- Manhattan, Kansas
-
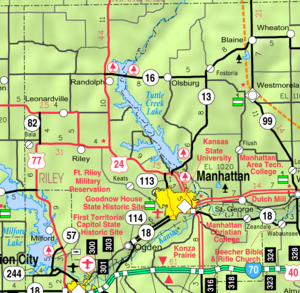
Manhattan, Kansas — City — Riley County Courthouse, 2005 Nickname(s): The Little Apple Location within Kansas Coordinates: 39°11′30″N 96°35′30″W / 39.19167°N 96.59167°WCoordinates: 39°11′30″N 96°35′30″W / 39.19167°N 96.59167°W Country United States State Kansas Counties Riley, Pottawatomie Settled 1855 Incorporated May 30, 1857 Government – Type Commission-Manager – Mayor Jim Sherow – Commissioner Rich Jankovich – Commissioner Wynn Butler – Commissioner Loren Pepperd – Commissioner John Matta Area – City 15.0 sq mi (38.9 km2) – Land 15.0 sq mi (38.9 km2) – Water 0.0 sq mi (0.0 km2) – Metro 1,888 sq mi (4,889 km2) Elevation 1,020 ft (311 m) Population (2010)[1] – City 52,281 – Density 3,485.4/sq mi (1,345.7/km2) Time zone CST (UTC-6) – Summer (DST) CDT (UTC-5) ZIP codes 66502–66503, 66505-66506 Area code(s) 785 FIPS code 20-44250[2] GNIS feature ID 0476378[3] Website www.ci.manhattan.ks.us Manhattan is a city located in the northeastern part of the state of Kansas in the United States, at the junction of the Kansas River and Big Blue River. It is the county seat[4] of Riley County and the city extends into Pottawatomie County. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 52,281.[1] It is the principal city of the Manhattan, Kansas Metropolitan Statistical Area – with an estimated population of 113,629, the Manhattan MSA is the fourth largest metropolitan area in the state.[5]
Nicknamed The Little Apple in 1977 as a play on New York City's "Big Apple", it is best known for being the home of Kansas State University and has a distinct college town feel. Eight miles (13 km) west of the city is Fort Riley, a United States Army post.
In 2007, CNN and Money magazine rated Manhattan as one of the ten best places in America to retire young.[6] The town was named an All-American City in 1952, becoming the first city in Kansas to win the award. In 2011, Forbes Magazine rated Manhattan No. 1 for "Best Small Communities for a Business and Career."[7]
Contents
History
Polistra and Canton
The Kansas-Nebraska Act opened the territory to settlement in 1854. That fall, George S. Park founded the first Euro-American settlement within the borders of the current Manhattan. Park named it Polistra (some historians refer to it as Poliska or Poleska).[8]
Later that same year, Samuel D. Houston and four other pioneers founded a neighboring community near the mouth of the Big Blue River that they named Canton.[9] Neither Canton nor Polistra ever grew to include anyone beyond their original founders.
Free-Staters
In March 1855, a group of New England Free-Staters traveled to Kansas Territory under the auspices of the New England Emigrant Aid Company to found a Free-State town. Led by Isaac Goodnow, the first members of the group (with the help of Samuel C. Pomeroy) selected the location of the Polistra and Canton claims for the Aid Company's new settlement. Soon after the New Englanders arrived at the site, in April 1855, they agreed to join together with Canton and Polistra to make one settlement named Boston.[8] They were soon joined by dozens more New Englanders, including Goodnow's brother-in-law Joseph Denison.
In June 1855, the paddle steamer Hartford, carrying 75 settlers from Ohio, ran aground in the Kansas River near the settlement. The Ohio settlers, who were members of the Cincinnati-Manhattan Company, had been headed twenty miles (32 km) further upstream to the headwaters of the Kansas River, the location today of Junction City.[10] After realizing they were stranded, the Hartford passengers accepted an invitation to join the new town, but insisted that it be renamed Manhattan, which was done on June 29, 1855. Manhattan was incorporated on May 30, 1857.[8]
Early events
Early Manhattan settlers sometimes found themselves in conflict with Native Americans and the town itself was threatened by pro-slavery Southerners, but the proximity of Fort Riley protected the settlement from the major violence visited upon other Free-State towns during the "Bleeding Kansas" era.
The young city received an early boost when gold was discovered in the Rocky Mountains in 1859 and Fifty-Niners began to stream through Manhattan on their way to prospect in the mountains. Manhattan was one of the last significant settlements on the route west, and the village's merchants did a brisk business selling supplies to miners.
At the same time, Manhattan was fast becoming a center of education. In 1858, the Territorial Legislature chartered a Methodist college in Manhattan, named Blue Mont Central College. In 1861, when the State of Kansas entered the Union, Isaac Goodnow, who had been a teacher in Rhode Island, began lobbying the legislature to convert Blue Mont Central College into the state university. The culmination of these efforts came on February 16, 1863, when the Kansas legislature established Kansas State Agricultural College (now Kansas State University) in Manhattan.
By the time the Kansas Pacific Railroad laid its tracks west through Manhattan in 1866, the 11-year-old settlement was permanently ensconced in the tallgrass prairie. Manhattan has steadily increased in population every decade since its founding.
Geography
Manhattan is located at 39°11′25″N 96°35′13″W / 39.19028°N 96.58694°W (39.190142, −96.586818),[11] or about 50 miles (80 km) west of Topeka on the Kansas River.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 15.0 square miles (38.9 km²), 0.07% of it water.
Geographic features
Manhattan is located in the Flint Hills region of Kansas, which consists of continuous rolling hills covered in tall grasses. However, the current downtown area – the original site of Manhattan – was built on a broad, flat floodplain at the junction of the Kansas and Big Blue rivers.
Tuttle Creek Reservoir is located 5 miles (8 km) north of Manhattan. The lake was formed when the Big Blue River was dammed for flood control in the 1960s, and it is now a state park that offers many recreational opportunities. South of the city is the Konza Prairie, a tallgrass prairie preserve jointly owned by The Nature Conservancy and Kansas State University.
Earthquakes
- See 1867 Manhattan, Kansas earthquake
Kansas is not known for earthquake activity, but Manhattan is near the Nemaha Ridge, a long structure that is bounded by several faults, and which is still active.[12] In particular, the Humboldt Fault Zone lies just 12 miles (19 km) eastward of Tuttle Creek Reservoir.
On April 24, 1867, the 1867 Manhattan earthquake struck Riley County. Measuring 5.1 on the Richter scale, the earthquake's epicenter was by Manhattan. To this day, it remains the strongest earthquake to originate in Kansas. The earthquake had an intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale, and was felt over an area of roughly 193,051 square miles (500,000 km2). It caused largely minor damage, reports of which were confined to Kansas, Iowa, and Missouri, according to the United States Geological Survey.
Despite the fact that Kansas is not seismically active, a strong earthquake could pose significant threats to the state. If an earthquake had occurred along the Nemaha Ridge prior to 2010, it could have destroyed the dam on Tuttle Creek Reservoir, releasing 300,000 feet (91,440 m) of water per second and flooding the nearby area, threatening roughly 13,000 people and 5,900 homes. A study in the 1980s found that a moderate earthquake "between 5.7 to 6.6 would cause sand underneath the dam to liquefy into quicksand, causing the dam to spread out and the top to drop up to three feet."[13] To address this threat, the Army Corps of Engineers completed a project in July 2010 that replaced the sand with more than 350 concrete walls and equipped the dam with sensors. Alarms are connected to these sensors, which would alert nearby citizens to the earthquake.[13]
Climate
Over the course of a year, temperatures range from an average low of almost 15 °F (−9 °C) in January to an average high of nearly 93 °F (34 °C) in July. The maximum temperature reaches 90 °F (32 °C) an average of 56 days per year and reaches 100 °F (38 °C) an average of 9 days per year. The minimum temperature falls below the freezing point (32 °F) an average of 118 days per year. Typically the first fall freeze occurs between the last week of September and the end of October, and the last spring freeze occurs between the first week of April and early May.
The area receives nearly 35 inches (890 mm) of precipitation during an average year with the largest share being received in May and June—the April–June period averages 33 days of measurable precipitation. During a typical year the total amount of precipitation may be anywhere from 24 to 46 inches (1,200 mm). There are on average 97 days of measurable precipitation per year. Winter snowfall averages almost 16 inches, but the median is less than 10 inches (250 mm). Measurable snowfall occurs an average of 10 days per year with at least an inch of snow being received on six of those days. Snow depth of at least an inch occurs an average of 20 days per year.
Source: Monthly Station Climate Summaries, 1971–2000, U.S. National Climatic Data Center Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Temperatures (°F) Mean high 39.5 46.8 57.5 67.9 77.5 87.1 92.5 90.8 82.1 70.7 54.5 42.9 67.5 Mean low 16.1 21.5 31.4 42.2 52.5 62.3 67.3 65.1 55.5 43.2 30.2 19.9 42.3 Highest recorded 74
(1939)84
(1972)95
(1907)99
(1910)103
(1934)112
(1911)115
(1936)116
(1936)112
(1947)98
(1947)87
(1909)77
(1939)116
(1936)Lowest recorded −31
(1947)−26
(1905)−12
(1948)5
(1920)23
(1907)39
(1946)38
(1902)40
(1916)26
(1995)13
(1993)−9
(1952)−22
(1989)−31
(1947)Precipitation (inches) Median 0.79 0.92 2.11 2.22 4.53 4.62 3.20 2.93 3.28 2.38 1.51 0.85 34.34 Mean number of days 5.4 5.2 7.9 10.0 12.0 10.9 8.6 9.2 8.1 7.7 7.0 5.2 97.2 Highest monthly 3.16
(1979)2.48
(1997)7.40
(1973)9.52
(1999)14.73
(1995)11.55
(1977)17.56
(1993)7.25
(1977)9.89
(1973)6.49
(1973)5.79
(1998)3.40
(1973)Snowfall (inches) Median 3.7 3.2 0.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.1 1.7 9.5 Mean number of days 4.5 3.2 1.7 0.6 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.5 3.5 15.0 Highest monthly 16.2
(1985)18.5
(1978)9.0
(1998)4.8
(1975)0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.1
(1991)8.8
(1975)14.6
(1983)Notes: Temperatures are in degrees Fahrenheit. Precipitation includes rain and melted snow or sleet in inches; median values are provided for precipitation and snowfall because mean averages may be misleading. Mean and median values are for the 30-year period 1971–2000; temperature extremes are for the station's period of record (1900–2001). The station is located in Manhattan at 39°13′N 96°36′W, elevation 1,065 feet (325 m). Tornadoes
The state of Kansas falls within an area sometimes called Tornado Alley. The most recent tornado in Manhattan touched down at approximately 10:30 pm on June 11, 2008. Thirty-one homes and several businesses were destroyed by the EF4 tornado. Additionally, Kansas State University's campus incurred about $20 million in damage – a number of university buildings sustained significant damage and the Wind Erosion Laboratory's garage was destroyed by the tornado's winds.[14] No one was killed.[15]
Previously, the most destructive tornado to hit Manhattan was on June 8, 1966. The 1966 tornado caused $5 million in damage and injured at least 65 people in Manhattan.[16][17]
Flooding
Manhattan was built on a floodplain at the junction of the Kansas and Big Blue rivers, and it has faced recurring problems with flooding during times of heavy precipitation. The largest floods in the town's history were the 1903 and 1908 floods, the Great Flood of 1951 and the Great Flood of 1993.[18][19]
Politics
Local
Manhattan is governed under a council-manager system, with a City Commission consisting of five members. Elections are nonpartisan and are held every other year, in odd-numbered years. Three City Commission positions are chosen in each election. The two highest vote recipients receive four-year terms, while the third highest vote recipient receives a two-year term. The highest vote winner in a general election is established to serve as mayor on the third year of a four-year term. The Mayor presides over Commission meetings, but has the same voting rights as other Commissioners and no veto power.
As of 2011, James (Jim) E. Sherow serves as the city's mayor, while Wynn Butler, Richard (Rich) B. Jankovich, John Matta, and Loren J. Pepperd make up the rest of the City Commission.[20]
State
Manhattan is located inside a number of State district boundaries. Most of Manhattan falls within two districts for the Kansas House of Representatives. Currently, both representatives are registered Democrats and have served multiple terms in the House. Representative Dr. Susan Mosier serves in District 67, which includes portions of south, west, and northern Riley County. Representative Sydney Carlin is the current representative of District 66, which includes most of downtown Manhattan, and the northeastern portions of the city. Small portions of Manhattan extend into other districts to the south and north.
Manhattan is included in the Kansas Senate District 22, and the state senator is Republican Dr. Roger Reitz. District 22 also includes nearby Junction City and rural Riley and Geary counties.
Federal
Manhattan is located in Kansas's 2nd congressional district, which is represented by Republican Lynn Jenkins. For federal elections, precise breakdowns are unavailable for only Manhattan, but a majority of voters in Riley County have never supported a Democratic candidate for President. Republicans have carried Riley County every presidential election, except for 1912, when a majority of the county's voters supported the Progressive candidate Theodore Roosevelt.[21]
Demographics
Historical populations Census Pop. %± 1870 1,173 — 1880 2,105 79.5% 1890 3,004 42.7% 1900 3,438 14.4% 1910 5,722 66.4% 1920 7,989 39.6% 1930 10,136 26.9% 1940 11,659 15.0% 1950 19,056 63.4% 1960 22,993 20.7% 1970 27,575 19.9% 1980 32,644 18.4% 1990 37,712 15.5% 2000 44,831 18.9% 2010 52,281 16.6% U.S. Decennial Census As of the census[2] of 2000, there were 44,831 people, 16,949 households, and 8,254 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,983.9 people per square mile (1,152.4/km²). There were 17,690 housing units at an average density of 1,177.4 per square mile (454.7/km²). The racial makeup of the city was 87.28% White, 4.86% African American, 0.48% Native American, 3.93% Asian, 0.07% Pacific Islander, 1.30% from other races, and 2.07% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.49% of the population.
There were 16,949 households out of which 22.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 39.6% were married couples living together, 6.6% had a female householder with no husband present, and 51.3% were non-families. 30.5% of all households were made up of individuals and 6.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.30 and the average family size was 2.89.
In the city the population was spread out with 15.8% under the age of 18, 39.2% from 18 to 24, 24.0% from 25 to 44, 13.2% from 45 to 64, and 7.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 24 years. For every 100 females there were 106.4 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 105.4 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $30,463, and the median income for a family was $48,289. Males had a median income of $31,396 versus $24,611 for females. The per capita income for the city was $16,566. About 8.7% of families and 24.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.1% of those under age 18 and 7.8% of those age 65 or over. However, traditional measures of income and poverty can be misleading when applied to cities with high student populations, such as Manhattan.
Sites of interest
Manhattan is the site of Kansas State University sporting events, Aggieville, performing arts, lecture series and the annual Country Stampede Music Festival – the largest music festival in Kansas.
The Marianna Kistler Beach Museum of Art[1] and the Kansas State University Gardens are located on the campus of Kansas State University. Next to campus is Aggieville, a shopping and retail center with enough bars to satisfy the college crowd. Aggieville is also home to the longest continuously-operating Pizza Hut restaurant in the world.
Manhattan's Sunset Zoo is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA). Colbert Hills Golf Course, which is annually ranked by Golf Digest among the best in the state, is home to the Earl Woods National Youth Golf Academy and a host site for the First Tee program. Manhattan is also the birthplace of Damon Runyon, the "Inventor of Broadway," and his Manhattan house is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
The buildings which house The Flint Hills Job Corps Training Center west of the city were once used as a nursing home and orphanage operated by the Fraternal Order of Odd Fellows.
The first capitol of the Kansas Territory is preserved nearby, on Fort Riley grounds. The Fort Riley military base covers 100,656 acres (407.34 km2) between Manhattan and Junction City, KS. Since 2006 it has, once again, become home to the Big Red One, the 1st Infantry Division of the United States.
Economy
Manhattan's economy is heavily based on governmentally-funded entities. Kansas State University is the largest employer in town, and its 23,000 students support the retail and entertainment venues in the city.[22] The second-largest employer in Manhattan is the city school district.[22] Additionally, nearby Fort Riley also brings in lots of retail business, although the majority of soldiers live either on post or in closer Junction City or Ogden.
Other large employers in Manhattan include the Mercy Regional Health Center and Farm Bureau.[22] Manhattan also supports a small industrial base. Manufacturing and commercial businesses include: GTM Sportswear,[23] Florence Manufacturing,[24] ICE Corporation,[25] Manko Windows,[26] The McCall Pattern Company and Farrar Corporation.[27] Some, like GTM and Farrar[28] have had success in the city – as college towns are known to outlive and sustain economic recessions better than most towns due to their economic base[29]
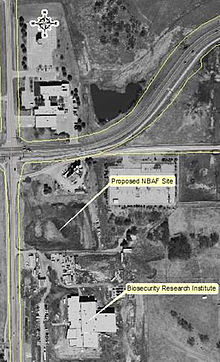
In 2009, the United States Department of Homeland Security announced that it would locate the National Bio and Agro-Defense Facility (NBAF) in Manhattan, with construction scheduled to begin in 2010. The NBAF is scheduled to open in 2014, and will be a federal lab to research biological threats involving human, zoonotic (i.e., transmitted from animals to humans) and foreign animal diseases. It is expected to employ between 250–350 people, including researchers, technical support and operations specialists.[30]
Education
Kansas State University is the largest employer and educator in the city of Manhattan with 23,520 students.[31] KSU is home to Wildcat sports, as well as a host to nationally recognized academics. Kansas State University has ranked first nationally among state universities in its total of Rhodes, Marshall, Truman, Goldwater, and Udall scholars since 1986.[32] Manhattanites are said to "Bleed purple" due to their pride in Kansas State athletics.
Manhattan is also home to Manhattan Christian College, Manhattan Area Technical College, the American Institute of Baking and The Flint Hills Job Corps Training Center, and the Kansas Building Science Institute.
Manhattan is served by USD 383 Manhattan-Ogden and has one public high school with two campuses (Manhattan High School), two middle schools (Susan B. Anthony and Dwight D. Eisenhower), and eight elementary schools (Amanda Arnold, Frank V. Bergman, Bluemont, Lee, Marlatt, Northview, Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson). The city also has two private school systems: Flint Hills Christian School and the Manhattan Catholic Schools. Manhattan Catholic Schools contains two buildings, the grade school building (K-5)and the Luckey Jr. High building (6–8), formerly called the Luckey high building dedicated to Monsignor Luckey. The school's mascot is "Luckey the Cardinal".
Culture
Culture in the city of Manhattan is largely defined by Kansas State University students. The city is normally full of activity while school is in session. Due to the city's vitality, the city was rated by CNN Money as one of the top ten places to retire young.[6] There are a number of cultural hot spots around the city that make it as vibrant as it is.
- Aggieville – Aggieville is the hub of Manhattan's nightlife. Due to its large number of bars and shops, the district is frequented by college students and citizens alike. Aggieville's bars play host to numerous bands on a nightly basis. Nearby, the Marianna Kistler Beach Museum of Art on the K-State campus is home to KSU's permanent art collection and traveling art exhibits. Entry to the museum is free of charge. Kansas State's McCain Auditorium, which draws major performances and tours from across the globe, is also located near Aggieville.
- Downtown – Downtown Manhattan, and the Manhattan Town Center Mall, is an anchor for shopping and entertainment in the eastern portions of Manhattan. Art galleries, fine dining options, and shopping are all major daytime draws to the area. The Manhattan Town Center Mall was built in the late 1980s and is located in the heart of downtown.
- Kansas State Sports – Bill Snyder Family Football Stadium, Bramlage Coliseum, and other sports venues relating to the university host events every week in their respective sports seasons, drawing fans from across the country. The facilities are sometimes used for lectures, concerts, and other non-sporting events.
There are also a number of events and conventions held every year, such as Juneteenth Celebration, the Country Stampede Music Festival and the Great Manhattan Mystery Conclave.
Transportation
Manhattan is served by numerous transportation methods.
Airports
Manhattan Regional Airport is located 4 kilometres (2 mi) west of Manhattan on K-18. The airport is served by American Eagle, which offers daily flights to Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport and to Chicago's O'Hare International Airport. The nearest major commercial airports are in Kansas City (MCI) and Wichita, Kansas (ICT).
Rail
A mainline of the Union Pacific Railroad passes through the city, which originally was the Kansas Pacific Railroad. Domestic passenger rail service was discontinued after the Amtrak takeover of passenger rail in 1971.
The Rock Island Railroad formerly served Manhattan as a stop on Rock Island's Kansas City–Colorado Springs Rocky Mountain Rocket service.[33] The Rock Island depot was located between Fifth and Sixth streets, along former El Paso Street (now Fort Riley Boulevard). The former railroad right-of-way was converted to Manhattan's southern arterial road as well as a rail-trail, linear park along Manhattan's west side.
Buses
Inter-city bus service, previously provided by Greyhound Lines, was discontinued years ago. However, Arrow Stage Line operates charter service out of local facilities on McCall Road. Also, KCI Roadrunner provides charter service as well as scheduled shuttle service to and from Kansas City International Airport (KCI), Lawrence, Topeka, Junction City, Ft. Riley, and Manhattan.
Within the City of Manhattan, limited mass-transit is provided by Riley County's subsidized paratransit service, ATA Bus. ATA Bus recently started its first set-route bus route in Manhattan connecting an apartment complex and an office campus, and is currently working with the city to develop a feasible mass-transit system. ATA uses four small buses and a number of minivans in its fleet.[34] Five twenty-passenger transit buses have been purchased for fixed-route service and the agency is awaiting operational funding from Kansas State University and the City.
Highways
Manhattan is served by several highways:
 Interstate 70 runs about 9 miles (14 km) south of Manhattan. Three exits have a direct connection to Manhattan.
Interstate 70 runs about 9 miles (14 km) south of Manhattan. Three exits have a direct connection to Manhattan.
 U.S. Route 24 runs through Manhattan. East on 24 is Wamego, west is Clay Center. US-24 comes in from Clay Center, runs north of the city, turns into a four-lane highway near Tuttle Creek State Park and travels downtown as Tuttle Creek Boulevard until an intersection with Poyntz Avenue and turns northeast towards Wamego.
U.S. Route 24 runs through Manhattan. East on 24 is Wamego, west is Clay Center. US-24 comes in from Clay Center, runs north of the city, turns into a four-lane highway near Tuttle Creek State Park and travels downtown as Tuttle Creek Boulevard until an intersection with Poyntz Avenue and turns northeast towards Wamego. K-177 runs north from I-70 as Bill Snyder Highway until the Kansas River viaduct. A half-leaf interchange with K-18 (Tuttle Creek Blvd. and Ft. Riley Blvd.) and travels north as US-24. It officially ends at the intersection with U.S. Route 77 near Randolph.
K-177 runs north from I-70 as Bill Snyder Highway until the Kansas River viaduct. A half-leaf interchange with K-18 (Tuttle Creek Blvd. and Ft. Riley Blvd.) and travels north as US-24. It officially ends at the intersection with U.S. Route 77 near Randolph. K-18 is a major connector in Manhattan. It begins about 18 miles (29 km) east of Manhattan, at K-99. It runs through Wabaunsee and Zeandale to K-177, crosses to Kansas River, and runs west toward the Manhattan Regional Airport and Ogden. It then travels south to I-70 as a major gateway to Manhattan.
K-18 is a major connector in Manhattan. It begins about 18 miles (29 km) east of Manhattan, at K-99. It runs through Wabaunsee and Zeandale to K-177, crosses to Kansas River, and runs west toward the Manhattan Regional Airport and Ogden. It then travels south to I-70 as a major gateway to Manhattan. K-113 (Seth Child Road) runs from K-18 in southern Manhattan to US-24, passing through the western areas of the City.
K-113 (Seth Child Road) runs from K-18 in southern Manhattan to US-24, passing through the western areas of the City.
Historically, Manhattan was located on the national Victory Highway, one of the original 1920s auto trails. With the creation of the numbered federal highway system in 1926, the highway became U.S. Route 40.
From 1926 to 1935, Route 40 diverged west of Manhattan into "40N" and "40S" routes; the two routes met again in Limon, Colorado.[35]
Media
Print
- The Kansas State Collegian, daily
- The Manhattan Free Press, weekly
- The Manhattan Mercury, daily[36]
Radio
The following radio stations are licensed to and/or broadcast from Manhattan:
AM
Frequency Callsign[37] Format[38] City of License Notes 1350 KMAN News/Talk Manhattan, Kansas - FM
Frequency Callsign[39] Format[38] City of License Notes 88.9 KGLV Contemporary Christian Manhattan, Kansas K-LOVE[40] 90.7 K214CZ Religious Manhattan, Kansas Translator of WPCS, Pensacola, Florida[41] 91.9 KSDB-FM Adult Album Alternative Manhattan, Kansas K-State college radio[42] 96.3 KACZ Top 40 Riley, Kansas Broadcasts from Manhattan[43] 97.9 K250AY Public Manhattan, Kansas NPR; Translator of KANU, Lawrence, Kansas[44] 99.5 K258BT Public Manhattan, Kansas NPR; Translator of KANU, Lawrence, Kansas[45] 101.5 KMKF Rock Manhattan, Kansas - 102.5 KBLS Adult Contemporary Fort Riley North, Kansas Broadcasts from Manhattan[46] 104.7 KXBZ Country Manhattan, Kansas - 105.5 KRMI-LP Religious Manhattan, Kansas - 106.1 K291BA Religious Manhattan, Kansas Translator of KCCV-FM, Overland Park, Kansas[47] Television
Manhattan is in the Topeka, Kansas television market.[48] The following television stations are licensed to and/or broadcast from Manhattan:
Digital Channel Digital Subchannel Analog Channel Callsign[49] Network City of License Notes - - 21 KKSU-LP - Manhattan, Kansas K-State television[50] 36 36.1 32 K36IO-D LegacyTV[51] Manhattan, Kansas - - - 35 K38GZ - Manhattan, Kansas - Notable people
- Bob Anderson – founder of Runner's World
- John Byers Anderson – military officer, businessman
- Elizabeth Williams Champney – author
- Louis Chaudet – film director, writer
- Del Close – comedian
- Jim Colbert – professional golfer
- Bobby Douglass – former National Football League player
- Brian Doyle-Murray – actor, scriptwriter[52]
- David Fairchild – botanist, explorer
- Philip Fox – astronomer
- Brian Giles – former Major League Baseball player
- James Harbord – military officer, businessman
- Jonathan Holden – first Poet Laureate of Kansas
- Richard Alonzo Jaccard – United States Navy pilot
- Lee Killough – author
- Albert E. Mead – fifth governor of Washington
- Benjamin Franklin Mudge – geologist
- Mitsugi Ohno – glassblower
- Cassandra Peterson – actress, model
- Merrill D. Peterson – historian
- Vince Rafferty – NFL player
- Deb Richard – professional golfer
- Damon Runyon – author
- Fred Andrew Seaton – former Senator for Nebraska, and Secretary of the Interior
- Bill Snyder – NCAA football head coach for Kansas State University
- Gary Spani – NFL Hall of Famer
- Walter J. Stoessel – diplomat
- Samuel Wendell Williston – scientist
- Robert A. Woodruff – space instrumentation scientist
- Earl Woods – father of Tiger Woods
- Eric Stonestreet – actor, ABCs Modern Family
- Jordy Nelson Riley Kansas – NFL football player, KSU Alumni
Twin or partner cities
 Dobřichovice, Czech Republic (since 2004)
Dobřichovice, Czech Republic (since 2004)
- In August 2004 the Manhattan City Commission approved a resolution establishing an advisory committee to explore and foster a formal partnership with an international city. In 2005, following a lengthy planning effort guided by Dr. Joseph Barton-Dobenin, a Czech native and now-retired professor at Kansas State University then-Commissioner Ed Klimek visited Dobřichovice, Czech Republic, to initiate a partnership with that city. Following Mr. Klimek’s visit, a number of local elected officials and other members of the community of Dobřichovice visited Manhattan to continue the effort towards establishing the formal relationship. In 2006, the Committee recommended and the City Commission chose the City of Dobřichovice as its partner city, and in April of that year then-Mayor Ed Klimek signed the Partner Cities Agreement, declaring that the two cities would thereafter engage each other in sharing cultural, educational, youth and civic understanding, and friendship, and further endeavor to promote and strengthen the peace among the two cities, their homelands, and the global community.
- Since its inception, Committee members and friends of the Committee have been continuously engaged in cultural and civic exchanges with their counterparts in Dobřichovice. Since the Dobřichovice delegation’s visit to Manhattan in 2005, a number of local elected officials and community members have traveled from Manhattan to Dobřichovice in the interest of continuing and strengthening this partnership.A delegation from Dobřichovice is expected to return to Manhattan in the upcoming years.The partnership has also benefited from the international student exchange program at Kansas State University, which has been successful in recruiting students from the Czech Republic.
In popular culture
- The eponymous character in Raymond Chandler's 1949 novel The Little Sister is from Manhattan.
- Kenneth S. Davis's 1951 novel Morning in Kansas is set in Manhattan (called New Boston in the book).
- In 1972, Glen Campbell recorded a No. 6 hit on the Country Music Charts with his song "Manhattan, Kansas."
- The 1975 documentary film Banjoman captures a concert held in Manhattan on January 23, 1973, to honor Earl Scruggs. The concert included performances by Joan Baez, David Bromberg, The Byrds, Ramblin' Jack Elliott, The Nitty Gritty Dirt Band, and Doc and Merle Watson.[53]
- Manhattan features in Vernor Vinge's 1985 science-fiction novella The Ungoverned.
- The main character in Sydney Sheldon's 1987 novel Windmills of the Gods starts out as a professor at Kansas State University in Manhattan.
- Manhattan is a principal setting for the 1992 novel Was, by Geoff Ryman, a contemporary examination of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz.
- W.E.B. Griffin mentions Manhattan as the hometown of a main character[who?] in his Brotherhood of War (novel series).
- The plot of the failed 1993 CBS television pilot The Elvira Show revolves around two witches, played by Elvira and Katherine Helmond, moving to Manhattan with their talking cat.[54]
- The opening scene for the trailer to the 2004 film Friday Night Lights is Poyntz Avenue in downtown Manhattan; this was stock footage purchased for the trailer.[55][56]
- The 2006 documentary film Manhattan, Kansas by Tara Wray is about her mentally unstable mother.[57]
See also
- Johnny Kaw – fictional Paul Bunyanesque character
- Freedom's Frontier National Heritage Area
- Great Flood of 1951
References
- ^ a b "2010 City Population and Housing Occupancy Status". U.S. Census Bureau. http://factfinder2.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=DEC_10_PL_GCTPL2.ST13&prodType=table. Retrieved March 6, 2011.
- ^ a b "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "US Board on Geographic Names". United States Geological Survey. 2007-10-25. http://geonames.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. http://www.naco.org/Counties/Pages/FindACounty.aspx. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ^ "Update of Statistical Area Definitions and Guidance on Their Uses (OMB Bulletin 09-01)" (CSV). Office of Management and Budget, Executive Office of the President. 2008-11-20. http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/bulletins/fy2009/09-01.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ a b "Best Places to Retire Young". CNN. http://money.cnn.com/galleries/2007/moneymag/0703/gallery.bp_retireyoung_new.moneymag/9.html. Retrieved 2007-10-02.
- ^ Badenhausen, Kurt. "Slide Show: The Best Small Places For Business And Careers". Forbes. http://www.forbes.com/2011/06/27/best-places-11-small_slide_2.html.
- ^ a b c Parrish, Donald (2004). This Land is Our Land: The Public Domain in the Vicinity of Riley County and Manhattan, Kansas. Riley County Historical Society. ISBN 0-9677686-2-4. OCLC 54769277.
- ^ Streeter, Floyd Benjamin (1975). The Kaw: The Heart of a Nation. New York: Arno Press. ISBN 9780405068898. OCLC 2180188. http://books.google.com/?id=MZEJR647HyIC.
- ^ GEARY COUNTY LEGENDS – jcks.com – Retrieved March 9, 2009
- ^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/gazetteer/gazette.html. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ^ Merriam, Daniel F. (April 1956). "History of earthquakes in Kansas". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 46 (2): 87–96.
- ^ a b Metz, Christine (May 2, 2008). "Earthquakes in Kansas a real threat". Lawrence Journal-World. http://www2.ljworld.com/news/2008/may/02/shaking_kansas/. Retrieved February 11, 2010.
- ^ Wichita Eagle-Beacon Tornadoes rip Manhattan, KSU damage more than $20 million
- ^ Hanna, John (2008-06-13). "Kansas residents assess damage after deadly twisters". Associated Press. http://ap.google.com/article/ALeqM5gvHC7Zr5kiY-lOpqndPZvOVefx8QD919534O2. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ "City Officials set Damage at $5 Million". Topeka Capital-Journal. 1966-06-10. http://www.cjonline.com/indepth/66tornado/stories/com_damageestimate.shtml. Retrieved 2008-08-13.
- ^ NOAA's National Weather Service. "The Topeka Tornado – June 8, 1966". http://www.crh.noaa.gov/top/events/66tornado.php. Retrieved 2008-08-13
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey. "The 1903 and 1993 Floods in Kansas". http://ks.water.usgs.gov/pubs/fact-sheets/fs.019-03.pdf. Retrieved 2008-12-06
- ^ Davis, Kenneth (1953). River on the Rampage. Doubleday.
- ^ "Meet the City Commission". City of Manhattan. http://www.ci.manhattan.ks.us/index.aspx?NID=219. Retrieved 2011-06-26.
- ^ http://geoelections.free.fr/USA/elec_comtes/1912.htm
- ^ a b c "General Statistical Information Concerning the City of Manhattan, Kansas" (pdf). http://www.ci.manhattan.ks.us/DocumentView.asp?DID=3597. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- ^ NationJob GTM Sportswear Retrieved on 2009-04-02
- ^ Auth-Florence Auth-Florence brings 250 job plant to Manhattan Retrieved on 2009-04-02
- ^ ICE Corporation ICE Retrieved on 2009-04-02
- ^ "About", Manko Windows, Retrieved on 2009-04-09
- ^ Farrar USA Farrar Retrieved on 2009-04-02
- ^ Farrar Corporation ...Future plans for the site include the construction of a foundry and heat treating facilities within the next 10 years Retrieved on 2009-04-02
- ^ USA Today College towns do OK in recession Retrieved on 2010-02-28
- ^ "Facility Research & Staffing for the NBAF" (English). U.S. Department of Homeland Security. http://www.dhs.gov/xres/labs/gc_1181073261627.shtm. Retrieved 2000-04-08.
- ^ "K-State media guide – Enrollment numbers 1990–current" (English). http://www.k-state.edu/media/mediaguide/enrollment.html. Retrieved 2009-03-30.
- ^ "Achivements" Kansas State University, Retrieved on 2009-04-20
- ^ http://www.streamlinerschedules.com/concourse/track8/rockymtrocket194106.html "Rocky Mountain Rocket" Schedule, Retrieved 15-3-11
- ^ "ATA Bus" Riley County, Kansas, Retrieved on 2009-04-08
- ^ Weingroff, Richard. "From Names to Numbers: The Origins of the U.S. Numbered Highway System". Federal Highway Administration. http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/infrastructure/numbers.cfm. Retrieved 2011-05-18
- ^ "About this Newspaper: The Manhattan mercury". Chronicling America. Library of Congress. http://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn85031900/. Retrieved 2009-09-20.
- ^ "AMQ AM Radio Database Query". Federal Communications Commission. http://www.fcc.gov/mb/audio/amq.html. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ a b "Radio Stations in Emporia, Kansas". Radio-Locator. http://www.radio-locator.com/cgi-bin/locate?select=city&city=Emporia&state=KS&x=0&y=0. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "FMQ FM Radio Database Query". Federal Communications Commission. http://www.fcc.gov/mb/audio/fmq.html. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "K-LOVE Master Station List". K-LOVE. http://www.klove.com/music/radio-stations/radio-station-download.aspx. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Local Stations". Pensacola Christian College. http://www.rejoice.org/LocalStations/Default.aspx. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "The Wildcat 91.9". The Wildcat 91.9 FM. http://www.wildcat919.com/index.php. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Contact Z". Z96.3 FM. http://www.z963.com/contact/index.html. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Kansas Public Radio". Kansas Public Radio. http://www.kansaspublicradio.org/index.php. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Kansas Public Radio". Kansas Public Radio. http://www.kansaspublicradio.org/index.php. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Sunny 102.5". Flint Hills Radio. http://www.sunny1025.com/. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Stations Map". Bott Radio Network. http://www.bottradionetwork.com/stations/stations-map/. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Topeka, Kansas (TV market map)". EchoStar Knowledge Base. http://dishuser.org/TVMarkets/City%20Maps/Topeka.gif. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "TVQ TV Database Query". Federal Communications Commission. http://www.fcc.gov/fcc-bin/audio/tvq.html. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "About Video Production Services". Kansas State University. http://www.k-state.edu/video/. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Affiliates". LegacyTV. http://legacytv.wordpress.com/affiliates-2/. Retrieved 2011-11-18.
- ^ "Bill Murray Coming to Manhattan (Kansas)". http://barfblog.foodsafety.ksu.edu/2008/01/articles/wacky-and-strange-but-true/bill-murray-coming-to-manhattan-kansas/. Retrieved 2008-10-21.
- ^ "Country Music Hall of Fame site". http://www.countrymusichalloffame.com/site/news_detail.aspx?cid=1493. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ "The Elvira Show on tv.com". http://www.tv.com/the-elvira-show/show/6439/summary.html. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ "IMDb "Friday Night Lights" filming locations". http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0390022/locations. Retrieved 2007-01-22.
- ^ The Trailer
- ^ ""Manhattan, Kansas" on IMDb". http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0449067/. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
Further reading
- History of the State of Kansas; William G. Cutler; A.T. Andreas Publisher; 1883. (Online HTML eBook)
- Kansas : A Cyclopedia of State History, Embracing Events, Institutions, Industries, Counties, Cities, Towns, Prominent Persons, Etc; 3 Volumes; Frank W. Blackmar; Standard Publishing Co; 944 / 955 / 824 pages; 1912. (Volume1 – Download 54MB PDF eBook),(Volume2 – Download 53MB PDF eBook), (Volume3 – Download 33MB PDF eBook)
External links
- City
- City of Manhattan
- Manhattan – Directory of Public Officials
- Manhattan – Convention and Visitor's Bureau
- Manhattan – Kansas business directory
- Schools
- USD 383, local school district
- Newspapers
- Other
- Manhattan's Sunset Zoo
- Manhattan's Insect Zoo
- The Great Manhattan Mystery Conclave
- Manhattan Kansas Travel and Recreation
- Maps
- Manhattan City Map, KDOT
- Riley County Map, KDOT
- Pottawatomie County Map, KDOT
Municipalities and communities of Riley County, Kansas Cities Leonardville | Manhattan‡ | Ogden | Randolph | Riley
CDP Unincorporated
communityFootnotes ‡This populated place also has portions in an adjacent county or counties
Municipalities and communities of Pottawatomie County, Kansas Cities Belvue | Emmett | Havensville | Louisville | Manhattan‡ | Olsburg | Onaga | St. George | St. Marys‡ | Wamego | Westmoreland | Wheaton
Unincorporated
communityFostoria
Footnotes ‡This populated place also has portions in an adjacent county or counties
Categories:- Cities in Kansas
- County seats in Kansas
- Populated places in Pottawatomie County, Kansas
- Populated places in Riley County, Kansas
- University towns in the United States
- Populated places established in 1855
- Manhattan, Kansas metropolitan area
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.