- Maniots
-
Part of a series on Greeks 
By region or country Greece · Cyprus
Greek diasporaSubgroups Antiochians · Arvanites/Souliotes
Cypriots · Grecanici
Karamanlides · Macedonians
Maniots · Northern Epirotes
Phanariotes · Pontians
Romaniotes · Sarakatsani
Sfakians · Slavophones
Tsakonians · UrumsGreek culture Art · Cinema · Cuisine
Dance · Dress · Education
Flag · Language · Literature
Music · Philosophy · Politics
Religion · Sport · TelevisionReligion Greek Orthodox Church
Greek Roman Catholicism
Greek Byzantine Catholicism
Greek Evangelicalism
Judaism · Islam · NeopaganismLanguages and dialects Greek
Calabrian Greek
Cappadocian Greek
Cretan Greek · Griko
Cypriot Greek
Cheimarriotika · Maniot Greek
Pontic Greek · Tsakonian
Yevanic · Arvanitika
Karamanlidika · Slavika
UrumHistory of Greece The Maniots or Maniates (Greek: Μανιάτες) are the Greek inhabitants of the Mani Peninsula (the middle leg of the Peloponnese) located in the southern Peloponnese in the Greek prefecture of Laconia and prefecture of Messinia. They were also formerly known as Mainotes and the peninsula as Maina. The Maniots are the direct descendants of the Spartans and through the Spartans, the Dorians. The terrain is mountainous and inaccessible (until recently many Mani villages could be accessed only by sea), and the regional name "Mani" is thought to have meant originally "dry" or "barren." Etymologically, the name "Maniot" is a diminutive implying "of Mani". Geographically, the peninsula itself is an extension of the Taygetus mountain range. Throughout history, the Maniots have been known by their neighbors and their enemies as fierce warriors who practice blood feuds - so fierce and savage, in fact, that they have been compared to the Nordic Berserkers. At times they were even referred to as the "super soldiers" of the 15th, 16th, 17th, 18th and early to mid 19th centuries.
Their surnames uniformly end in "-eas" in what is now the Messinian part of Mani, "-akos" in what is now the Laconian part of Mani and the occasional "-oggonas". The Maniot "-akos" is not to be confused with the Cretan "-akis", which was introduced into Mani by the first Cretan refugees who fled Crete once the Ottomans eventually fully occupied Crete in 1669. The Maniot "akos" denotes strength, power and masculinity as opposed to the Cretan "akis" which denotes weakness, being small, and being effeminate in nature.
During the early modern period, the Maniots were renowned pirates with Oitylo having the nickname Great Algiers. For the most part, the Maniots lived in fortified villages (and "house-towers") where they defended their lands against the Ottomans and even against the armies of William II Villehardouin.
Contents
Ancient Mani
Mycenaean Mani
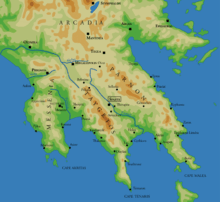
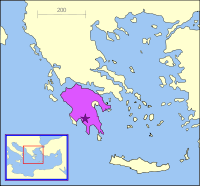
 Map showing the location of Mani Peninsula.
Map showing the location of Mani Peninsula.
Homer's "Catalogue of Ships" in the Iliad mentions the cities of Mani: Messi (Mezapos), Oetylus (Oitylo), Kardamili (or Skardamoula), Gerenia, Teuthone (Kotronas), and Las (Passavas).[1] Under the Mycenaeans, Mani flourished and a temple dedicated to the Greek god Apollo was built at Cape Tenaron. The temple was of such importance that it rivaled Delphi which was then a temple dedicated to Poseidon. Eventually, the temple of Tenaron was dedicated to Poseidon and the temple at Delphi was dedicated to Apollo. According to other legends, there is a cave near Tenaro that leads to Hades. Mani was also featured in other mythological tales such as the one where Helen of Troy and Paris spent their first night together on the island of Cranae, off the coast of Gytheio.[2]
During the 12th century BC, the Dorians invaded Laconia. The Dorians settled originally at Sparta, but they soon started to expand their territory and by around 800 BC they had occupied Mani and the rest of Laconia. Mani's inhabitants were given the social caste of Perioeci.[3] During that time, the Phoenicians came to Mani and were thought to have established a colony at Gythion (Roman name: Gythium). The Phoenicians built the colony at Gythion in order to collect murex, a sea shell that was used to make purple dye and was plentiful in the Laconian Gulf.[4]
Classical Mani
While the Spartans ruled Mani, Tenaron became an important gathering place for mercenaries.[5] Gythium became a major port under the Spartans as it was only 27 kilometres (17 mi) away from Sparta. In 455 BC, during the First Peloponnesian War, it was besieged and captured by the Athenian admiral, Tolmides, along with 50 triremes and 4,000 hoplites.[4] The city and the dockyards were rebuilt and by the late Peloponnesian War, Gythium was the main building place for the new Spartan fleet.[6] The Spartan leadership of the Peloponnese lasted until 371 BC, when the Thebans under Epaminondas defeated them at Leuctra. The Thebans began a campaign against Laconia and captured Gythium after a three-day siege. The Thebans only briefly managed to hold Gythium, which was captured by 100 elite warriors posing as athletes.[5]
Hellenistic Mani
During the Hellenistic period of Greece, Mani remained controlled by the Spartans. The Macedonians under the command of Philip V of Macedon invaded Mani and Laconia (219 BC-218 BC) and unsuccessfully besieged the cities of Gythium, Las and Asine.[5] When Nabis took over the Spartan throne in 207 BC, he implemented some reforms. One of these reforms entailed making Gythium into a major port and naval arsenal.[7] In 195 BC, during the Roman-Spartan War, the Roman Republic and the Achaean League with assistance from a combined Pergamene and Rhodian force captured Gythium after a lengthy siege.[8]
The allies went on to besiege Sparta and forced Nabis to surrender. As part of the terms of the peace treaty, the coastal cities of Mani were liberated. The cities formed the Koinon of Free Laconians with Gythium as the capitol under Achaean protection.[5] Nabis, not content with losing his land in Mani, built a fleet and strengthened his army and advanced upon Gythium in 192 BC.[9] The Achaean League's army and navy under Philopoemen, tried to relieve the city but the Achaean navy was defeated off Gythium and the army was forced to retreat to Tegea.[9] A Roman fleet under Atilius managed to re-capture Gythium later that year. Nabis was murdered later that year and Sparta was made part of the Achaean League.[10] However, the Spartans, while searching for a port captured Las. The Achaeans responded by seizing Sparta and forcing their laws on it.[11]
Roman Mani
The Maniots lived in peace until 146 BC with the advent of the Battle of Corinth. The conflict resulted in the destruction of Corinth by the forces of Lucius Mummius Achaicus and the annexation of the Achaean League by the Roman Republic. Even though the Romans conquered the Peloponnese, the Koinon was allowed to retain its independence. The Maniots suffered from pirate raids by Cretans and Cilicians who plundered Mani and pillaged the temple of Poseidon. The Maniots were delivered from the pirates when Pompey the Great defeated them. Most probably in gratitude, the Maniots supplied Pompey with archers in his battles against Julius Caesar during Caesar's civil war (49 BC-45 BC).[12]
During the Civil war between Antony and Octavian (32 BC-30 BC), the Maniots and Laconians assisted Augustus by sending him men to join his navy. Augustus defeated Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII of Egypt at the Battle of Actium (September 2, 31 BC) and in gratitude he officially recognized the Koinon and visited Psammathous, and it became a semi-independent state. This signified the beginning of the "Golden Age" of the Koinon.[12][13]
Mani flourished under the Romans. The Koinon consisted of 24 cities (later 18), of which Gythium remained the most prominent. However, some parts of Mani remained under the also semi-independent Sparta, the most notable being Asine and Karymili.[12] The Mani became a center for purple dye, which was popular in Rome, as well as being well known for its rose antique marble and porphyry.[4] Las is recorded to have been a comfortable city with Roman baths and a gymnasium.[14]
Pausanias has left us a description of the town as it existed during the reign of Marcus Aurelius (reigned 161-180). The agora, the Acropolis, the island of Cranae (Marathonisi) where Paris celebrated his nuptials with Helen of Troy, the Migonium or precinct of Aphrodite Migonitis (occupied by the modern town), and the hill Larysium (Koumaro) rising above it. Nowadays, the most noteworthy remains of the theatre and the buildings partially submerged by the sea all belong to the Roman period.[15]
The Koinon remained semi-independent until the provincial reforms of Roman Emperor Diocletian in 297. With the barbarian invasion affecting the Roman Empire, Mani became a haven for refugees. In 375, a massive earthquake in the area took its toll on Gythium, which was severely devastated.[13][14]
Medieval Mani
From Theodosius I to the Avar invasion
A map of the Byzantine Empire showing Mani and the eastern Peloponnese as part of the Empire (the rest of the Peloponnese was occupied by Slavic tribes), c. 717.
On January 17, 395, Theodosius I, who had managed to unite the Roman Empire under his control, died. His eldest son, Arcadius, succeeded him in the Eastern Roman Empire, while his younger son, Honorius, received the Western Roman Empire. The Roman Empire had divided for the last time, and Mani became part of the Eastern or Byzantine Empire. Between 395 and 397, Alaric I and his Visigoths plundered the Peloponnese and destroyed what was left of Gythium. Alaric captured the most famous cities, Corinth, Argos, and Sparta, selling many of their inhabitants into slavery. He was at last defeated by Stilicho and then crossed the Gulf of Corinth towards the north.[13]
In 468, Gaiseric of the Vandals attempted to conquer Mani with the purpose of using it as a base to raid and then conquer the Peloponnese. Gaiseric tried to land his fleet at Kenipolis, but as his army disembarked the inhabitants of the town attacked the Vandals and made them retreat after heavy casualties.[16]
Decades later, the famed Byzantine general Belisarius, on the way to his victorious campaign against the Vandals, stopped at Kenipolis to get supplies, honor the Kenipolitans for their victory, and recruit some soldiers.[17] According to Greenhalgh and Eliopoulos, the Eurasian Avars (along with the Slavs) attacked and occupied most of the western Peloponnese in 590.[18] However, there is no archaeological evidence for a Slavic (or Avar) penetration of imperial Byzantine territory before the end of the 6th century. Overall, traces of Slavic culture in Greece are very rare.[19]
During the Macedonian dynasty
There is a description of Mani and its inhabitants in Constantine VII's De Administrando Imperio:[18]
“ Be it known that the inhabitants of Castle Maina are not from the race of aforesaid Slavs but from the older Romaioi, who up to the present time are termed Hellenes by the local inhabitants on account of their being in olden times idolaters and worshippers of idols like the ancient Greeks, and who were baptized and became Christians in the reign of the glorious Basil. The place in which they live is waterless and inaccessible, but has olives from which they gain some consolation. ” The area inhabited by the Maniates was first called by the name "Maina" and was associated with the castle of Tigani. The Maniots at that time were called "Hellenes"—that is, pagans (see Names of the Greeks)—and were only Christianized fully in the 11th century AD, though some church ruins from the 4th century AD indicate that Christianity was practiced by some Maniots in the region at an earlier time. The Maniots were the last inhabitants of Greece to openly follow the pagan Hellenic religion. This can be explained by the mountainous nature of Mani's terrain, which enabled them to escape the attempts of the Eastern Roman Empire to Christianize Greece by force.[18]
Under the Principality of Achaea
During the Fourth Crusade (1201–1204), the Crusaders captured Constantinople. The Eastern Roman Empire was partitioned between several Greek and Latin successor states, notably including (from west to east) the Despotate of Epirus, the Latin Empire, the Empire of Nicaea, and the Empire of Trebizond. These four empires produced rival emperors, struggling for control over each other and the rest of the semi-independent states emerging in the area. William of Champlitte and Geoffrey I Villehardouin defeated the Peloponnesian Greeks at the Battle of the Olive Grove of Koundouros (1205), and the Peloponnese became the Principality of Achaea. In 1210, Mani was given to Baron Jean de Neuilly as Hereditary Marshal, and he built the castle of Passavas on the ruins of Laas. The castle occupied a significant position, as it controlled an important pass from Gythium to Oitylo and contained the Maniots.[20][21]
The Maniots, however, were not easily contained, and they were not the only threat to the Frankish occupation of the Peloponnese. The Melengi, a Slavic tribe in the Taygetus mountain range, raided Laconia from the west, and the Tsakonians also resisted the Franks. In 1249, the new prince, William II of Villehardouin, acted against the raiders. He used the newly captured fortress of Monemvasia to keep the Tsakones at bay, and he built the castle at Mystras in the Taygetus mountains overlooking Sparta in order to contain the Melengi. To stop the Maniot raids, he built the castle of Megali Maini, which is most probably Tigani. It is described as at a fearful cliff with a headland above. A Latin bishop was appointed for Mani during the 1250s. In 1259, the bishop was captured during the Battle of Pelagonia by the renewed Byzantine Empire under the leadership of Nicaea.[22]
Under the Despotate of Morea
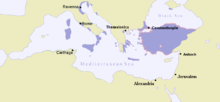
 Despotate of Morea, c. 1450.
Despotate of Morea, c. 1450.
On July 25, 1261, the Byzantines under Michael VIII Palaiologos recaptured Constantinople. Prince William was set free, on the condition that he had to surrender the fortresses of Megali Maina, Mystras, and Monemvasia, as well as surrender hostages including Lady Margaret, Baroness of Passavas. With the Franks gone from Laconia, the Maniots lived in peace under the Despotate of Morea, whose successive Despotes governed the province. Mani seems to have been dominated by the Nikliani family, who were refugees. However, the peace was terminated when the Ottoman Turks started their attacks on the Peloponnese.[22][Note 1]
Ottoman times
15th century
After the Ottoman Empire under Sultan Mehmet II took Constantinople in May 1453, Mani remained under the control of the Despotate of Morea. In May of 1460, Mehmet occupied the Peloponnese. The Despotate of Morea had been ruled by the two brothers of Constantine XI, who had died defending Constantinople. However, neither Demetrios Palaiologos nor Thomas Palaiologos chose to follow his example and defend the Peloponnese. Instead, Thomas fled to Italy, while Demetrios sought refuge with Mehmet. Helena Palaiologina, a daughter of Demetrios and Theodora Asanina, was given in marriage to Mehmet II.[22]
Kladas, a Greek from Laconia, was granted lordship by Mehmet over Elos and Varvounia in 1461. Mehmet hoped that Kladas would defend Laconia from the Maniots.[22] During that time, Mani's population grew as a result of an influx of refugees who came from other areas of Greece.[26][Note 2] In 1463, Kladas joined the Venetians in their ongoing war against the Ottomans. He led the Maniots against the Ottomans with Venetian aid until 1479, when the Venetians made peace with the Ottomans and gave the Ottomans the right to rule the Brazzo di Maina. Kladas refused to accept the conditions, and so the Venetians put a price on his head.[22]
After the end of the Turko-Venetian War, the Venetians left the Maniots to fend for themselves. Many of the Greeks who had revolted alongside the Venetians were massacred by the Ottomans, but many of them fled to find refuge in Mani. The Maniots continued to resist, and Mehmet sent an army of 2,000 infantry and 300 cavalry against Mani under the command of Ale Boumico.[28] The Venetians, trying to gain favor with the Porte, handed over some Maniot rebels. The Ottomans reached Oitylo before Kladas, and the Maniots attacked and massacred them. Only a few escaped; amongst them was Ale Boumico. Kladas invaded the Laconian plain with 14,000 Maniots and killed the Turkish inhabitants.[29]
A month later, a larger force under the command of Ahmed Bey invaded Mani and drove Kladas to Porto Kagio.[30] There, he was picked up by three galleys of King Ferdinand I of Naples.[30] To delay the Turks long enough for Kladas to escape, the Maniot rear guard attacked the Turkish army.[30] Kladas reached the Kingdom of Naples, whence he became a mercenary leader. He returned to Mani in 1490 and was killed in a battle at Monemvasia.[30]
16th century
From 1500 to 1570, Mani kept its autonomy without any invasion from the Ottomans.[29] The Ottomans were busy driving the Venetians out of the Peloponnese and succeeded in 1540, when they conquered Monemvasia and Nafplio. The Ottomans under Selim II, preparing to invade the Venetian island of Cyprus, built a fortress in Mani, at Porto Kagio, and they also garrisoned Passavas. The aim of this was to disrupt the Venetians' communication lines and to keep the Maniots at bay. Alarmed, the Maniots called upon Venetian assistance, and the Venetian navy in combination with the Maniot army captured the castle.[31]
Cyprus fell later that year, but the combined fleets of the Holy League defeated the Ottoman fleet at the Battle of Lepanto (1571). The Greeks assumed that John of Austria would champion their revolt under the command of the bishop of Monemvasia.[31] The promised army never arrived, and by 1572 the bishop was forced to retreat to Mani. The Maniots failed when they appealed to Pope Gregory VIII to convince Philip II of Spain in providing military support.[32]
17th century
 Vatheia, a typical Maniot village famous for its towers.
Vatheia, a typical Maniot village famous for its towers.
In 1603, the Maniots approached Pope Clement VIII, who had recently taken up the cross. Clement died two years later, and the Maniots began to seek a new champion, centering their attention on the King of Spain, Philip III.[32] They urged him to land his army at Porto Kagio and promised to join him with 15,000 armed men as well as 80,000 other Peloponnesians.[29] The Maniots also sent envoys to some major powers of the Mediterranean, as for example the Republic of Venice, the Kingdom of France, the Republic of Genoa, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany, and once again Spain. These states were interested and sent several expeditionary forces to Mani, but with the exception of a Spanish expedition that sacked Passavas they all failed to achieve anything.[32]
The Maniots found a champion in 1612, Charles Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua and Nevers. Charles was a descendant of the Byzantine Emperor Andronicus II Palaeologus through his grandmother, who was of the line of Theodore I of Montferrat, Andronicus' son.[33] Through this connection he claimed the throne of Constantinople. He began plotting with the Maniots, who addressed him as "King Constantine Palaeologus". When the Porte heard about this, they sent Arslan in command of an army of 20,000 men and 70 ships to invade Mani. He succeeded in ravaging Mani and imposing taxes on the Maniots (which they did not pay). This caused Nevers to move more actively for his crusade. Nevers sent envoys to the courts of Europe looking for support. In 1619, he recruited six ships and a number of men, but he was forced to abort the mission because of the beginning of the Thirty Years' War.[32][33] The idea of the crusade faded and Nevers died in 1637.[33]
In 1645, a new Turkish-Venetian War, the so-called "Cretan War" began, during which the Republic of Venice was attempting to defend Crete, one of their provinces since 1204, from the Ottoman Empire, initially under Ibrahim I. The Maniots supported the Venetians by offering them ships. In 1659, Admiral Francesco Morosini, with 13,000 Maniots as his allies, occupied Kalamata, a large city near Mani. In 1667, during the Siege of Candia, some Maniot pirate ships sneaked into the Ottoman fleet and managed to loot and burn some ships. However, Candia fell in 1669, and Crete became part of the Ottoman Empire.[32][33][Note 3]
With Crete captured, the Ottomans turned their attention to Mani. The Grand Vizier, Köprülü Fazıl Ahmet Pasha, sent the pirate Hasan Baba to subdue Mani. Baba arrived in Mani demanding that the Maniots surrender hostages, but instead he was answered with bullets. During the night, ten Maniots went and cut the hawsers of Hasan's ships. This caused some of Baba's ships to founder on some rocks, and the Maniots, taking advantage of the situation, attacked and killed the Turks and seized the ships. Baba managed to escape with only one ship.[36]
In the Bagnio of Constantinople, there was a notorious twenty-five-year-old Maniot pirate named Limberakis Gerakaris. At the age of fifteen, he was in the Venetian galleys as a rower. After being released by the Venetians, he continued piracy and was captured by the Turks in 1667. The Grand Vizier decided to give him amnesty if he cooperated with the Turks and helped them conquer Mani. Gerakaris agreed and in 1670 became the bey of Mani. One of Gerakis' first acts was to exile his clan's enemies, the Iatriani family and the Stephanopoulos family from Oitylo. The Iatriani fled in 1670 and settled in Livorno, Tuscany. The Stephanopoulos clan was forced to leave Oitylo in 1676, and after having gained permission from the Republic of Genoa, went to Corsica. The Stephanopoulos family first lived in the town of Paomia before moving to Cargese, and to this day consider themselves Greeks.[37] [Note 4]
Limberakis soon fell out of favor with the Turks since he joined his fellow Maniots in piracy and was captured in 1682.[39] With Ottoman forces preoccupied with the Austrians, the Venetians under Morosini saw their opportunity to take over Turkish-held territories in the Peloponnese, beginning the Morean War. The Turkish general in the Peloponnese, Ismael, discovered this plan and attacked Mani with 10,000 men. The Turks ravaged the plains, but during the night the Maniots attacked and killed 1,800 Turks. The other Turks retreated to the castles of Kelefa and Zarnatas, where they were besieged by the Maniots. After brief sieges, the Maniots managed to capture both Koroni and Kelefa. However, Ismael returned with 10,000 infantry and 2,500 artillery and started besieging the Maniots at Kelefa. The Turks nearly succeeded in breaching the walls before 4,500 Venetians under the command of Morosini arrived and forced the Turks to retreat to Kastania with the Maniots in pursuit.[40][35]
The Venetians, with assistance of the Greeks, conquered the rest of the Peloponnese and then besieged Athens. During the siege of Athens, the Ottomans were using the Parthenon as an ammunition depot. When artillery fire from the Venetians struck the depot, the resulting explosion damaged large portions of the Parthenon.[35] The desperate Ottomans freed Limberakis and gave him the title His Highness, the Ruler of Mani. Limberakis immediately launched several raids into Venetian-held territories of the Peloponnese. However, when the Ottomans attempted to poison Liberakis, he defected to the Venetian side.[41][42] The Venetians made Limberakis a Knight of St. Mark and recognized him as ruler of Roumeli. Limberakis first attacked the city of Arta, when the Ottomans destroyed his estates at Karpenisi. He captured and plundered the city before going back to Mani. The Arteans sent a committee to Venice and reported everything to the Doge. Ultimately, Limberakis moved to Italy where he died fourteen years later.[42]
18th century
In 1715, the Ottomans attacked the Peloponnese and managed to drive out the Venetians within seventy days. The Venetians won some minor naval battles off Mani but abandoned the Peloponnese in 1715. The next year, the Treaty of Passarowitz was signed, and the Venetians abandoned their claim to the Peloponnese.[43]
Orlov Revolt
Main article: Orlov RevoltPapazolis, a Greek living in Russia, was a friend of the Orlovs and had them convince Catherine the Great to send an army to Mani and liberate Greece.[43] A Russian fleet of five ships and 500 soldiers under the command of Aleksey Grigoryevich Orlov sailed from the Baltic Sea in 1769 and reached Mani in 1770.[41] The fleet landed at Oitylo, where it was met by the Maniots. It was decided to divide the army into two groups, the Western Legion and the Eastern Legion. The Eastern Legion, under the command of Barkof, Grigorakis, and Psaros, consisted of 500 Maniots and six Russians. The Western Legion, under the command of John Mavromichalis (nicknamed The Dog), Dolgorougoph, and Komoundouros, consisted of 200 Maniots and twelve Russians.[43]
Meanwhile, the Russian fleet was besieging Koroni with assistance from the Western Legion. The siege proved to be difficult, and soon Orlov got into a dispute with John the Dog. Mavromichalis stated to Orlov that if they wanted to start a real war, they had to occupy Koroni, and that if they did not, they should not excite the Greeks in vain. Orlov replied by calling the Maniots "ragged" and "rude booty men".[43] To this, Mavromichalis replied, "The last of these ragged booty men keeps his freedom with his own sword and deserves more than you, slave of a whore!"[44] The Russians left and conducted their own operations until the end of the year, when they ultimately sailed back to Russia.[41]
The Eastern Legion met with success when it defeated an army of 3,500 Turks.[43] The Ottomans responded to this by sending an army of 8,000 to invade the Peloponnese. The Ottoman army first plundered Attica before entering the Peloponnese. At Rizomylo in Messenia, they were blocked by John Mavromichalis and 400 of his followers. The Maniots held them off for a while, but the Ottoman forces eventually won due to their superior numbers. They captured John Mavromichalis, who was not only seriously wounded but also the last survivor of the battle. He was ultimately tortured to death. They then invaded Mani and began ravaging the land near Almiro. During the night, an army of 5,000 Maniot men and women attacked the enemy camp during the night. The Ottoman forces lost 1,700, while the Maniots only suffered thirty-nine casualties.[44]
Ottoman Invasion of Mani (1770)
Main article: Ottoman Invasion of Mani (1770)Around 1770, Haci Osman with 16,000 men besieged the two towers in Kastania. The defenders were Constantine Kolokotronis and Panagiotes Venetsanakis with 150 men and women. The fight lasted for twelve days: most of the defenders were killed, and all prisoners of war were tortured and dismembered. The wife of Constantine Kolokotronis was dressed like a warrior and fought her way out carrying her baby, Theodoros Kolokotronis, the future commander of the Greek War of Independence.[45]
From Kastania, Hasan Ghazi advanced towards Skoutari and laid siege to the tower of the powerful Grigorakis clan. The tower contained fifteen men, who held out for three days until the Turks placed gunpowder in a mine and blew up the overall garrison. By this time, the main Maniot army of 5,000 men and 2,000 women had established a defensive position at which was on mountainous terrain above the town of Parasyros. The entire army was under the command of Exarchos Grigorakis and his nephew Zanetos Grigorakis. The Ottoman army advanced to the plain of Agio Pigada (meaning "Holy Well"). They sent envoys to the Maniots telling them that Hasan wanted to negotiate. The Maniots knew that if they sent envoys to the Turks, they would be executed by Hassán if the negotiations failed. The Maniots sent six men to discuss the terms.[44]
Six Maniot envoys were sent to Hasan and, without bowing, asked him what he wanted. Hasan's demands entailed the children of ten captains as hostages, all Maniot-held arms, and an annual head-tax to be paid as punishment for supporting the Russians. The Maniots answered Hasan's demands saying, "We prefer to die rather than give to you our guns and children. We don't pay taxes, because our land is poor." Hasan became furious and had the six men decapitated and impaled on stakes so that the Maniots could see them.[46]
After the envoys were killed, the remaining Maniots attacked the Ottomans. The fighting was fierce, and only 6,000 Turks managed to reach Mystras. No one knew exactly how many casualties the Maniots suffered, but the Turks definitively lost 10,000 men.[46] In 1780, Hasan Ghazi, the Bey of the Peloponnese tried to weaken the Grigorakis family by arranging the assassination of the Exarchos. He invited him to Tripoli and treated him as an honored guest but then had him hung.[47] On Easter Sunday, Exarchos' mother incited the men of Skoutari to take revenge for the death of her son.[48] Commanded by Zanetos, the men of Skoutari dressed as priests and were allowed into Passavas. Once inside, the Skoutariotes took out their concealed weapons and killed all the inhabitants of Passavas.[49]
In 1782, the Ottomans lured Michalis Troupakis onto a ship and sent him to Mytilini, where he was executed for piracy. The Porte tried to get Zanetos to replace him, but Zanetos refused until he was lured onto a ship and forced to become a bey.[50]
Soon after the Orlov Expedition, a number of Maniots entered Russian military service. Remnants of the two legions joined Russian sea forces as marines, participating in operations in the Aegean and the eastern Mediterranean. Two leaders of these volunteers were scions of the main Maniot clans, Stephanos Mavromichalis and Dimitrios Grigorakis, each rising to the rank of major. Mavromichalis became the first native commander of the Albanskoi Voisko (meaning "Albanian Host"), a unit of refugees that was resettled in the Crimea and was later reformed into the Grecheskii Pekhotnyi Polk.
Lambros Katsonis
During Zanetos' rule, Mani became a base for many klephts and other Greek bandits. Among them was the famous Greek pirate Lambros Katsonis, who helped the Russians with their wars against the Ottomans, Andreas Androutsos, (father of Odysseas), and Zacharias Barbitsiotis.[51] On January 9, 1792, Catherine II of Russia had her representative Alexander Bezborodko sign the Treaty of Jassy with Grand Vizier Koca Yusuf Pasha of the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ended the Russo-Turkish War, recognized Russia's 1783 annexation of the Crimean Khanate, and transferred Yedisan to Russia, making the Dniester the Russo-Turkish frontier in Europe while leaving the Asiatic frontier (Kuban River) unchanged.[52] Lambros Katsonis said: "Aikaterini (Greek: Catherine) made her treaty, but Katsonis didn't make his treaty with the enemy."[51]
Katsonis, together with Androutsos and Zacharias, built a gun battery at Porto Kagio. He gathered a small army and a navy of eleven ships and attacked Ottoman ships in the area. However, not being able to maintain his ships, he started attacking ships from other countries. Later that year, he sank two French ships, which was the beginning of the end for Katsonis. An Ottoman fleet of thirty ships and a French destroyer attacked Katsonis at Porto Kagio. Katsonis' men fled to land; Katsonis himself escaped to Odessa on one of the ships.[52]
Androutsos with 500 men tried to cross the Peloponnese and enter Roumelia. Zacharias in a rear-guard action managed to help fight his way through the Peloponnese and into Roumelia.[51] In 1798, Napoleon Bonaparte, at the time a general serving in the French Revolutionary Wars under the orders of the French Directory, sent two members of the Stephanopoulos family to Mani in order to convince the Maniots to attack the Ottomans from the Peloponnese while he attacked from Egypt. Zacharias and Zanetbey accepted the offer, and Napoleon sent them weapons. When the Turks discovered this, they had Zanetos replaced as bey with Panagiotis Koumoundoureas.[50]
Modern Mani
Early 19th century
During 1803, the Ottomans deposed Koumoundourakis, because he was not capable of subduing Zanetbey, who was still receiving weapons from the French at his castle at Cranae. The Ottomans replaced him with Antony or Antonbey, Zanetbey's cousin.[50] The Turkish fleet under the command of the admiral Seremet,[51] was unable to capture Cranae and was soon forced to retreat.[50]
 View of Gytheio.
View of Gytheio.
In 1805, Seremet attacked Zacharias at his fortress in the Taygetus mountains and managed to kill him.[51] In 1807, the Ottomans attacked Antonbey at Gytheio, because he was unwilling to suppress his cousin, who was still attacking the Turks. The Turks were once again forced to retreat. Three years later, Antonbey resigned in favor of his son-in-law, Konstantis Zervakos, who was favorable to the bey of the Peloponnese. However, the Maniots did not agree with the Ottomans' choice and deposed Zervakos.[53]
Later that year, the Maniot leaders gathered at Gytheio and elected Theodoros Zanerakos or Theodorobey, Zanetbey's nephew, as bey. During 1815, the Ottomans attacked Mani but were driven back.[26] Theodorobey was removed from power later that year and was replaced by Petros Mavromichalis or Petrobey.[53]
Pierros Grigorakos, a son of Tzanetbey, entered Russian service on Zante and commanded a force of some 500 Maniates known as the Spartan Legion. This was part of the Legion of Light Riflemen, a force made up of mainland refugees that defended the Ionian Islands and participated in Russian operations in the Mediterranean in the years 1805–1807. Many veterans of this unit later joined the secret society Filiki Eteria ("Friendly Company") and participated with the Greek Revolution, including Elias Chrisospathis, who initiated the Maniots into the secret society, as well as Pierros and his brothers Giorgos and Zanetakos.
Petros Mavromichalis was John the Dog's nephew. He was the first Maniot bey from Messa Mani.[53] In 1798, he had also been approached by Napoleon to join the war on the Ottomans, but after the failure of the French invasion of Egypt, Petros joined the French army for a while and fought in the Ionian Islands. It was rumored at the time that he was appointed bey only because his uncle was not killed, had converted to Islam, and had become an officer in the Ottoman army. In 1819, he joined the Filiki Eteria, which by 1821 was prepared to revolt.[54]
Contributions to the Greek Revolution
Maniots, known for their martial qualities, were the first to join the Greek liberation movement. The society called the Filiki Eteria sent their representatives Perrevos and Chrisospathis to organize the Maniots.[55] On March 17, 1821, 12,000 Maniots gathered in the church of the Taxiarchs (Archangels) of Areopolis and declared war against the Ottoman Empire.[56] The flag of the revolution was white with a blue cross in the center. Atop the flag was the motto "Victory or death". The Maniots were responsible for writing "Victory" and not "Freedom" on their banner, since Mani was always free. At the bottom of the flag was an ancient inscription, "With the shield or on the shield."[57]
On March 21, an army of 2,000 Maniots under the command of Petros Mavromichalis, Theodoros Kolokotronis, and Papaflessas marched towards Kalamata. On March 23, they captured the city.[57] From Kalamata, Mavromichalis wrote letters to the states of Europe, informing them of what the Greeks were doing. The Messenian Senate was also held in Kalamata. Kolokotronis wanted to attack Tripolis and capture the main Turkish city in the Peloponnese. However, Mavromichalis wanted to capture the smaller towns first and then take Tripolis. The Senate agreed with Mavromichalis, and the Maniots attacked the Turks of Messenia and Laconia.[58]
Kolokotronis, convinced that he was correct, moved into Arcadia with 300 Maniots. When he entered Arcadia his band of 300 fought a Turkish force of 1,300 men and defeated them.[57] On April 28, a few thousand Maniot soldiers under the command of Mavromichalis's sons joined Kolokotronis' camp outside Tripolis. On September 12, 1821, the Turkish capital in the Peloponnese fell. On July 4, Kyriakoulis Mavromichalis was killed near the Souliote fortress of Kaiapha.
Mahmud II became desperate and during 1824 called on his Viceroy, Muhammad Ali of Egypt, to aid him. Ali promised to aid him in return for the islands of Crete and Cyprus, as well as making his eldest son, Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt, pasha of the Peloponnese. Ali accepted the offer and sent his son in command of the expedition. Meanwhile, the Greeks were in disarray because of political rivalries, which caused a civil war. Kolokotronis was arrested, his son Panos was killed, and his nephew Nikitaras fled.[59]
Ibrahim made good use of this turmoil and landed with his army at Methoni. Ibrahim soon had recaptured the Peloponnese except for Nafplio and Mani. When he tried to capture Nafplio, he was repelled by Dimitrios Ypsilantis and Konstantinos Mavromichalis, Petros' brother.[60]
Ibrahim then decided to head for Mani. He sent an envoy to the Maniots demanding that they surrender or else he would ravage their land. Instead of surrendering, the Maniots replied:[57]
From the few Greeks of Mani and the rest of Greeks who live there to Ibrahim Pasha. We received your letter in which you try to frighten us saying that if we don't surrender, you'll kill the Maniots and plunder Mani. That's why we are waiting for you and your army. We, the inhabitants of Mani, sign and await you.
Enraged by the reply, Ibrahim, commanding an army of 7,000 men, attacked Mani on June 21, 1826.[61] He was stopped at the walls of Almiro and Vergas, which ran for around 500 meters.[62] Defending the walls were 2,000 Maniots under the command of Ilias Mavromichalis and 500 Greek refugees.[61][63] As Ibrahim moved his infantry and cavalry against the Maniot position, he also ordered two of his ships, including the one he was on, to attack the Maniot fortifications from the sea with their artillery. The Egyptian army attacked the Maniot position eight times and was thrown back.[61] The fighting continued for a few more days before the Egyptians retreated when rumors that Kolokotronis was approaching their rear with 2,000 men proved true.[64] The Maniots pursued the Egyptians all the way to Kalamata before returning to Vergas. This battle not only was costly for Ibrahim, who suffered 2,500 casualties, but also ruined his plan to invade Mani from the north.[57][61]
While Ibrahim was beginning his attack on the Maniot position at Vergas, he decided to launch a small fleet and attack Areopolis. This plan was described by Greenhalgh and Eliopoulos as "excellent" because it would catch Areopolis by surprise since it was ill defended. By capturing Areopolis, Ibrahim could disrupt the Maniot communication lines and control the mountain passes that led to Gytheio. This would also allow the Egyptians to attack the Maniots at Vergas from the rear.[63]
On June 24, Ibrahim sent a small fleet carrying 1,500 troops to land at the Bay of Diros and capture Areopolis.[63] As the Egyptians landed on the beach, the alarm bells rang.[61] Soon, 300 women and old men who had been harvesting the crops gathered and, armed only with their scythes and cudgels, charged at the Egyptians. The Egyptians, not expecting any resistance, were caught by surprise at this sudden attack and were forced to retreat to a fortified position on the beach where they could receive support from their ships. Eventually, 300 Maniots arrived from other towns, and the Egyptians were forced to either swim to their ships or be slain.[63] Not only was Ibrahim's defeat costly, as he lost 1,000 men, but his plan to invade and conquer Mani was utterly ruined. Later on, the women of Diro were dubbed the 'Amazons of Diro'.[65]
Ibrahim, annoyed by his defeats at Vergas and Diro, plundered the Peloponnese for a month before turning his attention back to Mani. He sent an army of 6,000 Arabs to advance to the Taygetus and capture Gytheio and Laconian Mani. In command of the army was a Greek from Vordonia, Bosinas. As he advanced towards Polytsaravo, he was stopped by Theodoros Stathakos, who together with his family of thirteen people was waiting in their tower. Bosinas tried to make Stathakos surrender, and when the latter feigned surrender, Bosinas came towards the tower. However, once Bosinas was within range, Stathakos and his army killed him. In retaliation, Bosinas' army shot at the tower with their cannons and destroyed it.[66]
The Egyptians then proceeded towards the town of Polytsaravos and reached it on August 28. The inhabitants of the town had sent the women and children to take refuge in the mountains before improving the fortifications they had there. The town militia was reinforced by other Maniots, and soon the defenders numbered 2,500 men.[66] The Egyptians had trouble advancing to Polytsaravos, because it was surrounded by rocks situated on high ground.[67] As soon as the Arabs arrived, the Maniots rallied around their fortifications and attacked the Arabs. The Arabs retreated from Polytsaravos after sustaining 400 casualties while the Maniots only suffered nine.[66] This was the last invasion of Mani by the Egyptians or the Ottomans as the Peloponnese, central Greece, and some of the Aegean islands were liberated in 1828 after the naval forces of Bourbon Restoration France under Henri de Rigny, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland under Edward Codrington, and the Russian Empire under Login Geiden defeated Ibrahim at the Navarino in 1827.
Republic and Regency
 Ioannis Kapodistrias (1776-1831).
Ioannis Kapodistrias (1776-1831).
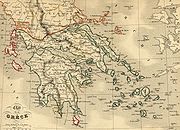 Map of the boundaries of the Kingdom of Greece after its independence.
Map of the boundaries of the Kingdom of Greece after its independence.
 King Otto, the first King of Greece.
King Otto, the first King of Greece.
In 1831, Ioannis Capodistrias became governor of Greece.[66] Capodistrias quarreled with the Mavromichalis clan because the Maniots refused to pay taxes to the government.[68] Capodistrias requested that Tzanis, Petros's brother, go to Nafplio, then capital of Greece, and negotiate. As soon as Tzanis arrived, he was arrested and imprisoned. Capodistrias then sent soldiers to Mani and had Petros arrested, imprisoned, and charged with high treason. His brother Konstantinos, the defender of Nafplio, and Petros' son, Georgios Mavromichalis, were put under house arrest in the capital.[69]
On September 27, 1831, (October 9 in the Gregorian calendar), Capodistrias went to attend a church service at the Church of Saint Spyridon. He noticed that Konstantinos and Georgios were waiting at the church doors. As he passed them, he briefly stopped before proceeding into the church. As he was about to step into the church, Konstantinos used his gun and the bullet hit Capodistrias at the back of the head while at the same time Georgios stabbed him through the heart. Capodistrias collapsed into the arms of his attendants. Capodistrias' bodyguard shot Konstantinos as he was running, and Konstantinos was hit by several more bullets before he died. Kostantinos' body was then dragged by an angry mob, who threw it into the sea. Georgios was captured and executed on the island of Bourzi, off the coast of Nafplio, while his father watched.[69]
In 1833, Otto von Wittelsbach, a son of Ludwig I of Bavaria and Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen, became King of Greece after he was appointed by the Great Powers. Since he was underage, he had a Council of Regency headed by Josef Ludwig von Armansperg governing the country for him.[56] One of the Council's first acts was to try to subdue the unruly Maniots and pull down their towers; another was to free Petros and Tzanis from their prisons.[70] The council sent an army of Bavarians in order to tame Messa Mani.[71] They made it to Areopolis, but during the night the Maniots surrounded and captured them, forcing them to leave the area.[72]
On May 14, 1834, four companies of Bavarian troops, assisted by four cannon, besieged the town of Petrovouni. Ultimately, 800 Maniots from the surrounding towns attacked the Bavarians. The Bavarians were massacred as most of them were either slain by the Maniots or fell into a ravine near the town while escaping. Later that year, an army of 6,000 men with five cannon under the command of General Christian von Schmaltz, assisted by five squadrons of royalist Maniots, once again besieged Petrovouni. When news of an army of 1,000 Maniots was approaching, they retreated to Gytheio.[72]
The Council decided that they could not subdue the Maniots by force, so they decided to send a diplomat, Max Feder, with the intention of subduing Mani. He went to different Maniot families and offered them positions if they supported the king. Many of the Achamnomeri (see note α below) and some Megalogenites were convinced by his offers and complied. However, several of the older families and the poorer Achamnomeri rejected the offer, because the former did not want to be dependent on a king and the latter did not want governors with superior rights. In Kitta, this division caused bloodshed when the king's supporters started fighting the other Maniots under the command of Giorgaros Skylakakos.[72] Feder soon arrived with his new allies and exploded Skylakakos and all his allies in his towers.[73]
Late 19th century
During Otto's rule, blood was spilled in Mani because of the vendettas, which have plagued the area for centuries.[73] The vendettas continued until 1870, when a Maniot vendetta was halted by the efforts of a regular army with artillery support.[74] In 1841, Crete revolted against the Ottomans. The Maniots, described as cousins of the Cretans, rushed to Crete to support them. The Cretans, together with the Maniots, forced the Turks into a fortress, where they besieged them. A combined Ottoman-British fleet managed to subdue the Cretans and make the Maniots go back to Mani. In 1866, a new revolution sparked in Crete, and 2,000 Maniots under the command of Petropoulakos went to assist their cousins. However, the Cretans were defeated, and the Maniots again returned to Mani.[73]
20th century
At the start of the 20th century, Greece was involved with the Macedonian Struggle, military conflicts against the Internal Macedonian Revolutionary Organization, and Turkish forces in Ottoman-occupied Macedonia. Many volunteers from Mani took part in the war such as soldiers from the Dritsakos, Koutsonikolakos, Kosteas, Georgopapadakos, Iliopiereas, Loukakos, Kyriakoulakos and Kalantzakos families. The Maniots also took part in the series of wars that followed including the Balkan Wars, World War I, and the Greco-Turkish War (1919-1922). The participation of troops from Mani in these wars under Constantine I of Greece, created strong royalist feelings amongst Maniots. That is why most Maniots remained loyal to Constantine during the Greek National Schism.[75]
The port of Gytheio, largest town of Mani.
During World War II, the Maniots significantly contributed to the Hellenic Army. During the Battle of Greece, a Maniot named Colonel Konstantinos Davakis was among the leaders of the armed forces.[75] Davakis, in command of the Pindus Detachment, defeated the Italians at the Battle of Pindus (October 28-November 13, 1940), despite the Italians having more advanced weaponry.
Later, the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom defeated the Regia Marina of Italy in the Battle of Cape Matapan (March 27-March 29, 1941) on Cape Tenaro. However, Nazi Germany attacked Greece in order to support the Italians. The Greeks were forced to retreat, and soon Mani revived its forgotten role as a center for refugees. During April 1941, the British started evacuating their troops from Porto Kagio. By the end of that month, Mani and the rest of Greece were under Italian and German occupation.[76]
During the occupation, Mani became a stonghold of the German-collaborating Security Battalions, because of the anti-communist sentiment of the Maniots. The Germans and Italians left Greece in 1944, but as soon as they left the Greek Civil War began. The armies of the Communist Party of Greece, ELAS, and DSE, fought against the Hellenic Army and the royalists.[77] Mani never recovered from both wars, and soon many of the young people of Mani left for Athens, the United States, and Australia.[78]
Nowadays, Mani is divided between two prefectures, Laconia and Messenia. Mani has around 18,000 inhabitants, with the most important and populous town being Gytheio. Mani's main source of income is tourism. The most famous of the tourist attractions are the Caves of Diro, which are two caves that have underwater rivers flowing through them.
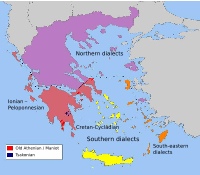
Maniot dialect
History of the
Greek language
(see also: Greek alphabet)
Proto-Greek (c. 3000–1600 BC) Mycenaean (c. 1600–1100 BC) Ancient Greek (c. 800–330 BC)
Dialects:
Aeolic, Arcadocypriot, Attic-Ionic,
Doric, Locrian, Pamphylian,
Homeric Greek,
Macedonian (?)Koine Greek (c. 330 BC–330) Medieval Greek (330–1453) Modern Greek (from 1453)
Dialects:
Calabrian, Cappadocian, Cheimarriotika, Cretan,
Cypriot, Demotic, Griko, Katharevousa,
Pontic, Tsakonian, Maniot, Yevanic
*Dates (beginning with Ancient Greek) from Wallace, D. B. (1996). Greek Grammar Beyond the Basics: An Exegetical Syntax of the New Testament. Grand Rapids: Zondervan. p. 12. ISBN 0310218950.The Greek dialect of Mani is characterised by the pronunciation of (/Υ/, /υ/, /ου/) from ypsilon from the modern Greek /οι, ι/ to the more ancient /ου/ i.e. “Ancient Greek υ and οι have become /i/ in nearly all varieties of Modern Greek, however, a number of areas (including Mani) have (/Υ/, /υ/, /ου/) ”, plus velar palatalisation, The deletion of Word Final /s/, /Σ/, /ς/, in Mani and its offspring dialect in Cargese, Corsica and shares vocabulary, phonological, and grammatical features with the Tsakonian and Greek Dialect.[79]
A very archaic feature shared by Tsakonian and the Maniot dialect is the divergent treatment of historical /y/ (<υ>). While this sound merged to /i/ everywhere else, these dialects have /u/ instead (e.g. [ˈksulo] versus standard [ˈksilo] 'wood'). Ancient Greek υ and οι have become /i/ in nearly all varieties of Modern Greek, however, a number of areas have /u/.[79] They are considered to be the ‘oasis’ dialects on the edges of (or surrounded by) the Arvanitika-speaking area — Kimi, Aegina, Megara, and Old Athenian; the Mani peninsula of the southern Peloponnese; and Tsakonian. Tsakonian is generally reckoned to be the only modern dialect that is not descended from the Ancient Greek Koiné and it is aberrant in very many respects. One obvious conclusion from the geographical configuration, is that the four, now extinct, ‘oasis’ dialects are the last remnants of a large, single area (Sprachbund) over all of which this feature was once found, before the penetration of Arvanitika which had the effect of dividing and separating these four relic areas from each other.
All varieties of Modern Greek front velar consonants in the environment before front vowels and /j/. However, a well-known feature associated with southern Greek dialects is the extreme palatalisation and (af)frication of velar consonants in this same position. Specifically, /k, ɡ, x, ɣ/ are fronted before /i, e, j/ to ([tɕ], [dʑ], [ɕ], [ʑ]) or to ([tʃ], [dʒ], [ʃ], [ʒ]). This is a well-known feature of Cretan, where the former (alveolo-palatal) pronunciations are more common, and in Cyprus, where the latter (palato-alveolar) realisations are usual; this feature is found in Mani, a dialect that has other affinities with Cretan. The geographically most widespread palatalisation is of /k/ —-i.e. some dialects have palatalisation and affrication of /k/ but not of the other velars.
Examples
- Κιχάμο - Εκεί
- Δοχάμο - Εδώ
- Τσαι - Και
- Ουτό/ς - Αυτό/ς
- Τήνο/ς - Εκείνο/ς
- Αλαργάρου - Μακριά
- Μπαούρδα - Πολύ ανoιχτό
- Σαλιγόρο - Σαλιγκάρι
- Ζατί - Γιατί
- Τίποτα/Τσίπτα - Τίποτε
- Τσιούτα - Κοίτα
- Γιάλεχτο - Διάλεκτο
- Παντέχου - Ελπίζω
- Περιγιάλη - Παραλία
- Σαρώνω - Σκουπίσω
- Ντάσκα - Τσάντα/Σακούλα
- Καφός - Αδελφός
Phrases: Τσι φιάνεις; - Τι κάνεις/Πως είσαι; Τόσιε αλαργάρου ενάϊ; - Τόσο μακριά είναι;
Economy
There is little information on the economy of Mani during the early stages of Ottoman dominance of Greece and what is known of the economy in the 17th and 18th centuries is from foreign observers. In Exo Mani, olives in great numbers but it was not until the 18th century that olives were widely spread in Mesa Mani. Exports from Exo Mani also included pine for masts as well turpentine, hides as well as a tanning agent and prinokoki, a crimson coloured dye. The north-west parts of Mesa mani were rich in mulberries and silk. Another important part of the Maniot economy was piracy. Now days the main industries in Mani are agriculture and tourism.[80]
Culture
Dances
Two dances come from Mani: Palio Maniatiko (meaning "Old Maniot") and the Modern Maniatiko. The Palio Maniatiko is only found in Mani and is described as an ancient dance.[81] The Modern Maniatiko is the modern version of the Palio Maniatiko dance and includes certain aspects of the Kalamatiano dance in it. Like the Palio Maniatiko, it is only performed in Mani.[81]
Piracy
"If any ship come to anchor on their coast, many arm themselves and go to the place, over against where the ship doth ride; some of them will be in priests habits, walking by the sea side, with their wallets, in which they will have some wine and bread. Their companions lye hid behind the bushes at some convenient post. When any strangers come ashore, who do not understand their language, the feigned priests make signes to them, shewing them their bread and wine, which they offer to them for money, by which the strangers being enticed from the sea side (and it may be to sit down and taste their wine) the hidden Manjotts come and make their prey. The priests will seem to be sorry, and endeavor to make the strangers to believe they were altogether ignorant of any such design. So a white flagg is put out, and a treaty held with the ship for their ransome. The priests endeavor to moderate the price, shewing a great deal of respect to their companions, who are clothed in Turkish habits. Many ships have been thus served." Bernard Randolph, Present State of the Morea.[82] Part of Maniot culture involved piracy. The Maniots were famous and fearsome pirates whose ships dominated the Maniot coastline. The Maniots became pirates because Mani was not a very fertile land and the Maniots did not have many natural resources. The Maniots considered piracy a legitimate response to the fact that their land was poor, and it became their main source of income.[83] The pirate raids were not stopped by the local priests of the Eastern Orthodox Church, who in fact blessed the ships before they left and sometimes accompanied them on raids. Most of the Maniot pirates came from Messa Mani.[84] The main victims of Maniot pirates were the Ottomans, but the Maniots also targeted ships of powerful European countries.[26]
Superstition
The Maniots are a very superstitious people.[85] Maniots mainly believe in witches, demons, vampires, and ghosts.[85] When Henry Herbert, 3rd Earl of Carnarvon, was touring Mani in 1839, he found a fresh egg by the side of the road and offered it to a Maniot soldier who escorted him, who declined the offer claiming that if a hag had enchanted it he would have to marry her.[85] The Maniots thought that certain areas were haunted by demons.[85]
Vendettas
Another important aspect of Maniot culture were the vendettas which frequently plagued Mani. Usually, the decision to start a vendetta was made at a family gathering. The main aim of a vendetta was usually to wipe out the other family.[86] The families involved locked themselves in their towers and whenever they got the chance murdered members of the opposing family.[86] The other families in the village normally locked themselves in their towers in order not to get in the way of the fighting.[86]
Some vendettas went on for months, sometimes years. In vendettas, the families could have a truce or treva, if one family needed to attend a religious ceremony or when it was time to harvest the crops.[86] As soon as the treva ended, the killing could resume. Vendettas usually ended when one family was exterminated or when the defeated family left the town. Sometimes families came to terms, and vendettas stopped when the Turks invaded.[86] The longest treva occurred when the Mavromichales declared war on the Turks in 1821. Vendettas continued after the liberation of Greece even though the Regency tried to demolish the towers.[86]
Ethnology
The inhabitants of Mani are the direct descendants of the ancient Spartans. After the Romans took over Laconia, many of the citizens who were loyal to the laws of Lycurgus decided to go to the mountains of Mani with the rest of the Spartans rather than be in Achean or, later, Roman service.[87] Kassis claims that Maniots rarely mated with non-Maniots until the 20th century.[88]
Mani became a refuge during the 4th century when the Barbarian invasions started in Europe. When the Avars and Slavs invaded the Peloponnese, many Greek refugees fled to Mani since the invaders could not infiltrate the mountainous terrain. According to Constantine Porphyrogenitus, the Maniots were not conquered by the Slavs and were descended from the ancient 'Romaioi'.[18] Historian David Howarth states: The only Greeks that have had an unbroken descent were the few small clans like the Maniotes who were so fierce, and lived so far up the mountain, that invaders left them alone.[89]
Notable Maniots
- Stephen Antonakos (artist, National Academy of Art Lifetime Achievement Award-Sculpture)
- Panagiotis Doxaras (painter, founder of the Heptanese School)
- Zacharias Pentalakos (klepht in the Peloponnese during the last decades of the Ottoman rule)
- Georgios Antonakos (General, Chief of Staff Greek Airforce under the King)
- Petros Mavromichalis (fighter during the Greek War of Independence)
- Nikolaos Pierrakos Mavromichalis (fighter during the Greek War of Independence)
- Panagiotis Giatrakos (fighter during the Greek War of Independence)
- Kyriakoulis Mavromichalis (military commander)
- Periklis Pierrakos-Mavromichalis
- Alexandros Koumoundouros
- Kyriakoulis Mavromichalis
- Panos Katsareas (Founder of E.A.O.K, the National Anti-Communist Party during the Greek Civil War)
- Kyriakos Kyriakoggonas (Leader of E.A.O.K after Panos Katsreas's death)
- Themistoklis Ketseas (Lt.Col of the Greek army during the Greco-Italian War)
- Georgos Koumanakos (Leader of the Spartan Batallion of the Greek Expeditionary Force in Korea during the Korean War)
- Aliki Vougiouklaki
- Giannis Poulopoulos (singer)
- Stamatis Bitakos (professional Muay Thai athlete)
- Angelos Charisteas (professional football player)
- Errica Prezerakou (professional athlete)
Notes
- ^ In the second Byzantine occupation of Mani, there were four social castes, the Nikliani, the Megalogenites, the Achamnomeri and the Fameyi. The Nikliani were the inhabitants of the town of Nikli before it was sacked by the Byzantine emperor, Andronicus II Palaeologus. Kyriakos Kassis claims that the Nikliani were a family[23] while Patrick Leigh Fermor claims they were the inhabitants of Nykli.[24] The Nikliani were wealthy, upper class people who started the building of castles in Mani.[23] The Megalogenites (meaning "great births"), were refugees from other parts of Greece who were from wealthy and renown families like the Commenoi, Palaeologoi, Medici and others. They mostly ignored the Niklianis' laws or tried to live in harmony with them. The Megalogenites also started building towers like the ones built by the Nikliani.[23] The Achamnormeri were the third Maniot class and was the middle class. It did not have as many rights as the first two classes. They had the right to build only one-story towers and they were not allowed to build towers out of limestone or marble. They owned most of the fields and had a right to a portion of common property like quail, salt, and fish. They also had the freedom of movement and means of production. If during the night, they managed to raise a tower larger than one of their neighbors, they were considered more powerful.[25] The last caste were the Fameyi who were serfs. They had no property and they were sometimes confused with the Achamnormeri by modern historians. They could be subject to emancipation and become Achamnormeri.[25]
- ^ In 1453, Mani's population grew drastically as a large number of refugees arrived from other parts of Greece, after the Fall of Constantinople.[26] Around that time, towns like Skoutari were founded by people who had escaped from Constantinople.[27] Kassis tells us that the population of Mani at that time was between 40,000 and 80,000.[26] Count Chateau-Reneau says that at the beginning of the 17th century, there were 700 cities and many villages in Mani which was thought to be an exaggerated number. In 1700, 14,773 people were recorded in the census despite the constant migrations in Mani. In 1805, William Martin Leake recorded that there were 30,000 people living in Mani. Twelve years later, K. Koumas writes in his geography that Mani had 100,000 inhabitants which was deemed a wildly exaggerated number. In 1820, Anagnostras composition for the Filiki Eteria says that Mani had 8,000 fighting men. Kassis comes to the conclusion that Mani had around 45,000 inhabitants in 1820.[26]
- ^ As a result of the many revolts against the Ottoman Empire, the Maniots welcomed new Greek refugees from various areas including Asia Minor, and especially Crete when the Turks acquired the island from the Venetians in 1669. The Cretan refugees settled in Mani and created villages with Cretan names that enriched the Maniot dialect with Cretan words and idioms.[34] The mass migration of refugees caused new problems in Mani. The limited area of good arable land led to many local wars between families, clans, and different villages. The era of vendettas began in Mani and it seemed that only a new Ottoman invasion could save the country from a civil war. Many Maniot people began to serve as mercenaries in the army of the Doge of Venice while some others became pirates to fulfill their patriotic duties. In fact, the Ottoman fleet near Chania, Crete was destroyed by Maniot pirates.[35]
- ^ Between 1600 and 1700, there was a mass exodus of Maniots leaving Mani for European countries. In 1570, some Maniots immigrated to Volterra.[38] Around 700 members of the Stephanopoulos clan migrated to Corsica, as well as the Latriani, (whose Latinized name happened to be Medici) who went to live in Tuscany after gaining Ferdinand Medici's permission.[39] There are still towers in Tuscany that look similar to the ones in Mani. The Duke of Genoa wanted some Maniots to colonize the western Italian coast and protect it from pirates. There are mentions of Maniots in Naples and T. Asanis Palaeologus building a church there. There are also tombs of Palaeologi in Cornwall, England, as well as one in Westminster of a Palaeologus who fought with Oliver Cromwell. Charles V, the King of Spain and the Holy Roman Empire, had distinguished an army corp name the Mainoti.[28]
References
Citations
- ^ Homer. The Iliad, 2.581.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 7.
- ^ Saitas 1990, p. 13.
- ^ a b c Fermor 1984, p. 302.
- ^ a b c d Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 20.
- ^ Xenophon. Hellenica, 1.4.11.
- ^ Green 1990, p. 302.
- ^ Livy. Ab urbe condita libri, 34.29.
- ^ a b Smith 1873, Nabis.
- ^ Livy. Ab urbe condita libri, 35.35.
- ^ Cartledge & Spawforth 2002, p. 78.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 16.
- ^ a b c Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 21.
- ^ a b Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 49.
- ^ Pausanias. Description of Greece, 3.21.8.
- ^ Fermor 1984, p. 120.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 19.
- ^ a b c d Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 22.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991, pp. 1916–1919 under SLAVS.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 23.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 23.
- ^ a b c d e Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 24.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 24.
- ^ Fermor 1984, p. 86.
- ^ a b Kassis 1979, p. 25.
- ^ a b c d e f Kassis 1979, p. 38.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 54.
- ^ a b Kassis 1979, p. 28.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 29.
- ^ a b c d John Chapman. "Turkokratia: Kladas Revolt". Mani: A Guide and a History. http://www.zorbas.de/maniguide/turkok.html. Retrieved 2007-01-19.
- ^ a b Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 25.
- ^ a b c d e Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 26.
- ^ a b c d Kassis 1979, p. 30.
- ^ Fermor 1984, p. 150.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 32.
- ^ Kassis 1979, pp. 30–31.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 31. See also Nicholas, 2006.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 27.
- ^ a b Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 27.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 28.
- ^ a b c Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 29.
- ^ a b Kassis 1979, p. 33.
- ^ a b c d e Kassis 1979, p. 34.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 35.
- ^ Roumeliōtēs 2002, p. 31.
- ^ a b Kassis 1979, p. 36.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 30.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 51.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 52.
- ^ a b c d Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 31.
- ^ a b c d e Kassis 1979, p. 37.
- ^ a b Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 140.
- ^ a b c Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 32.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 33.
- ^ Paroulakis 1984, p. 40.
- ^ a b Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 58.
- ^ a b c d e Kassis 1979, p. 39.
- ^ Paroulakis 1984, p. 58.
- ^ Paroulakis 1984, p. 113.
- ^ Paroulakis 1984, p. 125.
- ^ a b c d e Kassis 1979, p. 40.
- ^ Saitas 1990, p. 12.
- ^ a b c d Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 62.
- ^ Barrow 2000, p. 21.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 63.
- ^ a b c d Kassis 1979, p. 41.
- ^ Barrow 2000, p. 102.
- ^ Paroulakis 1984, p. 165.
- ^ a b Paroulakis 1984, p. 168.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 35.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 43.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 44.
- ^ a b c Kassis 1979, p. 45.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 36.
- ^ a b Kassis 1979, p. 46.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 141.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 38.
- ^ Greenhalgh & Eliopoulos 1985, p. 39.
- ^ a b Trudgill 2003, p. 59.
- ^ John Chapman. "The Economy". http://www.zorbas.de/maniguide/turkok.html. Retrieved 2008-01-02.
- ^ a b "Types of Dances". PMDG: Types of Dances. Archived from the original on 2006-08-20. http://web.archive.org/web/20060820234026/http://www.mani.org.au/dancegroup/dgDanceTypes.asp. Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ Eisner 1993, p. 60.
- ^ Barrow 2000, p. 16.
- ^ Barrow 2000, p. 17.
- ^ a b c d Barrow 2000, p. 18.
- ^ a b c d e f Venizeleas. "Vendetta". Mani: Traditions: Vendetta. http://www.mani.org.gr/en/history/venteta.htm. Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ Hellander 2008, p. 204.
- ^ Kassis 1979, p. 20.
- ^ Howarth 1976, p. 69.
Sources
- Barrow, Bob (2000). Mani: A Guide to the Villages, Towers and Churches of the Mani Peninsular. Antonis Thomeas Services. ISBN 0953751708.
- Cartledge, Paul; Spawforth, Antony (2002). Hellenistic and Roman Sparta: A Tale of Two Cities. London: Routledge. ISBN 0415262771.
- Eisner, Robert (1993). Travelers to an Antique Land: The History and Literature of Travel to Greece. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0472082205.
- Fermor, Patrick Leigh (1984). Mani: Travels in the Southern Peloponnese. Penguin Books. ISBN 0140115110.
- Green, Peter (1990). Alexander to Actium: The Historical Evolution of the Hellenistic Age (Second Edition). Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 050001485X.
- Greenhalgh, P. A. L.; Eliopoulos, Edward (1985). Deep into Mani: Journey to the Southern Tip of Greece. Faber and Faber. ISBN 0571135242.
- Hellander, Paul (2008). Greece. Lonely Planet. ISBN 1741046564.
- Howarth, David Armine (1976). The Greek Adventure: Lord Byron and Other Eccentrics in the War of Independence. Atheneum. ISBN 068910653X.
- Kassis, Kyriakos (1979). Mani's History. Athens: Presoft.
- Nicholas, Nick (2006). Negotiating a Greco-Corsican Identity. 24. Journal of Modern Greek Studies. pp. 91–133.
- Kazhdan, Alexander P. (1991). The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195046528.
- Paroulakis, Peter Harold (1984). The Greeks: Their Struggle for Independence. Hellenic International Press. ISBN 0959089403.
- Roumeliōtēs, Giannēs Ch. (2002). Herōides tēs Lakonias kai tēs Manēs holēs (1453-1944). Ekdoseis Adoulōtē Manē. ISBN 9608703018.
- Saitas, Yiannis (1990). Greek Traditional Architecture: Mani. Athens: Melissa Publishing House.
- Smith, William (1873). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology. London: John Murray.
- Trudgill, Peter (2003). Modern Greek Dialects: A Preliminary Classification. 4. Journal of Greek Linguistics. pp. 45–63.
Categories:- Greek people
- Maniots
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.