- 1978 South Lebanon conflict
-
1978 South Lebanon conflict Part of the Arab–Israeli conflict and Israeli–Lebanese conflict Date March 14–March 21, 1978 Location Southern Lebanon Result Israeli military victory - PLO withdrawal from Southern Lebanon
- UNIFIL bufferzone established
- SLA established
Belligerents  Israel
Israel
 South Lebanon Army
South Lebanon Army PLO
PLO
 LNM
LNMCommanders and leaders  Ariel Sharon
Ariel Sharon
 Saad Haddad
Saad Haddad
 Antoine Lahad
Antoine Lahad Yasser Arafat
Yasser Arafat
 Walid Jumblatt
Walid Jumblatt
 George Hawi
George HawiStrength 25,000 10,000 Casualties and losses 20 Killed 1,100–2,000 Killed 1968 IDF raid – Avivim (1970) – Lod Airport (1972) – 1972 IDF raid – 1973 IDF raid – Kiryat Shmona (1974) – Ma'alot (1974) – Savoy Hotel – Kfar Yuval – Coastal Road (1978) – 1978 conflict – Nahariya (1979) – Misgav Am (1980) –
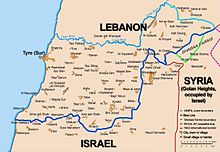
The 1978 South Lebanon conflict (code-named Operation Litani by Israel) was an invasion in Lebanon up to the Litani River carried out by the Israel Defense Forces in 1978. It was a military success for the Israeli Defense Forces, as PLO forces were pushed north of the river. However, objections from the Lebanese government led to the creation of the UNIFIL peacekeeping force and a partial Israeli withdrawal.
Contents
Background
Main article: Israeli–Lebanese conflictThough it took the form of an Israeli military incursion into Southern Lebanon, Operation Litani was grounded in the long-running Israeli-Palestinian conflict. From 1968 on, the PLO, Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine, and other Palestinian groups established a quasi-state in southern Lebanon, using it as a base for raids on civilian targets in northern Israel. This was exacerbated by an influx of 3,000 PLO militants fleeing a defeat in the Jordanian civil war and regrouping in southern Lebanon. Israel responded with damaging attacks against PLO bases.
During Israeli raids from 1968 to 1977, some of the Palestinian towns and camps in the area were totally leveled. According to estimations, by October 1977 about 300.000 refugees, mainly Shiite Muslims, fled South Lebanon [1].
In November 1977 Israeli initiated exchange of fire, that led to the death of several people from both sides of the border and finally Israeli bombing of the targets in South Lebanon during which 70 people, mainly Lebanese, were killed [1].
Violence escalated, eventually culminating in the 1982 Lebanon War and the ejection of the PLO from the country.
On 11 March 1978, 11 Fatah members led by the 18-year old female Dalal Mughrabi travelled from Lebanon and killed an American tourist on the beach. They then hijacked a bus on the coastal road near Haifa, and en route to Tel Aviv commandeered a second bus. After a lengthy chase and shootout, 37 Israelis were killed and 76 wounded.[2] Thus, the Coastal Road Massacre, was the proximate cause of the Israeli invasion three days later. (Cobban, p. 94, Shlaim p. 369), though the raiders came not from the area that was invaded, but from the area relatively far to the north from it [3]. The PLO-Israeli conflict increased political tensions between Maronite Christians and Druze to the Muslims, adding to the factors behind the 1975–1990 Lebanese Civil War.[4]
Course of fighting
On March 14, 1978, Israel launched Operation Litani, occupying the area south of the Litani River, excepting Tyre, with over 25,000 soldiers. Its stated goals were to push Palestinian militant groups, particularly the PLO, away from the border with Israel, and to bolster Israel's ally at the time, the South Lebanon Army because of the attacks against Lebanese Christians and Jews and because of the relentless shelling into Northern Israel. During the 7-day offensive, the Israeli Defence Forces first captured a belt of land approximately 10 kilometres deep, but later expanded north to the Litani river. 20 Israeli soldiers and 1,100–2,000 PLO fighters[citation needed] were killed . According to other source about 2000 Lebanese and Palestinian were killed and some 250,000 refugees fled the area [3]. The PLO retreated north of the Litani River, continuing to fire at the Israelis.
Outcome of the war
In response to the invasion, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 425 and Resolution 426 calling for the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Lebanon. The UN Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) was created to enforce this mandate, and restore peace and sovereignty to Lebanon. UNIFIL forces arrived in Lebanon on 23 March 1978, setting up headquarters in Naqoura.
Israeli forces withdrew later in 1978, turning over positions inside Lebanon to their ally, the South Lebanon Army (SLA) militia under the leadership of Maj. Saad Haddad. On 19 April 1978, the SLA shelled UNIFIL headquarters, killing 8 UN soldiers. (Fisk, 138). In April 1980, three Irish UN soldiers Privates Barrett, Smallhorne and O'Mahoney were kidnapped and two of them murdered by Christian gunmen, Private O'Mahoney survived (being shot by sub-machine gun during the incident) in SLA territory and another Irish soldier Private S. Griffen was shot by Haddad's men, and was medivaced to Israel where he subsequently died during medical treatment. The Israeli press at the time, particularly the Jerusalem Post, accused the Irish of pro-PLO bias. (Fisk, 152–154). However, Palestinian factions also attacked UNIFIL, kidnapping an Irish UNIFIL soldier in 1981 and continuing to occupy areas in southern Lebanon.[5]
Hostilities continued, and as the Lebanese civil war escalated, the fighting intensified in the south again, with a second Israeli invasion in 1982 resulting in a 1982 flare-up that persisted over the next decade.
Main articles: 1982 Lebanon War and South Lebanon conflict (1982–2000)Resolution 425
In 2000, the UN Security Council concluded that, as of 16 June 2000, Israel had withdrawn its forces from Lebanon in accordance with Resolution 425.[6]
Lebanon has not extended control over south Lebanon, though it was called on to do so by UN Resolution 1391 of 2002 and urged by UN Resolution 1496. Israel has lodged multiple complaints regarding Lebanon's conduct.[7]
Lebanon's claim that Israel has not fully withdrawn (see Shebaa Farms) was explicitly rejected by the UN's Secretary-General's report which led to UN Security Council Resolution 1583. The Syrian occupation of Lebanon led to UN Security Council Resolution 1559 demanding the remaining 14,000 (of 50,000 originally) Syrian troop withdrawal and the dismantling of Hezbollah and Palestinian militias. On April 26, 2005, after 29 years of Syrian military presence in Lebanon, the last of the Syrian troops withdrew in accordance with the resolution.
See also
- History of Lebanon
- Lebanese Civil War
- 1982 Lebanon War
- Israel-Lebanon conflict
- Israeli casualties of war
References
- ^ a b Chomsky. 1983 p.191
- ^ Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Statement to the press by Prime Minister Begin on the massacre of Israelis on the Haifa-Tel Aviv Road. Historical Documents Archive: 12 March 1978.
- ^ a b Chomsky, Noam (1983). The Fatefull Triangle. South End Press. ISBN 0-89608-187-7. p.192
- ^ Mor, Ben D.; Zeev Moaz (2002). "7". Bound by Struggle: The Strategic Evolution of Enduring International Rivalries. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-472-11274-6.
- ^ Private Kevin Joyce was kidnapped and is presumed dead. See Guardian article here 20-year hunt for kidnapped Irish soldier almost over | UK news | The Observer
- ^ SECURITY COUNCIL ENDORSES SECRETARY-GENERAL’S CONCLUSION ON ISRAELI WITHDRAWAL FROM LEBANON AS OF 16 JUNE
- ^ http://domino.un.org/UNISPAL.NSF/22f431edb91c6f548525678a0051be1d/bb095796d02d589785256b910058cc00!OpenDocument
Further reading
- Bregman, Ahron (2002). Israel's Wars: A History Since 1947. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-28716-6.
- Cobban, Helena (1984). The Palestinian Liberation Organization: People, Power and Politics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27216-2.
- Fisk, Robert (2002). Pity the Nation: The Abduction of Lebanon. Nation Books. ISBN 978-1-56025-442-3.
- Shlaim, Avi (2001). The Iron Wall: Israel and the Arab World. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-32112-8.
- Bregman, Ahron (2002). Israel's Wars. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-28716-2.
External links
- Operation Litani, ALS.Miniature
- Lebanese civil war 1978 Full of Pictures and Information
- Terrorist attacks in Israel, GlobalSecurity
- Conflict in Lebanon, GlobalSecurity
- www.lebanon-israel.info An ongoing discussion on the Lebanon-Israel conflict
Categories:- Conflicts in 1978
- Wars involving Israel
- Wars involving Lebanon
- Israel–Lebanon conflict
- Invasions
- 1978 in Israel
- 1978 in Lebanon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.