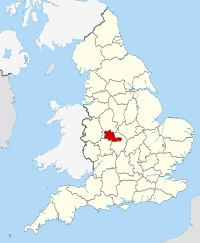
- West Midlands (county)
-
The West Midlands is a metropolitan county in western central England with a 2009 estimated population of 2,638,700. It came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972, formed from parts of Staffordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire. The county itself is a NUTS 2 region within the wider NUTS 1 region of the same name. The county consists of seven metropolitan boroughs: the City of Birmingham, the City of Coventry, and the City of Wolverhampton, as well as Dudley, Sandwell, Solihull, and Walsall. The West Midlands County Council was abolished on 31 March 1986, and so its districts (the metropolitan boroughs) are now effectively unitary authorities. However, the metropolitan county continues to exist in law and as a geographic frame of reference.[1][2][3]
The county is sometimes described as the "West Midlands metropolitan area" or the "West Midlands conurbation", although these have different, and less clearly defined, boundaries. The main conurbation, or urban area, does not include Coventry for example. The name "West Midlands" is also used for the much larger West Midlands region, which sometimes causes confusion.
Contents
Geography
The West Midlands is a landlocked county that borders the counties of Warwickshire to the east, Worcestershire to the south, and Staffordshire to the north and west.
The West Midlands County is one of the most heavily urbanised counties in the UK. Birmingham, Wolverhampton, the Black Country and Solihull together form the most populous conurbation in the United Kingdom outside London, with a combined population of around 2.27 million. However, the West Midlands is not entirely urban; Coventry is separated from the West Midlands conurbation by a stretch of green belt land roughly 15 miles (24 km) across, known as the "Meriden Gap", which retains a strongly rural character. A smaller piece of green belt between Birmingham, Walsall and West Bromwich includes Barr Beacon and the Sandwell Valley.
The highest point in the West Midlands is Turners Hill, with a height of 271 m (889 ft). The hill is a Site of Special Scientific Interest. Barr Beacon is another hill in the West Midlands, located on the border of Birmingham and Walsall, with a height of 227 m (745 ft).
There are 23 Sites of Special Scientific Interest in the county.[4] One of these SSSIs is Sutton Park in Sutton Coldfield, which has an area of 970 hectares (2,400 acres).[5] As a result, it is one of the largest urban parks in Europe, and the largest outside of a capital city in Europe.[citation needed] The park also has National Nature Reserve status.
There are numerous rivers that pass through the county, including the River Tame. The river basin is the most urbanised basin in the United Kingdom, with approximately 42% of the basin being urbanised.[6] The River Tame is fed by the River Rea, River Anker, and the River Blythe, which in turn is fed by the River Cole. The River Sowe and River Sherbourne both flow through Coventry. The River Stour flows through the west of the West Midlands county.
Towns and cities
See also: List of places in the West Midlands, Constituent areas of Birmingham, England, List of areas in Dudley, List of areas in Sandwell, List of areas in Walsall, and List of areas in Wolverhampton- Aldridge
- Bilston
- Birmingham *
- Blackheath
- Bloxwich
- Brierley Hill
- Brownhills
- Chelmsley Wood
- Brownhills
- Coseley
- Coventry *
- Cradley Heath
- Darlaston
- Dudley
- Fordbridge
- Halesowen
- Netherton
- Oldbury
- Rowley Regis
- Quarry Bank
- Rubery
- Smethwick
- Solihull
- Stourbridge
- Sutton Coldfield
- Tipton
- Walsall
- Wednesfield
- Wednesbury
- West Bromwich
- Willenhall
- Wolverhampton *
* = city
History
Although the modern county has only existed since 1974, the settlements of the West Midlands have long been important centres of commerce and industry. Coventry was one of England's most important cities during the Middle Ages, with its prosperity built upon wool and cloth manufacture. Birmingham and Wolverhampton have a tradition of industry dating back to the 16th century, when small metal-working industries developed. Birmingham was known for its manufacture of small arms, whereas Wolverhampton became a centre of lock manufacture and brass working. The coal and iron ore deposits of the Black Country area provided a ready source of raw materials. The area grew rapidly during the Industrial Revolution, and by the 20th century had grown into one large conurbation. Coventry was slower to develop, but by the early 20th century, it had become an important centre of bicycle and car manufacture.
1966 saw a substantial reform in the local government of the area as the patchwork of county boroughs with municipal boroughs and urban district councils in between was replaced by a core of county boroughs covering a contiguous area, roughly as follows:
- Birmingham, which remained substantially unaltered;
- Dudley, which absorbed all of Brierley Hill as well as most of Coseley and Sedgley, and part of Amblecote, Tipton and Rowley Regis;
- Solihull, which remained substantially unaltered;
- Walsall, which absorbed all of Darlaston and most of Willenhall, as well as parts of Wednesbury, Coseley, Wednesfield and Bilston;
- Warley, which was created by amalgamating the vast majority of Smethwick, Oldbury and Rowley Regis as well parts of Dudley, Tipton, West Bromwich and Halesowen;
- West Bromwich, which absorbed most of Wednesbury and Tipton, along with parts of Bilston, Oldbury, Smethwick and Walsall;
- Wolverhampton, which absorbed most of Bilston, Wednesfield and Tettenhall as well as parts of Sedgley, Coseley and Willenhall.
Around the periphery of this area, three other towns remained separate (Halesowen, Stourbridge and Sutton Coldfield), while Aldridge and Brownhills joined to form a single unit, called Aldridge-Brownhills. In the same year, a single West Midlands Constabulary was formed for the Black Country county boroughs, whilst Birmingham retained its Birmingham City Police and Solihull continued being policed by the Warwickshire Constabulary. The West Midlands Passenger Transport Authority was established in 1968.
In 1974, the Local Government Act 1972 came into effect, creating the metropolitan county of West Midlands. This area was based on the seven county boroughs and the other non-county boroughs and urban districts around the fringe of the conurbation. The new area consisted of seven new metropolitan boroughs, with Aldridge-Brownhills added to Walsall; Halesowen and Stourbridge to Dudley and Sutton Coldfield to Birmingham. A new borough of Sandwell was formed by the merger of West Bromwich and Warley. The actual designation of Warley itself was abolished and the three towns of Smethwick, Oldbury and Rowley Regis reinstated as component parts of Sandwell, although these areas formed the Warley postal district. Solihull took in much of the suburban fringe to the east of Birmingham, including the former villages of Chelmsley Wood and Castle Bromwich, also Birmingham Airport, and the area of countryside between Solihull and Coventry, whilst Coventry itself received only small changes and Wolverhampton was unaltered. This led to (apart from in the east, with Coventry and the Meriden Gap) quite a tightly defined metropolitan border, excluding such places as Burntwood, Bromsgrove, Cannock, Kidderminster, Lichfield and Wombourne which had been considered for inclusion in the West Midlands metropolitan area by the Redcliffe-Maud Report. The 1974 reform created the West Midlands County Council that covered the entire area and dealt with strategic issues. A new West Midlands Police service was formed covering the entire area, with the West Midlands Constabulary and Birmingham City Police abolished, and also taking over responsibility from the county forces.
post-1974 pre-1974 Metropolitan county Metropolitan borough County boroughs Non-county boroughs Urban districts Rural districts 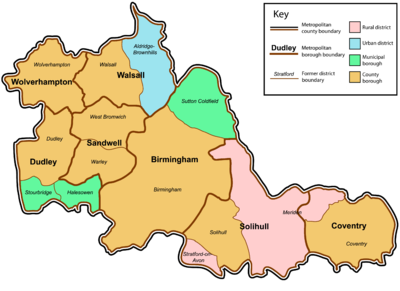
West Midlands is an amalgamation of 14 former local government districts, including eight county boroughs. Birmingham Birmingham Sutton Coldfield - - Coventry Coventry - - Meriden Dudley Dudley Halesowen • Stourbridge • - - Sandwell Warley • West Bromwich • - - - Solihull Solihull - - Meriden • Stratford-on-Avon • Walsall Walsall - Aldridge-Brownhills Wolverhampton Wolverhampton - - - Margaret Thatcher's government abolished the metropolitan county councils with the Local Government Act 1985, in March 1986, causing the seven metropolitan boroughs to become de facto unitary authorities with most of the county councils' functions given to the district councils.
Local government
The arms of the West Midlands County Council, depicted here, became redundant with the abolition of the council in 1986 (though similar arms are used by the West Midlands Fire Service).
Metropolitan boroughs
The West Midlands is divided into seven districts called metropolitan boroughs, these are: Birmingham, Coventry, Dudley, Sandwell, Solihull, Walsall and Wolverhampton (see map). Birmingham, Coventry and Wolverhampton have city status. Coventry is a city by ancient prescriptive usage;[7] Birmingham was granted city status in 1889;[8] and Wolverhampton in 2000 as a "Millennium City".[9]
Between 1974 and 1986, the county had a two-tier system of local government, and the seven districts shared power with the county council. However, when the county council was abolished in 1986, most of its functions were devolved to the districts which effectively became unitary authorities, with responsibility for most local authority functions.
County-wide services
Although the County Council was abolished, some local services continue to be run on a county-wide basis, administered by joint-boards, of the seven districts. These are:
- The West Midlands Passenger Transport Executive; also known as Centro, which is responsible for planning and co-ordinating public transport across the county.
- The West Midlands Police, who are overseen by a joint Police authority.
- The West Midlands Fire Service, which is administered by a joint "Fire and Rescue Authority".
These joint-boards are made up of councillors appointed from each of the seven West Midlands district councils. In addition to this, the West Midlands Joint Committee exists as a joint body of the seven districts to co-ordinate matters such as roads and planning. The seven West Midlands councils jointly produce a county-wide Local Transport Plan.[10]
The boroughs jointly own a share in Birmingham International Airport, which used to be owned by the county council.
Boundary changes
- 1 April 1994: The western/southern shores of Chasewater, plus the adjacent Jeffreys Swag, were transferred from the Metropolitan Borough of Walsall to the District of Lichfield, Staffordshire.[11]
- 1995: Part of the Hereford and Worcester parish of Frankley (including the south-west part of Bartley Reservoir) was transferred to Birmingham and became part of the county.
Places of interest
See also: :Category:Visitor attractions in Birmingham, West MidlandsKey 
Abbey/Priory/Cathedral 
Accessible open space 
Amusement/Theme Park 
Castle 
Country Park 
English Heritage 
Forestry Commission 
Heritage railway 
Historic House 
Museum (free/not free) 
National Trust 
Zoo - Aston Hall, Birmingham
- Bescot Stadium (Walsall F.C.)
- Birmingham Botanical Gardens
- Birmingham Bullring
- Birmingham Museum & Art Gallery
- Birmingham Hippodrome
- Black Country Living Museum
- Blakesley Hall
- Cadbury World, Bournville, Birmingham
- Coventry Cathedral
- Coventry SkyDome Arena
- Coventry Transport Museum
- Dudley Castle
- Dudley Zoo
- Edgbaston Cricket Ground, Birmingham
- International Convention Centre (including Symphony Hall), Birmingham
- Molineux stadium (Wolverhampton Wanderers F.C.)
- National Exhibition Centre
- National Indoor Arena (NIA), Birmingham
- Sea Life Centre, Birmingham
- Netherton tunnel
- Perrott's Folly
- Ricoh Arena (Coventry City Football Club)
- Sarehole Mill
- St Andrew's (Birmingham City Football Club)
- The Hawthorns, (West Bromwich Albion Football Club)
- Thinktank and IMAX Cinema[12], Millennium Point, Birmingham
- Tyseley Locomotive Works
- University of Birmingham
- Villa Park (Aston Villa Football Club)
- Walsall Art Gallery
- Wightwick Manor
Education
The West Midlands contains seven universities. Aston University, the University of Birmingham and Birmingham City University are all located in Birmingham. Coventry University and the University of Warwick are located in Coventry whilst Wolverhampton University is located in Wolverhampton with campuses in Telford and Walsall. It had a campus in Dudley until 2002, when it was replaced by a new building in Wolverhampton city centre and the Dudley site became part of Dudley College.
The Birmingham College of Food, Tourism and Creative Studies and Newman College, both in Birmingham, received university college status in 2008 and 2007, respectively. The colleges changed their names as a result and both pledged to become Birmingham's fourth university. University College Birmingham, formerly Birmingham College of Food, Tourism and Creative Studies, purchased a 2-acre (8,100 m2) site in the Jewellery Quarter area of Birmingham to expand its student capacity from 3,500 to 4,000 which would make it eligible for University status.[13]
Each of the local authorities has at least one further education college for students aged over 16, and since September 1992 all of the local authorities have operated traditional 5-7 infant, 7-11 junior, and 11-16/18 secondary schools for students in compulsory education. This followed the demise of 5-8 first, 8-12 middle and 12-16/18 secondary schools in the Sutton Coldfield area.[14]
For 18 years before September 1990, Dudley had operated 5-8 first, 8-12 middle, and 12-16/18 secondary schools before then, while Halesowen (September 1972 until July 1982) and Aldridge-Brownhills (September 1972 until July 1986) had both operated 5-9 first, 9-13 middle and 13-16/18 secondary schools.
Many local authorities still have sixth form facilities in secondary schools, though sixth form facilities had been axed by most secondary schools in Dudley since the early 1990s (and in Halesowen in 1982) as the local authorities changed direction towards further education colleges.
In August 2009, Matthew Boulton College and Sutton Coldfield College merged to become Birmingham Metropolitan College, one of the largest further and higher education institutions in the country. Plans are afoot for the construction of a new campus in the Perry Barr area of Birmingham.
Sport
Football
The West Midlands is home to numerous sports teams. In football, there are six Football League teams in the county of which three, Aston Villa, West Bromwich Albion and Wolverhampton Wanderers, play in the Barclays Premier League. Aston Villa, Birmingham City, Coventry City, Walsall, West Bromwich Albion and Wolverhampton Wanderers are often referred to as the West Midlands "Big Six".
Club League City/Town Stadium Capacity Aston Villa FC Barclays Premier League Birmingham Villa Park 42,788 West Bromwich Albion FC Barclays Premier League West Bromwich The Hawthorns 26,500 Wolverhampton Wanderers FC Barclays Premier League Wolverhampton The Molineux 28,525 Birmingham City FC NPower Championship Birmingham St Andrew's 30,079 Coventry City FC NPower Championship Coventry Ricoh Arena 32,609 Walsall FC NPower League 1 Walsall Bescot Stadium 11,300 Other Sports
The West Midlands is also home to Warwickshire County Cricket Club, who are based at Edgbaston Cricket Ground, which also hosts Test matches and One Day Internationals. The Birmingham Panthers basketball team replaced the Birmingham Bullets and are currently based at a facility provided by the University of Wolverhampton in Walsall. In rugby union, the West Midlands is home to Moseley Rugby Football Club, Birmingham & Solihull RFC, Dudley Kingswinford RFC, Stourbridge RFC, Walsall RFC and Coventry RFC.
See also
References
- ^ Office of National Statistics - Gazetteer of the old and new geographies of the United Kingdom, p48. URL accessed 10 March 2007.
- ^ Metropolitan Counties and Districts, Beginners' Guide to UK Geography, Office for National Statistics, 17 September 2004. URL accessed 10 March 2007.
- ^ West Midlands Counties, The Boundary Commission for England. URL accessed 10 March 2007.
- ^ "SSSIs in the West Midlands". Natural England. http://www.english-nature.org.uk/special/sssi/searchresults.cfm?sssi_name=&frmcounty=1043. Retrieved 2008-02-02.
- ^ Introduction To Sutton Park Birmingham City Council
- ^ John S. Rowan; R. W. Duck, A. Werritty (2006). Sediment Dynamics and the Hydromorphology of Fluvial Systems. IAHS. pp. 98. ISBN 1901502686.
- ^ Home Office List of English Cities by Ancient Prescriptive Right, 1927, cited in Beckett, J V (2005). City status in the British Isles, 1830–2002. Aldershot: Ashgate. p. 12. ISBN 0-7546-5067-7.
- ^ "History of Mayoralty". Birmingham.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 2008-05-10. http://web.archive.org/web/20080510232357/http://www.birmingham.gov.uk/mayors. Retrieved 2008-05-17.
- ^ "City winners named". BBC News. 2000-12-18. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk/1074434.stm. Retrieved 2008-05-17.
- ^ "What is the LTP?". West Midlands Local Transport Plan. http://www.westmidlandsltp.gov.uk/default.php?id=249. Retrieved 2008-03-24.
- ^ "The Hereford and Worcester, Staffordshire and West Midlands (County and Metropolitan Borough Boundaries) Order 1993". Office of Public Sector Information. 2000-09-20. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si1993/Uksi_19930492_en_1.htm. Retrieved 2008-01-20.
- ^ http://imax.ac
- ^ Shahid Naqvi (2008-01-08). "The race for Birmingham's fourth university". Birmingham Post. http://icbirmingham.icnetwork.co.uk/birminghampost/news/tm_method=full%26objectid=20325005%26siteid=50002-name_page.html. Retrieved 2008-02-02.
- ^ [1]
External links
- Photographs of Birmingham and the West Midlands
- Identity in the West Midlands
- West Midlands Joint Committee
- West Midlands (county) at the Open Directory Project
Ceremonial county of West Midlands Metropolitan districts Major settlements - Aldridge
- Bilston
- Birmingham
- Blackheath
- Bloxwich
- Brierley Hill
- Brownhills
- Coseley
- Coventry
- Cradley Heath
- Darlaston
- Dudley
- Fordbridge
- Halesowen
- Oldbury
- Rowley Regis
- Smethwick
- Solihull
- Stourbridge
- Sutton Coldfield
- Tipton
- Walsall
- Wednesbury
- Wednesfield
- West Bromwich
- Willenhall
- Wolverhampton
See also: West Midlands
Rivers Canals Topics - Black Country
- Centro
- Conservation areas
- Coventry/Bedworth Urban Area
- History of West Midlands County
- Museums
- West Midlands conurbation
Districts of the West Midlands Region Herefordshire 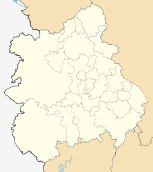
Shropshire Staffordshire Warwickshire West Midlands Birmingham · Coventry · Dudley · Sandwell · Solihull · Walsall · Wolverhampton
Worcestershire Bromsgrove · Malvern Hills · Redditch · Worcester · Wychavon · Wyre Forest
Metropolitan counties and metropolitan districts Greater Manchester 
Merseyside South Yorkshire Tyne and Wear West Midlands West Yorkshire Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.