- Islam in England
-
Part of a series on
Islam by countryThe AmericasIslam in England is the largest non-Christian religion, with most Muslims being immigrants from South Asia (in particular Pakistan, Bangladesh and India) or descendants of immigrants from that region. Many others are from Muslim-dominated regions such as the Middle East, Afghanistan, Malaysia and Somalia, while fewer come from Equatorial African countries such as Nigeria, Uganda and Sierra Leone.[1]
According to the 2001 census, 1.54 million Muslims live in England and Wales, where they form 3.3% of the population. According to research by The Times, there were 2.4 million Muslims in the United Kingdom in 2009. In 2010, a study by the Pew Research Center argued that there were 2.869 million Muslims in Britain as a whole.[2]
Contents
History
See also: List of Arabic loanwords in EnglishMiddle Ages
See also: Islamic contributions to Medieval Europe A mancus / gold dinar of king Offa, copied from the dinars of the Abbasid Caliphate (774); it includes the Arabic text Muhammad is the Apostle of Allah, a line from the Shahada.
A mancus / gold dinar of king Offa, copied from the dinars of the Abbasid Caliphate (774); it includes the Arabic text Muhammad is the Apostle of Allah, a line from the Shahada.
Although Islam is generally thought of as being a recent arrival in England, there has been minor contact between the English and Muslims for many centuries. An early example would be the decision of Offa, the eighth-century King of Mercia (one of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms existing at that time), to have a coin minted with an Islamic inscription - largely a copy of coins issued by the contemporary Muslim ruler, Caliph Al-Mansur. It is thought[by whom?] that they may have been minted simply for prestige or to facilitate trade with the expanding Islamic empire in Spain, as Islamic gold dinars were the most important coinage in the Mediterranean at the time. Offa's coin looked enough like the original that it would be readily accepted in southern Europe, while at the same time his own name was clearly visible.[3] References to Britain are also found in early Islamic geographical literature, such as the 9th century work of Ahmad ibn Rustah (d. 910) which describes the islands of "Bratiniya".[4]
Muslim scholarship, especially early Islamic philosophy and Islamic science, was well-known through Latin translation among the learned in England by 1386, when Geoffrey Chaucer was writing. In the Prologue to the Canterbury Tales, there is among the pilgrims wending their way to Canterbury, a 'Doctour of Phisyk' whose learning included Rhazes (Al-Razi), Avicenna (Ibn Sina, Arabic ابن سينا) and Averroes (Ibn Rushd, Arabic ابن رشد). In the Pardoner's Tale, Chaucer mentions part Avicenna's work concerning poisons.[5] Avicenna's The Canon of Medicine (1025), in Latin translation, was a standard text for medical students up until the 18th century.[6] Roger Bacon, one of the earliest European advocates of the scientific method,[7] is known to have studied the works of several early Muslim philosophers.[8][9] In particular, his work on optics in the 13th century was influenced by the Book of Optics (1021) by Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen).[10]
Professor John Makdisi's "The Islamic Origins of the Common Law" in the North Carolina Law Review,[11] curiously suggested that English common law was inspired by medieval Islamic law.[12] Makdisi drew comparisons between the "royal English contract protected by the action of debt" and the "Islamic Aqd", the "English assize of novel disseisin" (a petty assize adopted in the 1166 at the Assizes of Clarendon) and the "Islamic Istihqaq", and the "English jury" and the "Islamic Lafif" in the classical Maliki school of Islamic jurisprudence, and argued that these institutions were transmitted to England by the Normans,[11] "through the close connection between the Norman kingdoms of Roger II in Sicily — ruling over a conquered Islamic administration — and Henry II in England."[13] Makdisi also argued that the "law schools known as Inns of Court" in England (which he asserts are parallel to Madrasahs) may have also originated from Islamic law, although they bear more similarity to the much closer-to-home Oxbridge Colleges (at which most students would have previously studied) and arose in concentration in Holborn after the clergy were forbidden to teach common law by the Pope, and law schools were banished from the City of London (their current location being between the old City and the courts at Westminster).[11] He states that the methodology of legal precedent and reasoning by analogy (Qiyas) are also similar in both the Islamic and common law systems, although the English practice arises from the methodology of Bracton, resulting in the subsequent publication of law reports.[14] Other legal scholars such as Monica Gaudiosi, Gamal Moursi Badr and A. Hudson have argued that the English trust and agency institutions, which were introduced by Crusaders, may have been adapted from the Islamic Waqf and Hawala institutions they came across in the Middle East.[15][16][17] Paul Brand also notes parallels between the Waqf and the trusts used to establish Merton College by Walter de Merton, who had connections with the Knights Templar, but Brand also points out that the Knights Templar were primarily concerned with fighting the Muslims rather than learning from them, making it less likely that they would imitate Muslim legal institutions.[12] Moreover, the "waqf" concept refers to a charitable designation of property whereas the introduction of trust law was a reaction to the failure of persons to whom crusaders conveyed their lands whilst on crusade to return the lands when the crusaders returned (as opposed to the charitable trust which would be used to found an academic institution and has its origin in Roman law).[citation needed] The conventional accepted view is that English law is a continuation of Anglo-Saxon law centuries earlier.[citation needed]
Early modern period
The first English convert to Islam mentioned by name is John Nelson.[18] 16th century writer Richard Hakluyt claimed he was forced to convert, though he mentions in the same story other Englishmen who had converted willingly.
- This king had a son which was a ruler in an island called Gerbi, whereunto arrived an English ship called the Green Dragon, of the which was master one M. Blonket, who, having a very unhappy boy on that ship, and understanding that whosoever would turn Turk should be well entertained of the a yeoman of our Queen's guard, whom the king's son had enforced to turn Turk; his name was John Nelson.[19]
Captain John Ward of Kent was one of a number of British sailors who became pirates based in the Maghreb who also converted to Islam (see also Barbary pirates). Later, some Unitarians became interested in the faith, and Henry Stubbes wrote so favourably about Islam that it is thought he too had converted to the faith.
From 1609 to 1616, England lost 466 ships to Barbary pirates, who sold the passengers into slavery in North Africa.[20] In 1625, it was reported that Lundy, an island in the Bristol Channel which had been a pirate lair for much of the previous half century, had been occupied by three Ottoman pirates who were threatening to burn Ilfracombe; Algerine rovers were using the island as a base in 1635, although the island had itself been attacked and plundered by a Spanish raid in 1633.[21] In 1627, Barbary pirates under command of the Dutch renegade Jan Janszoon operating from the Moroccon port of Salé occupied Lundy, before they were expelled by Sir John Pennington.[21][22] During this time there were reports of captured slaves being sent to Algiers and of the Islamic flag flying over Lundy.[23][24]
The Muslim Moors had a noticeable influence on the works of George Peele and William Shakespeare. Some of their works featured Moorish characters, such as Peele's The Battle of Alcazar and Shakespeare's The Merchant of Venice, Titus Andronicus and Othello, which featured a Moorish Othello as its title character. These works are said to have been inspired by several Moorish delegations from Morocco to Elizabethan England around 1600.[25] A portrait was painted of one of the Moorish ambassadors, Abd el-Ouahed ben Messaoud ben Mohammed Anoun, who had come to promote an Anglo-Moroccan alliance.
Turbans can be found in Renaissance England. While friendly relations were formed between England and the Islamic civilization of the Middle East in the early sixteenth century, Persian and Turkish style fashions were sometimes worn by the higher classes as a form of party or fancy dress. During times of interaction with Istanbul, Queen Elizabeth I of England wore Turkish clothing styles.[citation needed] It was believed that she favoured working with the Islamic sultans of Istanbul rather than the Roman Catholic leaders of Europe. These suspicions were heightened when she asked Sultan Murad III and his son Mohammad III for military assistance. Although she never did receive any assistance from the sultans, her relations with the Sultan and his son did not waver.[26]
In 17th-century England, there was a 'second wave' of interest in the study of Arabic science and Islamic philosophy. Arabic manuscripts were considered the key to a 'treasure house' of ancient knowledge, which led to the founding of Arabic chairs at Oxford and Cambridge Universities, where Arabic was taught. A large collection of Arabic manuscripts were acquired, collected in places such as the Bodleian Library at Oxford. These Arabic manuscripts were sought after by natural philosophers for their research in subjects such as observational astronomy or mathematics, and also encompassed subjects ranging from science, religion, and medicine, to typography and garden plants.[27]
Besides scientific and philosophical literature, works of Arabic fictional literature were also translated into Latin and English during the 17th and 18th centuries. The most famous of these was the One Thousand and One Nights (Arabian Nights), which was first translated into English in 1706 and has since then had a profound influence on English literature. Another famous work was Ibn Tufail's philosophical novel[28][29] Hayy ibn Yaqdhan, which was translated into Latin as Philosophus Autodidactus by Edward Pococke the Younger in 1671 and then into English by Simon Ockley in 1708. The English translation of Hayy ibn Yaqdhan, set on a desert island, may have inspired Daniel Defoe to write Robinson Crusoe, considered the first novel in English, in 1719.[30][31][32][33] Later translated literary works include Layla and Majnun and Ibn al-Nafis' Theologus Autodidactus.
By the time of Union with Scotland in 1707, only small numbers of Muslims were living in England. The first large group of Muslims to arrive, in the 18th century, were lascars (sailors) recruited from the Indian subcontinent (largely from the Bengal region) to work for the British East India Company, most of whom settled down and took local wives.[34] Due to the majority being lascars, the earliest Muslim communities were found in port towns. Naval cooks also came, many of them from the Sylhet Division of what is now Bangladesh. One of the most famous early Bengali Muslim immigrants to England was Sake Dean Mahomet, a captain of the British East India Company who in 1810 founded London's first Indian restaurant, the Hindoostane Coffee House. He is also reputed for introducing shampoo and therapeutic massage to the United Kingdom.[35] The practice of Islam in the United Kingdom was legalized by the Trinitarian Act 1812.
Demography and ethnic background
According to the 2001 census, 1,546,626 Muslims live in England and Wales,[36] where they then formed 3.3% of the population (although this figure does not include unregistered, or 'illegal' immigrants). According to The Times, there were 2.4 million Muslims in Britain as a whole as of January 2009.[37]
British Muslim population by Ethnic group (Source: 2001 Census[38]) Number of Muslims Muslims as % of ethnic group Ethnic group as % of Muslims White 179,733 0.4 11.6 White British 63,042 0.1 4.1 White Irish 890 0.1 <0.1 Other White 115,841 8.6 7.5 Mixed 64,262 9.7 4.2 White & Black Caribbean 1,385 0.6 0.1 White & Black African 10,523 13.3 0.7 White & Asian 30,397 16.1 2.0 Other Mixed 21,957 14.1 1.4 Asian or Asian British 1,139,065 50.1 73.7 Indian 131,662 12.7 8.5 Pakistani 657,680 92.0 42.5 Bangladeshi 261,776 92.5 16.8 Other Asian 90,013 37.3 5.8 Black or Black British 106,345 9.3 6.9 Black Caribbean 4,477 0.8 0.3 Black African 96,136 20.0 6.2 Other Black 5,732 6.0 0.4 Chinese 752 0.3 <0.1 Other Ethnic Group 56,429 25.7 3.7 Total 1,546,626 3.0 100 In England, 40 percent of Muslims live in London, where 607,083 identified as Muslim in 2001, out of a population of 7,172,091.[39] There are also large numbers of Muslims in Birmingham, Manchester, Bradford, Luton, High Wycombe, Slough, Leicester and the mill towns of Northern England.
The local authorities with a Muslim population greater than 10 percent were:
- London Borough of Tower Hamlets 36.4% 71,389
- London Borough of Newham 24.3% 59,293
- Blackburn with Darwen 19.4% 26,674
- City of Bradford 16.1% 75,188
- London Borough of Waltham Forest 15.1% 32,902
- Luton 14.6% 26,963
- Birmingham 14.3% 139,771
- High Wycombe 14.1%, 9,708
- London Borough of Hackney 13.8% 27,908
- London Borough of Enfield 13.5% 37,388
- Pendle 13.4% 11,988
- Slough 13.4% 15,897
- London Borough of Brent 12.3% 32,290
- London Borough of Redbridge 11.9% 28,487
- City of Westminster 11.8% 21,346
- London Borough of Camden 11.6% 22,906
- London Borough of Haringey 11.3% 24,371
- Metropolitan Borough of Oldham 11.1% 24,039
- Leicester 11.0% 30,885
- London Borough of Ealing 10.3% 31,033
- Kirklees 10.1% 39,312
Most large cities have one area that is a majority Muslim even if the rest of the city has a fairly small Muslims population; see, for example, Harehills in Leeds. In addition, it is possible to find small areas that are almost entirely Muslim: for example, Savile Town in Dewsbury.[40]
In September 2009, the ONS published information showing that Mohammed (or variations of it) was the third most popular boys' name in England and Wales.[41]
Ethnic groups
Bangladeshis
See also: British BangladeshiPeople of Bangladeshi descent are one of the largest Muslim communities (after Pakistanis), 16.8% of Muslims in England and Wales are of Bangladeshi descent, the ethnic group in the UK with the largest proportion of people following a single religion, being 92% Muslim.[42] Majority of these Muslim come from the Sylhet region of Bangladesh, mainly concentrated in Tower Hamlets, and Newham, in London, as well as in Luton, Birmingham and Oldham. The Bangladeshi Muslim community in London form 24% of the Muslim population, larger than any other ethnic group.[43]
Bangladeshi Muslim women in East London
Initial limited mosque availability meant that prayers were conducted in small rooms of council flats until the 1980s when more and larger facilities became available. Some synagogues and community buildings were turned into mosques and existing mosques began to expand their buildings. This process has continued down to the present day with the East London Mosque recently expanding into a large former car park where the London Muslim Centre is now used for prayers, recreational facilities and housing.[44][45] Most people regard themselves as part of the ummah, and their identity based on their religion rather than their ethnic group.[46] Cultural aspects of a 'Bengali Islam' are seen as superstition and as un-Islamic.[46] The identity is far stronger in comparison to the native land. Younger Bangladeshis are more involved in Islamist activities and movement groups, whereas the older generation practice with Islamic rituals mixed with the Bengali culture.[citation needed] Many Bangladeshi women wear the burqa and many young women or girls also wear the headscarf.[citation needed]
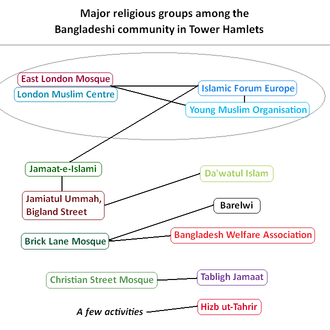
There are groups which are active throughout Bangladeshi communities such as The Young Muslim Organization. It is connected to the Islamic Forum Europe, associated with the East London Mosque and the London Muslim Centre – all of which have connections with the Bangladesh Islamic party, the Jamaat-e-Islami (linked with some community mosques, which also linked with the Dawat-e-Islami).[citation needed] Other groups also attract a few people, the Hizb ut-Tahrir – which calls for the Khilafah (caliphate) and influences by publishing annual magazines, and lectures through mainly political concepts,[47] and the other which is a movement within Sunni Islam is the Salafi – who view the teachings of the first generations as the correct one,[48] and appeals to younger Muslims as a way to differentiate themselves towards their elders.[44][49] Other large groups include another Sunni movement, the Barelwi – mainly of a Fultoli movement (led by Abdul Latif Chowdhury in Bangladesh), and the Tablighi Jamaat – which is a missionary and revival movement,[50] and avoids political attention. All these groups work to stimulate Islamic identity among local Bengalis or Muslims and particularly focus on the younger members of the communities.[45][51][52]
Indians
See also: British Indian8% of Muslims in England and Wales are of Indian descent, especially those who are from Gujarat, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Kerala. The Gujarati Muslims from Surat and Bharuch districts in India started to arrive from the 1930s, settling in the towns of Dewsbury and Batley in Yorkshire and parts of Lancashire. There are large numbers of Gujarati Muslims in Dewsbury, Blackburn, Bolton, Preston and in the London Boroughs of Newham, Waltham Forest and Hackney. Immigration of Muslims into UK, was primarily started off by Indians during the colonial rule.
Nigerians
See also: Nigerian BritishThere are also a number of Muslim immigrants in England that arrived from Nigeria. Nigerian Muslims in the UK are represented by several community organizations, including the Nigeria Muslim forum, which is affiliated with the Council of Nigerian Muslim Organisations in UK and Ireland (CNMO) and the Muslim Council of Britain (MCB).[53]
Pakistanis
See also: British PakistanisThe single largest group of Muslims in England and Wales are of Pakistani descent. Pakistanis from Mirpur District were one of the first South Asian Muslim communities to permanently settle in the United Kingdom, arriving in Birmingham and Bradford in the late 1930s. Immigration from Mirpur grew from the late 1950s, accompanied by immigration from other parts of Pakistan especially from Punjab which included cities like Sialkot, Jhelum, Gujar Khan and Gujrat and also from the north-west Punjab including the chhachhi pathans from Attock District, and some from villages of Ghazi, Nowshera and Peshwar. People of Pakistani extraction are particularly notable in West Midlands, West Yorkshire, Lancashire/Greater Manchester, and industrial towns in South East England like Luton, Slough, High Wycombe and Oxford.
Somalis
See also: Somalis in the United KingdomThe United Kingdom, with 43,532 Somali-born residents in 2001,[54] and an estimated 101,000 in 2008,[55] is home to the largest Somali community in Europe. A 2009 estimate by Somali community organisations puts the Somali population figure at 90,000 residents.[56] Although most Somalis in the UK are recent arrivals, the first Somali immigrants were seamen and traders who arrived and settled in port cities in the late 19th century.[56] Established Somali communities are found in London, Liverpool (estimated between 4,000 and 7,000 to 9,000[57][58]), Cardiff and Bristol, and newer ones have formed in Manchester, Sheffield and Leicester.[59][60] The Somali community has set up many mosques in the UK and especially London, where it has built large masjids in Hayes and Southall.
White (European)
In addition, there are groups of Muslims from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, and Turkey. There are almost 200,000 Muslims who described themselves as 'white' in the 2001 census.
Views on Terrorism
In March 2010, a historic Fatwa against terrorism was pronounced by a leading scholar in London.
Position in society
Poverty
According to analysis based on the 2001 census, Muslims in England face poor standards of housing, poorer levels of education and are more vulnerable to long-term illness,[61] and that Muslims in the UK had the highest rate of unemployment, the poorest health, the most disability and fewest educational qualifications among religious groups.[62] The figures were, to some extent, explained by the fact that Muslims were the least well-established group, having the youngest age profile.[62] There is also a growing substantial British Muslim business community, led by multi-millionaires such as Sir Anwar Pervez.[63]
Discrimination
See also: IslamophobiaThere have been cases of threats,[64] one alleged fatal attack,[65] and non-fatal attacks on Muslims and on Muslim targets, including attacks on Muslim graves[66] and mosques.[67] In January 2010, a report from the University of Exeter's European Muslim Research Centre noted that the number of anti-Muslim hate crimes has increased, ranging from "death threats and murder to persistent low-level assaults, such as spitting and name-calling," for which the media and politicians have been blamed with fueling anti-Muslim hatred.[68][69][70]
The British media has been criticised for propagating negative stereotypes of Muslims and fueling anti-Muslim prejudice.[71] In 2006, British cabinet ministers were criticised for helping to "unleash a public anti-Muslim backlash" by blaming the Muslim community over issues of integration despite a study commissioned by the Home Office on white and Asian-Muslim youths demonstrating otherwise: that Asian-Muslim youths "are in fact the most tolerant of all" and that white British youths "have far more intolerant attitudes," concluding that intolerance from the white British community was a greater "barrier to integration."[72][73] Another survey by Gallup in 2009 also found that the Muslim community claimed to feel more patriotic about Britain than the general British population,[74][75] while another survey found that Muslims assert that they support the role of Christianity in British life more so than Christians themselves.[76] In January 2010, the British Social Attitudes Survey found that the general British public "is far more likely to hold negative views of Muslims than of any other religious group," with "just one in four" feeling "positively about Islam," and a "majority of the country would be concerned if a mosque was built in their area, while only 15 per cent expressed similar qualms about the opening of a church."[77] The "scapegoating" of Muslims by the media and politicians in the 21st century has been compared in the media to the rise of antisemitism in the early 20th century.[78]
English Defence League (EDL)
In the year 2009, a far-right and anti-Muslim[79][80][81] group called the English Defence League (EDL) formed a street protest movement which opposes the alleged spread of Islamism, Sharia law and Islamic extremism in England, and also opposes immigration.[82][83][84][85] The EDL uses street marches to protest against Islamic extremism.[86][87] At many of their gatherings, EDL members have clashed with counter-demonstrators, including supporters of Unite Against Fascism (UAF).[88]
Mosques
 Baitul Futuh Mosque of the "Ahmadiyya Muslim Community", London. The largest Mosque in Western Europe.[89]
Baitul Futuh Mosque of the "Ahmadiyya Muslim Community", London. The largest Mosque in Western Europe.[89]
- Shah Jahan Mosque in Woking, Surrey was the first purpose built mosque in Britain
- Baitul Futuh Mosque of the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community (AMJ), London
- Fazl Mosque The first mosque in London, built in 1926 - AMJ
- Markazi mosque in Dewsbury
- Manchester Central Mosque
- Al-Rahma mosque in Liverpool
- Birmingham Central Mosque
- East London Mosque
- Leeds Grand Mosque
- Finsbury Park Mosque in London
- London Central Mosque
- London Markaz
- Medina Mosque in Sheffield
- Darul Barakaat Mosque in Birmingham - AMJ
- Al Mahdi Mosque in Bradford - AMJ
Activities
The East London Mosque organises an annual programme to attract people to its services which include ICT training, English classes, a Junior Muslim Circle, Saturday Halaqa (Islamic talks) and Madrasahs. According to the mosque, involvement in its activities has increased and it notes that: the five daily prayers have increased. Especially during Friday Jummah prayers, where it was difficult to accommodate the increasing number of people. During Ramadan, the prayer facilities attracted between 4,000 to 5,000 people every day. Much of these works by the people, show Islamic identity among the Muslims is increasingly rising due to many Islamic groups and facilities available throughout the communities in the UK.[90]
The Baitul Futuh Mosque organises several events to serve Muslims and the wider community. Other than holding regular prayers, its services to the wider community include annual Peace Conferences, School tours and community events such as hosting the BBC Radio 4 Any Questions?[91] and the 'Merton Youth Partnership Annual Conference.'[92] The Baitul Futuh Mosque has also been acting as the centre for the 'Loyalty, Freedom and Peace Campaign'[93] in order for the west to recognize Islam as a peaceful religion and to improve the Integration of Muslims and Non-Muslims.
Notable English muslims
- Rowland Allanson-Winn, 5th Baron Headley
- Sir Charles Edward Archibald Watkin Hamilton, 5th Baronet
- Faris Glubb
- Abdul-Aziz ibn Myatt
- Marmaduke Pickthall
- William Abdullah Quilliam
- Henry Stanley, 3rd Baron Stanley of Alderley
- Ahmad Thomson
- Timothy Winter
See also
- Islam in Northern Ireland
- Islam in Scotland
- Islam in Wales
- Islam by country
- Muslims in Western Europe
- Religion in the United Kingdom
- The Muslim Weekly
- British Muslims
- British Bangladeshi Muslims
- Islam in London
- English Defence League
Literature
- Lewis, Philip: Islamic Britain: religion, politics and identity among British Muslims; Bradford in the 1990s, London: Tauris, 1994. ISBN 1-85043-861-7
- Matar, Nabil Turks, Moors, and Englishmen in the Age of Discovery, Columbia University Press, 2000. ISBN 0-231-11015-4
References
- ^ Born Abroad - Countries of birth, BBC, 2005-09-07, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/shared/spl/hi/uk/05/born_abroad/countries/html/overview.stm?1a_total01_des, retrieved 2008-02-16
- ^ Muslim Networks and Movements in Western EuropePew Research Center, ANALYSIS September 15, 2010
- ^ Gold imitation dinar of Offa, British Museum
- ^ Bernard Lewis (1957), "The Muslim Discovery of Europe", Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies (Cambridge University Press) 20 (1/3): 409–416 [410], doi:10.1017/S0041977X00061954, JSTOR 610392
- ^ Chaucer The Canterbury Tales Harmondsworth Penguin 1951 p280 and note p522
- ^ Ziauddin Sardar, Science in Islamic philosophy
- ^ Randall Noon (1992), Introduction to Forensic Engineering, CRC Press, ISBN 9780849381027, ISSN 0849381029, http://books.google.com/?id=ru_E__W7euUC&pg=PA39&dq=roger-bacon+scientific-method
- ^ Glick, Thomas F.; Livesey, Steven John; Wallis, Faith: Medieval Science, Technology, and Medicine: An Encyclopedia, first edition, Routledge, 29 September 2005, ISBN 978-0415969307
- ^ Moorstein, Mark: Frameworks: Conflict in Balance, page 237, iUniverse, Inc., 9 June 2004, 308 pp, ISBN 978-0595318247
- ^ Lindberg, David C. (1996), Roger Bacon and the Origins of Perspectiva in the Middle Ages, Clarendon Press, p. 11
- ^ a b c (Makdisi 1999)
- ^ a b Mukul Devichand (24 September 2008), Is English law related to Muslim law?, BBC News, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/magazine/7631388.stm, retrieved 2008-10-05
- ^ Hussain, Jamila (2001), "Book Review: The Justice of Islam by Lawrence Rosen", Melbourne University Law Review 30
- ^ El-Gamal, Mahmoud A. (2006), Islamic Finance: Law, Economics, and Practice, Cambridge University Press, p. 16, ISBN 0521864143
- ^ Gaudiosi, Monica M. (April 1988), "The Influence of the Islamic Law of Waqf on the Development of the Trust in England: The Case of Merton College", University of Pennsylvania Law Review 136 (4): 1231–1261, doi:10.2307/3312162, JSTOR 3312162
- ^ Badr, Gamal Moursi (Spring, 1978), "Islamic Law: Its Relation to Other Legal Systems", The American Journal of Comparative Law 26 (2 – Proceedings of an International Conference on Comparative Law, Salt Lake City, Utah, February 24–25, 1977): 187–198 [196–8], doi:10.2307/839667, JSTOR 839667
- ^ Hudson, A. (2003), Equity and Trusts (3rd ed.), London: Cavendish Publishing, p. 32, ISBN 1-85941-729-9
- ^ [/religion/religions/islam/history/uk_1.shtml BBC]
- ^ Voyager's Tales, 3, The voyage made to Tripolis in Barbary,1584, Richard Haklyut
- ^ Rees Davies, British Slaves on the Barbary Coast, BBC, 1 July 2003
- ^ a b History of Lundy
- ^ Konstam, Angus (2008), Piracy: the complete history, Osprey Publishing, p. 91, ISBN 9781846032400, http://books.google.com/books?id=USiyy1ZA-BsC&pg=PA91, retrieved 2011-04-15
- ^ de Bruxelles, Simon (2007-02-28), "Pirates who got away with it", Study of sails on pirate ships (London), http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/africa/article1449736.ece, retrieved 2007-11-25
- ^ Davies, Norman (1996), "Europe a History", Norman Davis, ISBN 9780198201717, http://books.google.com/?id=jrVW9W9eiYMC&pg=PA561&lpg=PA561&dq=barbary+lundy, retrieved 2007-11-25
- ^ Professor Nabil Matar (April 2004), Shakespeare and the Elizabethan Stage Moor, Sam Wanamaker Fellowship Lecture, Shakespeare's Globe Theatre (cf. Mayor of London (2006), Muslims in London, pp. 14-15, Greater London Authority)
- ^ Nabil I. Matar, "Renaissance England and the Turban."
- ^ G. A. Russell (1994), The 'Arabick' interest of the natural philosophers in seventeenth-century England, Brill Publishers, ISBN 9004098887
- ^ Jon Mcginnis, Classical Arabic Philosophy: An Anthology of Sources, p. 284, Hackett Publishing Company, ISBN 0872208710.
- ^ Samar Attar, The Vital Roots of European Enlightenment: Ibn Tufayl's Influence on Modern Western Thought, Lexington Books, ISBN 0739119893.[1]
- ^ Nawal Muhammad Hassan (1980), Hayy bin Yaqzan and Robinson Crusoe: A study of an early Arabic impact on English literature, Al-Rashid House for Publication.
- ^ Cyril Glasse (2001), New Encyclopedia of Islam, p. 202, Rowman Altamira, ISBN 0759101906.
- ^ Amber Haque (2004), "Psychology from Islamic Perspective: Contributions of Early Muslim Scholars and Challenges to Contemporary Muslim Psychologists", Journal of Religion and Health 43 (4): 357-377 [369].
- ^ Martin Wainwright, Desert island scripts, The Guardian, 22 March 2003.
- ^ Fisher, Michael Herbert (2006), Counterflows to Colonialism, Orient Blackswan, pp. 111–9, 129–30, 140, 154–6, 160–8, 181, ISBN 8178241544
- ^ Curry house founder is honoured, BBC News, 29 September 2005, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/london/4290124.stm, retrieved 2008-10-09
- ^ "England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 13 February 2010. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/census2001/profiles/727.asp.
- ^ Kerbaj, Richard. Muslim population 'rising 10 times faster than rest of society', The Times, January 30, 2009.
- ^ Ethnic Group by Religion
- ^ Muslims in London, Greater London Authority, October 2006, accessed November 21, 2009.
- ^ ^ http://www.kirklees-pct.nhs.uk/fileadmin/documents/meetings/march_07/KPCT-07-42%20Report%20estate%20strategy.doc paragraph 4.3
- ^ Max Hastings (11 September 2009). "Mohammed is now the third most popular boy's name in England. So why this shabby effort to conceal it?". London: The Daily Mail. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/debate/columnists/article-1212368/Mohammed-popular-boys-England-So-shabby-effort-conceal-it.html. Retrieved 17 September 2010.
- ^ "Ethnicity and identity". National Statistics. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/CCI/nugget.asp?ID=1089&Pos=2&ColRank=2&Rank=768. Retrieved 2008-07-21.
- ^ "2001 Census Profiles: Bangladeshis in London" (PDF). Greater London Authority. http://www.london.gov.uk/gla/publications/factsandfigures/DMAG-Briefing2004-16-2001CensusProfilesBangladeshisinLondon.pdf. Retrieved 2004-08-01.[dead link]
- ^ a b "Bangladeshi Diaspora in the UK: Some observations on socio-culturaldynamics, religious trends and transnational politics" (PDF). University of Surry. http://www.surrey.ac.uk/Arts/CRONEM/SOASBangladeshi%20diaspora%20PaperDRAFT-7June2005.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-03.
- ^ a b "bdirectory: Islamist politics among Bangladeshis in the UK". David Garbin – Cronem, University of Surrey. http://www.bdirectory.co.uk/index.php?id=190l. Retrieved 2008-07-27.
- ^ a b "Genetics, Religion and Identity: A Study of British Bangladeshis – 2004-2007" (PDF). School of Social Sciences – Cardiff University – funded by the Economic and Social Research Council. http://www.cardiff.ac.uk/socsi/resources/wrkgpaper-93.pdf. Retrieved 2008-09-15.
- ^ "Draft Constitution by Hizb ut-Tahrir". The Media office of Hizb-ut-Tahrir. http://www.hizb-ut-tahrir.info/english/constitution.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-16.[dead link]
- ^ "Compendium of Muslim texts – Volume 3, Book 48, Number 819". University of Southern California. http://www.usc.edu/dept/MSA/fundamentals/hadithsunnah/bukhari/048.sbt.html#003.048.819. Retrieved 2008-08-16.
- ^ The Next Attack, By Daniel Benjamin Steven Simon, ISBN 0-80507941-6 – Page 55
- ^ M. Jawed Iqbal; Mufti Ebrahim Desai (9 June 2007), Inviting to Islam, www.askimam.org, http://www.askimam.org/fatwa/fatwa.php?askid=02baa777b4211ddad49f0b5256de3934, retrieved 2008-08-16
- ^ "East London Mosque and London Muslim Centre". East London Mosque. http://www.eastlondonmosque.org.uk/. Retrieved 2008-07-26.
- ^ "Bangladeshis in east London: from secular politics to Islam". Delwar Hussain – openDemocracy: free thinking for the world. http://www.opendemocracy.net/democracy-protest/bangladeshi_3715.jsp. Retrieved 2008-07-27.
- ^ Nigeria Muslim Forum UK
- ^ "Country-of-birth database". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. http://www.oecd.org/dataoecd/18/23/34792376.xls. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ^ "Table 1.3: Estimated population resident in the United Kingdom, by foreign country of birth, 60 most common countries of birth, January 2008 to December 2008". Office for National Statistics. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/downloads/theme_population/Population-by-country-of-birth-and-nationality-Jan08-Dec08.zip. Retrieved 2009-10-04. Figure given is the central estimate. See the source for 95 per cent confidence intervals.
- ^ a b Dissanayake, Samanthi (2008-12-04). "British Somalis play politics from afar". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/7747162.stm. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ^ http://www.liverpoolpct.nhs.uk/Library/Impact/IA0073.doc
- ^ "Integration of the Somali Community into Europe". Federation of Adult Education Associations. http://www.faea.es/english/oralidad.php. Retrieved 3 February 2010.
- ^ Casciani, Dominic (2006-05-30). "Somalis' struggle in the UK". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/magazine/5029390.stm. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ^ "Born abroad: Somalia". BBC News. 2005-09-07. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/shared/spl/hi/uk/05/born_abroad/countries/html/somalia.stm. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ^ "Muslim hardship under spotlight". BBC News. 14 May 2006. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/4771233.stm. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ^ a b John Carvel (12 October 2004). "Census shows Muslims' plight". London: The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/society/2004/oct/12/religion.news. Retrieved 17 June 2010.
- ^ http://www.islamictimes.co.uk/content/view/180/7
- ^ Muslims threatened after bombings BBC News 12 July 2005
- ^ Vikram Dood (13 July 2005), "Islamophobia blamed for attack", The Guardian (London), http://www.guardian.co.uk/uk/2005/jul/13/race.july7, retrieved 2010-04-04
- ^ Muslim graves damaged in cemetery BBC News, 2 November 2006
- ^ Muslim teenager stabbed during attack on UK mosque, Arabic News, 10/3/2006, http://www.arabicnews.com/ansub/Daily/Day/061003/2006100304.html, retrieved 2010-04-04
- ^ Vikram Dood (28 January 2010), "Media and politicians 'fuel rise in hate crimes against Muslims'", The Guardian (London), http://www.guardian.co.uk/uk/2010/jan/28/hate-crimes-muslims-media-politicians, retrieved 2010-04-04
- ^ Jonathan Githens-Mazer & Robert Lambert (28 January 2010), "Muslims in the UK: beyond the hype", The Guardian (London), http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/belief/2010/jan/28/muslims-media-hate-crimes, retrieved 2010-04-04
- ^ Dr. Jonathan Githens-Mazer & Dr. Robert Lambert, Islamophobia and Anti-Muslim Hate Crime: a London Case Study, University of Exeter, http://centres.exeter.ac.uk/emrc/publications/Islamophobia_and_Anti-Muslim_Hate_Crime.pdf, retrieved 2010-04-08
- ^ Richardson, John E. (2004), (Mis)representing Islam: the racism and rhetoric of British broadsheet newspapers, John Benjamins Publishing Company, ISBN 9027226997, http://books.google.com/?id=WanqiF2XULsC&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q=
- ^ Vikram Dood (21 October 2006), "White pupils less tolerant, survey shows", The Guardian (London), http://www.guardian.co.uk/uk/2006/oct/21/schools.religion, retrieved 2010-04-04
- ^ Muslim students 'more tolerant', BBC News, 11 October 2006, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/lancashire/6033155.stm, retrieved 2010-04-05
- ^ Ian Dunt (7 May 2009), Muslims more patriotic than Brits, Politics, http://www.politics.co.uk/news/equality/muslims-more-patriotic-than-brits-$1293822.htm, retrieved 2010-04-05
- ^ Poll: European Muslims more patriotic than average populace, Deutsche Presse-Agentur, 07/05/2009, http://www.haaretz.com/hasen/spages/1083892.html, retrieved 2010-04-05
- ^ Nick Allen (24 February 2009), "79 per cent of Muslims say Christianity should have strong role in Britain", The Daily Telegraph (London), http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/newstopics/religion/4799345/79-per-cent-of-Muslims-say-Christianity-should-have-strong-role-in-Britain.html, retrieved 2010-04-05
- ^ "Britain divided by Islam, survey finds", The Daily Telegraph (London), 11 Jan 2010, http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/newstopics/religion/6965276/Britain-divided-by-Islam-survey-finds.html, retrieved 2010-04-04
- ^ The Times: Fascism fears: John Denham speaks out over clashes
- ^ Patalong, Frank (25 July 2011). "Anders Breivik's Roots in Right-Wing Populism". Der Spiegel. http://www.spiegel.de/international/europe/0,1518,776413,00.html.
- ^ Bevanger, Lars (24 October 2010). "Anti-Muslim groups gain ground in Britain and across Europe". Deutsche Welle. http://www.dw-world.de/dw/article/0,,6140343,00.html.
- ^ "Anti-Muslim extremists plan Scots protest". The Scotsman. 17 September 2009. http://www.scotsman.com/news/anti_muslim_extremists_plan_scots_protest_1_775373.
- ^ "EDL Goons on Newsnight, part2". Newsnight. BBC. BBC2, London. 12 October 2009. 1:26 minutes in.
- ^ O'Brien, Paraic (12 October 2009). "Under the skin of English Defence League". BBC Newsnight. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/programmes/newsnight/8303786.stm.
- ^ Timesonline.co.uk[dead link]
- ^ Maryam Namazie. "Guardian.co.uk". Guardian.co.uk. http://www.guardian.co.uk/law/2010/jul/05/sharia-law-religious-courts. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Booth, Robert; Jones, Sam (11 August 2009). "'Defence league' recruiting football fans to march against Islamic extremism". The Guardian (London). http://guardian.co.uk/football/2009/aug/10/english-violence-militant-football-islamist.
- ^ Walker, Jonathan (26 August 2009). "MP opposes rally ban despite violence fears". Birmingham Post. http://birminghampost.net/news/politics-news/2009/08/26/mp-opposes-rally-ban-despite-violence-fears-65233-24531567.
- ^ Gunning, Dave (2010). Race and Antiracism in Black British and British Asian Literature. Liverpool University Press. pp. 151–152.
- See also: Morey, Peter; Yaqin, Amina. (2011). Framing Muslims: Stereotyping and Representation After 9/11. Harvard University Press. p. 215.
- ^ "Western Europe's largest mosque opens in Morden". The Guardian (London). 2003-10-02. http://www.guardian.co.uk/uk/2003/oct/02/religion.world.
- ^ "ELM Newsletter 2007" (PDF). East London Mosque. http://www.eastlondonmosque.org.uk/uploadedImage/pdf/Newsletter_2007.pdf. Retrieved 2008-07-26.[dead link]
- ^ http://www.prnewswire.co.uk/cgi/news/release?id=275738
- ^ http://www.mertonconnected.com/MYP-conference-2009
- ^ http://www.ekklesia.co.uk/node/11041
External links
- Ranking of Local Authorities in England and Wales according to percentage of Muslim population in the 2001 census
- Reassessing what we collect website – Muslim London History of Muslim London with objects and images
- Private Arrangements: Recognizing sharia in Britain - anthropologist John R. Bowen explores Islamic courts in England
Islam in Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.