- Pomeranian culture
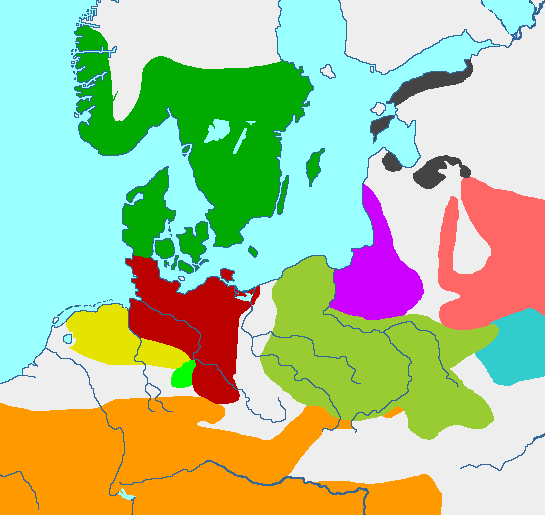
thumb|240px|European early Iron Age cultures: dark green - Nordic group dark red - Jastorf culture yellow - Harpstedt-Nienburger group orange - Celtic groups olive-green - Pomeranic culture bold green - House Urn culture light red - east-Baltic cultures of forest zone violet - west-Baltic culture of cairns turquoise - Milogrady culture black - Estonic group The Pomeranian culture was anIron Age culture inPoland . It grew out of the Kashubian group of theLusatian culture in the7th century B.C. and had its centre between the lowerVistula and the Western coast of the bay ofGdańsk in the East and the riversSłupia and Brda in the West.Burial urns with faces were very characteristic. The urns were often contained in stone
cist s. The face-urns have lids in the form of hats, often miniature ear-rings of real bronze are added. The faces are sometimes modelled very naturalistically, and no two urns show the same face. Incised drawings on the urns show hunting scenes, chariot races or riders.Brooch es of Tłukom-type and necklaces of multiple bronze rings are typical examples of metal work.The economy was similar to that of the Lusatian culture.
Rye was systematically cultivated for the first time, but still formed a minor component of the cereals. There were fewerhill forts than in the area of theLusatian culture further west. Southern imports were sparse as well.A related culture of the same age was the
House Urn culture in central Germany.In the later Iron Age, the Pomeranian culture spread West, into the area formerly belonging to the Lusatian, Wysoko- and
Milograd culture s. InMasovia and Poland this mixture led to the development of the group with bell-shaped burials (Glockengräbergruppe).Polish authors identify the Pomeranian culture with
Vistula Veneti , while German authors tend to identify it with theBastarnae , though those are described by Tacitus and other classic authors only at a later age, when they arrived and settled in the lower Danubian region.Literature
*"Hallstattzeit", Die Altertümer im Museum für Vor- und Frühgeschichte, Bd. 2 , 1999, ISBN: 3-8053-2566-5
*Tacitus : "Germania"
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.