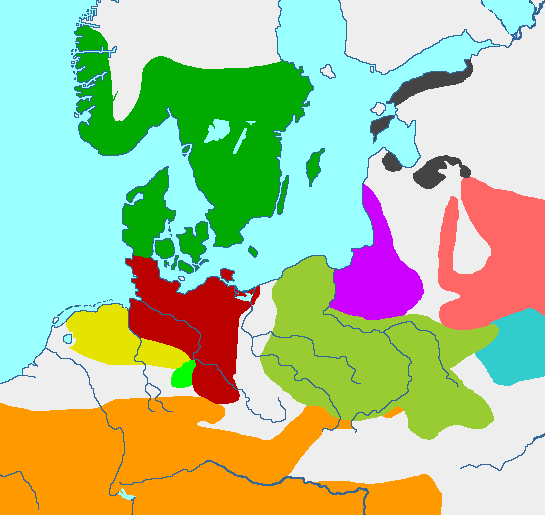
- Jastorf culture
thumb|200px|Early_Iron_Age:_dark_green_-_Nordic Bronze Age dark red -Jastorf culture yellow -Harpstedt-Nienburg group orange - Celtic groups olive -Pomeranian culture bright green -House urns culture pale red - East Baltic culture lilac - West Baltic cairns culture turquoiose - Milogrady culturer black - estonic group ] :
dark green - Nordic group
dark red - late phaseJastorf culture
ochre -Harpstedt-Nienburg group bright green -House Urns culture
dark brown -Oksywie culture
bright red -Gubin group of Jastorf
olive -Przeworsk culture
lilac - West-Baltic cairns culture
pale red - East-Baltic culture
turquoise -Zarubincy culture
orange - Celtic] The Jastorf culture is anIron Age material culture in what is now northGermany , spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming the southern part of thePre-Roman Iron Age The culture evolved out of the Nordic (or Northern) Bronze Age, through influence from the
Halstatt culture farther south. It is named after a site near the village ofJastorf ,Lower Saxony (coord|53|3|N|10|36|E|). The Jastorf culture was characterized by its use of cremation burials in extensive urnfields and link with the practices of the Northern Bronze Age. Archeology offers evidence concerning the crystallization of a group in terms of a shared material culture, in which the (impoverished) Northern Bronze Age continued to exert cultural influence, and in which the northward thrust of Hallstatt into the same area was instrumental, while extensive migrations "should be discounted". No homogeneous contribution to the Germanic-speaking northerners has been determined, while earlier notions holding proto-Germanic peoples to have emigrated from Denmark during the Northern Bronze Age have been abandoned by archaeologists. Jastorf culture extended south to the fringes of the northern Hallstatt provinces, while towards the north a general congruence with the late phases of the Northern Bronze Age can be noted. Gravefields in Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg, western Pomerania, in Brandenburg and in Lower Saxony show continuity of occupation from the Bronze Age far into the Jastorf period and beyond. The specific contributions from the various quarters witnessing the meeting of Celtic and indigenous cultures during the early periods can not be assessed by the present state of knowledge, although a shift to a northern focus has been noted to accompany the dwindling vitality of continental Celtic cultures later on. [The Prehistory of Germanic Europe - Herbert Schutz; ISBN 0300028636, Ch 6 The Northern Genesis(p309-311)]Its area was first restricted to northern
Lower Saxony andSchleswig-Holstein . It then developed a "very expansive" character (Wolfam 1999), expanding towards theHarz and reaching by about 500 BC Thuringia, lower Silesia and the lowerRhine [The Germanic Invasions, the Making of Europe 400-600 A.D. - Lucien Musset, ISBN 1-56619-326-5, 1993 Barnes & Nobles, p8] , thus covering the southern and western parts of Lower Saxony. In its mature phase, the Jastorf area proper in northern Lower Saxony (Lüneburger Heide , lowerElbe ) can be contrasted with the so-called Nienburg (alsoHarpstedt -Nienburg) group to the west, situated along theAller and the middleWeser , bordering theNordwestblock separating it from theLa Tène culture proper farther south. The Nienburg group has characteristics of material culture closer to Celtic cultures, and shows evidence of significant contact with the Hallstadt and Latène cultures. Isolated finds are scattered as far asBerlin andMecklenburg-Vorpommern .Finds are mostly from
tumuli , flat graves and Brandgruben graves. There are few and modestgrave good s, with the weapon deposits characteristic of migration period graves completely absent.Periodization is as follows (middle European culture counterparting in parenthesis):
* 6th century BC: Jastorf A (Hallstatt D)
* 5th century BC: Jastorf B (La Tène A)
* 400-350 BC: Jastorf C (La Tène B)
* 350-120 BC: Ripdorf (La Tène C)
* 120-1 BC: Seedorf (La Tène D)The southernmost extent of Germanic cultures beyond Jastorf has recently been accounted for at the final stages of the Pre-Roman Iron Age, with the paucity of Late-Laténe bracelet-types in Thuringia and northeastern Hessen proposed to suggest population movements between the central-Elbe/Saale region, Main-Franconia and the edge of the Alps and to have been triggered by the spread of the
Przeworsk culture . [Keltische Glasarmringe zwischen Thüringen und dem Niederrhein - Mathias Seidel, Germania (Germania) ISSN 0016-8874, 2005, vol. 83, no1, pp. 1-43 ]The cultures of the Pre-Roman Iron Age are sometimes hypothesized to be the origin of the
Germanic languages (Wolfram 1999 locates the initial stages ofGrimm's Law here).Notes
References
*J. Brandt, "Jastorf und Latène". Internat. Arch. 66 (2001)
* W. Künnemann, "Jastorf - Geschichte und Inhalt eines archäologischen Kulturbegriffs", Die Kunde N. F. 46 (1995), 61-122.
*Herwig Wolfram, "Die Germanen", Beck (1999).
* Heinrich Krüger: "Die Jastorfkultur in den Kreisen Lüchow-Dannenberg, Lüneburg, Uelzen und Soltau." 1961, ISBN 3529015016External links
* [http://www.swalin.de/xm/index.php?page=art&artid=38 Jastorf Kultur] (swalin.de)
* [http://www.ufg-va.uni-hd.de/agbronze/2005/abstracts/druck.html Kapitel: 5000 Bestattungen in Mühlen Eichsen - das größte Gräberfeld der Jastorfkultur?] (uni-hd.de, report on a large Jastorf cemetery found atMühlen-Eichsen )
* [http://www.urgeschichte.de/htm/eisen1.htm Pre-Roman Iron Age] (urgeschichte.de)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.