- Merlin (protein)
-
Merlin (also called Neurofibromin 2 or schwannomin) is a cytoskeletal protein. In humans, it is a tumor suppressor protein involved in Neurofibromatosis type II.[1][2] Sequence data reveal its similarity to the ERM protein family.
The name "merlin" is an acronym for "Moesin-Ezrin-Radixin-Like Protein".
Contents
Genes
Human merlin is coded by the gene NF2 in Chromosome 22. Mouse merlin gene is located on the chromosome 11[3] and rat merlin gene on the chromosome 17. Fruit fly merlin gene (symbol Mer) is located on chromosome 1 and shares 58% similarity to its human homologue. Other merlin-like genes are known from a wide range of animals, and the derivation of merlin is thought to be in early metazoa. Merlin is a member of the ERM family of proteins including ezrin, moesin, and radixin, which are in the protein 4.1 superfamily of proteins. Merlin is also known as schwannomin, a name derived from the most common type of tumor in the NF2 patient phenotype, the schwannoma.
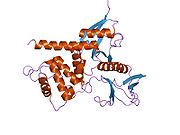
Structure
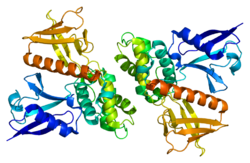
Vertebrate merlin is a 70 kDa protein. There are 10 known isoforms of human merlin molecule (the full molecule being 595 amino acids in length). The two most common these are also found in the mouse and are called type 1 and type 2, differing by the absence or presence of exon 16 or 17, respectively). All the known varieties have a conserved N-terminal part, which contains a FERM domain (a domain found in most cytoskeletal-membrane organizing proteins). The FERM domain is followed by an alpha-helical domain and a hydrophilic tail.[4] Merlin can dimerize with itself and heterodimerize with other ERM family proteins.
Function
Merlin is a membrane-cytoskeleton scaffolding protein, i.e. linking actin filaments to cell membrane or membrane glycoproteins.[5] Human merlin is predominantly found in nervous tissue, but also in several other fetal tissues, and is mainly located in adherens junctions.[6] Its tumor suppressor properties are probably associated with contact-mediated growth inhibition. Drosophila merlin is expressed in embryonic hindgut, salivary gland and imaginal discs and has apparently a slightly different role than in vertebrates.[7]
The phosphorylation of serine 518 is known to alter the functional state of merlin.[8] The signaling pathway of merlin is proposed to include several salient cell growth controlling molecules, including eIF3c, CD44, protein kinase A and p21 activated kinases.
Mutations of the NF2 gene cause a human autosomal dominant disease called neurofibromatosis type 2. It is characterized by the development of tumors of the nervous system, most commonly of bilateral vestibular schwannomas (also called acoustic neuromas). NF2 belongs to the tumor suppressor group of genes.[9]
Interactions
Merlin (protein) has been shown to interact with HGS,[10][11] CUL4A,[12] EZR,[13] SDCBP,[14] VPRBP,[12] RIT1,[12] SPTBN1,[15] MED28[16] and DDB1.[12]
External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Neurofibromatosis 2
- FlyBase synopsis of gene Mer
- UMich Orientation of Proteins in Membranes protein/pdbid-1gc6 - Calculated spatial position of Radixin in membrane
References
- ^ Rouleau GA, Merel P, Lutchman M, Sanson M, Zucman J, Marineau C, Hoang-Xuan K, Demczuk S, Desmaze C, Plougastel B (1993). "Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2". Nature 363 (6429): 515–21. doi:10.1038/363515a0. PMID 8379998.
- ^ Golovnina K, Blinov A, Akhmametyeva EM, Omelyanchuk LV, Chang LS (2005). "Evolution and origin of merlin, the product of the Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) tumor-suppressor gene". BMC Evol. Biol. 5: 69. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-5-69. PMC 1315344. PMID 16324214. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1315344.
- ^ Haase VH, Trofatter JA, MacCollin M, Tarttelin E, Gusella JF, Ramesh V (1994). "The murine NF2 homologue encodes a highly conserved merlin protein with alternative forms". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (3): 407–11. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.3.407. PMID 8012352.
- ^ Shimizu T, Seto A, Maita N, Hamada K, Tsukita S, Tsukita S, Hakoshima T (2002). "Structural basis for neurofibromatosis type 2. Crystal structure of the merlin FERM domain". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (12): 10332–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109979200. PMID 11756419.
- ^ McClatchey AI, Giovannini M (2005). "Membrane organization and tumorigenesis--the NF2 tumor suppressor, Merlin". Genes Dev. 19 (19): 2265–77. doi:10.1101/gad.1335605. PMID 16204178.
- ^ den Bakker MA, Vissers KJ, Molijn AC, Kros JM, Zwarthoff EC, van der Kwast TH (1999). "Expression of the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene in human tissues". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 47 (11): 1471–80. doi:10.1177/002215549904701113. PMID 10544220. http://www.jhc.org/cgi/content/abstract/47/11/1471.
- ^ LaJeunesse DR, McCartney BM, Fehon RG (1998). "Structural Analysis of Drosophila Merlin Reveals Functional Domains Important for Growth Control and Subcellular Localization". J. Cell Biol. 141 (7): 1589–99. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.7.1589. PMC 2133006. PMID 9647651. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2133006.
- ^ Alfthan K, Heiska L, Grönholm M, Renkema GH, Carpén O (2004). "Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates merlin at serine 518 independently of p21-activated kinase and promotes merlin-ezrin heterodimerization". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 18559–66. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313916200. PMID 14981079.
- ^ Scoles DR, Yong WH, Qin Y, Wawrowsky K, Pulst SM (2006). "Schwannomin inhibits tumorigenesis through direct interaction with the eukaryotic initiation factor subunit c (eIF3c)". Hum. Mol. Genet. 15 (7): 1059–70. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl021. PMID 16497727.
- ^ Gutmann, D H; Haipek C A, Burke S P, Sun C X, Scoles D R, Pulst S M (Apr. 2001). "The NF2 interactor, hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS), associates with merlin in the "open" conformation and suppresses cell growth and motility". Hum. Mol. Genet. (England) 10 (8): 825–34. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.8.825. ISSN 0964-6906. PMID 11285248.
- ^ Scoles, D R; Huynh D P, Chen M S, Burke S P, Gutmann D H, Pulst S M (Jul. 2000). "The neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein interacts with hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate". Hum. Mol. Genet. (ENGLAND) 9 (11): 1567–74. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.11.1567. ISSN 0964-6906. PMID 10861283.
- ^ a b c d Huang, J; Chen J (Jul. 2008). "VprBP targets Merlin to the Roc1-Cul4A-DDB1 E3 ligase complex for degradation". Oncogene (England) 27 (29): 4056–64. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.44. PMID 18332868.
- ^ Grönholm, M; Sainio M, Zhao F, Heiska L, Vaheri A, Carpén O (Mar. 1999). "Homotypic and heterotypic interaction of the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein merlin and the ERM protein ezrin". J. Cell. Sci. (ENGLAND) 112 ( Pt 6): 895–904. ISSN 0021-9533. PMID 10036239.
- ^ Jannatipour, M; Dion P, Khan S, Jindal H, Fan X, Laganière J, Chishti A H, Rouleau G A (Aug. 2001). "Schwannomin isoform-1 interacts with syntenin via PDZ domains". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (35): 33093–100. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105792200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11432873.
- ^ Neill, G W; Crompton M R (Sep. 2001). "Binding of the merlin-I product of the neurofibromatosis type 2 tumour suppressor gene to a novel site in beta-fodrin is regulated by association between merlin domains". Biochem. J. (England) 358 (Pt 3): 727–35. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3580727. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1222106. PMID 11535133. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1222106.
- ^ Wiederhold, Thorsten; Lee Ming-Fen, James Marianne, Neujahr Ralph, Smith Nicole, Murthy Anita, Hartwig John, Gusella James F, Ramesh Vijaya (Nov. 2004). "Magicin, a novel cytoskeletal protein associates with the NF2 tumor suppressor merlin and Grb2". Oncogene (England) 23 (54): 8815–25. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208110. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 15467741.
Neoplasm: Tumor suppressor genes/proteins and Oncogenes/Proto-oncogenes Ligand Receptor TSP: CDH1TSP: PTCH1TSP: TGF beta receptor 2Intracellular signaling P+Ps ONCO: Beta-catenin · TSP: APCHippo signaling pathwayTSP: Neurofibromin 2/MerlinOther/unknownNucleus TSP: VHL · ONCO: CBL - MDM2Mitochondria Other/ungrouped M: NEO
tsoc, mrkr
tumr, epon, para
drug (L1i/1e/V03)
Arrestin Membrane-spanning 4A Myelin Pulmonary surfactant Tetraspanin TSPAN1 · TSPAN2 · TSPAN3 · TSPAN4 · TSPAN5 · TSPAN6 · TSPAN7 · TSPAN8 · TSPAN9 · TSPAN10 · TSPAN11 · TSPAN12 · TSPAN13 · TSPAN14 · TSPAN15 · TSPAN16 · TSPAN17 · TSPAN18 · TSPAN19 · TSPAN20 · TSPAN21 · TSPAN22 · TSPAN23 · TSPAN24 · TSPAN25 · TSPAN26 · TSPAN27 · TSPAN28 · TSPAN29 · TSPAN30 · TSPAN31 · TSPAN32 · TSPAN33 · TSPAN34Other/ungrouped Calnexin · LDL-receptor-related protein associated protein · Neurofibromin 2 · Presenilin (PSEN1, PSEN2) · HFE · Phospholipid transfer proteins · Dysferlin · STRC · OTOFsee also other cell membrane protein disorders
B memb: cead, trns (1A, 1C, 1F, 2A, 3A1, 3A2-3, 3D), othrReceptor FAT4Adaptor protein Kinase Transcription factor Other/unknown B trdu: iter (nrpl/grfl/cytl/horl), csrc (lgic, enzr, gprc, igsr, intg, nrpr/grfr/cytr), itra (adap, gbpr, mapk), calc, lipd; path (hedp, wntp, tgfp+mapp, notp, jakp, fsap, hipp, tlrp) PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Cytoskeleton
- Peripheral membrane proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.