, asked Mrs. Meir. The king said he didn't think so. 'I think they [Egypt] would cooperate.'"[43] Surprisingly, this warning fell on deaf ears. Aman concluded that the king had not told anything that was not already known. "Eleven warnings of war were received by Israel during September from well placed sources. But [Mossad chief] Zvi Zamir continued to insist that war was not an Arab option. Not even Hussein's warnings succeeded in stirring his doubts."[44] He would later remark that "We simply didn't feel them capable [of War]."[44] Finally, Zvi Zamir personally went to Europe to meet with Marwan at midnight on October 5/6. Marwan informed him that a joint Syrian-Egyptian attack was imminent.
It was this warning in particular, combined with the large number of other warnings, that finally goaded the Israeli high command into action. Just hours before the attack began, orders went out for a partial call-up of the Israeli reserves.[45] Ironically, calling up the reserves proved to be easier than usual, as almost all of the troops were at synagogue or at home for the holiday.
The attack by the Egyptian and Syrian forces caught the United States by surprise. According to the future CIA Director and Defence Secretary Robert Gates, he was briefing a US arms negotiator on the improbability of armed conflict in the region when he heard the news of the outbreak of war on the radio. On the other hand, KGB learned about the attack in advance, probably from its intelligence sources in Egypt.[46]
Lack of Israeli pre-emptive attack
The Israeli strategy was, for the most part, based on the precept that if war was imminent, Israel would launch a pre-emptive strike. It was assumed that Israel's intelligence services would give, in the worst case, about 48 hours notice prior to an Arab attack.
 Upon learning of the impending attack, Prime Minister of Israel Golda Meir made the controversial decision not to launch a pre-emptive strike.
Upon learning of the impending attack, Prime Minister of Israel Golda Meir made the controversial decision not to launch a pre-emptive strike.
Golda Meir, Moshe Dayan, and General David Elazar met at 8:05 a.m. the morning of Yom Kippur, six hours before the war began. Dayan opened the meeting by arguing that war was not a certainty. Elazar then presented his argument in favor of a pre-emptive attack against Syrian airfields at noon, Syrian missiles at 3:00 p.m., and Syrian ground forces at 5:00 p.m. "When the presentations were done, the prime minister hemmed uncertainly for a few moments but then came to a clear decision. There would be no preemptive strike. Israel might be needing American assistance soon and it was imperative that it would not be blamed for starting the war. 'If we strike first, we won't get help from anybody', she said."[47] Other developed nations, being more dependent on OPEC oil, took more seriously the threat of an Arab oil embargo and trade boycott, and had stopped supplying Israel with munitions. As a result, Israel was totally dependent on the United States for military resupply, and particularly sensitive to anything that might endanger that relationship. After Meir made her decision, at 10:15 a.m. she met with US ambassador Kenneth Keating in order to inform the United States that Israel did not intend to preemptively start a war, and asked that US efforts be directed at preventing war. An electronic telegram with Keating's report on the meeting was sent to the US at 16:33 GMT (6:33 p.m. local time).[48][49] A message arrived later from United States Secretary of State Henry Kissinger saying, "Don't preempt."[50] At the same time, Kissinger also urged the Soviets to use their influence to prevent war, contacted Egypt with Israel's message of non-preemption, and sent messages to other Arab governments to enlist their help on the side of moderation. These late efforts were futile.[51] According to Henry Kissinger, had Israel struck first, they would not have received "so much as a nail."[52]
David Elazar proposed a mobilization of the entire Air Force and four armored divisions, a total of 100,000 to 120,000 troops, while Dayan favored a mobilization of the Air Force and two armored divisions, totaling around 70,000 troops. Meir chose Elazar's proposal.[53]
Combat operations
In the Sinai
 Wreckage from an Egyptian Sukhoi Su-7 shot down over the Sinai on October 6 on display at the Israeli Air Force Museum
Wreckage from an Egyptian Sukhoi Su-7 shot down over the Sinai on October 6 on display at the Israeli Air Force Museum
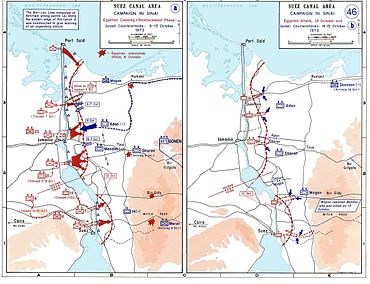
The Sinai was once again the arena of conflict between the Israelis and the Egyptians, the fifth such occasion. The Egyptians had prepared for an assault across the canal and deployed five divisions totaling 100,000 soldiers, 1,350 tanks and 2,000 guns and heavy mortars for the onslaught. Facing them were 450 soldiers of the Jerusalem Brigade, spread out in 16 forts along the length of the Canal. There were 290 Israeli tanks in all of Sinai divided into three armored brigades,[54] and only one of these was deployed near the Canal when hostilities commenced.[55] Large bridgeheads were established on the east bank on October 6. Israeli armoured forces launched counterattacks from October 6 to 8, but they were often piecemeal and inadequately supported and were beaten back principally by Egyptians using portable anti-tank missiles.
The Egyptian units generally would not advance beyond a shallow strip for fear of losing the protection of their surface-to-air missile (SAM) batteries, which were situated on the west bank of the canal. In the Six-Day War, the Israeli Air Force had pummelled the defenseless Arab armies. Egypt (and Syria) had heavily fortified their side of the ceasefire lines with SAM batteries provided by the Soviet Union, against which the Israeli Air Force had no time to execute a Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses (SEAD) operation due to the element of surprise.[56][57] Israel, which had invested much of its defense budget building the region's strongest air force, would see the effectiveness of its air force curtailed in the initial phases of the conflict by the SAM presence.
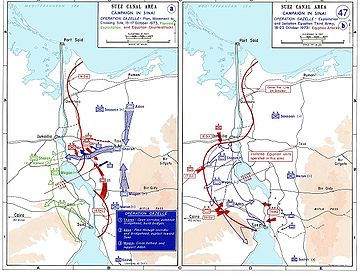
On October 9, the IDF chose to concentrate its reserves and build up its supplies while the Egyptians remained on the strategic defensive. It was decided to counterattack once Egyptian armour attempted to expand the bridgehead beyond the protective SAM umbrella. The riposte, codenamed Operation Gazelle, was launched on October 15. IDF forces spearheaded by Ariel Sharon's division broke through the Tasa corridor and crossed the Suez Canal to the north of the Great Bitter Lake. After intense fighting, Israeli progress towards Cairo was brought to a halt while the IDF advanced southwards on the east bank of the Great Bitter Lake and in the southern extent of the canal right up to Port Suez when the ceasefire was declared on October 24.
Egyptian attack
Anticipating a swift Israeli armored counterattack by three armored divisions,[58] the Egyptians had armed their assault force with large numbers of man-portable anti-tank weapons—rocket-propelled grenades and the less numerous but more advanced Sagger guided missiles, which proved devastating to the first Israeli armored counterattacks. Each of the five infantry divisions that was to cross the canal had been equipped with RPG-7 rockets and RPG-43 grenades, and reinforced with an anti-tank guided missile battalion, as they would not have any armor support for nearly 12 hours.[59] In addition, the Egyptians had built separate ramps at the crossing points, reaching as high as 21 metres (69 ft) to counter the Israeli sand wall, provide covering fire for the assaulting infantry and to counter the first Israeli armored counterattacks.[60] The scale and effectiveness of the Egyptian strategy of deploying these anti-tank weapons coupled with the Israelis' inability to disrupt their use with close air support (due to the SAM shield) greatly contributed to Israeli setbacks early in the war.
The Egyptian Army put great effort into finding a quick and effective way of breaching the Israeli defenses. The Israelis had built large 18 meter (59 foot) high sand walls with a 60 degree slope and reinforced with concrete at the water line. Egyptian engineers initially experimented with explosive charges and bulldozers to clear the obstacles, before a junior officer proposed using high pressure water cannons. The idea was tested and found to be a sound one, and several high pressure water cannons were imported from Britain and East Germany. The water cannons effectively breached the sand walls using water from the canal.[61] At 2:00 pm on October 6, Operation Badr began with a large airstrike. More than 200 Egyptian aircraft conducted simultaneous strikes against three airbases, Hawk missile batteries, three command centers, artillery positions, and several radar installations.[62] Airfields at Refidim and Bir Tamada were temporarily put out of service, and damage was inflicted on a Hawk battery at Ophir. The aerial assault was coupled with a barrage from more than 2,000 artillery pieces for a period of 53 minutes against the Bar Lev Line and rear area command posts and concentration bases.[63] Andrew McGregor claimed that the success of the first strike negated the need for a second planned strike.[64][65][66] Egyptian aircraft took losses during the attack. Egypt acknowledged the loss of 5 aircraft. However, Kenneth Pollack wrote that 18 Egyptian aircraft were shot down, and that these losses prompted the cancellation of the second planned wave.[67] In one notable engagement during this period, a pair of Israeli F-4E Phantoms challenged 28 MiGs over Sharm el-Sheikh and within half an hour, shot down between seven and eight Egyptian MiGs with no losses.[68][69] Simultaneously, two Egyptian Tupolev Tu-16 bombers launched two Kelt missiles at Tel Aviv. One missile was shot down by a patrolling Israeli Mirage fighter, and the second fell into the sea. The attack was an attempt to warn Israel that Egypt could retaliate if it bombed targets deep in Egyptian territory. A further 14 Egyptian Tupolevs attacked Israeli targets in the Sinai with Kelt missiles.[70]
 Israeli F-4E Phantom of the type present in the dogfight over Sharm el-Sheikh. Small Egyptian roundels on nose credit the aircraft with three aerial victories.
Israeli F-4E Phantom of the type present in the dogfight over Sharm el-Sheikh. Small Egyptian roundels on nose credit the aircraft with three aerial victories.
Under cover of the initial artillery barrage, the Egyptian assault force of 32,000 infantry began crossing the canal in twelve waves at five separate crossing areas, from 14:05 to 17:30, in what became known as The Crossing.[71] The Egyptians prevented Israeli forces from reinforcing the Bar Lev Line and proceeded to attack the Israeli fortifications. Meanwhile engineers crossed over to breach the sand wall.[72][73] The Israeli air force conducted air interdiction operations to try to prevent the bridges from being erected, but were met with heavy resistance from SAM batteries, and took losses. The air attacks were overall ineffective, as the sectional design of the bridges enabled quick repair when hit.[74] Despite fierce Israeli resistance, the Israeli reserve brigade garrisoning the Bar-Lev forts was overwhelmed, and according to Shazly, within six hours, fifteen strongpoints had been captured as Egyptian forces advanced several kilometers unto the Sinai. Shazly's account was disputed by Kenneth Pollack, who noted that for the most part, the forts only fell to repeated assaults by superior forces or prolonged sieges over many days.[75] The northernmost fortification of the Bar Lev Line, code-named 'Fort Budapest', withstood repeated assaults and remained in Israeli hands throughout the war. Once the bridges were laid, additional infantry with the remaining portable and recoilless anti-tank weapons began to cross the canal, while the first Egyptian tanks started to cross at 20:30.[76]
The Egyptians also attempted to land several heli-borne commando units in various areas in the Sinai to hamper the arrival of Israeli reserves. However, this attempt met with disaster as the Israelis shot down up to twenty helicopters, inflicting heavy casualties.[77][78] Israeli Major General (res.) Chaim Herzog placed Egyptian helicopter losses at fourteen.[79] Still, other sources claim that “several” helicopters were downed with “total loss of life” and that the few commandos that did filter through were ineffectual and presented nothing more than a “nuisance.”[80] However, Kenneth Pollack asserted that despite their heavy losses, the Egyptian commandos fought exceptionally hard and created considerable panic, prompting the Israelis to take precautions which hindered their ability to concentrate on stopping the assault across the canal.[81]
Egyptian forces advanced approximately 4 to 5 km into the Sinai Desert with two armies (both corps-sized by western standards, included the 2nd Infantry Division in the northern Second Army). By the following morning, some 850 tanks had crossed the canal.[63] In his account of the war, Saad El Shazly noted that the crossing cost the Egyptians 280 soldiers killed and 20 tanks destroyed, though this account is disputed.[82][83] Israeli forces defending the Bar Lev Line suffered heavy casualties.[10][84] For the next several days, the Israeli Air Force (IAF) played a minimal role in the fighting largely because it was needed to deal with the simultaneous, and ultimately more threatening, Syrian invasion of the Golan Heights.[85]
Egyptian forces then consolidated their initial positions. On October 7, the bridgeheads were enlarged an additional 4 km, at the same time repulsing Israeli counterattacks. In the north, the Egyptians managed to seize most of the town of Qantara by evening, clearing it completely by the next morning.[86]
Meanwhile the Egyptian commandos airdropped on October 6 began encountering Israeli reserves the following morning. Both sides suffered heavy losses, but the commandos were at times successful in delaying the movement of Israeli reserves to the front. These special operations often led to confusion and anxiety among Israeli commanders, who commended the Egyptian commandos.[87][88] However, this view was contradicted by another source which stated that few commandos made it to their objectives, and were usually nothing more than a nuisance.[89] Of the 1,700 Egyptian commandos inserted behind Israeli lines during the war, 740 were killed — many in downed helicopters — and 330 taken prisoner.[90]
Israeli counter-attack
On October 7, David Elazar visited Shmuel Gonen, commander of the Israeli Southern front—who had only taken the position three months before at the retirement of Ariel Sharon—and met with Israeli commanders. The Israelis planned a cautious counterattack for the following day by Abraham Adan's 162nd Armored Division.[91] The same day, the Israeli Air Force conducted Operation Tagar, aiming to neutralize Egyptian Air Force bases and its missile defense shield. Seven Egyptian airbases were damaged with the loss of two A-4 Skyhawks and their pilots, but two more planned attacks were called off due to the increasing need for airpower on the Syrian front.
On October 8, after Elazar had left, Gonen changed the plans on the basis of over-optimistic field reports. Adan's division was composed of three brigades totaling 183 tanks. One of the brigades was in still en route to the area, and would participate in the attack by noon, along with a supporting mechanized infantry brigade with an additional 44 tanks.[92][93] The Israeli counterattack was in the direction of the Bar Lev strongpoints opposite the city of Ismailia, against entrenched Egyptian infantry. In a series of ill-coordinated attacks, which were met by stiff resistance, the Israelis suffered heavy losses. That afternoon, Egyptian forces advanced once more to deepen their bridgeheads, and as a result the Israelis lost several strategic positions. Further Israeli attacks to regain the lost ground proved futile.[94] Towards nightfall, an Egyptian counterattack was repulsed by the Israeli 143rd Armoured Division, which was led by Ariel Sharon—Sharon had been reinstated as a division commander at the outset of the war. Garwych, citing Egyptian sources, documents Egyptian tank losses from October 6 through 13 at 240.[95]
According to Herzog, by October 9 the front lines had stabilized. The Egyptians were unable to advance further,[96] and Egyptian armored attacks on October 9 and 10 were repulsed with heavy losses. However, this claim was disputed by Shazly, who claimed that the Egyptians continued to advance and improve their positions well into October 10. He pointed to one engagement, which involved elements of the 1st Infantry Brigade, attached to the 19th Division, which captured Ayoun Mousa, south of Suez.[97] However, both Herzog and Shazly mentioned a failed Egyptian attack southward along the Gulf of Suez in the direction of Ras Sudar by the Egyptian 1st Mechanized Brigade. Leaving the safety of the SAM umbrella, the force was attacked by Israeli aircraft and suffered severe losses.[97][98] Shazly cited this experience as a basis to resist pressure by Minister of War, General Ahmad Ismail Ali to attack eastward toward the Mitla and Gidi Passes.
With the situation on the Syrian front stabilizing, the Israeli high command agreed that the time was ripe for an Israeli counterattack and strike across the canal. General Sharon advocated an immediate crossing at Deversoir at the northern edge of Great Bitter Lake. On October 9, a reconnaissance force attached to Colonel Amnon Reshef's Brigade detected a gap between the Egyptian Second and Third armies in this sector.[99] Chief of Staff Elazar and General Chaim Bar-Lev, who had by now replaced Gonen as Chief of Southern Command, agreed that this was the ideal spot for a crossing. However, given the size of the Egyptian armoured reserves, the Israelis chose to wait for an opportunity which would allow them to reduce Egyptian armored strength before initiating any crossing.
The opportunity arrived on October 12, when Israeli intelligence detected signs that the Egyptians were gearing up for a major armored thrust.[100] This was precisely the moment the Israelis were waiting for. They could finally utilize their advantages in speed, maneuver and tank gunnery, areas in which they excelled. Once Egyptian armored strength was sufficiently degraded, the Israelis would commence their own canal crossing. General Shazly strongly opposed any eastward advance that would leave his armor without adequate air cover. He was overruled by General Ismail and Sadat, whose aims were to seize the strategic Mitla and Gidi Passes and the Israeli nerve centre at Refidim, which they hoped would relieve pressure on the Syrians (who were by now on the defensive) by forcing Israel to shift divisions from the Golan to the Sinai.[101][102]
The 2nd and 3rd Armies were ordered to attack eastward in six simultaneous thrusts over a broad front, leaving behind five infantry divisions to hold the bridgeheads. The attacking forces, consisting of 800[103]-1,000 tanks[99] would not have SAM cover, so the Egyptian Air Force (EAF) was tasked with the defense of these forces from Israeli air attacks. Armored and mechanized units began the attack on October 14 with artillery support. They were up against 700[103]-750[99] Israeli tanks. Preparatory to the tank attack, Egyptian helicopters set down 100 commandos near the Lateral Road to disrupt the Israeli rear. An Israeli reconnaissance unit quickly subdued them, killing 60 and taking numerous prisoners. Still bruised by the extensive losses their commandos had suffered on the opening day of the war, the Egyptians were unable or unwilling to implement further commando operations that had been planned in conjunction with the armored attack.[104] The Egyptian armored thrust suffered heavy losses. Instead of concentrating forces of maneuvering, except for the wadi thrust, Egyptian units launched head-on-attacks against the waiting Israeli defenses.[105]
Kenneth Pollack credited a successful Israeli commando raid early on October 14 against an Egyptian signals-intercept site at Jebel Ataqah with seriously disrupting Egyptian command and control and contributing to its breakdown during the engagement.[106] The Egyptian attack was decisively repelled. At least 250 Egyptian tanks[107][108][109][110] and some 200 armored vehicles[108] were destroyed. Egyptian casualties exceeded 1,000.[110][111] Fewer than 40 Israeli tanks were hit and all but six of them were repaired by Israeli maintenance crews and returned to service.[108] Israeli casualties were light.
Israeli breakthrough
The Israelis immediately followed their success of October 14 with a multidivisional counterattack through the gap between the Egyptian 2nd and 3rd Armies. Sharon's 143rd Division, now reinforced with a paratroop brigade commanded by Colonel Danny Matt, was tasked with establishing bridgeheads on the east and west banks of the canal. The 162nd and 252nd Armored Divisions, commanded by Generals Bren Adan and Kalman Magen respectively, would then cross through the breach to the west bank of the canal and swing southward, encircling the 3rd Army.[112] The offensive was code-named Operation Stouthearted Men or alternatively, Operation Valiant. Egyptian commandos responded with incursions to prevent an Israeli crossing of the canal. Following a major raid by 70 Egyptian commandos, a twelve-man special forces squad was sent to locate and destroy the incursion. In the key engagement that followed, all 70 commandos were killed.[113]
On the night of October 15, 750 of Colonel Matt's paratroopers crossed the canal in rubber dinghies.[114] They were soon joined by tanks ferried on motorized rafts and additional infantry. The force encountered no resistance initially and fanned out in raiding parties, attacking supply convoys, SAM sites, logistic centers and anything of military value, with priority given to the SAMs. Several SAM batteries were destroyed, punching a hole in the Egyptian anti-aircraft screen and enabling the Israeli Air Force to more aggressively strike Egyptian ground targets.[115] By now, the Syrians no longer posed a credible threat and the Israelis were able to shift their air power to the south in support of the offensive.[116] The combination of a weakened Egyptian SAM umbrella and a greater concentration of Israeli fighter-bombers meant that the IAF was capable of greatly increasing sorties against Egyptian targets. Egyptian attempts to interdict the IAF sorties resulted in one-sided dogfights which usually ended in Israeli victories and resulted in heavy Egyptian aircraft losses, with comparatively light Israeli losses.[117]
Despite the success the Israelis were having on the West Bank, Generals Bar-Lev and Elazar ordered Sharon to concentrate on securing the bridgehead on the East Bank. He was ordered to clear the roads leading to the canal as well as a position known as the Chinese Farm, just north of Deversoir, the Israeli crossing point. Sharon objected and requested permission to expand and breakout of the bridgehead on the west bank, arguing that such a maneuver would cause the collapse of Egyptian forces on the east bank. But the Israeli high command was insistent, believing that until the east bank was secure, forces on the west bank could be cut off. Sharon was overruled by his superiors and relented.[118] On October 16, he dispatched Amnon Reshef's Brigade to attack the Chinese Farm. Other IDF forces attacked entrenched Egyptian forces overlooking the roads to the canal. After three days of bitter and close-quarters fighting, the Israelis succeeded in dislodging the numerically superior Egyptian forces. Sharon's division lost about 300 killed and 1,000 wounded, but inflicted heavier casualties on the Egyptians. Tank losses on both sides were also severe.[119][120][121][122][123]
 Israeli soldiers during the Battle of Ismailia. One of them has a captured Egyptian RPG-7.
Israeli soldiers during the Battle of Ismailia. One of them has a captured Egyptian RPG-7.
The Egyptians meanwhile failed to grasp the extent and magnitude of the Israeli crossing nor did they appreciate its intent and purpose. This was partly due to attempts by Egyptian field commanders to obfuscate reports concerning the Israeli crossing[124] and partly due to a false assumption that the canal crossing was merely a diversion for a major IDF offensive targeting the right flank of the Second Army.[125] Consequently, on October 16, General Shazly ordered the 21st Armored Division to attack southward and the T-62-equipped 25th Independent Armored Brigade to attack northward in a pincer action to eliminate the perceived threat to the Second Army. However, the Egyptians failed to scout the area and were unaware that by now, Adan's 162nd Armored Division was in the vicinity. Moreover, the 21st and 25th failed to coordinate their attacks, allowing General Adan's Division to meet each force individually. Adan first concentrated his attack on the 21st Armored Division, destroying 50–60 Egyptian tanks and forcing the remainder to retreat. He then turned southward and ambushed the 25th Independent Armored Brigade, destroying 86 of its 96 tanks and all of its APCs while losing 3 tanks.[126]
After the failure of the October 17 counterattacks, the Egyptian General Staff slowly began to realize the magnitude of the Israeli offensive. Early on October 18, the Soviets showed Sadat satellite imagery of Israeli forces operating on the west bank. Alarmed, Sadat dispatched Shazly to the front to assess the situation first hand. He no longer trusted his field commanders to provide accurate reports.[127] Shazly confirmed that the Israelis had at least one division on the west bank and were widening their bridgehead. He advocated withdrawing most of Egypt's armor from the east bank to confront the growing Israeli threat on the west bank. Sadat rejected this recommendation outright and even threatened Shazly with a court martial.[128] Ahmad Ismail Ali recommended that Sadat's push for a cease-fire so as to prevent the Israelis from exploiting their successes.[127]
Israeli forces were by now pouring across the canal on two bridges, including one of indigenous design, and motorized rafts. Adan's division rolled south toward Suez City while Magen's division pushed west toward Cairo and south toward Adabiya.[129][130] Sharon's continued to drive north, and his forces advanced towards Ismailia in an attempt to seize the city and thereby sever the logistical and supply lines for most of the Egyptian Second Army. Breaking out from the newly-established Israeli bridehead on the west bank of the Suez Canal, the IDF launched an offensive towards Ismailia.[131] A combined force of Egyptian paratroopers and commandos fought a delaying battle, falling into defensive positions further north as they came under increasing pressure. On October 22, the outnumbered Egyptians were occupying their last line of defense, but managed to repel an Israeli attack, stopping the advance 10 km south of Ismailia shortly before the ceasefire came into effect. Both sides suffered heavy losses. However, Adan and Magen decisively defeated the Egyptians in a series of engagements as their forces moved south, though they often encountered determined Egyptian resistance which caused heavy casualties.[131]
By the end of the war, the Israelis had advanced to positions some 101 kilometers from Egypt's capital, Cairo, and occupied 1,600 square kilometers west of the Suez Canal.[132] The Israelis had also cut the Cairo-Suez road and encircled the bulk of Egypt's Third Army. The Egyptians held a narrow strip on the east bank of the canal, occupying some 1,200 square kilometers of the Sinai.[133] One source estimated that the Egyptians had 70,000 men and 720 tanks on the east bank of the canal.[134] However, between 30,000 to 45,000 of these were now encircled by the Israelis.[135][136]
Egypt's trapped Third Army
The United Nations Security Council passed (14–0) Resolution 338 calling for a cease-fire, largely negotiated between the U.S. and Soviet Union, on October 22. It called upon the belligerents to immediately cease all military activity. The cease-fire was to come into effect 12 hours later at 6:52 p.m. Israeli time.[137] Because this was after dark, it was impossible for satellite surveillance to determine where the front lines were when the fighting was supposed to stop.[138] U.S. Secretary of State Henry Kissinger intimated to Prime Minister Meir that he would not object to offensive action during the night before the ceasefire was to come into effect.[139]
Several minutes before the ceasefire came into effect, three Scud missiles were fired at Israeli targets by either Egyptian forces or Soviet personnel in Egypt. This was first combat use of Scud missiles. One Scud targeted the port of Arish and two targeted the Israeli bridgehead on the Suez Canal. One hit an Israeli supply convoy and killed seven soldiers.[140] When the time for the ceasefire arrived, Sharon's division had failed to capture Ismailia and cut off the Second Army's supply lines, but Israeli forces were just a few hundred meters short of their southern goal—the last road linking Cairo and Suez.[141] Adan's drive south had left Israeli and Egyptian units scattered throughout the battlefield, with no clear lines between them. As Egyptian and Israeli units tried to regroup, regular firefights broke out. During the night, Elazar reported that the Egyptians were attacking in an attempt to regain land at various locations, and that nine Israeli tanks had been destroyed. He asked permission from Dayan to respond to the attacks and Dayan agreed. Israel then resumed its drive south.[142] It is unclear which side fired first[143] but Israeli field commanders used the skirmishes as justification to resume the attacks. When Sadat protested alleged Israeli truce violations, Israel said that Egyptian troops had fired first. William B. Quandt noted that regardless of who fired the first post-ceasefire shot, it was the Israeli Army that was advancing beyond the 22 October cease-fire lines.[144]
Adan resumed his attack on October 23.[145][146] Israeli troops finished the drive south, captured the last ancillary road, and encircled the Egyptian Third Army east of the Suez Canal.[147] The Israelis then transported enormous amounts of military equipment across the canal, which Egypt claimed was in violation of the ceasefire.[143] Israeli armor and paratroopers also entered Suez in an attempt to capture the city, but they were confronted by Egyptian soldiers and hastily raised local militia forces. They were surrounded, but towards night the Israeli forces managed to extricate themselves. The Israelis had lost 80 dead and 120 wounded, with an unknown number of Egyptian casualties, for no tactical gain (see Battle of Suez).[146][148]
The next morning, October 23, a flurry of diplomatic activity occurred. Soviet reconnaissance flights had confirmed that Israeli forces were moving south, and the Soviets accused the Israelis of treachery. Kissinger called Meir in an effort to persuade her to withdraw a few hundred yards and she indicated that Israel's tactical position on the ground had improved. Kissinger found out about the Third Army's encirclement shortly thereafter.[149]
Kissinger considered that the situation presented the United States with a tremendous opportunity and that Egypt was dependent on the United States to prevent Israel from destroying its trapped army. The position could be parlayed later into allowing the United States to mediate the dispute and wean Egypt from Soviet influence. As a result, the United States exerted tremendous pressure on the Israelis to refrain from destroying the trapped army, even threatening to support a UN resolution to force the Israelis to pull back to their October 22 positions if they did not allow non-military supplies to reach the army. In a phone call with Israeli ambassador Simcha Dinitz, Kissinger told the ambassador that the destruction of the Egyptian Third Army "is an option that does not exist."[150]
Despite being surrounded however, the Third Army managed to maintain its combat integrity east of the canal and keep up its defensive positions, to the surprise of many.[151] According to Trevor N. Dupuy, the Israelis, Russians and Americans overestimated the vulnerability of the Third Army at the time. It was not on the verge of collapse, and he writes that while a renewed Israeli offensive would probably overcome it but this was not a certainty.[152] David T. Buckwalter agrees that despite the isolation of the Third Army, it was unclear if the Israelis could have protected their forces on the west bank of the canal from a determined Egyptian assault and still maintain sufficient strength along the rest of the front.[153] This assessment however was challenged by Patrick Seale, who states that the Third Army was “on the brink of collapse.”[154] Seale's position finds support from P.R. Kumaraswamy who wrote that intense American pressure prevented the Israelis from annihilating the stranded Third Army.[155] Herzog notes that given the Third Army's desperate situation, in terms of being cut off from re-supply and reassertion of Israeli air superiority, the destruction of the Third Army was inevitable and could have been achieved within a very brief period.[156] Shazly himself described the Third Army's plight as “desperate” and classified its encirclement as a “catastrophe that was too big to hide.”[157] He further notes that, “the fate of the Egyptian Third Army was in the hands of Israel. Once the Third Army was encircled by Israeli troops every bit of bread to be sent to our men was paid for by meeting Israeli demands.”[158]
On the morning of October 26, the Egyptian Third Army violated the ceasefire by attempting to break through surrounding Israeli forces. The attack was repulsed by Israeli air and ground forces.[159]
On the Golan Heights
Syrian attack
 An Israeli M107 Self-Propelled Gun at the Golan front
An Israeli M107 Self-Propelled Gun at the Golan front
In the Golan Heights, the Syrians attacked two Israeli brigades and eleven artillery batteries with five divisions and 188 batteries. They began their attack with an airstrike by about 100 aircraft, followed by a 50-minute artillery barrage. The forward brigades of three divisions then penetrated the cease-fire lines and bypassed United Nations observer posts, followed by the main assault force, which was covered by mobile anti-aircraft batteries, bulldozers to penetrate anti-tank ditches, bridge-layers to overcome obstacles and mine-clearance vehicles. The engineering vehicles were priority targets for Israeli gunners and took heavy losses, but Syrian infantrymen, braving intense fire, advanced forward and used their entrenching tools to build up earthen causeways for the tanks, enabling them to overcome anti-tank ditches.[161] At the onset of the battle, the Israeli brigades of some 3,000 troops, 180 tanks and 60 artillery pieces faced off against three infantry divisions with large armour components comprising 28,000 Syrian troops, 800 tanks and 600 artillery pieces. In addition, the Syrians deployed two armoured divisions from the second day onwards.[14][15][162][163] Every Israeli tank deployed on the Golan Heights was engaged during the initial attacks. Syrian commandos dropped by helicopter also took the most important Israeli stronghold at Mount Hermon, which had a variety of surveillance equipment. An Israeli force attempting to counterattack was stopped by a Syrian ambush.
The Golan Heights front was given priority by the Israeli High Command. The fighting in the Sinai was sufficiently far away that Israeli population centers were not immediately threatened. The Golan however, was in close proximity to Israeli population centers, and should the Syrians regain the area, it would pose a serious threat to major Israeli cities such as Tiberias, Safed, Haifa and Netanya. Reservists were directed to the Golan as quickly as possible. They were assigned to tanks and sent to the front as soon as they arrived at army depots, without waiting for the crews they trained with to arrive, machine guns to be installed on the tanks, or taking the time to calibrate the tank guns (a time-consuming process known as bore-sighting). The Syrians had expected it to take at least 24 hours for Israeli reserves to reach the front lines; in fact, reserve units began reaching the battle lines only 15 hours after the war began. Israeli reserve forces approaching the Golan Heights were subjected to Syrian artillery fire directed from Mount Hermon.
As the Egyptians had in the Sinai, the Syrians took care to stay under cover of their SAM batteries. Also as in the Sinai, the Syrians made use of Soviet anti-tank weapons, though they were not as effective as in the Sinai because of the uneven terrain.
The Israeli Air Force initially lost 40 planes from Syrian anti-aircraft batteries, but Israeli pilots soon adopted a different tactic; flying in low over Jordan and diving in over the Golan heights, catching the Syrians in the flank and avoiding many of their batteries. Israeli aircraft dropped both conventional bombs and napalm, devastating Syrian armored columns. On the second day of the war, the Israeli Air Force attempted to take out the Syrian anti-aircraft batteries. Codenamed Doogman 5, the attempt was a costly failure. The Israelis destroyed only one Syrian missile battery, and lost six aircraft.
Syrian forces suffered heavy losses as Israeli tanks and infantry fought desperately to buy time for reserve forces to reach to front lines, and conducted stopgap blocking actions whenever the Syrians were on the verge of breaking through. Having practiced on the Golan Heights numerous times, Israeli gunners made effective use of mobile artillery. However, the Syrians pressed the attack in spite of their losses, and the vastly outnumbered defenders lost a number of tanks.[161] Within six hours of the initial assault, the first Israeli line of defense was overrun by sheer weight of numbers, but the Israelis continued to resist.
A Syrian tank brigade passing through the Rafid Gap turned northwest up a little-used route known as the Tapline Road, which cut diagonally across the Golan. This roadway would prove one of the main strategic hinges of the battle. It led straight from the main Syrian breakthrough points to Nafah, which was not only the location of Israeli divisional headquarters but the most important crossroads on the Heights.[164]
During the night, Israeli forces successfully held back numerically superior Syrian forces. The Syrians were equipped with night-vision goggles, and struck with precision. The Israelis had to allow the Syrians to advance to ranges close enough for night fighting, and then open fire. Whenever Syrian tanks penetrated the Israeli lines, Israeli gunners would immediately rotate their turrets and destroy them before turning their attention back to the oncoming forces. Israeli tank commander Avigdor Kahalani lined up his tanks and began a barrage of gunfire into the valley beyond their position, leading the Syrians to believe that they were facing a vast Israeli tank armada. During the night, the Syrians regained some of the high ground that Israel had held since the Six Day War, but were soon pushed off by an Israeli counterattack.[165] Captain Zvika Greengold, who had just arrived unattached to any unit, fought running battles with Syrian armor for 20 hours, sometimes with his single tank and other times as part of a larger unit, changing tanks half a dozen times as they were knocked out. Greengold suffered burn injuries, but stayed in action and repeatedly showed up at critical moments from an unexpected direction to change the course of a skirmish.[164] For his actions, received Israel's highest decoration, the Medal of Valor.
During over four days of fighting, the Israeli 7th Armoured Brigade in the north (commanded by Avigdor Ben-Gal) managed to hold the rocky hill line defending the northern flank of their headquarters in Nafah, inflicting heavy losses on the Syrians. Syrian Brigadier-General Omar Abrash was killed on the third day of the fighting when his command tank was hit as he was preparing for an attack. However, the Syrians continued to press their attack, and Israelis also took losses. By the afternoon of October 9, only six of the 7th Armored Brigade's tanks remained in action. Just as it was starting to be pushed back, it was bolstered by a force of 15 repaired tanks whose crews included injured men. As individual Israeli tanks arrived to bolster the 7th Brigade, the Syrians, exhausted from three days of continuous fighting, began to retreat.[161]
To the south, Israeli Barak Armored Brigade was bereft of any natural defenses. The Syrians were initially slowed down by a minefield. The Barak Brigade's gunners inflicted severe losses on the Syrians with accurate cannon fire. Undeterred by their losses, the Syrians continued pushing and the Barak Brigade began to take heavy casualties. The Israelis continued to fight desperately, hoping to buy time for reserve forces to reach the front lines. In several instances, some Israeli tank crews sacrificed themselves rather than voluntarily give ground. At night, the Syrians made deadly use of infrared technology, while the Israelis responded by using illumination rounds and xenon light projectors on their tanks and carried out a series of small blocking actions. Israeli Brigade Commander Colonel Shoham was killed on the second day, along with his second-in-command and operations officer, as the Syrians desperately tried to advance towards the Sea of Galilee and Nafah. At this point, the Barak Brigade stopped functioning as a cohesive force although the surviving tanks and crewmen continued fighting independently. The Syrians were close to reaching the Israeli defenders at Nafah, yet stopped the advance on Nafah's fences at 1700; the pause lasted all night, allowing Israeli forces to form a defensive line.[163] It is surmised that the Syrians had calculated estimated advances, and the commanders in the field did not want to diverge from the plan.
The tide in the Golan began to turn as the arriving Israeli reserve forces were able to contain and, beginning on October 8, push back the Syrians to the pre-war ceasefire lines. The tiny Golan Heights were too small to act as an effective territorial buffer, unlike the Sinai Peninsula in the south, but it proved to be a strategic geographical stronghold and was a crucial key in preventing the Syrian army from bombarding the cities below. The Israelis considered limiting casualties a priority, and relied heavily on artillery to dislodge the Syrains at long-range.
 The aftermath of an Israeli airstrike on the Syrian General Staff headquarters in Damascus
The aftermath of an Israeli airstrike on the Syrian General Staff headquarters in Damascus
On October 9, Syrian FROG-7 surface-to-surface missiles struck the Israeli Air Force base of Ramat David, killing a pilot and injuring several soldiers. Additional missiles struck civilian settlements. In retaliation, seven Israeli F-4 Phantoms flew into Syria and struck the Syrian General Staff Headquarters in Damascus. The upper floors of the Syrian GHQ and the Air Force Command were badly damaged, and a nearby Soviet cultural center was also mistakenly hit. One Israeli Phantom was shot down.[166] The strike prompted the Syrians to transfer air defense units from the Golan Heights to the home front, allowing the Israeli Air Force greater freedom of action.[161] By October 10, the last Syrian unit in the Central sector had been pushed back across the Purple Line (the pre-war ceasefire line). After four days of intense and incessant combat, the Israelis succeeded in ejecting the Syrians from the entire Golan.[161]
 A destroyed Syrian T-62 tank
A destroyed Syrian T-62 tank
A decision now had to be made—whether to stop at the post-1967 border or to continue advancing into Syrian territory. Israeli High Command spent all of October 10 debating this well into the night. Some favored disengagement, which would allow soldiers to be redeployed to the Sinai (Shmuel Gonen's defeat at Hizayon in the Sinai had taken place two days earlier). Others favored continuing the attack into Syria, towards Damascus, which would knock Syria out of the war; it would also restore Israel's image as the supreme military power in the Middle East and would give Israel a valuable bargaining chip once the war ended. Others countered that Syria had strong defenses—antitank ditches, minefields, and strongpoints— and that it would be better to fight from defensive positions in the Golan Heights (rather than the flat terrain deeper in Syria) in the event of another war with Syria. However, Prime Minister Golda Meir realized the most crucial point of the whole debate:
It would take four days to shift a division to the Sinai. If the war ended during this period, the war would end with a territorial loss for Israel in the Sinai and no gain in the north—an unmitigated defeat. This was a political matter and her decision was unmitigating—to cross the purple line... The attack would be launched tomorrow, Thursday, October 11.[167]
 Abandoned Syrian T-62s on the Golan Heights
Abandoned Syrian T-62s on the Golan Heights
Israeli advance
On October 11, Israeli forces pushed into Syria and advanced towards Damascus until October 14, encountering stiff resistance by Syrian reservists in prepared defenses. Israeli troops reached the main defensive line around Sassa, and conquered a further 50 square kilometers of territory in the Bashan [[Salients, re-entrants and pockets|salient. From there, they were able to shell the outskirts of Damascus, only 40 km away, using M107 heavy artillery.
On October 12, Israeli paratroopers from the elite Sayeret Tzanhanim reconnaissance unit infiltrated deep into Syria and conducted Operation Gown. The paratroopers destroyed a bridge in the tri-border area of Syria, Iraq, and Jordan, disrupting the flow of weapons and troops to Syria. During the operation, the paratroopers destroyed a number of tank transports and killed several Syrian soldiers. There were no Israeli casualties.[168]
As the Syrian position deteriorated, Jordan sent an expeditionary force into Syria. King Hussein, who had come under intense pressure to enter the war, told Israel of his intentions through US intermediaries, in the hope that Israel would accept that this was not a casus belli justifying an attack on Jordan. Israeli Defense Minister Moshe Dayan declined to offer any such assurance, but said that Israel had no intention of opening another front.[169] Iraq also sent an expeditionary force to Syria, consisting of the 3rd Armoured Division, 6th Armoured Division, some 30,000 men, 250–500 tanks, and 700 APCs.[16][170][171]
The Iraqi divisions were a strategic surprise for the IDF, which expected 24-hour-plus advance intelligence of such moves. This turned into an operational surprise, as the Iraqis attacked the exposed southern flank of the advancing Israeli armor, forcing its advance units to retreat a few kilometers in order to prevent encirclement. Combined Syrian, Iraqi and Jordanian counterattacks prevented any further Israeli gains. However, they were also unable to push the Israelis back from the Bashan salient, and suffered heavy losses in their engagements with the Israelis. The Syrian Air Force attacked Israeli columns, but its operations were highly limited due to Israeli air superiority. The Syrians took heavy losses in dogfights with Israeli jets. On October 23, a large air battle took place near Damascus during which the Israelis shot down 10 Syrian aircraft. The Syrians claimed a similar toll against Israel.[172] The IDF also destroyed the Syrian missile defense system.
The Israeli Air Force utilized its air superiority to attack strategic targets throughout Syria, including important power plants, petrol supplies, bridges and main roads. The strikes damaged the Syrian war effort, disrupted Soviet efforts to airlift military equipment into Syria, and disrupted normal life inside the country.[173]
On October 22, the Golani Brigade and Sayeret Matkal commandos recaptured the outpost on Mount Hermon, after a hard fought battle that involved hand-to-hand combat and Syrian sniper attacks. An unsuccessful attack two weeks prior had cost the Israelis 23 dead and 55 wounded and the Syrians 29 dead and 11 wounded, while this second attack cost Israel an additional 55 dead and 79 wounded.[174] An unknown number of Syrians were also killed and some were taken prisoner. An IDF D9 bulldozer supported by infantry forced its way to the peak. An Israeli paratroop force, landing by helicopter took the corresponding Syrian Hermon outposts on the mountain, killing more than a dozen Syrians. Seven Syrian MiGs and two Syrian helicopters carrying reinforcements were shot down as they attempted to intercede. The paratroopers lost one killed and four wounded.[175]
Northern front de-escalation
The Syrians prepared for a massive counteroffensive to drive Israeli forces out of Syria, scheduled for October 23. A total of five Syrian divisions were to take part, alongside the Iraqi and Jordanian expeditionary forces. The Soviets had replaced most of the losses Syria's tank forces had suffered during the first weeks of the war.
However, the day before the offensive was to begin, the United Nations imposed its ceasefire (following the acquiescence of both Israel and Egypt). Abraham Rabinovich claimed that "The acceptance by Egypt of the cease-fire on Monday [October 22] created a major dilemma for Assad. The cease-fire did not bind him, but its implications could not be ignored. Some on the Syrian General Staff favored going ahead with the attack, arguing that if it did so Egypt would feel obliged to continue fighting as well... Others, however, argued that continuation of the war would legitimize Israel's efforts to destroy the Egyptian Third Army. In that case, Egypt would not come to Syria's assistance when Israel turned its full might northward, destroying Syria's infrastructure and perhaps attacking Damascus"[176] Ultimately, Syrian President Hafez al-Assad decided to cancel the offensive. On October 23, the day the offensive was to begin, Syria announced that it had accepted the ceasefire, and ordered its troops to cease-fire, while the Iraqi government ordered its forces home.
Syrian atrocities against prisoners
 Israeli prisoners of war held by Syria. Syria ignored the Geneva Conventions and Israeli POWs were subjected to physical and psychological torture.[177]
Israeli prisoners of war held by Syria. Syria ignored the Geneva Conventions and Israeli POWs were subjected to physical and psychological torture.[177]
Syria ignored the Geneva Conventions and many Israeli prisoners of war (POW) were reportedly tortured or killed.[178] Advancing Israeli forces, re-capturing land taken by the Syrians early in the war, came across the bodies of 28 Israeli soldiers who had been blindfolded with their hands bound and summarily executed.[179] The Syrians employed brutal interrogation techniques utilizing electric shocks to the genitals. Some Israeli POWs reported having their fingernails ripped out while others were described as being turned into human ashtrays as their Syrian guards burned them with lit cigarettes.[177] A report submitted by the chief medical officer of the Israeli army notes that, “the vast majority of (Israeli) prisoners were exposed during their imprisonment to severe physical and mental torture. The usual methods of torture were beatings aimed at various parts of the body, electric shocks, wounds deliberately inflicted on the ears, burns on the legs, suspension in painful positions and other methods."[180] Following the conclusion of hostilities, Syria would not release the names of prisoners it was holding to the International Committee of the Red Cross and in fact, did not even acknowledge holding any prisoners despite the fact they were publicly exhibited by the Syrians for TV crews.[181] The Syrians, having been thoroughly defeated by Israel, were attempting to use their captives as their sole bargaining chip in the post-war negotiations.[182] One of the most famous Israeli POWs was Avraham Lanir, an Israeli pilot who bailed out over Syria and was taken prisoner.[183] Lanir died under Syrian interrogation.[184][185][186] When his body was returned in 1974, it exhibited signs of torture.[184]
At sea
 Diagram of the Battle of Latakia
Diagram of the Battle of Latakia
At the beginning of the war, Egyptian missile boats bombarded seven ports in the Sinai, while naval frogmen raided oil installations at Bala'eem, disabling a driller.[187] The Israeli naval base at Sharm el-Sheikh was attacked with Egyptian Raguda KSR-2 cruise missiles.[188]
The Battle of Latakia, a revolutionary naval battle between the Israeli and Syrian navies, took place on October 7, the second day of the war. Five Israeli missile boats had been heading towards the Syrian port of Latakia, and sank a Syrian torpedo boat and minesweeper before encountering five Syrian missile boats. The Israelis used electronic countermeasures and chaff rockets to evade Syrian missiles, then sank all five Syrian missile boats. This revolutionary engagement, the first between missile boats using surface-to-surface missiles, proved the potency of small, fast missile boats equipped with advanced ECM packages. The battle also established the Israeli Navy, long derided as the "black sheep" of the Israeli military, as a formidable and effective force in its own right. Following this and other smaller naval engagements, the Syrian Navy remained bottled up in its home ports throughout most of the war, enabling the Mediterranean sea lanes to Israel to remain open.
On October 7, the Israeli Navy defeated the Egyptian Navy in what became known as the Battle of Marsa Talamat. Two Israeli Dabur class patrol boats were patrolling in the Gulf of Suez, and encountered two Egyptian Zodiac boats loaded with Egyptian naval commandos, a patrol boat, and coastal guns. The Israeli patrol boats sank both Zodiacs and the patrol boat. Both Israeli patrol boats suffered damage during the battle.[189] Israeli naval vessels fought several other engagements with the Egyptians that resulted full Israeli control of the Gulf of Suez. Dozens of Egyptian fishing boats mobilized for the war effort that were loaded with troops, ammunition and supplies bound for the Israeli side of the Gulf were destroyed or confined to their anchorages. The Israeli Navy's control of the Gulf of Suez made possible the continued deployment of an Israeli SAM battery near an Israeli naval base close to the southern end of the Suez Canal, depriving the Egyptian Third Army of air support and preventing it from moving southward and attempting to capture the southern Sinai.[190]
The second naval battle which ended in a decisive Israeli victory was the Battle of Baltim, which took place on October 8-9 off the coast of Baltim and Damietta. Six Israeli missile boats heading towards Port Said encountered four Egyptian missile boats coming from Alexandria. In an engagement lasting about forty minutes, the Israelis evaded Egyptian Styx missiles using electronic countermeasures and sank three of the Egyptian missile boats with Gabriel missiles and gunfire.[191][192][193][194][195] The Battles of Latakia and Baltim "drastically changed the operational situation at sea to Israeli advantage".[196]
Israeli commandos from Shayetet 13, the Israeli Navy's elite special unit, infiltrated the Egyptian port of Arkada on the night of October 9–10 and sank a Kumar-class missile boat after four previous attempts had failed. After another infiltration attempt failed, the commandos successfully infiltrated Arkada again on the night of October 21–22 and heavily damaged a missile boat with M72 LAW rockets. On October 16, Shayetet 13 commandos infiltrated Port Said in two Hazir mini-submarines to strike Egyptian naval targets. During the raid, the commandos sank a torpedo boat, a coast guard boat, a tank landing craft, and a missile boat. Two frogmen went missing during the operation.[197]
According to Israeli and Western sources, the Israelis lost no vessels in the war.[191][192][198][199] Israeli vessels were "targeted by as many as 52 Soviet-made anti-ship missiles", but none hit their targets.[200] According to historian Benny Morris, the Egyptians lost seven missile boats and four torpedo boats and coastal defense craft, while the Syrians lost five missile boats, one minesweeper, and one coastal defense vessel.[198] All together, the Israeli Navy suffered three dead or missing and seven wounded.
Having decisively beaten the Egyptian and Syrian navies, the Israeli Navy had the run of the coastlines. Israeli missile boats utilized their 76mm cannons and other armaments to attack Syrian coastal oil installations as well as radar stations and other targets of military value on both Syrian and Egyptian coastlines. The Israeli Navy even attacked some of Egypt's northernmost SAM batteries.[201]
The Egyptian Navy managed to enforce a blockade at Bab-el-Mandeb. Eighteen million tons of oil were transported yearly from Iran to Israel through the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb. The naval blockade, which lasted throughout the war until November 1, halted shipping destined for Israel through the Gulf of Eilat but left shipping in the Mediterranean unaffected. The Gulf of Suez was also mined to prevent the transportation of oil from the Bala'eem and Abu Rudeis oil fields in southwestern Sinai to Eilat in Southern Israel. Two oil tankers, one with a 48,000 ton capacity and one with a 2,000 ton capacity, sank after hitting mines in the Gulf of Suez.[202][203]
Israel responded with a counter-blockade of Egypt, which was enforced by naval vessels based at Sharm el-Sheikh and the Sinai coast in the Gulf of Suez. The Israeli blockade had a substantial negative impact on the Egyptian economy. Throughout the war, the Israeli Navy enjoyed complete command of the seas both in the Mediterranean approaches and in the Gulf of Suez.[204]
Soviet threat of intervention
 October 24. A UN-arranged meeting between IDF Lt. Gen. Haim Bar-Lev and an Egyptian general in Sinai.
October 24. A UN-arranged meeting between IDF Lt. Gen. Haim Bar-Lev and an Egyptian general in Sinai.
During the cease-fire, Henry Kissinger mediated a series of exchanges with the Egyptians, Israelis and the Soviets. On October 24, Sadat publicly appealed for American and Soviet contingents to oversee the ceasefire; it was quickly rejected in a White House statement. Kissinger also met with Soviet Ambassador Dobrynin to discuss convening a peace conference with Geneva as the venue. Later in the evening (9:35pm) of October 24–25, Brezhnev sent Nixon a "very urgent" letter. In that letter, Brezhnev began by noting that Israel was continuing to violate the ceasefire and it posed a challenge to both the US and USSR. He stressed the need to "implement" the ceasefire resolution and "invited" the US to join the Soviets "to compel observance of the cease-fire without delay" He then threatened "I will say it straight that if you find it impossible to act jointly with us in this matter, we should be faced with the necessity urgently to consider taking appropriate steps unilaterally. We cannot allow arbitrariness on the part of Israel."[205][206] The Soviets were threatening to militarily intervene in the war on Egypt's side if they could not work together to enforce the ceasefire.
Kissinger immediately passed the message to Haig, who met with Nixon for 20 minutes around 10:30 pm, and reportedly empowered Kissinger to take any necessary action.[205] Kissinger immediately called a meeting of senior officials, including Defense Secretary James Schlesinger, CIA Director William Colby, and White House Chief of Staff Alexander Haig. The Watergate scandal had reached its apex, and Nixon was so agitated and discomposed that they decided to handle the matter without him:
When Kissinger asked Haig whether [Nixon] should be wakened, the White House chief of staff replied firmly 'No.' Haig clearly shared Kissinger's feelings that Nixon was in no shape to make weighty decisions.[207]
The meeting produced a conciliatory response, which was sent (in Nixon's name) to Brezhnev. At the same time, it was decided to increase the Defense Condition (DEFCON) from four to three. Lastly, they approved a message to Sadat (again, in Nixon's name) asking him to drop his request for Soviet assistance, and threatening that if the Soviets were to intervene, so would the United States.[207]
The Soviets placed seven airborne divisions on alert and airlift was marshaled to transport them to the Middle East. An airborne command post was set up in the southern Soviet Union, and several air force units were also alerted. "Reports also indicated that at least one of the divisions and a squadron of transport planes had been moved from the Soviet Union to an airbase in Yugoslavia".[208] The Soviets also deployed seven amphibious warfare craft with some 40,000 naval infantry in the Mediterranean.
The Soviets quickly detected the increased American defense condition, and were astonished and bewildered at the response. "Who could have imagined the Americans would be so easily frightened," said Nikolai Podgorny. "It is not reasonable to become engaged in a war with the United States because of Egypt and Syria," said Premier Alexei Kosygin, while KGB chief Yuri Andropov added that "We shall not unleash the Third World War."[209] The letter from the American cabinet arrived during the meeting. Brezhnev decided that the Americans were too nervous, and that the best course of action would be to wait to reply.[210] The next morning, the Egyptians agreed to the American suggestion, and dropped their request for assistance from the Soviets, bringing the crisis to an end.
Participation by other states
Aid to Israel
Based on intelligence estimates at the commencement of hostilities, American leaders expected the tide of the war to quickly shift in Israel's favor, and that Arab armies would be completely defeated within 72 to 96 hours.[211] On October 6, Secretary of State Kissinger convened the National Security Council's official crisis management group, the Washington Special Actions Group, which debated whether the U.S. should supply additional arms to Israel. High-ranking representatives of the Defense and State Departments opposed such a move. Kissinger was the sole dissenter; he said that if the US refused aid, Israel would have little incentive to conform to American views in postwar diplomacy. Kissinger argued the sending of U.S. aid might cause Israel to moderate its territorial claims, but this thesis raised a protracted debate whether U.S. aid was likely to make it more accommodating or more intransigent toward the Arab world.[212]
By October 8, Israel had encountered military difficulties on both fronts; in the Sinai, its effort to break through Egyptian lines with armor had been thwarted, and despite advances in the Golan, Syrian air defense systems were taking a high toll of Israeli planes, Israeli forces were retreating, and Syrian forces were overlooking the Jordan River.[213][214][215] It became clear by October 9 that no quick reversal in Israel's favor would occur and that IDF losses were unexpectedly high.[216]
During the night of 8–9 October, an alarmed Dayan told Meir that "this is the end of the third temple."[214] He was warning of Israel's impending total defeat, but "Temple" was also the code word for nuclear weapons.[215] Dayan again raised the nuclear topic in a cabinet meeting, warning that the country was approaching a point of "last resort."[217] That night Meir authorized the assembly of thirteen 20-kiloton-of-TNT (84 TJ) tactical atomic weapons for Jericho missiles at Hirbat Zachariah, and F-4 aircraft at Tel Nof, for use against Syrian and Egyptian targets.[215] They would be used if absolutely necessary to prevent total defeat, but the preparation was done in an easily detectable way, likely as a signal to the United States.[217] Kissinger learned of the nuclear alert on the morning of October 9. That day, President Nixon ordered the commencement of Operation Nickel Grass, an American airlift to replace all of Israel's material losses.[218] Anecdotal evidence suggests that Kissinger told Sadat that the reason for the U.S. airlift was that the Israelis were close to "going nuclear."[215]
 An M60 delivered during Operation Nickel Grass
An M60 delivered during Operation Nickel Grass
Israel began receiving supplies via US cargo airplanes on October 14,[219] although some equipment had arrived before this date. According to Abraham Rabinovich, "while the American airlift of supplies did not immediately replace Israel's losses in equipment, it did allow Israel to expend what it did have more freely".[220] By the end of Nickel Grass, the United States had shipped 22,395 tons of matériel to Israel. 8,755 tons of it arrived before the end of the war.[221] American C-141 Starlifter and C-5 Galaxy aircraft flew 567 missions throughout the airlift.[222] The Israeli national airline El Al conducted its own airlift and flew in an additional 5,500 tons of matériel in 170 flights.[223][224] The United States also delivered approximately 90,000 tons of matériel to Israel by sea until the beginning of December, using 16 ships.[221] 33,210 tons of it arrived by October 30.[225]
By the beginning of December, Israel had received between 34 to 40 F-4 fighter-bombers, 46 A-4 attack airplanes, 12 C-130 cargo airplanes, 8 CH-53 helicopters, 40 unmanned aerial vehicles, 200 M-60/M-48A3 tanks, 250 armored personnel carriers, 226 utility vehicles, 12 MIM-72 Chaparral surface-to-air missile systems, 3 MIM-23 Hawk surface-to-air missile systems, 36 155 mm artillery pieces, 7 175 mm artillery pieces, large quantities of 105 mm, 155 mm and 175 mm ammunition, state of the art equipment, such as the AGM-65 Maverick missile and the BGM-71 TOW, weapons that had only entered production one or more years prior, as well as highly advanced electronic jamming equipment. Most of the combat airplanes arrived during the war, and many were taken directly from United States Air Force units. Most of the large equipment arrived after the ceasefire. The total cost of the equipment was approximately US$800 million (US$3.95 billion today).[223][224][226][227]
On October 13 and 15, Egyptian air defense radars detected an aircraft at an altitude of 25,000 metres (82,000 ft) and a speed of Mach 3, making it impossible to intercept either by fighter or SAM missiles. The aircraft proceeded to cross the whole of the canal zone, the naval ports of the Red Sea (Hurghada and Safaga), flew over the airbases and air defenses in the Nile delta, and finally disappeared from radar screens over the Mediterranean Sea. The speed and altitude were those of the US SR-71 Blackbird, a long-range strategic-reconnaissance aircraft. According to Egyptian commanders, the intelligence provided by both reconnaissance flights helped the Israelis prepare for the Egyptian attack on October 14 and assisted it in conducting Operation Stouthearted Men.[228][229][230]
Aid to Egypt and Syria
Soviet Aid
Starting on October 9, the Soviet Union began supplying Egypt and Syria by air and by sea. The Soviets airlifted 12,500–15,000 tons of supplies, of which 6,000 tons went to Egypt, 3,750 tons went to Syria and 575 tons went to Iraq. General Shazly, the former Egyptian chief of staff, claimed that more than half of the airlifted Soviet hardware actually went to Syria. According to Ze'ev Schiff, Arab losses were so high and the attrition rate so great that equipment was taken directly from Soviet and Warsaw Pact stores to supply the airlift.[231] Antonov An-12 and AN-22 aircraft flew over 900 missions during the airlift.[232]
The Soviets supplied another 63,000 tons, mainly to Syria, by means of a sealift by October 30.[233][234] Historian Gamal Hammad asserts that 400 T-55 and T-62 tanks supplied by the sealift were directed towards replacing Syrian losses, transported from Odessa on the Black Sea to the Syrian port of Latakia, while Egypt did not receive any tanks from the Soviets.[235] However, this is disputed by military historian Ze'ev Schiff, who states that freighters loaded with tanks and other weapons reached Egyptian, Algerian and Syrian ports throughout the war. The sealift may have included Soviet nuclear weapons, which were not unloaded but kept in Alexandria harbor until November to counter the Israeli nuclear preparations, which Soviet satellites had detected. American concern over possible evidence of nuclear warheads for the Soviet Scud missiles in Egypt contributed to Washington's decision to go to DEFCON 3.[215]
 A Soviet made BMP-1 captured by Israeli forces
A Soviet made BMP-1 captured by Israeli forces
Other countries
In total, Arab countries added up to 100,000 troops to Egypt and Syria's frontline ranks.[8] Besides Egypt, Syria, Jordan, and Iraq, several other Arab states were also involved in this war, providing additional weapons and financing. Algeria sent a squadron each of MiG-21s and Su-7s to Egypt, which arrived at the front between October 9 and October 11. It also sent an armored brigade of 150 tanks, the advance elements of which began to arrive on October 17, but reached the front only on October 24, too late to participate in the fighting.
Libyan forces were stationed in Egypt before the outbreak of the war. Libya provided one armored brigade and two squadrons of Mirage V fighters, of which one squadron was to be piloted by the Egyptian Air Force and the other by Libyan pilots, and also sent financial aid. Morocco sent one infantry brigade to Egypt and one armored regiment to Syria.[236][237] An infantry brigade composed of Palestinians was in Egypt before the outbreak of the war.[170][237] A Saudi brigade of 3,000 soldiers and the Kuwaiti Al Jahra Brigade Group were sent to Syria. These arrived with additional Jordanian and Iraqi reinforcements in time for a new Syrian offensive scheduled for October 23. The offensive was cancelled however.[176] Saudi Arabia and Kuwait also provided financial aid.[237] Tunisia sent 1,000-2,000 soldiers to Egypt, where they were stationed in the Nile Delta and some of them were stationed to defend Port Said.[170] Lebanon sent radar units to Syria for air defense.[238]
In addition to its forces in Syria, Iraq sent a single Hawker Hunter squadron to Egypt. The squadron quickly gained a reputation amongst Egyptian field commanders for its skill in air support, particularly in anti-armor strikes.[236]
A 3,500-strong Sudanese brigade was deployed to Egypt. It arrived on October 28, again too late to participate in the war. Nearly all Arab reinforcements came with no logistical plan or support, expecting their hosts to supply them, and in several cases causing logistical problems. On the Syrian front, a lack of coordination between Arab forces led to several instances of friendly fire.[170][239]
After the war, during the first days of November, Algeria deposited around US$200 million with the Soviet Union to finance arms purchases for Egypt and Syria.[239]
Cuba sent approximately 1,500 troops, including tank and helicopter crews, who reportedly engaged in combat operations against the IDF.[240] North Korea sent 20 pilots and 19 non-combat personnel. The unit had four to six encounters with the Israelis from August through the end of the war.[241] Israeli military intelligence reported that Soviet-piloted MiG-25 Foxbat interceptor/reconnaissance aircraft conducted flyovers over the Canal Zone.[242]
Weapons
The Arab armies were equipped with predominantly Soviet-made weapons while Israel's armaments were mostly Western-made. The Arabs' T-54/55s and T-62s were equipped with night vision equipment, which the Israeli tanks lacked, giving them an advantage in fighting at night, while Israel tanks had better armor and/or better armament. Israeli tanks also had a distinct advantage in the “hull-down” position where steeper angles of depression resulted in less exposure. The main guns of Soviet tanks could only depress 4 degrees. By contrast, the 105 mm guns on Centurion and Patton tanks could depress 10 degrees.[243]
Home front during the war
The war created a state of emergency in the countries involved in fighting. The Egyptian government began to evacuate foreign tourists, and on October 11, 1973, the Egyptian ship Syria left Alexandria to Piraeus with a load of tourists wishing to exit Egypt. The US Interest Section in Cairo also requested US government assistance in removing US tourists to Greece.[244] On October 12, Kissinger ordered the US Interest Section in Cairo to speed up preparations for the departure of US tourists staying in Egypt, while notifying such actions to the IDF in order to avoid accidental military operations against them.[245]
Post-ceasefire negotiations
On October 24, the UNSC passed Resolution 339, serving as a renewed call for all parties to adhere to the ceasefire terms established in Resolution 338. Most heavy fighting on the Egyptian front ended by October 26, but several airstrikes took place against Third Army from October 25 to 28.[246][247] The ceasefire did not end the sporadic clashes along the ceasefire lines nor did it dissipate military tensions.
With continuing Israeli advances, Kissinger threatened to support a UN withdrawal resolution, but before Israel could respond, Egyptian national security advisor Hafez Ismail sent Kissinger a stunning message—Egypt was willing to enter into direct talks with the Israelis, provided that the Israelis agree to allow non-military supplies to reach their army and agree to a complete ceasefire.
About noon on October 25, Kissinger appeared before the press at the State Department. He described the various stages of the crisis and the evolution of US policy. He reviewed the first two weeks of the crisis and the nuclear alert, reiterated opposition to US and Soviet troops in the area and more strongly opposed unilateral Soviet moves. He then reviewed the prospects for a peace agreement, which he termed “quite promising”, and had conciliatory words for Israel, Egypt and even the USSR. Kissinger concluded his remarks by spelling out the principles of a new US policy toward the Arab-Israeli conflict saying:[248]
Our position is that... the conditions that produced this war were clearly intolerable to the Arab nations and that in the process of negotiations it will be necessary to make substantial concessions. The problem will be to relate the Arab concern for the sovereignty over the territories to the Israeli concern for secure boundaries. We believe that the process of negotiations between the parties is an essential component of this.
Quandt considers, “It was a brilliant performance, one of his most impressive.” One hour later the United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 340. This time the ceasefire held, and the fourth Arab-Israeli war was over.
Disengagement talks took place on October 28 at "Kilometer 101" between Israeli Major General Aharon Yariv and Egyptian Major General Abdel Ghani el-Gamasy. Ultimately, Kissinger took the proposal to Sadat, who agreed. United Nations checkpoints were brought in to replace Israeli ones, nonmilitary supplies were allowed to pass, and prisoners-of-war were to be exchanged. A summit conference in Geneva followed, and ultimately, an armistice agreement was worked out. On January 18, Israel signed a pullback agreement to the east side of the canal, and the last of their troops withdrew from the west side on March 5, 1974,[249] giving Egypt control of the Suez Canal. Between the UN ceasefire and the armistice agreement in January, a minor war of attrition took place between the belligerents, during which the Egyptians claimed to have killed 187 Israeli soldiers, destroyed 41 tanks, and downed 11 planes.[250][251] The IDF acknowledged the loss of 14 soldiers during this postwar period. Egyptian losses were higher especially in the sector controlled by General Ariel Sharon, who ordered his troops to respond with massive firepower to any Egyptian provocation.[252]
On the Syrian front, continuing Syrian shelling was, according to Syrian foreign minister Abdel Halim Khaddam, "part of a deliberate war of attrition designed to paralyse the Israeli economy", and was intended to pressure Israel into yielding the occupied territory.[253] Shuttle diplomacy by Henry Kissinger eventually produced a disengagement agreement on May 31, 1974, based on exchange of prisoners-of-war, Israeli withdrawal to the Purple Line and the establishment of a UN buffer zone. The agreement ended the skirmishes and exchanges of artillery fire that had occurred frequently along the Israeli-Syrian ceasefire line. The UN Disengagement and Observer Force (UNDOF) was established as a peacekeeping force in the Golan.
Casualties
See also: Israeli casualties of warIsrael suffered between 2,520[26][20][254] and 2,800 killed in action.[19] An additional 7,250[255] to 8,800[19] soldiers were wounded. Some 293 Israelis were captured.[256] Approximately 400 Israeli tanks were destroyed. Another 600 were disabled but returned to battle after repairs.[28] A major Israeli advantage, noted by many observers, was their ability to quickly return damaged tanks to combat.[111][257] The Israeli Air Force lost 102 aircraft: 32 F-4s, 53 A-4s, 11 Mirages and 6 Super Mysteres. Two helicopters, a Bell 205 and a CH-53, were also shot down.[29] According to Defense Minister Moshe Dayan, nearly half of these were shot down during the first three days of the war.[24] IAF losses per combat sortie were less than in the preceding Six Day War of 1967.[258]
Arab casualties were known to be much higher than Israel's, though precise figures are difficult to ascertain as Egypt and Syria never disclosed official figures. The lowest casualty estimate is 8,000 (5,000 Egyptian and 3,000 Syrian) killed and 18,000 wounded.[19] The highest estimate is 18,500 killed in action of which 15,000 were Egyptian and 3,500 Syrian.[20] Most estimates lie somewhere in between the two, with the Insight Team of the The Sunday Times of London claiming combined Arab losses of 16,000 killed[259] and yet another source citing a figure of some 15,000 dead and 35,000 wounded.[22] Some 8,372 Egyptians and 392 Syrians were captured. Thirteen Iraqis and six Moroccans were also captured.[256][260] Arab tank losses amounted to 2,250[22][261] though Garwych cites a figure of 2,300.[23] 400 of these fell into Israeli hands in good working order and were incorporated into Israeli service.[22] Between 341[19] and 514[24] Arab aircraft were shot down. According to Herzog, 334 of these aircraft were shot down by the Israeli Air Force in air-to-air combat for the loss of only five Israeli planes.[24] The Insight Team of The Sunday Times notes Arab aircraft losses of 450.[254] At sea, 19 Arab naval vessels, 10 of which were missile boats, were sunk for no Israeli losses.[25]
Long-term effects
The peace discussion at the end of the war was the first time that Arab and Israeli officials met for direct public discussions since the aftermath of the 1948 war.
Response in Israel
Though the war reinforced Israel’s military deterrence, it had a stunning effect on the population in Israel. Following their victory in the Six-Day War, the Israeli military had become complacent. The shock and sudden reversals that occurred at the beginning of the war inflicted a terrible psychological blow to the Israelis, who had hitherto experienced no serious military challenges.[262]
A protest against the Israeli government started four months after the war ended. It was led by Motti Ashkenazi, commander of Budapest, the northernmost of the Bar-Lev forts and the only one during the war not to be captured by the Egyptians.[263] Anger against the Israeli government (and Dayan in particular) was high. Shimon Agranat, President of the Israeli Supreme Court, was asked to lead an inquiry, the Agranat Commission, into the events leading up to the war and the setbacks of the first few days.[264]
The Agranat Commission published its preliminary findings on April 2, 1974. Six people were held particularly responsible for Israel's failings:
- Though his performance and conduct during the war was lauded,[265] IDF Chief of Staff David Elazar was recommended for dismissal after the Commission found he bore "personal responsibility for the assessment of the situation and the preparedness of the IDF."
- Intelligence Chief, Aluf Eli Zeira, and his deputy, head of Research, Brigadier-General Aryeh Shalev, were recommended for dismissal.
- Lt. Colonel Bandman, head of the Aman desk for Egypt, and Lt. Colonel Gedelia, chief of intelligence for the Southern Command, were recommended for transfer away from intelligence duties.
- Shmuel Gonen, commander of the Southern front, was recommended by the initial report to be relieved of active duty.[266] He was forced to leave the army after the publication of the Commission's final report, on January 30, 1975, which found that "he failed to fulfill his duties adequately, and bears much of the responsibility for the dangerous situation in which our troops were caught."[267]
Rather than quieting public discontent, the report—which "had stressed that it was judging the ministers' responsibility for security failings, not their parliamentary responsibility, which fell outside its mandate"—inflamed it. Although it had absolved Meir and Dayan of all responsibility, public calls for their resignations (especially Dayan's) intensified.[266]
On April 11, 1974, Golda Meir resigned. Her cabinet followed suit, including Dayan, who had previously offered to resign twice and was turned down both times by Meir. Yitzhak Rabin, who had spent most of the war as an advisor to Elazar in an unofficial capacity,[268] became head of the new government, which was seated in June.
In 1999, the issue was revisited by the Israeli political leadership to prevent similar shortcomings from being repeated. The Israeli National Security Council was created to improve coordination between the different security and intelligence bodies, and the political branch of government.
Response in Egypt and Syria
For the Arab states (and Egypt in particular), the psychological trauma of their defeat in the Six-Day War had been healed, allowing them to negotiate with the Israelis as equals. Due to the later setbacks in the war (which saw Israel gain a large salient on African soil and even more territory on the Syrian front), some believe that the war helped convince many in the Arab world that Israel could not be defeated militarily, thereby strengthening peace movements and ending the old Arab ambition of destroying Israel by force.[269]
General Shazli had angered Sadat for advocating the withdrawal of Egyptian forces from Sinai to meet the Israeli incursion on the West Bank of the Canal. Six weeks after the war, he was relieved of command and forced out of the army. Ultimately, he went into political exile for years. Upon his return to Egypt, he was placed under house arrest.[270] Following his release, he advocated the formation of a "Supreme High Committee" modeled after Israel's Agranat Commission, to “probe, examine and analyze” the performance of Egyptian forces and command decisions during the war. His requests were ignored.[271] His book, which candidly described Egyptian military failings and sharp disagreements he had with Ismail, Sadat and others in connection with the prosecution of the war, was banned in Egypt.[272]
The commanders of the Second and Third Armies, Generals Khalil and Wasel, were likewise dismissed from the army.[273] The commander of the Egyptian Second Army at the start of the war, General Mamoun, suffered a heart attack[111] or alternatively, a breakdown[274][275] after the 14 October Sinai tank battle and was replaced by General Khalil.
The Seventh Division commander, Gen. Omar Abash, who failed to break through Col. Avigdor Ben-Gal's brigade, was alternatively reported to have been killed in the fighting or to have died of a heart attack.[273]
In Syria, the Druze commander of an infantry brigade that had collapsed during the Israeli breakthrough – Colonel Rafik Halawi – was executed even before the war ended.[273]
Camp David Accords
Main article: Camp David Accords (1978)The Yom Kippur War upset the status quo in the Middle East, and the war served as a direct antecedent of the 1979 Camp David Accords.[153]
Rabin's government was hamstrung by a pair of scandals, and he was forced to step down in 1977. The right-wing Likud party, under the prime ministership of Menachem Begin, won the elections that followed. This marked a historic change in the Israeli political landscape: for the first time since Israel's founding, a coalition not led by the Labor Party was in control of the government.
 Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin acknowledge applause during a joint session of Congress in Washington, D.C., during which President Jimmy Carter announced the results of the Camp David Accords, 18 September 1978.
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin acknowledge applause during a joint session of Congress in Washington, D.C., during which President Jimmy Carter announced the results of the Camp David Accords, 18 September 1978.
Sadat, who had entered the war in order to recover the Sinai from Israel, grew frustrated at the slow pace of the peace process. In a 1977 interview with CBS News anchorman Walter Cronkite, Sadat admitted under pointed questioning that he was open to a more constructive dialog for peace, including a state visit. This seemed to open the floodgates, as in a later interview with the same reporter, the normally hard-line Begin – perhaps not wishing to be compared unfavorably to Sadat – said he too would be amenable to better relations and offered his invitation for such a visit. Thus, in November of that year, Sadat took the unprecedented step of visiting Israel, becoming the first Arab leader to do so, and so implicitly recognized Israel.
The act jump-started the peace process. United States President Jimmy Carter invited both Sadat and Begin to a summit at Camp David to negotiate a final peace. The talks took place from September 5–17, 1978. Ultimately, the talks succeeded, and Israel and Egypt signed the Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty in 1979. Israel withdrew its troops and settlers from the Sinai, in exchange for normal relations with Egypt and a lasting peace.
Many in the Arab community were outraged at Egypt's peace with Israel. Egypt was expelled from the Arab League. Until then, Egypt had been "at the helm of the Arab world."[276] Egypt's tensions with its Arab neighbors culminated in 1977 in the short-lived Libyan–Egyptian War.
Sadat was assassinated two years later on October 6, 1981, while attending a parade marking the eighth anniversary of the start of the war, by Islamist army members who were outraged at his negotiations with Israel.
Oil embargo
In response to U.S. support of Israel, the Arab members of OPEC, led by Saudi Arabia, decided to reduce oil production by 5% per month on October 17. On October 19, President Nixon authorized a major allocation of arms supplies and $2.2 billion in appropriations for Israel. In response, Saudi Arabia declared an embargo against the United States, later joined by other oil exporters and extended against the Netherlands and other states, causing the 1973 energy crisis.[277]
Commemorations
October 6 is a national holiday in Egypt called Armed Forces Day. It is a national holiday in Syria as well, where it is called "Tishreen Liberation Day".[278] Marking the 35th anniversary in 2006, Hosni Mubarak said that the conflict "breathed new life" into Egypt. He said Egypt and Syria's initial victories in the conflict eased Arab bitterness over Israel's victory in the 1967 Six-Day War and ultimately put the two nations on a path of peaceful coexistence.[279]
In Egypt, many places were named after the October 6 date and Ramadan 10, its equivalent in the Islamic calendar. Examples of these commemorations are the 6th October Bridge in Cairo and the cities 6th of October City and 10th of Ramadan City.
The "Museum of 6 October War" was built in 1989 in the Heliopolis district of Cairo. The center of the museum is occupied by a rotunda housing a panoramic painting of the struggle between Egyptian and Israeli armed forces. The panorama, the creation of which was outsourced to a group of North Korean artists and architects, is equipped with engines to rotate it 360° during a 30-minutes presentation accompanied by commentary in various languages.[280] A similar museum, which was also built with North Korean assistance—the October War Panorama—operates in Damascus.[281]
See also
- 1970 Syrian Corrective Revolution
- List of modern conflicts in the Middle East
References
Notes
- ^ Herzog (1975). The War of Atonement. Little, Brown and Company.. Foreword.
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times (1974). Yom Kippur War. Double Day and Company. p. 450.
- ^ Luttwak; Horowitz (1983). The Israeli Army. Cambridge, MA: Abt Books.
- ^ Rabinovich (2004). The Yom Kippur War. Schocken Books. p. 498.
- ^ Kumaraswamy, PR (2000-03-30). Revisiting The Yom Kippur War. pp. 1–2. ISBN 9780714650074. http://books.google.com/books?id=z58nmWqS94MC&printsec=frontcover&dq=related:ISBN0313313024#v=onepage&q=&f=false.
- ^ Johnson; Tierney. Failing To Win, Perception of Victory and Defeat in International Politics. p. 177.
- ^ Liebman, Charles (July 1993) (PDF). The Myth of Defeat: The Memory of the Yom Kippur war in Israeli Society. Middle Eastern Studies. 29. London: Frank Cass. p. 411.. https://www.policyarchive.org/bitstream/handle/10207/10011/Liebman-MiddleEasternStudies29.pdf.[dead link]
- ^ a b c d e Rabinovich. p. 54.
- ^ Herzog. p. 239..
- ^ a b Shazly, p. 244
- ^ a b c The number reflects artillery units of caliber 100 mm and up
- ^ Shazly, p. 272.
- ^ Haber & Schiff, p 30 31
- ^ a b USMC Major Michael C. Jordan (1997). "The 1973 Arab-Israeli War: Arab Policies, Strategies, and Campaigns". GlobalSecurity.org. http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/library/report/1997/Jordan.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-20.
- ^ a b Major George E. Knapp (1992). "4: Antiarmor Operations on the Golan Heights". Combined Arms in battle since 1939. U.S. Army Command and General Staff College. http://www.cgsc.edu/carl/resources/csi/Spiller/Spiller.asp#4AO. Retrieved 2009-06-01
- ^ a b c Rabinovich, 314
- ^ Bar-On, Mordechai (2004). A Never Ending Conflict. Greenwood Publishing. p. 170.
- ^ Insight Team. London, ENG: Sunday Times. pp. 372–3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Garwych, p. 243
- ^ a b c Herzog, Encyclopedia Judaica, Keter Publishing House, 1974, @ p.87
- ^ Rabinovich p. 497
- ^ a b c d Rabinovich, 496-7
- ^ a b Garwych p 244
- ^ a b c d Herzog, 260
- ^ a b Herzog, War of Atonement, p 269
- ^ a b Schiff, A History of the Israeli Army, page 328
- ^ Rabinovich. p. 497.
- ^ a b Rabinovich, 496
- ^ a b "White House Military Briefing" (PDF). http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB98/octwar-56.pdf. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ William B.Quandt, Peace Process: American diplomacy and the Arab-Israeli conflict since 1967, p. 104
- ^ Herzog, Heroes of Israel, p.253
- ^ Shlaim, p.254.
- ^ "The Jarring initiative and the response," Israel's Foreign Relations, Selected Documents, vols. 1–2, 1947–1974 . Retrieved June 9, 2005.
- ^ Rabinovich, 13.
- ^ Rabinovich p.12
- ^ Morris 2001, p. 390.
- ^ Heikal, 22
- ^ Rabinovich, 39.
- ^ Rabinovich, 25.
- ^ Shazly, p. 207
- ^ Gawrych 1996, p. 24
- ^ Rabinovich, 51.
- ^ Rabinovich, 50.
- ^ a b Rabinovich, 57.
- ^ Doron Geller, "Israeli Intelligence and the Yom Kippur War of 1973," "JUICE", The Department for Jewish Zionist Education, The Jewish Agency for Israel . Retrieved November 27, 2005.
- ^ Christopher Andrew and Vasili Mitrokhin, The World Was Going Our Way. The KGB and the Battle for the Third World, Basic Books, 2006.
- ^ Rabinovich, 89.
- ^ "Government of Israel Concern about possible Syrian and Egyptian attack today". United States Department of State. 1973-10-06. http://aad.archives.gov/aad/createpdf?rid=77417&dt=1573&dl=823. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ^ Quandt 2005, p.105
- ^ Sachar, Howard M. A History of Israel from the Rise of Zionism to Our Time. Alfred A. Knopf, 2007, p. 755.
- ^ William B. Quandt, Peace Process, p105
- ^ Rabinovich, 454
- ^ Gawrych 1996, p. 27
- ^ Rabinovich, prologue
- ^ Rabinovich, p 62
- ^ Abudi, Joseph (October 1, 2003). "[The missile did not bend the wing]" (in Hebrew). Journal of the Israeli Air Force. http://www.iaf.org.il/1213-21478-he/IAF.aspx. Retrieved February 15, 2011.
- ^ Abudi, Joseph (October, 2005). "[What between 'challenge' and 'model']" (in Hebrew). The Fisher Institute. http://www.fisherinstitute.org.il/_Uploads/dbsAttachedFiles/num27.pdf. Retrieved February 15, 2011.
- ^ Shazly, pp. 224–225
- ^ Shazly, pp. 225–226
- ^ Shazly, p. 189
- ^ Shazly, pp. 55–56
- ^ Garwych p.28
- ^ a b The Crossing of the Suez Canal, October 6, 1973 (The Ramadan War), page 9
- ^ Shazly, p. 232
- ^ Hammad, pp.90–92, 108
- ^ Andrew James McGregor, A military history of modern Egypt: from the Ottoman Conquest to the Ramadan War, p. 278
- ^ Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness (Pollack), page 108
- ^ Rabinovich, p.115
- ^ Pollack p.125
- ^ The Yom Kippur War 1973: The Sinai - Simon Dunstan and Kevin Lyles
- ^ Shazly, p. 228
- ^ Shazly, p. 229
- ^ Nassar, Galal (8–14 October 1998). Into the breach, dear friends. Cairo: Al-Ahram Weekly On-line. para. 10. http://weekly.ahram.org.eg/1998/398/oct12.htm.
- ^ Cohen, Israel's Best Defense, p.354
- ^ Pollack, p. 11
- ^ Shazly, p. 233
- ^ Haber & Schiff, p. 32
- ^ Schiff, page 294
- ^ Herzog, The War of Atonement, Little, Brown and Company, 1975, page 156
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, Yom Kippur War, Double Day and Company, Inc, 1974, pages 169 and 170
- ^ Pollack, Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness 1948–1991, University of Nebraska Press, p. 110
- ^ "Israel Air Force". Iaf.org.il. http://www.iaf.org.il/Templates/FlightLog/FlightLog.aspx?lang=EN&lobbyID=40&folderID=48&subfolderID=322&docfolderID=939&docID=13279&docType=EVENT. Retrieved 2010-03-28.[dead link]
- ^ Pollack, Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness 1948–1991, University of Nebraska Press, p. 108
- ^ Nicolle & Cooper p. 40
- ^ Pollack, p. 112
- ^ Hammad, pp.712–714
- ^ Hammad, pp.717–722
- ^ Gawrych 1996, p. 38. In his memoirs, Adan, commenting on one of the commando operations in the north, noted that "Natke's experience fighting the stubborn Egyptian commandos who tried to cut off the road around Romani showed again that this was not the Egyptian Army we had crushed in four days in 1967. We were now dealing with a well-trained enemy, fighting with skill and dedication."
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, Yom Kippur War, Double Day and Company, Inc, 1974, pp.169–170
- ^ Rabinovich, 354
- ^ Gawrych 1996, pp. 41–42
- ^ Gawrych 1996, pp. 43–44
- ^ Rabinovich, 234
- ^ Gawrych 1996, pp. 44–52
- ^ Gawrych 2000, pp. 192, 208
- ^ Herzog 1982, pp. 255–256
- ^ a b Shazly p. 241
- ^ Herzog 1982, p. 256
- ^ a b c Zabecki, David T. (2008-12-03). "Arab-Israeli Wars: 60 Years of Conflict". Historyandtheheadlines.abc-clio.com. Chinese Farm, Battle of The. http://www.historyandtheheadlines.abc-clio.com/ContentPages/ContentPage.aspx?entryId=1281396¤tSection=1271019&productid=16. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Herzog 1982, p. 257–258
- ^ Herzog 1982, p. 258
- ^ Shazly p. 317
- ^ a b Schiff, A History of the Israeli Army, p.310
- ^ Rabinovich, 353
- ^ Rabinovich, 355.
- ^ Pollack, Kenneth, Arabs at War: Military Effectiveness 1948–91, University of Nebraska Press,, pp. 116, 126 & 129.
- ^ Haber & Schiff, p. 144
- ^ a b c Pollack, p. 117
- ^ Van Creveld, Martin (1975). Military Lessons of the Yom Kippur War: Historical Perspectives. Sage. p. 17. ISBN 9780803905627. http://csel.eng.ohio-state.edu/courses/ise817/papers/creveld_military_lessons.pdf.
- ^ a b Herzog, The Arab-Israeli Wars, Random House, p. 260
- ^ a b c John Pike. "Operation Valiant: Turning the Tide in the Sinai 1973 Arab-Israeli War CSC 1984". Globalsecurity.org. http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/library/report/1984/ORL.htm. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Pollack, p. 118
- ^ http://www.jpost.com/DiplomacyAndPolitics/Article.aspx?id=240891
- ^ Rabinovich, pp. 374–75
- ^ Rabinovich, pp. 389–91
- ^ Pollack, p. 511
- ^ Pollack, pp. 124–25
- ^ Rabinovich, pp. 393–393
- ^ Sharon, Gilad: Sharon: The Life of A Leader (2011)
- ^ Rabinovich, p. 427
- ^ Pollack, pp. 118–19
- ^ Hammad (2002), pp. 335-408
- ^ Gawrych (1996), pp. 62-64
- ^ Pollack, p. 129
- ^ Pollack, p. 119
- ^ Pollack, pp. 119–20
- ^ a b Pollack, p. 120
- ^ Rabinovich, p. 401
- ^ Herzog, The War of Atonement, Little, Brown and Company (1975) 236-7
- ^ Pollack, p. 122
- ^ a b Gawrych, p. 223
- ^ Rabinovich, 477
- ^ Rabinovich, Id
- ^ Neff, p. 306. plus 994 artillery pieces
- ^ Johnson and Tierney, p. 176
- ^ Shazly, p. 295
- ^ Rabinovich, 452
- ^ Rabinovich, 458
- ^ "22 October Memorandum of Conversation between Meir and Kissinger" (PDF). http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB98/octwar-54.pdf. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Adan, p. 284
- ^ Gawrych pp. 73;ndash&74
- ^ Rabinovich, 463
- ^ a b The October War and U.S. Policy, Collapse of the Ceasefire
- ^ William B. Quandt, Peace Process, p120
- ^ Piccirilli, Major Steven J (1989). "The 1973 Arab Israeli war". Globalsecurity.org. http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/library/report/1989/PSJ.htm. Retrieved 2011-09-29.
- ^ a b Gawrych 1996, p. 73
- ^ Hammad, pp. 483, 487–490.
- ^ Rabinovich 466–475
- ^ Rabinovich, 465
- ^ Rabinovich, 487
- ^ Gawrych, p.74
- ^ Dupuy, pp. 543–545, 589
- ^ a b David T. Buckwalter, The 1973 Arab-Israeli War
- ^ Asad of Syria: the struggle for the Middle East, p. 227
- ^ Kumaraswamy, Revisiting the Yom Kippur War, p. 1
- ^ Herzog, Arab-Israeli Wars, p 283
- ^ Shazly, p. 293
- ^ Shazly, p. 323
- ^ "Department of State Operations Center, Situation Report in the Middle East as of 10/26/73" (PDF). http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB98/octwar-77.pdf. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times p.291-93
- ^ a b c d e http://www.historynet.com/yom-kippur-war-sacrificial-stand-in-the-golan-heights.htm
- ^ Peter Caddick-Adams "Golan Heights, battles of" The Oxford Companion to Military History. Ed. Richard Holmes. Oxford University Press, 2001.
- ^ a b O'Ballance (1978). Chapter 7 : "The Syrians attack", pp 119-146.
- ^ a b Rabinovich, Abraham (September 25, 1998). Shattered Heights: Part 1. Jerusalem Post. http://info.jpost.com/C003/Supplements/30YK/art.23.html. Retrieved June 9, 2005.
- ^ [1][dead link]
- ^ "The Air Raid on the Syrian General Command". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/History/syria_raid.html. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ Rabinovich, 304
- ^ (in Hebrew) המלחמה שלי רב-אלוף שאול מופז (מיל):300 קילומטר בעומק סוריה, http://www.nrg.co.il/online/archive/ART/550/213.html[unreliable source?]
- ^ Rabinovich, 433
- ^ a b c d Hussain, Hamid (November 2002). "Opinion: The Fourth Round — A Critical Review of 1973 Arab-Israeli War A Critical Review of 1973 Arab-Israeli War". defencejournal.com. http://www.defencejournal.com/2002/nov/4th-round.htm
- ^ Pollack, Arabs at War, 2002, p.167 gives total numbers for the Iraqi force by the end of the conflict as 60,000 men, over 700 T-55 tanks, 500 APCs, over 200 artillery pieces, two armoured divisions, two infantry brigades, twelve artillery battalions, and a special forces brigade.
- ^ Situation Report in the Middle East as of 1200 EDT, 10/23/73, Department of State Operations Center
- ^ Noam Ophir, The Long Shadow of the Scud, Israeli Air Force Official Website, Oct. 2006
- ^ Rabinovich, 450
- ^ Rabinovich, p.450-51
- ^ a b Rabinovich, 464–465
- ^ a b "War and Lack of Inner Peace", Michael S. Arnold, The Jerusalem Post, 1999-09-17.
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, pages 279 & 429
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, pgs429 and 449
- ^ "Statement in the Knesset on the treatment of Israeli prisoners of war in Syria by Defence Minister Peres and Knesset Resolution- 12 June 1974". Mfa.gov.il. http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/Foreign+Relations/Israels+Foreign+Relations+since+1947/1974-1977/5+Statement+in+the+Knesset+on+the+treatment+of+Isr.htm?DisplayMode=print. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, p429
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, p.449-450
- ^ Igal Sarna, The Man Who Fell Into a Puddle: Israeli Lives, Vintage Books/Random House (2000) pages 144 through 148
- ^ a b Sarna p. 148
- ^ Abraham Rabinovich, The Yom Kippur War: The Epic Encounter That Transformed the Middle East, Random House/Schocken Books (2004) p.115
- ^ Yemini, Galya (2008-04-02). "Noam Lanir plans to float Empire Online at $1b value". Haaretz.com. http://www.haaretz.com/print-edition/business/noam-lanir-plans-to-float-empire-online-at-1b-value-1.159508. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ Hammad, pp. 100-1001
- ^ Rabinovich (p. 245)
- ^ Almog, "Israel's Navy beat the odds", United States Naval Institute — Proceedings (Mar 1997), Vol. 123, Iss. 3; p. 106.
- ^ Almog, Ze'ev (March 1997). "Israel's Navy beat the odds" - United States Naval Institute - Proceedings (Annapolis: United States Naval Institute)
- ^ a b Dunstan, The Yom Kippur War, p. 114
- ^ a b Bolia, Overreliance on Technology: Yom Kippur Case Study[dead link]
- ^ Rabonovich, The Boats of Cherbourg, pp. 256–262
- ^ Dupuy, Elusive Victory, pp. 562–563
- ^ Herzog, The Arab-Israeli Wars, p. 312
- ^ Vego, Naval Strategy and Operations in Narrow Seas (Routledge: 1999), at p.151
- ^ "Shayetet 13". Zionism-israel.com. http://www.zionism-israel.com/dic/Shayetet_13.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ a b Morris, Righteous Victims, p. 432
- ^ Herzog, The Arab-Israeli Wars, p. 314
- ^ Annati, Anti-ship missiles and countermeasures—part I (ASM), Naval Forces (2001), Vol. 22, Iss. 1; p. 20.
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, pgs. 212-213
- ^ El Gammasy, The October War, 1973 p.215–216
- ^ Shazly, p.287
- ^ Herzog (1975), 268-269
- ^ a b William B Quandt,Peace Process, p 121
- ^ Rabinovich, 479
- ^ a b Rabinovich, 480
- ^ "Effects-Based Operations: the Yom Kippur War Case Study" (PDF). http://www.dodccrp.org/events/2004_CCRTS/CD/papers/190.pdf. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Rabinovich, 484
- ^ Rabinovich, 485
- ^ October 6 conversation between Henry Kissinger, Brent Scowcroft and Chinese Ambassador to the United States Huan Chen. Transcript. George Washington University National Security Archive.
- ^ George Lenczowski, American Presidents and the Middle East (1990), p.129
- ^ William B. Quandt, Peace Process, p.109
- ^ a b "Violent Week: The Politics of Death". Time. 1976-04-12. http://www.time.com/time/printout/0,8816,914023,00.html. Retrieved March 4, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Farr, Warner D. "The Third Temple's Holy of Holies: Israel's Nuclear Weapons." Counterproliferation Paper No. 2, USAF Counterproliferation Center, Air War College, September 1999.
- ^ October 9, 1973 conversation (8:20–8:40 am) between Israeli Ambassador to the United States Simcha Dinitz, military attaché General Mordechai Gur, Henry Kissinger, Brent Scowcroft, and Peter Rodman. Transcript George Washington University National Security Archive
- ^ a b Cohen, Avner. "The Last Nuclear Moment" The New York Times, 6 October 2003.
- ^ October 9, 1973 conversation (6:10–6:35 pm) between Israeli Ambassador to the United States Simcha Dinitz, Henry Kissinger, Brent Scowcroft, and Peter Rodman. Transcript George Washington University National Security Archive.
- ^ Krisinger, Chris J. Operation Nickel Grass – Airlift in Support of National Policy, Aerospace Power Journal, Spring 1989.
- ^ Rabinovich, 491.
- ^ a b Haber & Schiff, p. 382
- ^ John Lacomia. "Remember When... Operation Nickel Grass". Travis: Air Force. http://www.travis.af.mil/news/story.asp?id=123122053. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ a b Shazli p.275–276
- ^ a b Haber & Schiff, p. 282.
- ^ Shazly. p. 276. "...the USA mounted a seaborne resupply operation of 33,210 tons by October 30"
- ^ Gawrych 1996, p. 56
- ^ "McDonnell F-4 Phantom: Essential Aircraft in the Air Warfare in the Middle East". Historynet.com. http://www.historynet.com/mcdonnell-f-4-phantom-essential-aircraft-in-the-air-warfare-in-the-middle-east.htm/4. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ El Gamasy The October War, 1973 p.276
- ^ Shazly, pp. 251–252
- ^ O'ballance, p 182
- ^ Schiff, 303
- ^ Shazly, p.275
- ^ Shazly, pp. 274–275 Shazly states that "...the Soviet Union mounted a sea-borne resupply operation: no less than 63,000 tons, mainly to Syria, by October 30"
- ^ Quandt, 25–26 (pdf pages 37–38) gives the airlift total as approximately 12,500 tons; Quandt 23 (pdf page 35) gives the sealift total as approximately 63,000 tons.
- ^ Hammad, p.382
- ^ a b Shazly, pp. 277–278
- ^ a b c Rabinovich, 464
- ^ "The Yom Kippur War". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. 1973-10-06. http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/History/73_War.html. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ a b Shazly, p. 278
- ^ Perez, Cuba: Between Reform and Revolution, p. 377–379
- ^ Shazly, pp.83–84
- ^ "White House Military Briefing, Oct 22" (PDF). http://www.gwu.edu/~nsarchiv/NSAEBB/NSAEBB98/octwar-56.pdf. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
- ^ Dunstan, Simon (2009). Centurion Vs T-55: Yom Kippur War 1973. Osprey. pp. 28, 69. ISBN 9781846033698.
- ^ "Smith (US Interest Section in Cairo) to Department of State, October 11, 1973". http://aad.archives.gov/aad/createpdf?rid=84225&dt=2472&dl=1345. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ "Kissinger to the US Interest Section in Cairo, October 12, 1973". http://aad.archives.gov/aad/createpdf?rid=84739&dt=2472&dl=1345. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ Shazly, p. 282
- ^ Trevor N. Dupuy Elusive Victory: The Arab-Israeli Wars, 1947–1974 p.542
- ^ Quandt 2005, p. 123–124
- ^ Rabinovich, 493
- ^ El Gamasy The October War 1973 p.302
- ^ Gawrych 1996, p. 76
- ^ Rabinovich p. 493
- ^ Jonathan B. A. Bailey. Field artillery and firepower. Naval Institute Press, 2004. pg. 398. ISBN 1591140293.
- ^ a b Yom Kippur War, Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, Doubleday and Company Inc., page 450
- ^ Rabinovich, 497
- ^ a b "Ministry of Foreign Affairs". Mfa.gov.il. http://www.mfa.gov.il/MFA/MFAArchive/2000_2009/2004/1/Background%20on%20Israeli%20POWs%20and%20MIAs. Retrieved 2011-10-22.
- ^ Reuven Gal, A Portrait of the Israeli Soldier, Greenwood Publishing Group (1986), p.161
- ^ John Pimlott and Michael Orr, The Middle East Conflicts: From 1945 to the Present, P. 99, Obris Publishing, London (1983)
- ^ Insight Team of the London Sunday Times, Yom Kippur War p. 450
- ^ "Middle East: Sandstorm at Kilometer 101". TIME. 1973-12-03. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,908222,00.html. Retrieved 2010-05-21.
- ^ Military Lessons of the Yom Kippur War: Historical Perspectives, Martin van Creveld, page 47
- ^ Rabinovich, 497–498
- ^ Rabinovich, 499
- ^ Rabinovich, 501
- ^ Rabinovich, p. 503
- ^ a b Rabinovich, 502
- ^ Findings of the Agranat Commission[dead link], The Jewish Agency for Israel, see "January 30" on linked page . Retrieved June 9, 2005.
- ^ Rabinovich, 237
- ^ The Middle East: a glossary of terms. Guardian Unlimited, May 15, 2001
- ^ Rabinovich, p. 507
- ^ Shazly, p. 331
- ^ Shazly, p. 334
- ^ a b c Rabinovich, 507
- ^ Rabinovich, p. 356
- ^ Howard Blum, The Untold Story of the Yom Kippur War, HarperCollins Publishers 2007, Page 298
- ^ Karsh, 86
- ^ Charles D. Smith, Palestine and the Arab-Israeli Conflict, New York: Bedford, 2006, p. 329.
- ^ Doing Business in Syria: 2010 Country Commercial Guide for U.S. Companies, U.S. Commercial Service, United States of America Department of Commerce, retrieved May 21, 2010.
- ^ "Mubarak reflects on 1973 Yom Kippur War". UPI. 2008-10-06. http://www.upi.com/Top_News/2008/10/06/Mubarak-reflects-on-1973-Yom-Kippur-War/UPI-59221223312625/. Retrieved 2010-04-20.
- ^ "Egypt State Information Service". http://www.sis.gov.eg/VR/october/english/5.htm. Retrieved 2009-06-19.
- ^ "Lonely Planet". http://www.lonelyplanet.com/syria/damascus/sights/museum/tishreen-october-war.
Bibliography
- el Badri, Hassan (1979). The Ramadan War, 1973. Fairfax, Va: T. N. Dupuy Associates Books. ISBN 0882446002.
- Bregman, Ahron (2002). Israel's Wars: A History Since 1947. London: Routledge. ISBN 0415287162.
- Dupuy, Trevor Nevitt (1978). Elusive victory: The Arab-Israeli Wars, 1947–1974. San Francisco: Harper & Row. ISBN 006-011-112-7.
- Gawrych, George (2000). The Albatross of Decisive Victory: War and Policy Between Egypt and Israel in the 1967 and 1973 Arab-Israeli Wars. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 031-331-302-4.
- Gawrych, Dr. George W. (1996). The 1973 Arab-Israeli War: The Albatross of Decisive Victory. Combat Studies Insitute, U.S. Army Command and General Staff College. Intro[dead link], Part I, Part II, Part III, Part IV, Part V, Part VI, Part VII, Notes[dead link]
- Haber, Eitan; Schiff, Ze'ev (2003) (in Hebrew). Yom Kippur War Lexicon. Or-Yehuda, Israel: Zmora-Bitan-Dvir. ISBN 965-517-124-8.
- Hammad, Gamal (2002) (in Arabic). al-Maʻārik al-ḥarbīyah ʻalá al-jabhah al-Miṣrīyah: (Ḥarb Uktūbar 1973, al-ʻĀshir min Ramaḍān) [Military Battles on the Egyptian Front] (First ed.). Dār al-Shurūq. p. 903. ISBN 9770908665.
- Heikal, Mohamed (1975). The Road to Ramadan. London: Collins. ISBN 0812905679.
- Herzog, Chaim (2003) [1975]. The War of Atonement: The Inside Story of the Yom Kippur War. London: Greenhill Books. ISBN 9781853675690.
- Herzog, Chaim (1982). the Arab-Israeli Wars. Random House. ISBN 978-0394503790.
- Herzog, Chaim (1989). Heroes of Israel. Boston: Little, Brown. ISBN 0-316-35901-7.
- Israeli, Raphael (1985). Man of Defiance: A Political Biography of Anwar Sadat. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0389205796.
- Israelyan, Victor (2003) [1995]. Inside the Kremlin During the Yom Kippur War. University Park, PA: Pennsylvania State University Press. ISBN 0271017376.
- Karsh, Efraim (2002). The Iran-Iraq War, 1980–1988. Oxford: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 1841763713.
- Lanir, Zvi (2002) [1983] (in Hebrew). ha-Haftaʻah ha-basisit : modiʻin ba-mashber [Fundamental Surprise: Intelligence in Crisis]. Tel-Aviv: Hakibbutz Hameuchad. OCLC 65842089.
- Morris, Benny (2001). Righteous Victims. New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 978-067-974-475-7.
- Ma'Oz, Moshe (1995). Syria and Israel: From War to Peacemaking. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0198280181.
- Neff, Donald (1988). Warriors against Israel. Brattleboro, Vermont: Amana Books. ISBN 9780915597598.
- Nicolle, David; Cooper, Tom (2004-05-25). Arab MiG-19 and MiG-21 units in combat. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 184-176-655-0.
- O'Ballance, Edgar (November 1996) [1978]. No Victor, No Vanquished: the Yom Kippur War. Presidio Press. ISBN 978-089-141-615-9.
- Pape, Robert A (Fall, 1997). "Why Economic Sanctions Do Not Work". International Security 22 (2). OCLC 482431341.
- Quandt, William (2005). Peace Process: American diplomacy and the Arab-Israeli conflict since 1967. Washington, DC: Brookings Institution / Univ. of California Press. ISBN 0520223748.
- Quandt, William B (May 1976). Soviet Policy in the October 1973 War. Rand Corp. R-1864-ISA. http://www.rand.org/pubs/reports/2006/R1864.pdf
- Rabinovich, Abraham (2005) [2004]. The Yom Kippur War: The Epic Encounter That Transformed the Middle East. New York, NY: Schocken Books. ISBN 0805241760.
- al Sadat, Muhammad Anwar (1978). In Search of Identity: An Autobiography. London: Collins. ISBN 0002163446.
- Shazly, Lieutenant General Saad el (2003). The Crossing of the Suez, Revised Edition (Revised ed.). American Mideast Research. ISBN 0960456228.
- Shlaim, Avi (2001). The Iron Wall: Israel and the Arab World. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-32112-6.
External links
 Media related to Yom Kippur War at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Yom Kippur War at Wikimedia Commons
Recognized wars involving the Israeli Defense Forces 1948 Arab–Israeli War
1948–1949Suez Crisis
1956Six-Day War
1967War of Attrition
1967–1970Yom Kippur War
19731982 Lebanon War
19822006 Lebanon War
20061940s Yalta Conference · Operation Unthinkable · Potsdam Conference · Gouzenko Affair · War in Vietnam (1945–1946) · Iran crisis of 1946 · Greek Civil War · Corfu Channel Incident · Restatement of Policy on Germany · First Indochina War · Truman Doctrine · Asian Relations Conference · Marshall Plan · Czechoslovak coup d'état of 1948 · Tito–Stalin split · Berlin Blockade · Western betrayal · Iron Curtain · Eastern Bloc · Chinese Civil War (Second round)1950s Korean War · 1953 Iranian coup d'état · Uprising of 1953 in East Germany · 1954 Guatemalan coup d'état · Partition of Vietnam · First Taiwan Strait Crisis · Geneva Summit (1955) · Poznań 1956 protests · Hungarian Revolution of 1956 · Suez Crisis · Sputnik crisis · Second Taiwan Strait Crisis · Cuban Revolution · Kitchen Debate · Asian–African Conference · Bricker Amendment · McCarthyism · Operation Gladio · Hallstein Doctrine1960s Congo Crisis · Sino–Soviet split · 1960 U-2 incident · Bay of Pigs Invasion · Berlin Wall · Cuban Missile Crisis · Vietnam War · 1964 Brazilian coup d'état · United States occupation of the Dominican Republic (1965–1966) · South African Border War · Rhodesian Bush War · Transition to the New Order · Domino theory · ASEAN Declaration · Laotian Civil War · Greek military junta of 1967–1974 · Six-Day War · War of Attrition · Cultural Revolution · Sino-Indian War · Prague Spring · Goulash Communism · Sino–Soviet border conflict1970s Détente · Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty · Black September in Jordan · Cambodian Civil War · Realpolitik · Ping Pong Diplomacy · Four Power Agreement on Berlin · 1972 Nixon visit to China · 1973 Chilean coup d'état · Yom Kippur War · Strategic Arms Limitation Talks · Angolan Civil War · Mozambican Civil War · Ogaden War · Sino-Albanian split · Cambodian–Vietnamese War · Sino-Vietnamese War · Iranian Revolution · Operation Condor · Bangladesh Liberation War · Korean Air Lines Flight 9021980s Soviet war in Afghanistan · 1980 and 1984 Summer Olympics boycotts · Solidarity (Soviet reaction) · Contras · Central American crisis · RYAN · Korean Air Lines Flight 007 · Able Archer 83 · Star Wars · Invasion of Grenada · People Power Revolution · Tiananmen Square protests of 1989 · United States invasion of Panama · Fall of the Berlin Wall · Revolutions of 1989 · Glasnost · Perestroika1990s Foreign
policyIdeologies Capitalism (Chicago school · Keynesianism · Monetarism · Neoclassical economics · Supply-side economics · Thatcherism · Reaganomics) · Communism (Marxism–Leninism · Castroism · Eurocommunism · Guevarism · Juche · Left communism · Maoism · Stalinism · Titoism · Trotskyism) · Liberal democracy · Social democracyOrganizations Propaganda Races See also Brinkmanship · NATO–Russia relations · Soviet and Russian espionage in U.S. · Soviet Union – United States relations · US–Soviet summitsCategories:- Yom Kippur War
- 1973 in Egypt
- Conflicts in 1973
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.