- Miami International Airport
-
Miami International Airport 

Miami International Airport terminal IATA: MIA – ICAO: KMIA – FAA LID: MIA Summary Airport type Public Owner Miami-Dade County Operator Miami-Dade Aviation Department (MDAD) Serves South Florida metropolitan area Location Miami-Dade County, Florida Hub for Elevation AMSL 8 ft / 2 m Coordinates 25°47′36″N 080°17′26″W / 25.79333°N 80.29056°WCoordinates: 25°47′36″N 080°17′26″W / 25.79333°N 80.29056°W Website Maps FAA airport diagram Location within Miami Runways Direction Length Surface ft m 8L/26R 8,600 2,621 Asphalt 8R/26L 10,506 3,202 Asphalt 9/27 13,000 3,962 Asphalt 12/30 9,354 2,851 Asphalt Statistics (2010) Aircraft operations Based aircraft 250 Passengers 35,698,025 Source: Federal Aviation Administration[1] Miami International Airport (IATA: MIA, ICAO: KMIA, FAA LID: MIA), also known as MIA and historically Wilcox Field, is the primary airport serving the South Florida area. The airport is in an unincorporated area in Miami-Dade County, Florida, eight miles (13 km) northwest of Downtown Miami, in metropolitan Miami,[1] between the cities of Miami, Hialeah, Doral, Miami Springs, the village of Virginia Gardens, and unincorporated Fontainebleau.
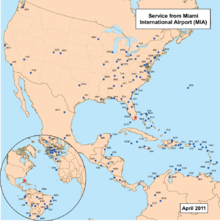
The airport is a hub for passenger airlines American Airlines, Executive Airlines under the American Eagle name; cargo airlines, UPS Airlines and FedEx Express; and charter airline Miami Air. It is a focus airport for LAN Airlines and its subsidiaries, both for passengers and cargo operations. Miami International Airport has passenger and cargo flights to cities throughout the Americas and Europe, as well as the Canary Islands off the African coast, and cargo flights to Asia; it is South Florida's main airport for long-haul international flights.
Miami International Airport is the largest gateway between the United States and Latin America, and is one of the largest airline hubs in the United States, owing to its proximity to tourist attractions, local economic growth, large local Latin American and European populations, and strategic location to handle connecting traffic between North America, Latin America, and Europe. In the past, it has been a hub for Braniff International Airways, Eastern Air Lines, Air Florida, the original National Airlines, the original Pan Am, United Airlines, and Iberia. Miami International is also the proposed hub of two new start-up airlines, one of which hopes to use the Eastern Airlines name.[2]
In 2010 the airport ranked first in the United States by percentage of international flights and second by volume of international passengers, behind only New York-JFK.[3] In 2010, 35,698,025 passengers traveled through the airport,[4] making the airport the 28th busiest airport in the world by passenger traffic. The Airport also ranks as the 12th busiest airport in the United States by annual passenger count and is the largest airport in the state of Florida, surpassing Orlando by a small margin.[5] The airport also handled more international cargo than any other airport in the United States.[6]
Contents
History
The airport opened to flights in 1928 as Pan American Field, the operating base of Pan American Airways Corporation, on the north side of the modern airport property. After Pan Am acquired the New York, Rio, and Buenos Aires Line it shifted most of its operations to the Dinner Key seaplane base, leaving Pan Am Field largely unused until Eastern Air Lines began flying there in 1934, followed by National Airlines in 1937.
In 1945 the City of Miami established a Port Authority and raised bond revenue to purchase the airport, which had meanwhile been renamed 36th Street Airport, from Pan Am. It was merged with an adjoining Army airfield in 1949 and expanded further in 1951. The old terminal on 36th Street was closed in 1959 when the modern passenger terminal (since greatly expanded) opened for service. Air Force Reserve troop carrier and rescue squadrons also operated from Miami International from 1949 through 1959, when the last such unit relocated to nearby Homestead Air Force Base, now Homestead Air Reserve Base.[citation needed]
During the late 1970s and early 1980s Air Florida had a hub at MIA, with a nonstop flight to London which it acquired from National upon the latter's merger with Pan Am. Air Florida ceased operations in 1982 following the crash of Air Florida Flight 90.[7]
After Frank Borman became president of Eastern in 1975, he moved Eastern's headquarters from Rockefeller Center in New York City to a campus adjacent to MIA.[8] Eastern remained one of the largest employers in the Miami metropolitan area until ongoing labor union unrest, coupled with the airline's acquisition by union antagonist Frank Lorenzo in 1986, ultimately forced the airline into bankruptcy in 1989.[7]
In the midst of Eastern's turmoil, American Airlines CEO Bob Crandall sought a new hub in order to utilize new aircraft which AA had on order at the time. AA studies indicated that Delta Air Lines would provide strong competition on most routes from Eastern's hub at Atlanta, but that MIA had many key routes only served by Eastern. American announced that it would establish a base at MIA in August 1988. Lorenzo considered selling Eastern's profitable Latin American routes to AA as part of a Chapter 11 reorganization of Eastern in early 1989, but backed out in a last-ditch effort to rebuild the MIA hub. The effort quickly proved futile, and American purchased the routes (including the route authority between Miami and London then held by Eastern sister company Continental Airlines) in a liquidation of Eastern which was completed in 1990.[7] Later in the 1990s, American transferred more employees and equipment to MIA from its failed domestic hubs at Nashville and Raleigh-Durham. Today Miami is American's largest air freight hub and is the main connecting point in the airline's north-south international route network.
Pan Am, the other key carrier at MIA, was acquired by Delta Air Lines in 1991, but filed for bankruptcy shortly thereafter. Its remaining international routes from Miami to Europe and Latin America were sold to United Airlines for $135 million as part of Pan Am's emergency liquidation that December.[7] United maintained a Latin American hub at MIA through the 1990s but ended flights from Miami to South America, and shut down its Miami crew base, in May 2004, reallocating most Miami resources to its main hub in Chicago.[9]
Stricter visa requirements for aliens in transit (a result, in part, of the September 11, 2001 attacks) have lessened MIA's role as an intercontinental connecting hub, but it nonetheless remains the most important hub between Europe and Latin America. In 2004, Iberia Airlines ended its hub operation in Miami, opting instead to run more direct flights from Spain to Central America. Air France continues to run flights to Port-au-Prince using Airbus A320 aircraft.[citation needed] Today, more European carriers serve Miami International Airport than any other airport in the United States, except New York City's John F. Kennedy.
AeroSur, American Airlines, American Eagle, Gulfstream International Airlines, Sky King Airlines, TACA International Airlines, and Vision Airlines all operate regular flights between MIA and several airports in Cuba, one of a few airports with direct airlink between the two nations. However, these flights must be booked through agents with special authorization from the Office of Foreign Assets Control, and are only generally available to government officials, journalists, researchers, professionals attending conferences, or expatriates visiting Cuban family.
Operations
The budget for operations was $600 million in 2009.[10]
Facilities and aircraft
Miami International Airport covers an area of 3,300 acres (1,335 ha) which contains four runways:[1]
- Runway 8L/26R: 8,600 x 150 ft (2,621 x 46 m), Surface: Asphalt
- Runway 8R/26L: 10,506 x 200 ft (3,202 x 61 m), Surface: Asphalt
- Runway 9/27: 13,000 x 150 ft (3,962 x 46 m), Surface: Asphalt
- Runway 12/30: 9,354 x 150 ft (2,851 x 46 m), Surface: Asphalt
For the 12-month period ending April 30, 2009, the airport had 358,705 aircraft operations, an average of 982 per day: 82% scheduled commercial, 12% air taxi, 5% general aviation and <1% military. There are 28 aircraft based at this airport: 46% multi-engine and 54% jet.[1]
Fire protection at the airport is provided by Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Department[11] Station 12.[12]
Terminal
The main terminal at MIA dates back to 1959, with several new additions. Semicircular in shape, the terminal has one linear concourse (Concourse D) and five pier-shaped concourses, lettered counter-clockwise from E to J (Concourse A is now part of Concourse D; Concourses B and C were demolished so that Concourse D gates could be added in their place; I was skipped to avoid confusion with the number 1.). From the terminal's opening until the mid-1970s the concourses were numbered clockwise from 1 to 6.
Level 1 of the terminal contains baggage carousels and ground transportation access. Level 2 contains ticketing/check-in, shopping and dining, and access to the concourses. The airport currently has two immigration and customs facilities, located in Concourse E, Level 1 and in Concourse J, Level 3. The Concourse E FIS can be utilized by flights arriving at all gates in Concourse E and most gates in Concourses D (all D gates will be able to route passengers to the FIS by fall 2011) and Concourse F. The Concourse J FIS can be utilized by flights arriving at all gates in Concourse J and most gates in Concourse H. However, all gates in Concourse G and some gates in Concourses D (temporarily), F, and H, do not have the facilities to route passengers to any FIS, and therefore can only be used for domestic arrivals. MIA is unique among American airports in that all of its facilities are common-use, meaning that they are assigned by the airport and no one airline holds ownership or leases on any terminal space or gates, thus giving the airport much more flexibility in terminal and gate assignments and allowing it to make full use of existing facilities. The entire airport became common-use by the 1990s.
The airport has three parking facilities: a two-level short-term parking lot directly in front of Concourse E, and two seven-story parking garages (North and South) within the terminal's curvature and connected to the terminal via overhead walkways on Level 3.[13] In the late 1990s, the Dolphin Garage was expanded to better serve the then-new Concourse A; it is expected that the Flamingo Garage will be similarly expanded in the near future to serve the new Concourse J. The two parking garages are connected at their west ends; at the top of this connection are the airport's SIDA and ID Section offices. The single terminal facility is divided into three sections known as the North Terminal, Central Terminal, and South Terminal.
North Terminal (Concourse D)
The North Terminal consists of one concourse, Concourse D, a 3,600,000-square-foot (330,000 m2) linear concourse 1.2 miles (1.9 km) long with a capacity of 30 million passengers annually. It has one bus station and 45 gates: D1-D12, D14-D17, D19-D25, D29-D33 D37-D40, D42-D51, D53, D55, D60.[14] It currently houses departures and domestic arrivals for American Airlines and American Eagle; their respective international arrivals are processed in the Central Terminal at Concourse E because of the lack of customs and immigration facilities in the North Terminal. American operates two Admirals Clubs within the concourse; one located near Gate D30, and another near Gate D15. American Eagle uses Gates D53, D55, and D60.[15]
The North Terminal was previously the site of Concourses A, B, C, and D, each a separate pier. Concourse D was one of the airport's original 1959 concourses, having opened as Concourse 5. After modifications similar to that of former Concourse C during the 1960s, it was completely rebuilt in the 1980s and connected to the immigration and customs hall in Concourse E, allowing it to handle international arrivals. Along with former Concourses B and C, the concourse once housed the Eastern Air Lines base of operations. Two other Texas Air Corporation affiliates joined Eastern during the 1980s: Concourse D was also used by Braniff International Airways for Latin American operations up until their shutdown in 1982, and Continental Airlines used gates on the west side of the concourse during the 1980s.
The North Terminal construction merged the four piers into a single linear concourse designated Concourse D. This configuration was adopted in order to increase the number of aircraft that can simultaneously arrive and depart from the terminal, allowing each gate to handle approximately twice as many operations per day.[16] The construction process started with the extension of the original A and D concourses in the late 1990s. By the mid-2000s, the gates on the east side of Concourse D were closed in order to make room for new gates being constructed as part of the North Terminal Development project. In 2004, a new extension to the west was opened, consisting of Gates D39 through D51. Concourse B was demolished in 2005; in the summer of 2009, Gates D21 to D25 entered service where Concourse B once stood. Concourse C was demolished in 2009.[17] Concourse A was closed in November 2007 and re-opened in July 2010 as a 14-gate eastern extension of Concourse D. In August 2010, a further extension for American Eagle flights was opened.[18]
The Skytrain automated people mover, built by Parsons[disambiguation needed
 ] and Odebrecht with trains from Sumitomo Corporation and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, opened to the public on September 15, 2010.[18] Skytrain transports passengers between four stations within Concourse D, located at gates D17, D24, D29 and D46.[19]
] and Odebrecht with trains from Sumitomo Corporation and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, opened to the public on September 15, 2010.[18] Skytrain transports passengers between four stations within Concourse D, located at gates D17, D24, D29 and D46.[19]The North Terminal construction began in 1998 and was slated for completion in 2005, but was delayed several times due to cost overruns. The project was managed by American Airlines until the Miami-Dade County Aviation Department took over in 2005.[20] With sections of the terminal opening in phases, a significant majority of the structure has already been completed and opened for airline use.[21] As of July 2011, the North Terminal construction is scheduled for completion in early 2012; current construction activity include a customs and immigration area, a re-check inspection area for international-to-international connections, a new checked baggage delivery system, and last three gates.[18]
Central Terminal
The Central Terminal consists of three concourses, labeled E, F, and G, with a combined total of 47 gates.[14]
The Central Terminal consists of Concourses E, F, and G. The Miami-Dade Aviation Department expects to rebuild the central terminal following the completion of the north terminal, and intends to seek bids by the first quarter of 2011.[22] Upon completion of the North Terminal project and the reopening, the Central Terminal will be used to house airlines not affiliated with any of the "big three" airline alliances as well as the low-cost carriers the airport hopes to attract.
Concourse E
Concourse E has two bus stations and 17 gates: E2, E4-E11, E20-E25, E30, E33[14]
Concourse E also dates back to the terminal's 1959 opening, and was originally known as Concourse 4. From the start, it was the airport's only international concourse, containing its own immigration and customs facilities. In the 1960s it underwent some minor renovations similar to the airport's other original concourses, but didn't receive its first major addition until the opening of the International Satellite Terminal in 1976. Featuring Gates E20-E35 (commonly known as "High E"), the satellite added 12 international gates capable of handling the largest jet aircraft as well as an international intransit lounge for arriving international passengers connecting to other international flights. The concourse and its satellite were briefly linked by buses until the airport's first automated people mover (Adtranz C-100) opened in the late 1970s. At the same time Concourse E's immigration and customs facilities were radically overhauled and expanded. During the 1980s the original portion of Concourse E ("Low E") was rebuilt to match the satellite.
Since then, both portions of the concourse have seen little change. Gate E3 was closed in the 1990s to accommodate a connector between Concourses D and E. In the mid-2000s, the Low E and High E security checkpoints were expanded and merged into one, linking both portions of the concourse without requiring passengers to reclear security. At the same time Gates E32, E34, and E35 were closed to make way for a second parallel taxiway between the Concourse D extension and Concourse E. Concourse E also contains the Central Terminal's immigration and customs halls.
The seven story Miami-International Airport hotel and many Miami-Dade Aviation Department executive offices are in the Concourse E portion of the terminal. Level 1 houses the Customs E Greeter's Lobby, car rental agency counters, baggage re-check for connecting international passengers, the Public Bus Terminal, and two domestic baggage carousels. Level 2 is used for check-in by several North American carriers. Concourse E, along with Concourse F, was once the base of operations for Pan Am and many of MIA's international carriers.
Concourse F
Concourse F has one bus station and 15 gates: F3-F10, F14-F19, F23[14]
Concourse F dates back to 1959 and was originally known as Concourse 3. Like Concourses D and E, it received minor renovations in the 1960s and was largely rebuilt in the 1980s. The gates at the far end of the pier were demolished and replaced by new widebody Gates F10 to F23, all of which were capable of processing international arrivals. The departure lounges for Gates F3, F5, F7, and F9 were also rebuilt, and these also became international gates. Currently the concourse retains a distinctly 1980s feel, and is part of the Central Terminal area.
The south side of the concourse was used by Northeast Airlines until its 1972 merger with Delta Air Lines. Likewise, National Airlines flew out of the north side of Concourse F until its 1980 merger with Pan Am, which continued to use the concourse until its 1991 shutdown. When United Airlines acquired Pan Am's Latin American operations, the airline carried on operating a focus city out of Concourse F until completely dismantling it by 2004. From 1993 to 2004, Concourse F was also used by Iberia Airlines for its Miami focus city operation, which linked Central American capitals to Madrid using MIA as the connecting point; Iberia continues to fly from the concourse.
Level 1 of the Concourse F portion of the terminal is used for domestic baggage claim and cruise line counters. Level 2 contains check-in facilities for European airlines.
Concourse G
Concourse G has one bus station and 15 gates: G2-G12, G14-G16, G19[14]
Concourse G is the only one of the original 1959 concourses that has largely remained in its original state, save for the modifications the rest of the airport received in the 1960s. It is the only concourse at the airport not capable of handling international arrivals, though it is frequently used for departing international charters.
South Terminal
The South Terminal consists of two concourses, H and J, with a combined total of 26 gates.[14]
The South Terminal building and Concourse J opened on August 29, 2007(photo). The new addition is seven stories tall and has 15 international-capable gates, and a total floor area of 1.3 million square feet (120,000 m2), including two airline lounges and several offices. Concourse H serves Delta Air Lines and its partners in the SkyTeam alliance (except Continental and Copa Airlines which also use Concourse H), while Concourse J serves United Airlines and its partners in the Star Alliance.
Concourse H
Concourse H has one bus station and 11 gates: H3-H12, H15[14]
Concourse H was the 20th Street Terminal's first extension, originally built in 1961 as Concourse 1 for Delta Air Lines, which remains in the concourse to this day. This concourse featured a third floor, the sole purpose of which was to expedite access to the "headhouse" gates at the far end. In the late 1970s, a commuter satellite terminal was built just to the east of the concourse. Known as "Gate H2", it featured seven parking spaces (numbered H2a through H2g) designed to handle smaller commuter aircraft. The concourse was dramatically renovated during the mid-1990s, to match the style of the then-new Concourse A. Moving walkways were added to the third floor, the H1 Bus Station and Gates H3-H11 were completely rebuilt, and the H2 commuter satellite had jetways installed. Due to financial difficulties, headhouse gates H12-H20 were left in their original state.
With the construction of the Concourse J extension in the 2000s, the H2 commuter satellite was demolished. In 2007, with the opening of the South Terminal's immigration and customs facilities, the third floor of Concourse H was closed off and converted into a "sterile circulation" area for arriving international passengers. Gates H4, H6, H8, and H10 were made capable of handling international arrivals, and currently serve Copa Airlines, Air France, and Alitalia. Simultaneously, headhouse gates H16, H17, H18, and H20 were closed to allow for the construction of a second parallel taxiway leading to the new Concourse J.
There are plans to convert Gates H11 and H15 into additional international-capable gates, but the concourse does not yet require their use. Instead, the airport is focusing on completing the long-delayed North Terminal project.
Concourse H historically served as the base of operations for Piedmont's Miami focus city and US Air Express's commuter operations. Concourse H continues to serve original tenant Delta Air Lines, which uses all but one of the gates on the west side of the pier.
Concourse J
Concourse J has one bus station and 15 gates: J2-J5, J7-J12, J14-J18[14]
Concourse J is the newest concourse, having entered service on August 29, 2007. Part of the airport's South Terminal project,[23] the concourse was designed by Carlos Zapata and M.G.E., one of the largest Hispanic-owned architecture firms in Florida. The concourse features 15 international-capable gates as well as the airport's only gate capable of handling the Airbus A380. The concourse added a third international arrivals hall to the airport, supplementing the existing ones at Concourses B (now closed) and E while significantly relieving overcrowding at these two facilities.
In the initial stages of its development, the South Terminal (Concourses H and J) was planned to serve United Airlines and its partners in the Star Alliance. Concourse H would serve United's partner airlines, while Concourse J would be the new home of United's Latin American hub. When United dismantled its MIA hub in 2004, Concourse H became intended to serve Delta Air Lines and its partners in the SkyTeam alliance, while Concourse J would serve United's remaining operations as well as their partner carriers. Once the North Terminal is completed, oneworld member airlines will be housed in Concourse D (North Terminal), with SkyTeam and Star Alliance members in Concourses H and J (South Terminal).
Former Concourses
Concourse A
At the time of its closure, Concourse A had one bus station and 16 gates: A3, A5, A7, A10, A12, A14, A16-A26
Concourse A is a recent addition to the airport, opening in two phases between 1995 and 1998. The concourse is now part of the North Terminal. Between 1995 and 2007, the concourse housed many of American Airlines' domestic and international flights, as well as those of many European and Latin American carriers.
On November 9, 2007, Concourse A was closed as part of the North Terminal Development Project. It had been closed in order to speed up completion of the North Terminal project, as well as facilitate the addition of the Automated People Mover (APM) system that now spans the length of the North Terminal. The infrastructure of Concourse A reopened on July 20, 2010 as an extension of Concourse D.
Concourse B
At its peak, Concourse B had one bus station and 12 gates: B1, B2-B12, B15
Concourse B was constructed in the 1970s for Eastern Air Lines as part of the airport's ambitions "Program 70's" initiative, and first opened in 1983. During the 1980s, the existing concourse was rebuilt and expanded, and a new immigration and customs hall was built in the Concourse B section of the terminal, allowing the concourse to process international arrivals. Along with Concourse C and most of Concourse D, it served as Eastern Air Lines' historical base of operations.
After Eastern's shutdown in 1991 it was used by a variety of European and Latin American airlines; by the 2000s American Airlines was its sole tenant. The concourse was closed in 2004 and torn down the following year as part of the North Terminal Development project. The immigration and customs hall remained open until 2007, when it was closed along with Concourse A.
Concourse C
At the time of its closure, Concourse C had 3 gates: C5, C7, C9
Concourse C opened as Concourse 6 in 1959, serving Eastern Air Lines. During the 1960s Concourse C received an extension of its second floor and was equipped with air conditioning. Since then, it did not receive any major interior modifications or renovations. Following the renumbering of gates and concourses in the 1970s, Concourse C had Gates C1 to C10. The opening of an international arrivals hall in Concourse B during the 1980s saw Gate C1 receive the ability to process international arrivals.
Following the demise of Eastern Air Lines in 1991 the concourse was used by a variety of African and Latin American carriers. Many of these airlines' flights would arrive at Concourse B and then be towed to Concourse C for departure. By the end of the decade, the construction of American Airlines' baggage sorting facility between Concourses C and D saw the closure of all gates on the west side of the concourse, with Gate C1 following soon afterward. From the 2000s on, the concourse consisted of just four domestic-only gates, each of which were capable of accommodating small-to-medium jet aircraft from the Boeing 737 up to the Airbus A300, and had American Airlines as its sole tenant.
As part of the North Terminal Development project, Concourse C closed on September 1, 2009, and was demolished. The demolition of Concourse C allowed for the construction of new gates where the concourse stood.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger services
Note: All flights to Cuba are operated as scheduled Special Authority Charters
Airlines Destinations Concourse Aerolíneas Argentinas Buenos Aires-Ezeiza J Aeroméxico Cancún, Mexico City, Monterrey F Aeroméxico operated by Aeroméxico Connect Mérida, Mexico City F Aerosur Santa Cruz de la Sierra-Viru Viru F Air Berlin Berlin-Tegel , Düsseldorf E Air Canada Toronto-Pearson
Seasonal: Montréal-TrudeauJ Air Europa Madrid
Seasonal: Tenerife-NorthF Air France Paris-Charles de Gaulle, Pointe-à-Pitre, Port-au-Prince
Seasonal: Santo DomingoH AirTran Airways Baltimore [ends June 3, 2012][24] G Alaska Airlines Seattle/Tacoma E Alitalia Milan-Malpensa, Rome-Fiumicino J American Airlines Antigua, Aruba, Atlanta, Austin, Barbados, Baltimore, Belize City, Belo Horizonte-Confins, Bermuda, Bogotá, Boston, Brasília, Buenos Aires-Ezeiza, Cali, Cancún, Caracas, Chicago-O'Hare, Curaçao, Dallas/Fort Worth, Denver, Detroit, Grand Cayman, Grenada, Guatemala City, Guayaquil, Hartford, Houston-Intercontinental, Kingston, La Paz, Las Vegas, Liberia (Costa Rica), Lima, London-Heathrow, Los Angeles, Madrid, Managua, Maracaibo, Medellín-Córdova, Mexico City, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montego Bay, Montevideo, Montréal-Trudeau, New Orleans, New York-JFK, New York-LaGuardia, Newark, Orlando, Panama City, Paris-Charles de Gaulle, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Port-au-Prince, Port of Spain, Providenciales, Puerto Plata, Punta Cana, Quito, Raleigh/Durham, Recife, Rio de Janeiro-Galeão, St. Croix, St. Kitts, St. Louis, St. Lucia, St. Maarten, St. Thomas, Salvador da Bahia, San Salvador, Santa Cruz de la Sierra-Viru Viru, San Francisco, San José de Costa Rica, San Juan, San Pedro Sula, Santiago de Chile, Santiago de los Caballeros, Santo Domingo, São Paulo-Guarulhos, Tampa, Tegucigalpa, Toronto-Pearson, Valencia (Venezuela), Washington-Dulles, Washington-National
Seasonal: Eagle/Vail, La Romana, Nashville, Tulsa
Charter: HavanaD, E American Eagle Atlanta, Birmingham (AL), Charleston (SC), Charlotte, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky, Cleveland, Columbus (OH), Fort Myers, George Town, Greensboro, Indianapolis, Knoxville, Jacksonville, La Romana, Louisville, Memphis, Nashville, Nassau, Norfolk, Pensacola, Pittsburgh, Richmond, Savannah, Tallahassee D, E American Eagle operated by Executive Airlines Camagüey, Cienfuegos, Fort Myers, Freeport, Gainesville, George Town, Governor's Harbour, Havana, Holguín, Jacksonville (FL), Key West, Marsh Harbour, Nassau, North Eleuthera, Santiago de Cuba, Treasure Cay
Charter: HavanaD Arkefly Amsterdam [25] F Avianca Barranquilla, Bogotá, Cali, Cartagena de Indias, Medellín-Córdova J Avior Airlines Barcelona (Venezuela) F Bahamasair Nassau G British Airways London-Heathrow E Caribbean Airlines Georgetown, Kingston-Norman Manley [begins December 13], Port of Spain J Cayman Airways Cayman Brac, Grand Cayman F Continental Airlines Houston-Intercontinental, Newark
Seasonal: Cleveland
Charter: HavanaG Continental Express operated by ExpressJet Airlines Cleveland G Copa Airlines Panama City H, J Corsairfly Paris-Orly F Delta Air Lines Atlanta, Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky, Detroit, London-Heathrow, Los Angeles, Memphis, Minneapolis/St. Paul, New York-JFK
Charter: Havana[26]H Delta Connection operated by Comair Orlando, Washington-National H Delta Connection operated by Pinnacle Airlines Tampa
Seasonal: Raleigh/DurhamH ExecAir Naples [27] J IBC Airways Cap Haitien J Iberia Barcelona,[28] Madrid E Insel Air Bonaire, Curaçao, Port-au-Prince, Punta Cana, St. Maarten F KLM Amsterdam H LAN Airlines Bogotá, Caracas, Guayaquil, Punta Cana, Santiago de Chile J LAN Argentina Buenos Aires-Ezeiza, Punta Cana J LAN Ecuador Guayaquil, Quito J LAN Perú Lima J Lufthansa Frankfurt
Seasonal: Düsseldorf [29]J PAWA Dominicana Santo Domingo F SBA Airlines Caracas
Seasonal: MaracaiboF Sky King Cienfuegos, Havana, Holguín, Santiago de Cuba F, G Sun Country Airlines Seasonal: Minneapolis/St. Paul F Surinam Airways Aruba, Paramaribo F Swiss International Air Lines Zürich J TACA Airlines Guatemala City, Managua, San Pedro Sula, San Salvador, Tegucigalpa
Seasonal: RoatánJ TACA Airlines operated by Lacsa San José de Costa Rica J TACA Perú Lima J TAM Airlines Belo Horizonte-Confins, Brasília, Manaus, Rio de Janeiro-Galeão, São Paulo-Guarulhos J Transaero Airlines Moscow-Domodedovo F TAP Portugal Lisbon[30] J United Airlines Denver
Seasonal: Chicago-O'Hare, Washington-DullesG United Express operated by Mesa Airlines Chicago-O'Hare, Washington-Dulles G United Express operated by Shuttle America Chicago-O'Hare G US Airways Charlotte, Philadelphia J Virgin Atlantic Airways London-Heathrow F VivaAerobus Monterrey G Vision Airlines Camagüey, Fort Walton Beach, Havana, Holguín, Santiago de Cuba F, G WestJet Toronto-Pearson F Statistics
Busiest International Routes Out of Miami International Airport (2010)[31][32] Rank City Passengers Top Carriers 1  London, United Kingdom (Heathrow)
London, United Kingdom (Heathrow)813,941 American, British Airways, Delta, Virgin Atlantic 2  Sao Paulo, Brazil (Guarulhos)
Sao Paulo, Brazil (Guarulhos)640,298 American, TAM Airlines 3  Caracas Venezuela
Caracas Venezuela600,020 American, SBA Airlines 4  Buenos Aires, Argentina (Ezeiza)
Buenos Aires, Argentina (Ezeiza)530,850 Aerolineas Argentinas, American, LAN Argentina 5  Mexico City, Mexico
Mexico City, Mexico511,047 Aeromexico, American 6  Lima, Peru
Lima, Peru293,340 American, LAN Peru, TACA Peru 7  Port Au Prince, Haiti
Port Au Prince, Haiti272,496 American, Insel Air 8  Nassau, The Bahamas
Nassau, The Bahamas217,356 American, Bahamas Air 9  Panama City, Panama
Panama City, Panama198,987 American, Copa 10  Bogota, Colombia
Bogota, Colombia494,257 American, Avianca, LAN Airlines Busiest Domestic Routes Out of Miami International Airport[33] Rank City Passengers per 12 months Top Carriers 1  Atlanta, GA
Atlanta, GA675,000 American, Delta 2  New York, NY (JFK)
New York, NY (JFK)597,000 American, Delta 3  Chicago, IL
Chicago, IL586,000 American, United 4  Dallas/Fort Worth, TX
Dallas/Fort Worth, TX552,000 American 5  New York, NY (LGA)
New York, NY (LGA)546,000 American 6  Los Angeles, CA
Los Angeles, CA466,000 American, Delta 7  Orlando, FL
Orlando, FL450,000 American, Delta 8  Washington, DC (DCA)
Washington, DC (DCA)432,000 American, Delta 9  San Juan, PR
San Juan, PR425,000 American 10  Boston, MA
Boston, MA377,000 American Cargo
The airport is one of the largest in terms of cargo in the United States,[34] and is the main connecting point for cargo between Latin America and the world[citation needed]. It was first in International freight and third in total freight for 2008. In 2000, LAN Cargo opened up a major operations base at the airport and currently operates one of the largest cargo facilities at the airport, second only to UPS[citation needed]. Most major passenger airlines, such as American Airlines use the airport to carry hold cargo on passenger flights, though most cargo is transported by all-cargo cairlines. UPS Airlines and FedEx Express both base their major Latin American operations at MIA.
Airlines Destinations ABSA Cargo Airline Bogota, Caracas, Fortaleza, Guayaquil, Lima, Manaus, Medellín-Córdova, Panama City, Quito, Campinas-Viracopos, Vitoria ABX Air Cincinnati, Paramaribo, Santo Domingo Air Atlanta Icelandic New York-JFK, Oslo-Garderomen Air Jamaica Cargo Kingston, Montego Bay Air Transport International Guatemala City, Medellín-Cordova, Panama City, San Jose de Costa Rica Amerijet International Aruba, Belize City, Campinas, Curitiba, Lima, Manaus, Maracaibo, Merida, Mexico City, Paramaribo, Port of Spain, Salvador, San Juan, San Pedro Sula, San Salvador, Santiago de los Caballeros, Santo Domingo, St. Maarten Atlas Air Chicago-O'Hare, Lima, Manaus, Oslo-Gardermoen, Campinas-Viracopos, Rio de Janeiro (From September 3rd) Cathay Pacific Cargo Anchorage, Hong Kong, Houston-Intercontinental Capital Cargo International Airlines Merida, Orlando, Toledo Caribbean Airlines Cargo Barbados, Port of Spain Cargolux Houston-Intercontinental, Luxembourg, Mexico City Cayman Airways Cargo Grand Cayman Centurion Air Cargo Bogota, Caracas, Iquitos, Lima, Manaus, Medellin, Quito, Santiago de Chile, Campinas-Viracopos, San Juan China Airlines Cargo Anchorage, Atlanta, Seattle/Tacoma, Taipei-Taoyuan Cielos del Peru Bogotá, Caracas, Iquitos, Lima, Managua, Manaus, Montevideo, Quito DHL Express Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky, Toledo DHL Aero Expreso Panama City, Quito, San Jose de Costa Rica Estafeta Carga Aérea Cancun, Merida FedEx Express Memphis, Quito, San Juan, Valencia (Venezuela) Florida West International Airways Bogotá, Guatemala City, Guayaquil, Lima, Los Angeles, Manaus, Medellin, Quito, Santo Domingo, San Jose de Costa Rica IBC Airways Freeport, Grand Cayman, Havana, Kingston, Marsh Harbour, Montego Bay, Nassau, Port-au-Prince, Providenciales Korean Air Cargo Anchorage, Brussels, Dallas/Fort Worth, New York-JFK, Seoul-Incheon, Toronto-Pearson LAN Cargo Amsterdam, Buenos Aires-Ezeiza, Campinas-ViracoposCaracas, Curitiba, Guatemala City, Guayaquil, Lima, Manaus, Montevideo, Porto Alegre, Quito, San Jose de Costa Rica, San Miguel de Tucumán Linea Aérea Carguera de Colombia Bogotá, Curitiba, Manaus, Medellin, Quito, Campinas-Viracropos Martinair Cargo Amsterdam, Bogotá, Buenos Aires-Ezezia, Campinas-Viracopos, Guayaquil, Lima, Quito, Santiago de Chile MasAir Mexico City Mountain Air Cargo Freeport, Kingston Skyway Enterprises Nassau Tampa Cargo Asunción, Barranquilla, Bogotá, Cali, Lima, Manaus, Medellin-Córdova, Montevideo, Quito Tradewinds Airlines Lima Transportes Aéreos Bolivianos Cochabamba, Panama City, Santa Cruz de la Sierra UPS Airlines Bogotá, Greenville/Spartanburg, Guatemala City, Guayaquil, Jacksonville (FL), Lima, Louisville, Managua, Philadelphia, Quito, San Jose de Costa Rica, San Pedro Sula, Santo Domingo, Campinas-Viracopos, West Palm Beach Venezolana Servicios Expresos Caracas, Maracaibo World Airways Cargo Bogota, Caracas, Cali, Campinas-Viracopos, Lima, Manaus, Quito Ground transportation
Main article: Miami Intermodal CenterMiami International Airport has direct public transport links to Miami-Dade Transit's Metrobus network; free shuttles are also provided to and from the Miami Airport and Hialeah Market Stations on the Tri-Rail commuter rail line. Both stations are close, within a 5 minute drive from the main terminal. The Miami-Dade Aviation Department is currently constructing the MIA Mover, a link to the airport by people mover, to the upcoming Miami Intermodal Center which already opened its Rental Car Center (RCC) in July 2010 and provides access to car rentals. Soon to follow will be a new airport Metrorail station, a relocated Tri-Rail station, and an Amtrak station located within the Miami Central Station, scheduled to open in late 2011/early 2012. A consolidated shuttle service will run to-and-from the terminals at MIA and the RCC for approximately one year until the MIA Mover begins service. Once the MIA Mover is in service, car rental desks and shuttles will disappear from the airport's arrivals level.
Taxis, shuttle services, limousines, and rental cars are currently available within the airport. Taxis and shuttles provide flat rates to popular destinations within Miami, such as the beaches or the city center.
To/from Metrorail, Downtown and South Beach
Miami-Dade Transit operates the Airport Flyer bus which connects MIA directly to the Metrorail (Miami's heavy-rail system) at Earlington Heights Station, which allows for transfers to Downtown Miami and beyond, and ends in the heart of South Beach on Lincoln Road. The bus operates seven days a week from 6am to 11pm with buses running every 30 minutes between South Beach and MIA. The fare costs $2.35 and takes about 30 minutes to get from MIA to South Beach, and about 10 minutes from MIA to the Metrorail.[35] The Airport Flyer, along with all other MDT buses depart from the Ground Level of Concourse E.
To/from Tri-Rail, Broward and Palm Beach
Tri-Rail, Miami's commuter rail system serves MIA directly at the Miami Airport Station. Tri-Rail connects MIA to Metrorail, northern Miami-Dade, Fort Lauderdale, Broward County, and Palm Beach County up to West Palm Beach. Until September 12, 2011, Tri-Rail operates a shuttle which connects the rail station to MIA at the Ground Level of Concourse E. After September 12, 2011, the MIA Mover train opens, and allows for direct connections from the MIA terminals to the Miami Airport Station and Tri-Rail, with future connections to Amtrak, Metrorail, Greyhound Lines, the Rental Car Center and all other transit type (to be completed in 2012).
To/from Rental Car Center and Miami Central Station
MIA's newly-completed Rental Car Center has all of MIA's rental car companies (17 companies in total) under the same roof. White shuttles labeled 'Rental Car Shuttle' operate all day between the Rental Car Center and MIA's main terminal entrances. After September 12, 2011, the shuttles will be replaced with the MIA Mover train, which allows for direct connections from the MIA terminals to the Rental Car Center and the new Miami Central Station.[36]
Accidents and incidents
Airline accidents and incidents involving MIA include:
- On April 25, 1951 Cubana de Aviación Flight 493, a Douglas DC-4 en route from Miami, Florida to Havana, Cuba, collides in mid-air with a United States Navy Beech SNB-1 Kansan off Key West. All 43 aboard both aircraft are killed.
- On February 1, 1957, Miami-bound Northeast Airlines Flight 823 crashed on take-off from New York's LaGuardia Airport.
- On 2 October 1959, a Vickers Viscount of Cubana de Aviación was hijacked on a flight from José Martí International Airport, Havana to Antonio Maceo Airport, Santiago. The aircraft landed at Miami International Airport.[37]
- On January 6, 1960, National Airlines Flight 2511, a Douglas DC-6B bound from New York to Miami, crashes near Bolivia, North Carolina, when a bomb planted on board explodes in mid-air. All 34 people on board are killed.
- On 12 April 1960, All three crew and a passenger of a Vickers Viscount of Cubana de Aviación claimed political asylum after the aircraft landed at Miami International Airport.[38]
- On February 12, 1963, Northwest Orient Airlines Flight 705 crashed into the Everglades while en route from Miami to Portland, Oregon via Chicago O'Hare, Spokane, and Seattle.
- On June 23, 1969, a Dominicana Air Lines DC-4, en route to Santo Domingo was circling back to Miami International Airport with an engine fire when it crashed onto 36th Street. 5 dead; 7 injured.[39]
- On December 29, 1972, Eastern Air Lines Flight 401, a Lockheed L-1011, crashed into the Everglades. The plane had left JFK International Airport in New York City bound for Miami. (the subject of Hollywood movie, The Ghost Of Flight 401).
- On 15 January 1977, Douglas DC-3 N73KW of Air Sunshine crashed shortly after take-off on a domestic scheduled passenger flight to Key West International Airport, Florida. All 33 people on board survived.[40]
- On January 1, 1985 Eastern Air Lines Flight 980, a Boeing 727, crashed into the mountains in Bolivia. The plane originated in Asunción and was bound to Miami via La Paz, Bolivia and Guayaquil.
- On December 20, 1995, American Airlines Flight 965, a Boeing 757, crashed into a mountain while en route from Miami to Cali, Colombia.
- On May 11, 1996, ValuJet Flight 592, a DC-9, crashed into the Everglades after take-off from Miami en route to Atlanta.
- On October 2, 1996, Aeroperú Flight 603 crashed after takeoff from Lima, Peru. The flight, which originated in Miami, was continuing to Santiago, Chile.
- On August 7, 1997, Fine Air 101, a Douglas DC-8 cargo plane, crashed onto NW 72nd Avenue less than a mile (1.6 km) from the airport.
- On February 2, 1998, two Skyway Enterprises Shorts 330-200 aircraft (N2630A and N2629Y) were damaged beyond repair by a tornado at Miami International Airport. Both aircraft had to be written off. No one was injured.[41]
- On December 22, 2001, American Airlines Flight 63, en route from Paris to Miami, was the target of "shoe bomber" Richard Reid.
- On December 7, 2005, forty-four year old Rigoberto Alpizar, a passenger aboard American Airlines Flight 924, claimed to have a bomb in his carry-on luggage while boarding the flight's second leg to Orlando, Florida after arriving on a flight from Quito, Ecuador; the flight had just arrived from Medellín, Colombia. Federal air marshals reportedly shot and killed the man in the jetway of Gate D42 as he attempted to escape the plane after being confronted onboard, marking the first time an air marshal has fired a weapon on or near an airplane.
- On August 31, 2006, US Airways Flight 431 from Charlotte caught fire on the runway. All 118 passengers and crew on board were evacuated safely and there were no injuries. The fire occurred in the left wheel well of the 737 after the tires blew upon landing, and was extinguished with foam by firefighters. Passengers have stated that the plane was shaking violently as it landed.[42]
Satellite Transit Shuttle (STS) Accident:
- On November 28, 2008, the airport's automated people mover system overran its stop at Concourse E and crashed into a buffer at the end of the track, injuring five people.[43] The Miami Automated People Mover System is a Bombardier C-100 APM and was built in the late 1970s. Although it was scheduled for decommission in 2004, construction delays on the airport's North Terminal have resulted in continued operation of the system. In 2007, Bombardier expressed concerns about the safety of the system during a period of renewal of the operations and maintenance contract. In January 2008, Johnson Controls Inc was contracted to provide operations and maintenance for the system.[44] The south train has remained inoperative since the accident, leaving the satellite terminal reliant on the sole north train. Due to excessive down-time, poor maintenance, and the resulting crash of the South train, Miami-Dade County Aviation Department officially terminated its contract with Johnson Controls Inc on December 1, 2009 and took over the operation and maintenance of the system.
Military use
The Army Air Force began using Miami Airport in the 1930s, assigning the 21st Reconnaissance Squadron to the airfield to fly search and rescue along with weather reconnaissance patrols.
After the Pearl Harbor attack and the United States entry into World War II, the Air Force's use of the airport changed to being a base for antisubmarine patrols, with the airport becoming the Headquarters, for the 26th Antisubmarine Wing of the Army Air Forces Antisubmarine Command (AAFAC) from 20 November 1942 – 15 October 1943. The AAFAC flew antisubmarine patrols, searching for and attacking German U-Boats from the airport using B-18 Bolo and B-24 Liberator bombers specially equipped with RADAR.
After the war, Miami Airport became the home of numerous cargo and troop carrier units of the United States Air Force Reserve, the major one being the 435th Troop Carrier Group (later Wing), operating from the airport from July 1949 to February 1951, and again from December 1952 to December 1958.
See also
- Transportation in Miami
- Busiest airports in the United States by international passenger traffic
- Florida World War II Army Airfields
References
- ^ a b c d FAA Airport Master Record for MIA (Form 5010 PDF), effective 2007-10-25
- ^ "New airline could have famous name - Mass High Tech: The Journal of New England Technology:". http://www.bizjournals.com/masshightech/othercities/southflorida/stories/2008/04/14/story1.html?b=1208145600%5E1617931.
- ^ Miami Airport's rising international status | Centre for Asia Pacific Aviation - CAPA
- ^ Airports Council International - Passenger Traffic 2008 FINAL
- ^ anna.aero (27 April 2010). "Miami dominates US to Latin America and Caribbean". anna.aero Airline News & Analysis. http://www.anna.aero/2010/04/27/miami-dominates-us-to-latin-america-and-caribbean/.
- ^ http://www.miami-airport.com/pdfdoc/facts_at_a_glance.pdf
- ^ a b c d Petzinger, Thomas (1996). Hard Landing: The Epic Contest For Power and Profits That Plunged the Airlines into Chaos. Random House. ISBN 978-0-307-77449-1.
- ^ Bernstein, Aaron. Grounded: Frank Lorenzo and the Destruction of Eastern Airlines. Beard Books, 1999. p. 22. 22. Retrieved on August 28, 2009.
- ^ "United plans flight, staff cuts in Miami". January 23, 2004. http://www.bizjournals.com/southflorida/stories/2004/01/19/daily44.html.
- ^ Vasquez, Michael (10 January 2010). "Slot machines at Miami airport aren't dead yet". Miami, Florida: Miami Herald. pp. 37–39. http://www.miamiherald.com/news/breaking-news/story/1418406.html.
- ^ "Airport Fire Rescue Division". Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Department. Miami-Dade County. http://www.miamidade.gov/mdfr/airport.asp. Retrieved August 30, 2006.[dead link]
- ^ "Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Stations". Miami-Dade Fire Rescue Department. Miami-Dade County. http://www.miamidade.gov/MDFR/stations_units.asp. Retrieved August 30, 2006.[dead link]
- ^ [1] Where to Park
- ^ a b c d e f g h [2] Airport Terminal Gates
- ^ [3] Miami Airport Regional Commuter Facility Press Release
- ^ http://www.iflymia.com/pdfdoc/clips_Airports-Int%27l-New-MIA-section-12-10.pdf
- ^ North Terminal Development Miami International Airport
- ^ a b c Miami International Airport North Terminal (accessed July 29, 2011)
- ^ [4] Miami International Airport Skytrain
- ^ http://www.iflymia.com/PDFDOC/MIA_an_entire_new_facility.pdf
- ^ North Terminal Development Program Gantt Chart
- ^ Developers get wide range to roam for air terminal revamp
- ^ http://www.miamiherald.com/103/story/50030.html
- ^ http://pressroom.airtran.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=201565&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1629590&highlight=
- ^ TUI Nederland
- ^ http://www.baynews9.com/article/news/2011/november/339828/Delta-airlines-to-provide-chartered-flights-to-Cuba?cid=rss
- ^ http://www.naplesnews.com/news/2011/jun/16/exec-air-flights-naples-miami-begin-july-fourth/
- ^ http://www.miami-airport.com/pdfdoc/clip_iberia-barcelona.pdf
- ^ Lufthansa - Lufthansa to operate A380 on Miami route
- ^ http://miami-airport.com/pdfdoc/clip_TAP-begins-flights-to-MIA-in-2011.pdf
- ^ [5]
- ^ [6]
- ^ "Miami, FL: Miami International (MIA)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. July 2011. http://www.transtats.bts.gov/airports.asp?pn=1&Airport=MIA.
- ^ Airports Council International
- ^ http://www.miamidade.gov/transit/library/airport_flyer_brochure.pdf
- ^ Miami International Airport :: MIA Rental Car Center (RCC) :: Miami-Dade County
- ^ "Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. http://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19591002-0. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ "Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. http://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19600412-1. Retrieved 8 September 2009.
- ^ Miami, FL Plane Crashes On Street, June 1969 | GenDisasters ... Genealogy in Tragedy, Disasters, Fires, Floods
- ^ "N73KW Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. http://aviation-safety.net/database/record.php?id=19770115-2. Retrieved 4 August 2010.
- ^ Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 26 November 2006.
- ^ "Jetliner evacuated after fire in wheel well", CNN
- ^ Miami Herald "MIA train hits building; riders injured" 11/28/08
- ^ Award Recommendation for Maintenance of Satellite Transit Shuttle at Miami International Airport
Flying Training Flying Schools Eastern Flying Training Command · Central Flying Training Command · Western Flying Training CommandSpecialized Schools Bombardier · Contract Flying · Glider Training · Gunnery · Navigator
Technical Training Eastern Technical Training Command · Central Technical Training Command · Western Technical Training CommandMajor airports of the United States Atlanta (Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport – ATL) · Baltimore (Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport – BWI) · Boston (Logan International Airport – BOS) · Charlotte (Charlotte/Douglas International Airport – CLT) · Chicago (O'Hare International Airport – ORD) · Dallas-Fort Worth (Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport – DFW) · Denver (Denver International Airport – DEN) · Detroit (Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport – DTW) · Fort Lauderdale (Fort Lauderdale – Hollywood International Airport – FLL) · Honolulu (Honolulu International Airport – HNL) · Houston (George Bush Intercontinental Airport – IAH) · Las Vegas (McCarran International Airport – LAS) · Los Angeles (Los Angeles International Airport – LAX) · Miami (Miami International Airport – MIA) · Minneapolis – Saint Paul (Minneapolis-Saint Paul International Airport – MSP) · Newark (Newark Liberty International Airport – EWR) · New York (John F. Kennedy International Airport – JFK) · New York (LaGuardia Airport – LGA) · Orlando (Orlando International Airport – MCO) · Philadelphia (Philadelphia International Airport – PHL) · Phoenix (Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport – PHX) · Salt Lake City (Salt Lake City International Airport – SLC) · San Diego (San Diego International Airport – SAN) · San Francisco (San Francisco International Airport – SFO) · Seattle (Seattle–Tacoma International Airport – SEA) · Tampa (Tampa International Airport – TPA) · Washington, D.C. (Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport – DCA) · Washington, D.C. (Washington Dulles International Airport – IAD)
FedEx Corporation Established 1971Founder 
Subsidiaries
and DivisionsFedEx Express · FedEx Ground · FedEx Freight · FedEx Custom Critical · FedEx Office · FedEx Trade Networks · FedEx Supply Chain · FedEx Corporate Services · FedEx TechConnect ·Air hubs Memphis · Indianapolis · Anchorage · Oakland · Newark · Fort Worth · Miami · Paris · Guangzhou · Cologne · TorontoRelated Flying Tiger Line · American Freightways · Asia Airfreight · FedEx Institute of Technology · KIAC · FedEx Field · FedEx Racing · Cast Away
Annual Revenue: $34.7 billion USD (2010) · Employees: 290,000 (2010) · Stock Symbol: FDX · Website: fedex.com · Products: Freight Forwarding Services, Logistics ServicesCategories:
$34.7 billion USD (2010) · Employees: 290,000 (2010) · Stock Symbol: FDX · Website: fedex.com · Products: Freight Forwarding Services, Logistics ServicesCategories:- Airports in Florida
- Airports in Miami-Dade County, Florida
- Buildings and structures in Miami-Dade County, Florida
- USAAF Contract Flying School Airfields
- USAAF Eastern Technical Training Command
- Airfields of the United States Army Air Forces in Florida
- Transportation in Miami, Florida
- Airports established in 1928
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.