- Mumbai Pune Expressway
-
Mumbai Pune Expressway मुंबई-पुणे द्रुतगती मार्ग Yashwantrao Chavan Expressway
यशवंतराव चव्हाण द्रुतगती मार्ग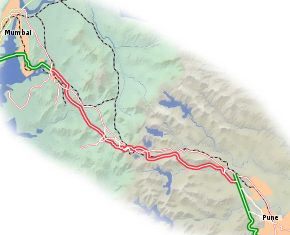
Expressway mapRoute information Maintained by MSRDC Length: 93 km (58 mi) Major junctions From: Kalamboli (Near Panvel) To: Dehu Road (Near Pune) Location States: Maharashtra Highway system Indian Road Network
National • Expressways • StateThe Mumbai Pune Expressway (Marathi: मुंबई-पुणे द्रुतगती मार्ग), officially the Yashwantrao Chavan Expressway (Marathi: यशवंतराव चव्हाण द्रुतगती मार्ग) is India's first six-lane concrete, high-speed, access controlled tolled expressway.[1] It spans a distance of 93 km (58 mi) connecting Mumbai, the administrative capital of Maharashtra and the financial capital of India, with Pune, an industrial and educational hub[citation needed]. This expressway introduced new levels of speed and safety in automobile transportation to Indian roads.[2]
The expressway has reduced the travel time between the cities of Mumbai and Pune to approximately two hours. For most practical purposes, it has replaced the older Mumbai-Pune stretch of the Mumbai-Chennai National Highway (NH 4), which had become extremely congested and accident-prone over time. The expressway starts at Kalamboli (near Panvel) and ends at Dehu Rd. (near Pune). It cleaves through the scenic Sahyadri mountain ranges via passes (Marathi: घाट) and tunnels. It has five interchanges Kon (Shedung), Chowk, Khalapur, Kusgaon and Talegaon.
The expressway has two carriageways with three concrete lanes each separated by a central divider and a tarmac or concrete shoulder on either side. Vehicles with fewer than four wheels and agricultural tractors are not permitted, although tractor-trailers (semi-trailer rigs are permitted). The expressway handles about 30,000 PCUs daily, and is designed to handle up to 1,000,000 PCUs.
Contents
History
 The Mumbai-Pune Expressway at night as seen from Khandala
The Mumbai-Pune Expressway at night as seen from Khandala
In 1990, the Government of Maharashtra appointed RITES and Scott Wilson Kirkpatrick of United Kingdom to carry out feasibility studies for the new expressway to be operated on toll basis. RITES submitted their report in 1994 with the estimated cost of project at
 1,146 crore (US$232.41 million). The Government of Maharashtra entrusted the work of the construction of Mumbai-Pune expressway to MSRDC in March 1997 on Build-Operate-Transfer basis with permission to collect toll for 30 years. The environmental clearance from the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India was received on October 13, 1997. The Forest Clearance was received on November 11, 1997.
1,146 crore (US$232.41 million). The Government of Maharashtra entrusted the work of the construction of Mumbai-Pune expressway to MSRDC in March 1997 on Build-Operate-Transfer basis with permission to collect toll for 30 years. The environmental clearance from the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India was received on October 13, 1997. The Forest Clearance was received on November 11, 1997.The tender notice was published in leading newspapers all over India and also on the Internet. Due to wide publicity, 133 tenders were sold and on December 18, 1997, 55 tenders were received. After technical and financial evaluation, tenders were accepted and work orders were given on January 1, 1998 to four contractors. Thereafter tenders for widening of Khandala and Lonavala-Khandala bypass works were invited. The tenders were received on August 24, 1998 and orders were issued on September 4, 1998.
Construction
 The Mumbai-Pune Expressway as seen from Khandala
The Mumbai-Pune Expressway as seen from Khandala
The project was completed under the stewardship of the Maharashtra State Road Development Corporation (MSRDC).
The expressway cost 1,630 crore (US$330.56 million) to construct.
1,630 crore (US$330.56 million) to construct.
The first sections opened in 2000, and the entire route was completed, opened to traffic and made fully operational from April 2002.Tunnels
It has five illuminated, ventilated tunnels totalling 5,724 metres. These tunnels were built by the Konkan Railway Corporation Ltd.
These are:
Tunnels Tunnel Description 1 Bhatan This tunnel opened in April 2000.
The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 1,053 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 1,088 m long.2 Madap This tunnel also opened in April 2000.
The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 305.3 m and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 359.3 m long.3 Adoshi This only has a Pune-Mumbai tube.
The Mumbai-Pune carriageway skirts the eastern edge of the tunnel
while the Pune-Mumbai carriageway traverses the 258 m long tunnel.4 Khandala This is a curved pair of tubes. The Mumbai-Pune (North) tube is 293.5 m
and the Pune-Mumbai (South) tube is 400 m long.5 Kamshet-1 It has 2 tubes roughly 900 m each. 6 Kamshet-2 359 m The entire length of expressway has a single layer of barbed wire fencing to keep out stray cattle.
Distances
Distances Description Distance 1 Start of Expressway (Mumbai end) (19°01′11.47″N 73°06′13.21″E / 19.0198528°N 73.1036694°E) to Kon-Shedung interchange 8.5 km (5.3 mi) 2 Kon-Shedung interchange to Bhatan tunnel 6.3 km (3.9 mi) 3 Bhatan tunnel to Madap tunnel 10.6 km (6.6 mi) 4 Madap tunnel to Khalapur toll station 7.3 km (4.5 mi) 5 Khalapur toll station to Khalapur-Sajgaon gas station & rest area 1.6 km (0.99 mi) 6 Khalapur-Sajgaon rest area to Adoshi tunnel.
The Mumbai-Pune carriageway skirts the eastern edge of the tunnel
while the Pune-Mumbai carriageway traverses the 256 m long tunnel.6.9 km (4.3 mi) 7 Adoshi tunnel to the old British-built Deccan-Konkan stone trestle.
This is the site of the old (1830–1928) GIPR reversing station.4.5 km (2.8 mi) 8 Stone trestle to Khandala tunnel 0.8 km (0.50 mi) 9 Khandala tunnel to Khandala 2.7 km (1.7 mi) 10 Khandala to Tungarli 3.5 km (2.2 mi) 11 Tungarli to Kamshet-1 tunnel 17.1 km (10.6 mi) 12 Kamshet-1 tunnel to Kamshet-2 tunnel 1.2 km (0.75 mi) 13 Kamshet-2 tunnel to Talegaon toll station 11.1 km (6.9 mi) 14 Talegaon toll station to Somatne interchange 3.4 km (2.1 mi) 16 Somatne interchange to End of Expressway (Pune end) (18°39′45.85″N 73°43′35.61″E / 18.6627361°N 73.7265583°E) 7.6 km (4.7 mi) Total length of Expressway: Start to End 93.1 km (57.8 mi) Tolls
Toll is collected at Khalapur (Pali Phata) (for the Mumbai-Pune direction) and at Talegaon (for the Pune-Mumbai direction). The toll ranges from
 165 (US$3.35) for private cars, to
165 (US$3.35) for private cars, to  1,175 (US$23.83) for multi-axle trailer trucks.
1,175 (US$23.83) for multi-axle trailer trucks.Safety
The Expressway has witnessed a large number of accidents, attributed to human errors and the large volume of traffic. In 10 years there were 1758 accidents, with more than 400 fatalities. .[3] Sporadic instances of robbery have also been reported in the highway. [4] [5] [6]
Future Expansion
MSRDC has decided to extend the Mumbai Pune Expressway from the current endpoint of Kalamboli near Panvel and to extend it till Sion in Mumbai. The extended stretch will reduce commuting time between Mumbai and Pune by 30 minutes. Under the plan, the Sion Panvel Expressway corridor will be widened, with dedicated lanes for heavy and light vehicles. Service roads will be built for entry and exit at various points. It will also involve constructing a brand new bridge over the Thane creek parallelly to the current Vashi Mankhurd Bridge. MSRDC will undertake the expansion project. Work is expected to commence in March 2009 and complete by September 2011. The new 22-km link is expected to cost
 800 crore (US$162.24 million).
800 crore (US$162.24 million).Controversy about naming the expressway
The expressway was conceived and the work started when the BJP and Shiv Sena ruled the Maharashtra State. At some point they decided to name the expressway after one of the greatest Marathi litterateur Late Pu. La. Deshpande.[citation needed] Eventually, in 2009, the ruling coalition (Congress, NCP) named the expressway after the first Chief Minister of Maharashtra, Late Yashavantrao Chavan.
Gallery
See also
- Expressways in India
- Roads in Pune
References
- ^ "Mumbai-Pune Expressway, India". Road Traffic Technology. http://www.roadtraffic-technology.com/projects/mumbai/. Retrieved 2010-08-21.
- ^ "Expressway pune mumbai pune , mumbai pune mumbai , express high way nh-4 national highway no4". Punediary.com. http://www.punediary.com/html/eway.html. Retrieved 2010-08-21.
- ^ "A bloody track record". Pune Mirror. 20 July 2010. http://www.punemirror.in/index.aspx?page=article§id=2&contentid=201007202010072022483262929141dd6§xslt=. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ "Asiad bus looted on expressway". Times of India. 23 February 2004. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/pune/Asiad-bus-looted-on-expressway/articleshow/512862.cms. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ Umbrajkar, Manish (13 May 2009). "MSRDC should handle security on e-way: Bokey". The Times Of India. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/City/Pune/MSRDC-should-handle-security-on-e-way-Bokey/articleshow/4522403.cms. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ "Expressway turns into a fast lane for robbers". The Times Of India. 25 February 2002. http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/pune/Expressway-turns-into-a-fast-lane-for-robbers/articleshow/23204791.cms. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
External links
Pune topics History Sinhagad · Shaniwar Wada · Battle of Khadki · Baji Rao I · Nanasaheb Peshwa · Bal Gangadhar Tilak · Pune Terror Attacks
Civic Landmarks BuildingsTemplesChaturshringi Temple · Dagadusheth Halwai Ganapati Temple · Pataleshwar · Kasba Ganapati · Dashabhuja Ganapati TempleMuseumsRaja Dinkar Kelkar Museum · Mahatma Phule Museum · Babasaheb Ambedkar Museum · Pune Tribal Museum · National War MuseumParks and ZoosBund Garden · Rajiv Gandhi Zoological Park · Shunyo Park · Shahu Udyan · Peshwe Park · Saras Baug · Empress Garden · Kamala Nehru Park · Sambhaji Park · Pu La Deshpane UdyanOthersEconomy Transport AirPune International Airport · New Pune International Airport * · NDA Glider Airport · Hadapsar AirportRailPune Railway Station · Pune Suburban Service · Shivajinagar Station · Khadki Station · Ahmedabad - Mumbai - Pune Bullet train *RoadMumbai-Pune Expressway · Old Pune-Mumbai Highway · Pune Station Bus Stand · Swargate Bus Stand · Shivajinagar Bus Stand · Maharashtra State Road Transport Corporation · Ring Road †InternalShivajinagar Station - Swargate Skywalk * · Pune Mahanagar Parivahan Mahamandal Limited · Pune BRTS † · Pune Metro * · Pune Monorail *Roads Mumbai-Bangalore NH 4 · Pune-Nashik NH 50 · Pune-Solapur (Part of NH 9) · Karve Road · F C Road · J M Road · Tilak Road · M G Road · Laxmi Road · Sinhgad Road · Pune-Paud · Law College Road · Canal Road · Chhatrapati Shivaji Road · Bajirao RoadCulture Education College of Engineering · National Defence Academy · Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute · Fergusson College · University of Pune · Film and Television Institute of India · Gokhale Institute of Politics and Economics · Symbiosis Institute of Business Management · Symbiosis Institute of Management Studies · Pune Institute of Computer Technology · National Chemical Laboratory · Deccan College · Armed Forces Medical College · Bharti Vidyapeeth · Law college ·Sports EventsPune Marathon · 2008 Commonwealth Youth Games · 2009 FIVB Men's Junior World Championship · FIBA Asia Under-16 Championship for Women 2009 · 2011 Rollball World CupTeamsPune FC · Pune Warriors · Maharashtra cricket team · Chetak FC · Deccan XI FC · CMS Falcons FC · Fatima XI FC · Khadki Blues FCVenuesRoyal Connaught Boat Club · Nehru Cricket Ground · Pune International Cricket Centre · Shree Shiv Chhatrapati Sports Complex · Pune Race course · CAFVD Sports Stadium · Sanas Sports CiyGeography Hills and MountainsVetal Hill (Hanuman Tekdi) · Fergussen Hill · Parvati Hill · Baner Hill · Sutarwadi Hill · Katraj Hill · Ramtekdi · GultekdiWater BodiesMula River · Mutha River · Mula-Mutha River · Peacock Bay · Katraj Lake · Pashan Lake · Ramnadi · AmbilodhaCity Areas Somwar Peth · Mangalwar Peth · Budhwar Peth · Guruwar Peth · Shukrawar Peth · Shaniwar Peth · Raviwar Peth · Kasba Peth · Ganj Peth (Mahatma Phule Peth) · Bhavani Peth · Ghorpade Peth · Ganesh Peth · Sadashiv Peth · Narayan Peth · Rasta Peth · Nana Peth · Navi PethPune Cantonment (Camp) · Yerwada · Kalyani Nagar · Koregaon Park · Kothrud · Swargate · Shivajinagar · Aundh · Lohegaon · Sopan Baug · Deccan Gymkhana · Nal Stop · Erandavane · Paud Phata · Parvati · Mukundnagar · Maharshinagar · Gultekdi · Erandwane · Salisbury Park · Bopodi · Heera BaugRange Hills · Khadki · Khadki Cantonment · Ganeshkhind · Dattawadi · Sahakarnagar · Dhankawadi · Bibvewadi · Lullanagar · Upper Kondhwa · Ghorpadi · Fatimanagar · Wanowrie · Vishrantwadi · Ramwadi · Vanaz · Kharadi · Gokhale Nagar* Planned · † Under construction Indian Highways Network National Expressways NE 1 • NE 2
State Expressways Mumbai-Pune • Delhi-Gurgaon • DND Flyway • Bengaluru-Mysore • Chennai HSCTC • Hyderabad Elevated ExpresswaysNational Highways 1 • 1A • 1B • 1C • 1D • 2 • 2A • 3 • 4 • 4A • 4B • 5 • 5A • 6 • 7 • 7A • 8 • 8A • 8B • 8C • 8D • 8E • 9 • 10 • 11 • 11A • 11B • 12 • 12A • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 17A • 17B • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 21A • 22 • 23 • 24 • 24A • 24B • 25 • 25A • 26 • 26A • 27 • 28 • 28A • 28B • 28C • 29 • 30 • 30A • 31 • 31A • 31B • 31C • 31D • 32 • 33 • 34 • 35 • 36 • 37 • 37A • 38 • 39 • 40 • 41 • 42 • 43 • 44 • 44A • 45 • 45A • 45B • 45C • 46 • 47 • 47A • 47B • 47C • 48 • 49 • 50 • 51 • 52 • 52A • 52B • 53 • 54 • 54A • 55 • 56 • 57 • 57A • 58 • 59 • 59A • 60 • 60A • 61 • 62 • 63 • 64 • 65 • 66 • 67 • 68 • 69 • 70 • 71 • 71A • 71B • 72 • 72A • 73 • 73A • 74 • 75 • 76 • 77 • 78 • 79 • 79A • 80 • 81 • 82 • 83 • 84 • 85 • 86 • 86A • 87 • 88 • 89 • 90 • 91 • 91A • 92 • 93 • 94 • 95 • 96 • 97 • 98 • 99 • 100 • 101 • 102 • 103 • 104 • 105 • 106 • 107 • 108 • 109 • 110 • 111 • 112 • 113 • 114 • 116 • 117 • 119 • 121 • 123 • 125 • 126 • 127 • 128 • 129 • 150 • 151 • 152 • 153 • 154 • 155 • 200 • 201 • 202 • 203 • 203A • 204 • 205 • 206 • 207 • 208 • 209 • 210 • 211 • 212 • 213 • 214 • 214A • 215 • 216 • 217 • 218 • 219 • 220 • 221 • 222 • 223 • 224 • 226 • 227 • 228 • 229 • 234 • 235State Highways Andhra Pradesh • Arunachal Pradesh • Assam • Bihar • Chhattisgarh • Goa • Gujarat • Haryana • Himachal Pradesh • Jammu and Kashmir • Jharkhand • Karnataka • Kerala • Madhya Pradesh • Maharashtra • Manipur • Meghalaya • Mizoram • Nagaland • Orissa • Punjab • Rajasthan • Sikkim • Tamil Nadu • Tripura • Uttarakhand • Uttar Pradesh • West BengalNotable Categories:- Transport in Pune
- Transport in Mumbai
- Limited-access roads
- Expressways in India
- Roads in Maharashtra
- Toll roads in India
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.








