- Anglo-Saxons
-
The parade helmet found at Sutton Hoo, probably belonging to Raedwald of East Anglia circa 625. Based on a Roman parade-helmet design (of a general class known as spangenhelm), it has decorations like those found in contemporary Swedish helmets found at Old Uppsala (Collection of the British Museum)

Anglo-Saxon is a term used by historians to designate the Germanic tribes who invaded the south and east of Great Britain beginning in the early 5th century AD, and the period from their creation of the English nation to the Norman conquest. The Anglo-Saxon Era denotes the period of English history between about 550 and 1066 AD.[1][2] The term is also used for the language now called Old English, spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons and their descendants in much of what is now England and some of southeastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century.[3]
The Benedictine monk, Bede, writing in the early 8th century, identified the English as the descendants of three Germanic tribes:[4]
- The Angles, who may have come from Angeln (in modern Germany); Bede wrote that their whole nation came to Britain,[5] leaving their former land empty. The name England (Old English: Engla land or Ængla land) originates from this tribe.[6]
- The Saxons, from Lower Saxony (in modern Germany; German: Niedersachsen) and the Low Countries.
- The Jutes, possibly from the Jutland peninsula (in modern Denmark; Danish: Jylland).
Their language, Old English, derived from "Ingvaeonic" West Germanic dialects and transformed into Middle English from the 11th century. Old English was divided into four main dialects: West Saxon, Mercian, Northumbrian and Kentish.
Contents
Etymology
The term Anglo-Saxon is from writings going back to the time of King Alfred the Great, who seems to have frequently used the title rex Anglorum Saxonum or rex Angul-Saxonum (king of the English Saxons).[7]
The Old English terms ænglisc and Angelcynn ("Angle-kin", gens Anglorum) when they are first attested had already lost their original sense of referring to the Angles, as distinct from, the Saxons, and in their earliest recorded sense refers to the nation of Germanic peoples who settled eastern Britain in and after the 5th century.[citation needed]
The indigenous British people, who wrote in both Latin and Welsh, referred to these invaders as Saxones or Saeson – the latter is still used today in the Welsh word for English people;[8] in the Scottish Gaelic word for English people, Sasannach; and in the Irish word for English people, Sasanach.
The term Angli Saxones seems to have first been used in continental writing nearly a century before Alfred's time by Paul the Deacon, historian of the Lombards, probably to distinguish the English Saxons from the continental Saxons (Ealdseaxe, literally, "old Saxons").[citation needed]
The Angles (Old English Engle, Angle) presumably took their name from their ancestral home in Jutland, Angul (modern Angeln), an area shaped like a hook (cf. Old English angel, angul "fishhook", anga "hook").
Anglo-Saxon history
The history of Anglo-Saxon England broadly covers early medieval England from the end of Roman rule and the establishment of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms in the 5th century until the Conquest by the Normans in 1066.
Origins (AD 400–600)
Migration of Germanic peoples to Britain from what is now northern Germany, the northern part of the Netherlands and southern Scandinavia is attested from the 5th century (e.g. Undley bracteate). Based on Bede's Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum, the intruding population is traditionally divided into Angles, Saxons, and Jutes, but their composition was likely less clear-cut and may also have included Frisians and Franks. Also, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle contains text that may be the first recorded indications of the movement of these Germanic tribes to Britain.
Heptarchy (600–800)
Christianisation of the Anglo-Saxons began in 597 and was at least nominally completed in 686. Throughout the 7th and 8th centuries, power fluctuated between the larger kingdoms. Bede records Aethelbert of Kent as being dominant at the close of the 6th century, but power seems to have shifted northwards to the kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria.
Aethelbert and some of the later kings of the other kingdoms were recognised by their fellow kings as Bretwalda (ruler of Britain). The so-called 'Mercian Supremacy' dominated the 8th century, though again it was not constant. Aethelbald and Offa, the two most powerful kings, achieved high status. This period has been described as the Heptarchy, though this term has now fallen out of academic use.
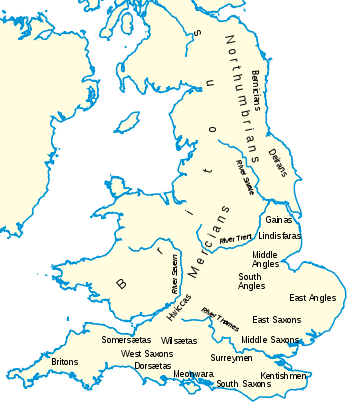
The word arose on the basis that the seven kingdoms of Northumbria, Mercia, Kent, East Anglia, Essex, Sussex and Wessex were the main polities of south Britain. More recent scholarship has shown that theories of the 'heptarchy' are not grounded in evidence, and it is far more likely that power fluctuated between many more 'kingdoms'. Other politically important 'kingdoms' across this period include: Hwicce, Magonsaete, Kingdom of Lindsey and Middle Anglia.
Viking Age and the Norman Conquest (800–1066)
In the 9th century, the Viking challenge grew to serious proportions. Alfred the Great's victory at Edington, Wiltshire, in 878 brought intermittent peace, but with their possession of Jorvik, the Danes gained a solid foothold in England.
An important development in the 9th century was the rise of the Kingdom of Wessex; by the end of his reign Alfred was recognised as overlord by several southern kingdoms. Æthelstan was the first king to achieve direct rule over what is considered "England".
Near the end of the 10th century, there was renewed Scandinavian interest in England, with the conquests of Sweyn of Denmark and his son Cnut the Great. By 1066 there were three lords with claims to the English throne, resulting in two invasions and the battles of Stamford Bridge and Hastings. The latter, which heralded the Norman conquest of England, resulted in the overthrow of the Anglo-Saxon polity and its replacement with Norman rule.
After the Norman Conquest
Following the conquest, the Anglo-Saxon nobility were either exiled or joined the ranks of the peasantry.[9] It has been estimated that only about 8 per cent of the land was under Anglo-Saxon control by 1087.[10] Many Anglo-Saxon nobles fled to Scotland, Ireland, and Scandinavia.[11][12] The Byzantine Empire became a popular destination for many Anglo-Saxon soldiers, as the Byzantines were in need of mercenaries.[13] The Anglo-Saxons became the predominant element in the elite Varangian Guard, hitherto a largely Scandinavian unit, from which the emperor's bodyguard was drawn and continued to serve the empire until the early 15th century.[14] However, the population of England at home remained largely Anglo-Saxon; for them, little changed immediately except that their Anglo-Saxon lord was replaced by a Norman lord.[15]
Culture
Architecture
Early Anglo-Saxon buildings in Britain were generally simple, not using masonry except in foundations but constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. Generally preferring not to settle within the old Roman cities, the Anglo-Saxons built small towns near their centres of agriculture, at fords in rivers or sited to serve as ports. In each town, a main hall was in the centre, provided with a central hearth.[16]
There are few remains of Anglo-Saxon architecture, with but one secular work remaining above ground – a 10m. x 5m. houscarl's dwelling re-using local Roman materials.[where?] This is still completely standing as an undivided single room with a single central north-facing door, belonging to the Godwin estates, so can be dated 1018–1066. At least fifty churches are of Anglo-Saxon origin, with many more claimed to be, in part from their dedication to local Anglo-Saxon saints, although in some cases the Anglo-Saxon part is small and much-altered. All surviving churches, except one timber church, are built of stone or brick and in some cases show evidence of re-used Roman work.
The character of Anglo-Saxon ecclesiastical buildings ranges from Celtic influenced architecture in the early period; basilica influenced Romanesque architecture; to in the later Anglo-Saxon period, an architecture characterised by pilaster-strips, blank arcading, baluster shafts and triangular headed openings.
Art
Anglo-Saxon art before roughly the time of Alfred (ruled 871–899) is mostly in varieties of the Hiberno-Saxon or Insular style, a fusion of Anglo-Saxon and Celtic techniques and motifs. The Sutton Hoo treasure is an exceptional survival of very early Anglo-Saxon metalwork and jewellery, from a royal grave of the early 7th century. The period between Alfred and the Norman Conquest, with the revival of the English economy and culture after the end of the Viking raids, saw a distinct Anglo-Saxon style in art, though one in touch with trends on the Continent.
Anglo-Saxon art is mainly known today through illuminated manuscripts, including the Benedictional of St. Æthelwold (British Library) and Leofric Missal (Oxford, Bodleian Library, MS Bodl, 579), masterpieces of the late "Winchester style", which drew on Hiberno-Saxon art, Carolingian art and Byzantine art for style and iconography, and combined both northern ornamental traditions with Mediterranean figural traditions. The Harley Psalter was a copy of the Carolingian Utrecht Psalter — which was a particular influence in creating an Anglo-Saxon style of very lively pen drawings.
Manuscripts were far from the only Anglo-Saxon art form, but they have survived in much greater numbers than other types of object. Contemporaries in Europe regarded Anglo-Saxon goldsmithing and embroidery (Opus Anglicanum) as especially fine. Perhaps the best known piece of Anglo-Saxon art is the Bayeux Tapestry which was commissioned by a Norman patron from English artists working in the traditional Anglo-Saxon style. The most common example of Anglo-Saxon art is coins, with thousands of examples extant. Anglo-Saxon artists also worked in fresco, ivory, stone carving, metalwork (see Fuller brooch for example) and enamel, but few of these pieces have survived.
Language
Old English, sometimes called Anglo-Saxon, was the language spoken under Alfred the Great and continued to be the common language of England (non-Danelaw) until after the Norman Conquest of 1066 when, under the influence of the Anglo-Norman language spoken by the Norman ruling class, it changed into Middle English roughly between 1150–1500.
Old English is far closer to early Germanic than Middle English. It is less Latinised and retains many morphological features (nominal and verbal inflection) that were lost during the 12th to 14th centuries. The languages today which are closest to Old English are the Frisian languages, which are spoken by a few hundred thousand people in the northern part of Germany and the Netherlands.
Before literacy in the vernacular Old English or Latin became widespread, a runic alphabet, the futhorc, was used for inscriptions. When literacy became more prevalent, a form of Latin script was used with a couple of letters derived from the futhorc: 'thorn' ‹þ› and 'wynn' ‹ƿ› (generally replaced with ‹w› in modern reproductions).
The letters regularly used in printed and edited texts of Old English are the following:
with only rare occurrences of j, k, q, v, and z.
Law
Main article: Anglo-Saxon lawsVery few law codes exist from the Anglo-Saxon period to provide an insight into legal culture beyond the influence of Roman law and how this legal culture developed over the course of time. The Saxons chopped off hands and noses for punishment (if the offender stole something or committed another crime). If someone killed a Saxon, he had to pay money called wergild, the amount varying according to the social rank of the victim.
Literature
Old English literary works include genres such as epic poetry, hagiography, sermons, Bible translations, legal works, chronicles, riddles and others. In all there are about 400 surviving manuscripts from the period, a significant corpus of both popular interest and specialist research.
The most famous works from this period include the poem Beowulf, which has achieved national epic status in Britain. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of important early English history. Cædmon's Hymn from the 7th century is the earliest attested literary text in English.
Religion
The indigenous pre-Christian belief system of the Anglo-Saxons was a form of Germanic paganism and therefore closely related to the Old Norse religion, as well as other Germanic pre-Christian cultures.
Christianity gradually replaced the indigenous religion of the English around the 7th and 8th centuries. Celtic Christianity was introduced into Northumbria and Mercia by monks from Ireland, but the Synod of Whitby settled the choice for Roman Christianity. As the new clerics became the chroniclers, the old religion was partially lost before it was recorded, and today historians' knowledge of it is largely based on surviving customs and lore, texts, etymological links and archaeological finds.
One of the few recorded references is that a Kentish King would only meet the missionary St. Augustine in the open air, where he would be under the protection of the sky god, Woden. Written Christian prohibitions on acts of paganism are one of historians' main sources of information on pre-Christian beliefs.
Despite these prohibitions, numerous elements of the pre-Christian culture of the Anglo-Saxon people survived the Christianisation process. Examples include the English language names for days of the week:
- Tiw, the Anglo-Saxon equivalent of Tyr: Tuesday
- Woden, the Anglo-Saxon equivalent of Odin: Wednesday
- Þunor, the Anglo-Saxon equivalent of Thor: Thursday
- *Fríge, the Anglo-Saxon equivalent of Frigg: Friday
Contemporary meanings
"Anglo-Saxon" in linguistics is still used as a term for the original West Germanic component of the modern English language, which was later expanded and developed through the influence of Old Norse and Norman French, though linguists now more often refer to it as Old English. In the 19th century the term "Anglo-Saxon" was broadly used in philology, and is sometimes so used at present. In Victorian Britain, some writers such as Robert Knox, James Anthony Froude, Charles Kingsley[17] and Edward A. Freeman[18] used the term "Anglo-Saxon" to justify racism and imperialism, claiming that the "Anglo-Saxon" ancestry of the English made them racially superior to the colonised peoples. Similar racist ideas were advocated in the 19th Century United States by Samuel George Morton and George Fitzhugh.[19]
The term "Anglo-Saxon" is sometimes used to refer to peoples descended or associated in some way with the English ethnic group. The definition has varied from time to time and varies from place to place. In contemporary Anglophone cultures outside the United Kingdom, the term is most commonly found in certain contexts, such as the term "White Anglo-Saxon Protestant" or "WASP". Such terms are often politicised, and bear little connection to the precise ethnological or historical definition of the term "Anglo-Saxon". It often encapsulates socio-economic identifiers more than ethnic ones.[citation needed]
Outside Anglophone countries, both in Europe and in the rest of the world, the term "Anglo-Saxon" and its direct translations are used to refer to the Anglophone peoples and societies of Britain, the United States, and other countries such as Australia, Canada and New Zealand - areas which are sometimes referred to as the Anglosphere. The term "Anglo-Saxon" can be used in a variety of contexts, often to identify the English-speaking world's distinctive language, culture, technology, wealth, markets, economy, and legal systems. Variations include the German "Angelsachsen", French "Anglo-Saxon", Spanish "anglosajón", Portuguese "anglo-saxão", Italian "anglosassone", Catalan "anglosaxó", Japanese "Angurosakuson" and Ukrainian "aнглосакси" (anhlosaksy). As with the English language use of the term, what constitutes the "Anglo-Saxon" varies from speaker to speaker.[citation needed]
See also
- Angles
- Anglo-Frisian
- Anglo-Saxon architecture
- Anglo-Saxon dress
- Anglo-Saxon military organization
- Anglophile
- Britons
- Frisia
- Ingvaeones
- Jutes
- Saxons
- States in Medieval Britain
- Timeline of Anglo-Saxon settlement in Britain
- Staffordshire Hoard
Modern concepts:
- English people
- Anglo-Saxon economy
Notes
- ^ Frank M. Stenton, The Oxford history of England: Anglo-saxon England: Volume 2: 550-1087 (3rd ed. 1971)
- ^ BBC - History - Anglo-Saxons
- ^ Richard M. Hogg, ed. The Cambridge History of the English Language: Vol 1: the Beginnings to 1066 (1992)
- ^ English and Welsh are races apart
- ^ Bede's Ecclesiastical History of England Chap XV
- ^ The Monarchy of England: Volume I – The Beginnings by David Starkey (extract at Channel 4 programme 'Monarchy')
- ^ The Life of King Alfred
- ^ The History of Wales, John Davies, Penguin Books, 1990. ISBN01.2570 1
- ^ Bartlett, Robert (2000). J.M.Roberts. ed. England Under the Norman and Angevin Kings 1075 -1225. London: OUP. ISBN 9780199251018., p.1
- ^ Wood, Michael (2005). In Search of the Dark Ages. London: BBC. ISBN 9780563522768.p.248-249
- ^ From Norman Conquest to Magna Carta: England, 1066-1215, pp.13,14, Christopher Daniell, 2003, ISBN 0 415 22216 8
- ^ Slaves and warriors in medieval Britain and Ireland, 800-1200, p.385, David R. Wyatt, 2009, ISBN 978 90 04 17533 4
- ^ Western travellers to Constantinople: the West and Byzantium, 962-1204, pp. 140,141, Krijna Nelly Ciggaar, 1996, ISBN 90 04 10637 5
- ^ "Byzantine Armies AD 1118-1461", p.23, Ian Heath, Osprey Publishing, 1995, ISBN 978 1 85532 347 6
- ^ "The Norman conquest: England after William the Conqueror", p.98, Hugh M. Thomas, 2008, ISBN 978 0 7425 3840 5
- ^ York and London both offer examples of this trend.
- ^ Rule of Darkness: British Literature and Imperialism, 1830–1914 by Patrick Brantlinger. Cornell University Press, 1990
- ^ Race and Empire in British Politics by Paul B. Rich. CUP Archive, 1990
- ^ Race and Manifest Destiny: The Origins of American Racial Anglo-Saxonism by Reginald Horsman.Harvard University Press, 1981. (pgs. 126,273)
References
- Oppenheimer, Stephen. The Origins of the British(2006). Constable and Robinson, London. ISBN 1-84529-158-1
Further reading
- Clark, David, and Nicholas Perkins, eds. Anglo-Saxon Culture and the Modern Imagination (2010)
- F.M. Stenton, Anglo-Saxon England, 3rd edition, (Oxford: University Press, 1971)
- J. Campbell et al., The Anglo-Saxons, (London: Penguin, 1991)
- E. James, Britain in the First Millennium, (London: Arnold, 2001)
- M. Lapidge et al., The Blackwell Encyclopaedia of Anglo-Saxon England, (Oxford: Blackwell, 1999)
- Donald Henson, The Origins of the Anglo-Saxons, (Anglo-Saxon Books, 2006)
Primary sources
- D. Whitelock, ed. English Historical Documents c.500–1042, (London: Eyre and Spottiswoode, 1955)
- Bede, Ecclesiastical History of the English People, trans. L. Sherly-Price, (London: Penguin, 1990)
External links
- Photos of over 600 items found in the Anglo-Saxon Hoard in Staffordshire Sept. 2009
- Anglo-Saxon gold hoard September 2009: largest ever hoard officially declared treasure
- Huge Anglo-Saxon gold hoard found, BBC News, with photos.
- Fides Angliarum Regum: the faith of the English kings
- Anglo-Saxon Origins: The Reality of the Myth by Malcolm Todd
- An Anglo-Saxon Dictionary
- Simon Keynes' bibliography of Anglo-Saxon topics
Germanic peoples Languages Prehistory Roman Iron Age Migration Period Germanic Iron Age · Alamanni · Anglo-Saxons (Angles · Jutes · Saxons) · Burgundians · Dani · Franks · Frisii · Geats · Goths (Visigoths · Ostrogoths · Valagoths · Gothic Wars) · Gotlanders · Lombards · Suebi · Suiones · Vandals · Varangians · Christianization of the Germanic peoples · RomanizationSociety and culture Mead hall · Poetry · Migration Period art · Runes (Runic calendar) · Sippe · Law (Lawspeaker · Thing) · Calendar · King · Names · Numbers · Romano-Germanic cultureReligion Wodanaz · Veleda · Tuisto · Mannus · Paganism (Anglo-Saxon · Continental Germanic mythology · Frankish · Norse) · Christianity (Arianism · Gothic)Dress Warfare Burial practices List of Germanic peoples · Portal:Ancient Germanic culture Categories:- Germanic paganism
- Invasions of England
- West Germanic peoples
- Anglo-Saxon England
- Sub-Roman Britain
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.