- Bedfordshire
-
Bedfordshire 
Flag of BedfordshireMotto of County Council: Constant Be 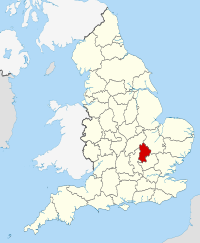
Geography Status Ceremonial county Origin Historic Region East of England Area
- TotalRanked 41st
1,235 km2 (477 sq mi)ISO 3166-2 GB-BDF ONS code 09 NUTS 3 UKH22 Demography Population
- Total (2010 est.)
- DensityRanked 36th
614,800
498 /km2 (1,290 /sq mi)Ethnicity 86.3% White
8.3% S.Asian
2.9% Black.Politics No county council Members of Parliament - Alistair Burt (C)
- Nadine Dorries (C)
- Richard Fuller (C)
- Kelvin Hopkins (L)
- Gavin Shuker (L)
- Andrew Selous (C)
Districts 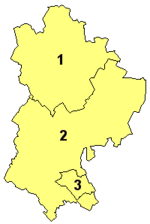
Bedfordshire (
 /ˈbɛdfərdʃər/ or /ˈbɛdfərdʃɪər/; abbreviated Beds.) is a ceremonial county of historic origin in England that forms part of the East of England region.
/ˈbɛdfərdʃər/ or /ˈbɛdfərdʃɪər/; abbreviated Beds.) is a ceremonial county of historic origin in England that forms part of the East of England region.It borders Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Northamptonshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the west and Hertfordshire to the south-east.
The highest elevation point is 243 metres (797 ft) on Dunstable Downs in the Chilterns.
As part of a 2002 marketing campaign, the plant conservation charity Plantlife chose the Bee Orchid as the county flower.[1]
The traditional nickname for people from Bedfordshire is "Bedfordshire Bulldogs" or "Clangers", this last deriving from a local dish comprising a suet crust dumpling filled with meat or jam or both.
Contents
History
Main article: History of BedfordshireThe first recorded use of the name was in 1011 as "Bedanfordscir," meaning the shire or county of Bedford, which itself means "Beda's ford" (river crossing).
Bedfordshire was historically divided into the nine hundreds: Barford, Biggleswade, Clifton, Flitt, Manshead, Redbournestoke, Stodden, Willey, Wixamtree, along with the liberty and borough of Bedford. There have been several minor changes to the county boundary; for example, in 1897 Kensworth and part of Caddington were transferred from Hertfordshire to Bedfordshire.
Geography
The southern end of the county is part of the chalk ridge known as the Chiltern Hills. The remainder is part of the broad drainage basin of the River Great Ouse and its tributaries. Most of Bedfordshire's rocks are clays and sandstones from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, with some limestone. Local clay has been used for brick-making of Fletton style bricks in the Marston Vale. Glacial erosion of chalk has left the hard flint nodules deposited as gravel—this has been commercially extracted in the past at pits which are now lakes, at Priory Country Park, Wyboston and Felmersham. The Greensand Ridge is an escarpment across the county from near Leighton Buzzard to near Gamlingay in Cambridgeshire.
Climate
Bedfordshire is relatively dry, being situated in the east of England. Average annual rainfall is 584.4mm at Bedford.[2] June is the wettest month with 56.9mm, February the driest with 36.6mm. While there is little difference from month to month there are more wet days in autumn and winter but often heavier individual falls in spring and summer, of note were the 1998 Easter floods.[3]
Average temperatures in Bedford range from a minimum of 0.6C overnight in February to 21.5C during the day in July and August. In the last 20 years the highest temperature recorded was 35.9C.[4] During the cold December 2010, temperatures fell beneath -15C in parts of the county (i.e. Woburn).
Politics
Local government
For local government purposes, Bedfordshire is divided into three unitary authorities: the boroughs of Bedford and Luton, and the District of Central Bedfordshire. Bedfordshire County Council was abolished on 1 April 2009, although the three districts continue to form a county for ceremonial functions such as lieutenancy and High Sheriff.[5] Many services in the county, such as education and public libraries, continue to be provided jointly by Central Bedfordshire and Bedford as if they were a single unitary authority.[6]
Emergency services
Policing, fire and rescue services continue to be provided on a county-wide basis, with the Bedfordshire Police Authority and Bedfordshire and Luton Combined Fire Authority consisting of members of the three councils.[7]
Parliamentary constituencies
For elections to the House of Commons, Bedfordshire is divided into six constituencies, each returning a single member of parliament:
The present constituencies date from 1997.[8] The boundaries were slightly modified for the 2010 general election.[9]
Economy
This is a chart of trend of regional gross value added of Bedfordshire at current basic prices published (pp. 240–253) by Office for National Statistics with figures in millions of British Pounds Sterling.
Year Regional Gross Value Added[10] Agriculture[11] Industry[12] Services[13] 1995 4,109 81 1,584 2,444 2000 4,716 53 1,296 3,367 2003 5,466 52 1,311 4,102 Bedfordshire is the location of a number of notable UK and international companies who have either headquarters or major bases in the county. Autoglass, Boxclever and Charles Wells Pubs are all based in Bedford, while the Kier Group and Kingspan Off-Site are based in Sandy, and Jordans Cereals are based in Biggleswade.
The Alexon Group, Blue Arrow, EasyJet, Monarch Airlines, Thomson Airways and Vauxhall Motors are all based in Luton, while Whitbread (including Costa Coffee) is based in nearby Dunstable. UltraVision is based in Leighton Buzzard, while Moto Hospitality is based at Toddington service station.
Visitor attractions
Key 
Abbey/Priory/Cathedral 
Accessible open space 
Amusement/Theme Park 
Castle 
Country Park 
English Heritage 
Forestry Commission 
Heritage railway 
Historic House 
Museum (free/not free) 
National Trust 
Zoo  Bedford Castle
Bedford Castle- Bedford Corn Exchange
 Bedford Museum & Art Gallery
Bedford Museum & Art Gallery- Bedford Park
- Cardington (R101 hangar)
 Chiltern Hills
Chiltern Hills De Grey Mausoleum
De Grey Mausoleum Dunstable Downs
Dunstable Downs Imperial War Museum Duxford
Imperial War Museum Duxford Elstow Moot Hall
Elstow Moot Hall Houghton House
Houghton House Leighton Buzzard Light Railway
Leighton Buzzard Light Railway Luton Hoo
Luton Hoo Luton Museum & Art Gallery
Luton Museum & Art Gallery Marston Vale Community Forest
Marston Vale Community Forest Mossman Collection
Mossman Collection Priory Country Park
Priory Country Park
 RAF Henlow
RAF Henlow- RSPB The Lodge, Sandy
 Someries Castle
Someries Castle The Shuttleworth Collection
The Shuttleworth Collection Stockwood Craft Museum
Stockwood Craft Museum Wardown Park
Wardown Park Waulud's Bank
Waulud's Bank Whipsnade Wildlife Park
Whipsnade Wildlife Park Whipsnade Tree Cathedral
Whipsnade Tree Cathedral Willington Dovecote & Stables
Willington Dovecote & Stables Woburn Abbey
Woburn Abbey Woburn Safari Park
Woburn Safari Park Woodside Farm and Wildfowl Park
Woodside Farm and Wildfowl Park Wrest Park Gardens
Wrest Park Gardens
Transport
See also: List of future transport developments in the East of EnglandAlthough not a major transport destination, Bedfordshire lies on many of the main transport routes which link London to the Midlands and Northern England.
Roads
Two of England's six main trunk roads pass through Bedfordshire:
- The A1 London to Edinburgh road (the Great North Road) runs close by Biggleswade and Sandy
- The A5 London to Holyhead road (Watling Street), passes through Dunstable
To these was added in 1959 the M1 motorway, the London to Leeds motorway. This has three junctions around Luton, one serving Bedford and another serving Milton Keynes.
Former trunk roads, now local roads managed by the local highway authority include A428 running east-west through Bedford Borough, and A6 from Rushden to Luton.
Railways
Three of England's main lines pass through Bedfordshire:
- The West Coast Main Line has but a short section in the far west of the county. The one station at Leighton Buzzard is served by London Midland trains to London Euston and Northampton.
- The East Coast Main Line has stations at Arlesey, Biggleswade and Sandy, served by First Capital Connect services to King's Cross and Peterborough
- The Midland Main Line serves Luton and Bedford with trains to many destinations operated by East Midlands Trains and First Capital Connect.
There are rural services also running between Bedford and Bletchley along the Marston Vale Line.
Taxis
Bedfordshire is served by a large number of taxi companies. Luton is reported to have the highest number of taxicabs per head of population in the United Kingdom with a number of firms competing for work in the town and from London Luton Airport.
Waterways
The River Great Ouse links Bedfordshire to the Fenland waterways. As of 2004 there are plans by the Bedford & Milton Keynes Waterway Trust to construct a canal linking the Great Ouse at Bedford to the Grand Union Canal at Milton Keynes, 14 miles (23 km) distant.[14]
Air
London Luton Airport has flights to many UK, European, Middle Eastern and North African destinations, operated largely but not exclusively by low-cost airlines.
Settlements in Bedfordshire
Main article: List of places in BedfordshireFurther information: List of Bedfordshire settlements by population and Civil parishes in BedfordshireVery large towns (population over 50,000)
- Luton 203,800
- Bedford 79,190
Large settlements (population between 5,000 and 49,999)
- Leighton Buzzard 37,000
- Dunstable 35,120
- Kempston 19,440
- Houghton Regis 16,670
- Biggleswade 16,420
- Arlesey 5,449
- Cranfield 5,443
- Shefford 5,400
- Barton-Le-Clay 5,000
Mid-size settlements (population between 1,000 and 4,999)
- Bromham 4,765
- Potton 4,473
- Wootton 4,230
- Toddington 4,195
- Marston Moretaine 4,000
- Clapham 3,643
- Eaton Bray 3,240
- Henlow 3,084
- Sharnbrook ~3,000
- Langford 2,882
- Wilstead 2,550
- Woburn 2,547
- Campton 2,510
- Oakley 2,438
- Harlington 2,260
- Westoning 2,020
- Maulden 2,000
- Stewartby 1,212
- Houghton Conquest 1,320
- Roxton 1,264
- Lidlington 1,145
- Studham 1,120
- Turvey 1,192
- Totternhoe 1,180
Small settlements (population between 100 and 1,000)
- Pulloxhill 850
- Hockliffe 730
- Ravensden 706
- Felmersham 601
- Thurleigh 696
- Pavenham 593
- Whipsnade 457
- Milton Ernest 754
- Ridgmont 418
- Old Warden 340
- Cardington 316
- Bletsoe 281
- Odell 260
- Radwell 250
- Millbrook 150
- Pertenhall 107
- Tingrith149
Hamlets (population less than 100)
- Sutton???
- Willington???
- Beeston ???
- Gravenhurst ???
- Greenfield ???
Education
The state education system for all of Bedfordshire used to be organised by Bedfordshire County Council. Unlike most of the United Kingdom, Bedfordshire County Council operated a three-tier education system arranged into lower, middle and upper schools, as recommended in the Plowden Report of 1967, although Luton continued to operate a two-tier system. The three-tier arrangement continues in the rest of the county, though in 2006 a vote was held with a view to moving to the two-tier model, but this was rejected.[15]
After the 2009 structural changes to local government in England, Bedfordshire County Council was abolished, and its responsibilities for education were passed to Bedford Borough Council and Central Bedfordshire Council. Though Central Bedfordshire plans to continue with the three-tier model in its area, Bedford Borough Council voted in November 2009 to change to the two-tier model in its area.[16][17] The change will be introduced over a five year period and be completed in 2015.[18]
Bedford and Central Bedfordshire
Until the division into two unitary authorities in April 2009, education in the area continued to be administered by Bedfordshire County Council.
All of the two councils' upper schools offer 6th form courses (such as A Levels), though Bedford College, Central Bedfordshire College and Shuttleworth College also offer a range of further education courses. Additionally, Stella Mann College is a private college (based in Bedford), which offers a range of further education courses relating to the performing arts.[19][20]
There are a number of independent schools, many of which have links to the Harpur Trust.
Luton
Main article: Education in LutonLuton also operates a three-tier education system though Luton's organisation of infant, junior and high schools mirrors the traditional transfer age into secondary education of 11 years. However most of Luton's high schools do not offer 6th form education. Instead this is handled by Luton Sixth Form College, though Barnfield College also offers a range of further education courses.
Higher education
There are two universities based in the county – the University of Bedfordshire and Cranfield University. These institutions attract students from all over the UK and abroad, as well as from Bedfordshire.
Landmarks
The enormous Cardington Hangers are situated to the south of Bedford near the village of Cardington. They were built to house the construction of airships in WW1 and whilst one has been used for many purposes, such as a film set and rehearsal space for Take That, the other is in severe disrepair.
Sports
Main article: Sport in BedfordshireBedfordshire is home to Luton Town F.C. amongst other various sporting teams.
Notable people from Bedfordshire
- Asher Hucklesby
- Trevor Huddleston
- Sir Alec Jeffreys
- Andy Johnson
- Wayne Larkins
- John Le Mesurier
- Steve Linsdell, motorcyclist
- Sir William Morgan
- John Oliver
- Monty Panesar
- Sir Joseph Paxton
- Victoria Pendleton
- Paula Radcliffe
- Mark Rutherford
- Robert Sedgwick
- Lil Silva
- Matt Skelton
- Sir Malcolm Stewart
- Carol Vorderman
- Charles Wells
- Paul Young
- Gurpareet Bains
- Ben Whishaw
Bibliographical references
- Bedfordshire Magazine (quarterly)[21]
- Elstow Moot Hall leaflets on John Bunyan and 17th century subjects[21]
- Guide to the Bedfordshire Record Office 1957 with supplements.[21]
- Guide to the Russell Estate Collections Published in 1966.[21]
- Conisbe, L. R. (1962) A Bedfordshire Bibliography (supplement, 1967)[21]
- Dony, John (1953) A Bedfordshire Flora. Luton: Corporation of Luton Museum & Art Gallery[21]
- Dony, John (1942) A History of the Straw Hat Industry. Luton: Gibbs, Bamforth & Co.[21]
- Freeman, Charles (1958) Pillow Lace in the East Midlands. Luton: Luton Museum and Art Gallery[21]
- Godber, Joyce (1969) History of Bedfordshire 1066-1888[21]
- White, H. O. Bedfordshire Historical Record Society (published annually)[21]
See also
References
- ^ County flowers in Britain www.plantlife.org.uk
- ^ Met Office Bedford Averages 1971-2000 http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/climate/uk/averages/19712000/sites/bedford.html
- ^ Met Office: Easter 1998 - Heavy rainfall http://www.metoffice.gov.uk/climate/uk/interesting/easter1998/
- ^ CLIMATE BEDFORD - Weather http://www.tutiempo.net/en/Climate/BEDFORD/35600.htm
- ^ "The Bedfordshire (Structural Changes) Order 2008 (S.I 2008 No. 907)". Office of Public Sector Information. 27 March 2008. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si2008/uksi_20080907_en_1. Retrieved 2009-03-27.
- ^ "Bedford Borough and Central Bedfordshire and Libraries - About Your Library - Bedfordshire's Virtual Library". Galaxy.bedfordshire.gov.uk. http://www.galaxy.bedfordshire.gov.uk/webingres/bedfordshire/vlib/0.beds_libraries/unitary_library.htm. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ "The Local Government (Structural Changes) (Areas and Membership of Public Bodies in Bedfordshire and Cheshire) Order 2009 (S.I 2009 No. 119)". Office of Public Sector Information. 28 January 2009. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si2009/uksi_20090119_en_1. Retrieved 2009-03-27.
- ^ "The Parliamentary Constituencies (England) Order 1995". Office of Oublic Sector Information. 1995. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si1995/Uksi_19951626_en_2.htm#end. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ "The Parliamentary Constituencies (England) Order 2007". oofice of Public Sector Information. 2007. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si2007/uksi_20071681_en_2. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ Components may not sum to totals due to rounding
- ^ includes hunting and forestry
- ^ includes energy and construction
- ^ includes financial intermediation services indirectly measured
- ^ "Bedford & Milton Keynes Waterway Trust". B-mkwaterway.co.uk. http://www.b-mkwaterway.co.uk/trust/index.html. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ "Two-tier school proposal rejected". BBC News. 2006-07-13. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/beds/bucks/herts/5173424.stm. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ "Middle schools to be abolished - Biggleswade News". Bedford Today. http://www.bedfordtoday.co.uk/bed-news/Middle-Schools-Abolished.5829267.jp. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ "'Momentous decision' for schools". BBC News. 2009-11-17. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/beds/bucks/herts/8363976.stm. Retrieved 2010-04-26.
- ^ "Tiers to be shed in school restructure? - Local". Bedford Today. http://www.bedfordtoday.co.uk/news/Tiers-to-be-shed-in.5800585.jp. Retrieved 2010-09-25.
- ^ "Education in Bedford". Bedford Borough Council. 2004. http://www.bedford.gov.uk/Default.aspx/Web/EducationinBedford. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ "Education and Schools Information". Creating Central Bedfordshire. Central Bedfordshire Council. http://www.centralbeds.gov.uk/Images/Education%20and%20Schools%20Facts%20and%20Figures_tcm5-27833.pdf. Retrieved 2009-03-31.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Detail from a copy of History of Bedfordshire published by Bedfordshire County Council in 1969
External links
Neighbouring counties 
Northamptonshire Northamptonshire, Cambridgeshire Cambridgeshire 
Buckinghamshire 
Cambridgeshire
Hertfordshire Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire 

Buckinghamshire Hertfordshire Hertfordshire England Portal Unitary authorities Major settlements Ampthill · Arlesey · Bedford · Biggleswade · Dunstable · Flitwick · Houghton Regis · Kempston · Leighton Buzzard · Linslade · Luton · Potton · Sandy · Shefford · Stotfold · Wixams ·
See also: List of civil parishes in BedfordshireTopics Unitary authorities of England Districts Bath and North East Somerset · Bedford · Blackburn with Darwen · Blackpool · Bournemouth · Bracknell Forest · Brighton and Hove · Bristol · Central Bedfordshire · Cheshire East · Cheshire West and Chester · Cornwall · County Durham · Darlington · Derby · East Riding of Yorkshire · Halton · Hartlepool · Herefordshire · Isle of Wight · Kingston upon Hull · Leicester · Luton · Medway · Middlesbrough · Milton Keynes · North East Lincolnshire · North Lincolnshire · North Somerset · Northumberland · Nottingham · Peterborough · Plymouth · Poole · Portsmouth · Reading · Redcar and Cleveland · Rutland · Shropshire · Slough · Southampton · Southend-on-Sea · South Gloucestershire · Stockton-on-Tees · Stoke-on-Trent · Swindon · Telford and Wrekin · Thurrock · Torbay · Warrington · West Berkshire · Wiltshire · Windsor and Maidenhead · Wokingham · York
Councils Bournemouth · Cornwall · Herefordshire · Isle of Wight · Kingston upon Hull · Leicester · Middlesbrough · Northumberland · Nottingham · Poole · Rutland · Shropshire · Slough · Thurrock · Wiltshire
Categories:- Bedfordshire
- English unitary authorities created in 2009
- Unitary authorities of England
- Former non-metropolitan counties
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
