- Keyboard layout
-
A keyboard layout is any specific mechanical, visual, or functional arrangement of the keys, legends, or key–meaning associations (respectively) of a computer, typewriter, or other typographic keyboard.
- Mechanical layout
- The placements and keys of a keyboard.
- Visual layout
- The arrangement of the legends (labels, markings, engravings) that appear on the keys of a keyboard.
- Functional layout
- The arrangement of the key–meaning associations, determined in software, of all the keys of a keyboard.
The mechanical keyboard merely sends key codes to the associated computer; software in the computer, usually part of the operating system, totally determines how the codes are interpreted, and this can be changed in software. It is usually possible for an advanced user to change keyboard operation, and third-party software is available to modify or extend keyboard functionality.
Keyboard structure
A key labeled with only a single letter (usually the capital form) can generally be struck to type either a lower case or a capital letter, the latter requiring the simultaneous holding of the shift key, often labeled "⇧". The shift key is also used to type the upper of two symbols on a given key, the lower being typed without using the shift key.
Many languages use the Latin alphabet but have diacritically marked or other special letters and punctuation for which unique keys do not exist on all keyboards. Therefore, keyboards often have what is effectively a secondary shift key, labeled Alt Gr or option. It can be used to type symbols beyond the two otherwise available with each key. On the visual layout, the secondary symbols may appear to the right of the main symbols engraved on the keys, or they may be unmarked.
The shift and Alt Gr or option keys, along with e.g. caps lock, control and alternative (alt) keys, are called modifier keys. There are also function keys, with various functions as determined by software.
Scan codes
Most computer keyboards are designed to send scan codes to the operating system, rather than directly sending characters. From there, the series of scan codes is converted into a character stream by keyboard layout software. This allows a physical keyboard to be dynamically mapped to any number of layouts without switching hardware components — merely by changing the software that interprets the keystrokes.
Dead key
A dead key is a special kind of a modifier key that, instead of being held while another key is struck, is pressed and released before the other key. The dead key does not generate a character by itself, but it modifies the character generated by the key struck immediately after, typically making it possible to type a letter with a specific diacritic. For example, on some keyboard layouts, the acute accent key is a dead key; in this case, striking acute accent and then a results in á, whereas acute accent followed by e results in é. An acute accent in isolated form can be typed by striking acute accent and then space.
A key may function as a dead key by default, or sometimes a normal key can temporarily be altered to function as a dead key by simultaneously holding down the secondary-shift key (Alt Gr or option). In some systems, there is no indication to the user that a dead key has been struck, so the key appears dead, but in some text-entry systems the diacritical mark is displayed along with an indication that the system is waiting for another keystroke: either the base character to be marked, an additional diacritical mark, or space to produce the diacritical mark in isolation.
Compared with the secondary-shift modifier key, the dead-key approach may be a little more complicated, but it allows of more additional letters. Using the secondary shift, you may only type one or (if you use it simultaneously with the normal shift key) two additional letters with each key, whereas using a dead key, a specific diacritic can be attached to a number of different base letters.
Most modern keyboards conform to the ISO 9995 layout. This layout was first defined by the user group at AFNOR in 1984 working under the direction of Alain Souloumiac.[1] Based on this work, a well known ergonomic expert wrote a report (Yves Neuville, Le clavier bureautique et informatique, Cedic-Natan 1985) which was adopted at the ISO Berlin meeting in 1985 and became the reference for the keyboards' layout.[clarification needed]
Compose key
A Compose key can be characterized as a generic dead key that may in some systems be available instead of or in addition to the more specific dead keys. It allows access to a wide range of predefined extra characters by interpreting a whole sequence of keystrokes following it. For example, striking compose followed by apostrophe and then a results in á, compose followed by a and then e results in æ, and compose followed by o and then c results in © (circled c, copyright symbol).
The Compose key is supported by the X Window System (used by most Unix-like operating systems, including most GNU/Linux distributions). Some keyboards have a key labelled "Compose", but any key can be configured to serve this function. The otherwise redundant right-hand Windows key is a common choice, when available.[citation needed]
History
 Keyboard of a Letter-Printing Telegraph Set built by Siemens and Halske in Saint Petersburg, Russia, ca. 1900
Keyboard of a Letter-Printing Telegraph Set built by Siemens and Halske in Saint Petersburg, Russia, ca. 1900
Keyboard layouts have evolved over time. The earliest mechanical keyboards were used in musical instruments to play particular notes. With the advent of printing telegraph, a keyboard was needed to select characters. Some of the earliest printing telegraph machines used a layout similar to a piano keyboard.[2][3]
The center, alphanumeric portion of the modern keyboard is based on the QWERTY design by Christopher Sholes, who laid out the keys in such a way that common two-letter combinations were placed on opposite sides of the keyboard so that his mechanical keyboard would not jam, and laid out the keys in rows offset horizontally from each other by three-eighths, three-sixteenths, and three-eighths inches to provide room for the levers. Although it has been proven that the QWERTY layout is not the most efficient layout for typing[citation needed], it has become such a standard that people will not change to a more efficient alphanumeric layout[citation needed].
Sholes chose the size of the keys to be on three-quarter inch (0.75-inch) centers (about 19 mm, versus musical piano keys which are 23.5 mm or about 0.93 inches wide). Actually, 0.75 inches has turned out to be optimum for fast key entry by the average size hand[citation needed], and keyboards with this key size are called "full-sized keyboards"[citation needed].
The following layouts assume that the physical locations of the keys are the same as a standard 101/102-key PC keyboard. This keyboard layout was invented by Mark Tiddens of Key Tronic Corporation in 1982, which IBM adopted on its PC AT in 1984 (after previously using an 84-key keyboard which did not have separate cursor and numeric key pads).
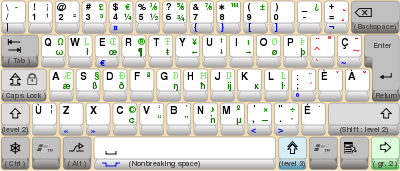
The U.S. PC keyboard has 101 keys, while the PC keyboards for most other countries have 102 keys. If you use an operating system configured for a non-English language, the keys are placed differently; "dead keys" appear in red, and characters accessed using the AltGr key appear at the bottom right of the corresponding key, or in some images in blue.
"National" layouts may change the physical configuration of keys. Keyboards designed for typing in Spanish have some characters shifted, to release the space for Ñ ñ; similarly, those for French and other European languages may have a special key for the character Ç ç. Keyboards designed for Japanese may have special keys to switch between Japanese and Latin alphabets, and the character ¥ instead of \. Using a keyboard for alternative languages leads to a conflict: the image on the key does not correspond to the character. In such cases, each new language may require an additional label on the key, because the standard keyboard layouts do not even share similar characters of different languages.
Most operating systems allow switching between keyboard layouts, using a key combination involving register keys that are not used for normal operations (e.g. Microsoft reserve Alt+Shift or Ctrl+Shift register control keys for sequential layout switching; those keys were inherited from old DOS keyboard drivers). Keyboard manufacturers usually print the second alphabet on the empty part of the key. The second alphabet can also be added with keyboard stickers manufactured by third parties.
Apple Keyboards have Command and Option keys instead of Alt and AltGr. Option is used much like Alt Gr and Command like Control on PCs, to access menu options and shortcuts. There is also a Fn key on modern Mac keyboards, which is used for switching between use of the F1, F2 etc. keys either as function keys F1, F2 etc. or for other functions like media control, accessing dashboard widgets, controlling the volume, handling exposé &c. The main use of the control key on Macs is to produce a right-click, and to provide support for programs running in X11 (a Unix environment included with OS X as an install option) or MS Windows. In the past some glyphs for drawing ASCII "window" glyphs commonly used on BBSes were found by using the ctrl key combined with other keys in some keyboard layouts.
Many Unix workstation keyboards place the Control key to the left of the letter A, and the Caps Lock key in the bottom left. This layout is often preferred by programmers as it makes the Control key easier to reach. This position of the Control key is also used on the XO laptop, although the XO does not have a Caps Lock.
Mechanical, visual and functional layouts
Today, most keyboards use one of three different mechanical layouts, usually referred to as simply ISO (ISO/IEC 9995-2), ANSI (ISO 9995-3, and JIS, referring roughly to the organizations issuing the relevant worldwide, United States, and Japanese standards, respectively. Keyboard layout in this sense may refer either to this broad categorization or to finer distinctions within these categories. For example, as of May 2008[update] Apple Inc produces ISO, ANSI, and JIS desktop keyboards, each in both extended and compact forms. The extended keyboards have 110, 109, and 112 keys (ISO, ANSI, and JIS, respectively), and the compact models have 79, 78, and 80.
Mechanical layouts only address tangible differences among keyboards. When a key is pressed, a keyboard sends a message such as the left-most main key of the home row is depressed, not A. (Technically, each key has an internal reference number, "raw keycodes", and these numbers are what is sent to the computer when a key is pressed or released.) The keyboard and the computer each have no information about what is marked on that key, and it could equally well be the letter A or the digit 9. In fact, it is up to the user of the computer to identify the visual layout of the keyboard, a question usually presented when installing the operating system. Visual layouts vary by language, country, and user preference, and the same mechanical layout can be produced with a number of different visual layouts. For example, the "ISO" keyboard layout is used throughout Europe, but typical French, German, and UK variants of mechanically identical keyboards appear different because they bear different legends on their keys. Even blank keyboards—with no legends—are sometimes used to learn typing skills or by user preference.
The functional layout of the keyboard refers to the mapping between the physical keys and software events, such as the "A" key and the letter "A" appearing on the screen. Usually the functional layout is set to match the visual layout of the keyboard being used, so that pressing a key will produce the expected result, corresponding to the legends on the keyboard. However, most operating systems have software that allow the user to easily switch between functional layouts, such as the language bar in Microsoft Windows. For example, a user with a Swedish keyboard who wishes to type more easily in German may switch to a functional layout intended for German—without regard to key markings—just as a Dvorak touch typist may choose a Dvorak layout regardless of the visual layout of the keyboard used. The visual layout of any keyboard can also be changed by simply replacing its keys or attaching labels to them, such as to change an English-language keyboard from the common QWERTY to the Dvorak layout, although for touch typists, the placement of the tactile bumps on the home keys is of more practical importance than that of the visual markings.
Functional layouts can be redefined or customized within the operating system, by reconfiguring operating system keyboard driver, or with a use of a separate software application. Transliteration is one example of that whereby letters in other language get matched to visible Latin letters on the keyboard by the way they sound. Thus, touch typist can type various foreign languages with visible English-language keyboard only. Alternatively, mixed hardware-to-software keyboard extensions exist to overcome above discrepancies between functional and visual layouts. A user applies keyboard stickers with an extra imprinted language alphabet and adds another keyboad layout via language support options in the operating system.[4]
The United States keyboard layout is used as default in the currently most popular operating systems: Windows,[citation needed] Mac OS X[citation needed] and Linux.[5]
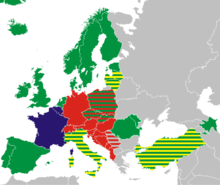
QWERTY based layouts for Latin script
Green — QWERTY
Red — QWERTZ
Blue — AZERTY
Yellow — National layouts (Turkish FGĞIOD, Latvian ŪGJRMV, Lithuanian ĄŽERTY, Italian QZERTY)
Grey — Non-Latin scripts
Note 1: Outside Europe QWERTY is used
Note 2: The symbols on the upper row and the extreme right keys can differ by countries
Note 3: In the Azeri Latin layout Üü is instead of WwAlthough there are a large number of different keyboard layouts used for different languages written in Latin script, most of these layouts are quite similar. They can be divided into three main families according to where the Q, A, Z, M, and Y keys are placed on the keyboard. These are usually named after the first six letters.
While the core of the keyboard, the alphabetic section, remains fairly constant, and the numbers from 1–9 are almost invariably on the top row, keyboards differ vastly in:
- the placement of punctuation characters,
- which punctuation characters are included,
- whether numbers are accessible directly or in a shift-state,
- the presence and placement of accent dead keys and accented characters.
The actual mechanical keyboard is of the basic ISO, ANSI, or JIS type; functioning is entirely determined by operating-system or other software. It is customary for keyboards to be used with a particular software keyboard mapping to be engraved appropriately; for example, when the shift and numeric 2 keys are pressed simultaneously on a US keyboard; "@" is generated, and the key is engraved appropriately. On a UK keyboard this generates the double-quote character, and UK keyboards are so engraved.
QWERTY
By far the most widespread layout in use, and the only one that is not confined to a particular geographical area. Some varieties have keys like "enter" and "caps lock" not translated to the language of the keyboard in question. In other varieties such keys have been translated, such as "Bloq mayús" for "Caps Lock", in the Spanish[6] and Latin American keyboards. On Macintosh computers these keys are usually just represented by symbols without the word "enter", "Shift", "Command", "option/alt" or "Control".
Canadian French (Quebec)
This keyboard layout is commonly used in Canada by French-speaking Canadians. It is the most popular layout for laptops and stand-alone keyboards targeting French speakers. Although not as versatile as the Canadian Multilingual Standard keyboard, it can be used to type all accented French characters. It also serves all English functions as well. It is popular mainly because of its close similarity to the basic US keyboard commonly used by English-speaking Canadians, and is the standard for keyboards in Quebec. In general, Canadians do not use the AZERTY keyboard layout, which is used in France and other francophone countries. Another keyboard layout available in Quebec is ACNOR, similar to the CMS. Neither of these layouts is widely used in Quebec.
In some variants of this keyboard "Caps Lock" is "Fix Maj" or "Verr Maj", "Enter" is "Entrée",[7] and "Esc" is "Échapp".
Canadian Multilingual Standard
This keyboard layout is used by some Canadians. English-speaking Canadians mostly use the same keyboard layout as in the United States, unless they are in a position where they have to write French on a regular basis while French-speaking Canadians favour the Canadian French keyboard layout.
A remarkable characteristic of the Canadian Multilingual Standard keyboard is the number and variety of its shift states and dead keys, thanks to which it can be used to type many accented Latin characters, including such exotic letters as the ġ (dotted g) of Maltese or the ĵ (circumflexed j) of Esperanto. Though this keyboard lacks the caret (^) character, this is easily accomplished by typing the accent circumflex followed by a space.
Czech
Typewriter came to the Czech area from Germany in late 19th century, Czech typewriters have got the QWERTZ layout. However QWERTY keyboard layout is frequently used for Czech, alongside the QWERTZ layout.
Gamer note: It's been several years now that Czech or other european gamer who uses cheats can say "The tilde key is NOT working for me". The issue wasn't really serious until Windows 7 came into stores and homes of users, where it automatically sets Czech language layout (which got ° and ; instead of ~ and `) for games instead of pre-set US layout that can be set in Windows itself. Such games where the cheats become a problematic issue for getting around bugs is for example Star Wars: Knights of the Old Republic , Battlezone II: Combat Commander and such "older" games which weren't properly taken care of after newer operating system came into stores. There isn't a solution to this problem on home computers so far.
Danish
The Danish and Norwegian keyboard layouts have the same rendering of the Nordic letters Æ/æ, Ø/ø and Å/å (all the Nordic countries have these letters on their keyboard layouts, but their glyphs might also look like Ä/ä and Ö/ö) Although the Danish and Norwegian alphabet has the same order of these three last letters, the placement of Ø/ø and Æ/æ are reversed between the Norwegian and the Danish keyboard layouts. The Swedish and Norwegian keyboard layouts have Ö/Ø/ö/ø and Ä/Æ/ä/æ at the same place. (On Macintosh computers holding the option/alt key while typing Ö/ö on a Swedish or Finnish keyboard gives Ø/ø and the same for Ä/ä and Æ/æ and vice versa on a Danish or Norwegian keyboard using option/alt with Ø/ø gives Ö/ö and the same with Æ/æ and Ä/ä. Unfortunately this is not yet implemented on PCs with Windows, so writing Swedish on a Norwegian or Danish keyboard or Danish or Norwegian on a Swedish keyboard involves dead keys or cumbersome Alt Gr+four digit code.)
Dutch (Netherlands)
This is a modern version of the Dutch layout. In the 1990s there was a version with the now-obsolete florin sign (Dutch: guldenteken) for IBM PCs. It has additions for the € sign, the ¨ (diaresis) and more, and the braces ("{ }") and other symbols are differently located. The Dutch layout is historical and seldom used. A Dutch keyboard uses "qwerty" not "azerty" Most computers in The Netherlands use the US International layout instead.
Estonian
The keyboard layout used in Estonia is virtually the same as the Swedish layout. The main difference is that the Å and ¨ keys (to the right of P) are replaced with the letters Ü and Õ respectively, the latter being the most distinguishing feature of the Estonian alphabet. Some special symbols and dead-keys are also moved around.
Faroese
Basically the same as the Danish layout with added Đ since the Faroese islands are a self-governed part of the Kingdom of Denmark.
Finnish multilingual
The visual layout used in Finland is basically the same as the Swedish layout. This is practical, as Finnish and Swedish share the special characters ä and ö, and while the Swedish å is unnecessary for writing Finnish, it is needed by Swedish-speaking Finns.
As of 2008, there is a new standard for the Finnish Multilingual Keyboard layout, developed as part of a localization project by CSC. All the engravings of the traditional Finnish-Swedish visual layout have been retained, so there is no need to change the hardware, but the functionality has been extended considerably, as several additional characters are available through the AltGr key and particularly dead-key diacritics.[8][9]
The layout has three main objectives. First, it provides for easy entering of text in both Finnish and Swedish, the two official languages of Finland, using the familiar keyboard layout but adding some advanced punctuation options (e.g. dashes, typographical quotation marks, and non-breaking space).
Second, it is designed to give an indirect but intuitively recognizable way to enter the special characters or diacritics needed by the other three Nordic national languages (Danish, Norwegian and Icelandic) as well as the regional and minority languages (Northern Sámi, Southern Sámi, Lule Sámi, Inari Sámi, Skolt Sámi, Romani language as spoken in Finland, Faroese, Kalaallisut aka Greenlandic, and German).
As a third objective, it allows for relatively easy entering of particularly names (of persons, places or products) in a variety of European languages using a more or less extended Latin alphabet, such as the official languages of the European Union (excluding Bulgarian and Greek).
Icelandic
The Icelandic keyboard layout is different from the standard QWERTY keyboard because the Icelandic alphabet has some special letters, most of which it shares with the other Nordic countries: Þ/þ, Ð/ð, Æ/æ and Ö/ö. (Æ/æ also occurs in Norwegian, Danish and Faroese, Ð/ð in Faroese, and Ö/ö in Swedish, Finnish and Estonian.)
The letters å,ä,ÿ,ü and ï can be found on the Icelandic keyboard by pressing the ° or shift+° (¨) dead key located below the Esc key, and then the corresponding letter. (i.e. [°] followed by [a] yields [å]) These letters are not used natively in Icelandic, but may have been implemented for ease of communication in other Nordic languages.[citation needed]
Irish
The default keyboard layout for Irish on Microsoft Windows is similar to the UK layout with two exceptions. The keyboards have the same keys with the same markings but (1) the default use for key left of "1", is a grave dead key (this change is also made on UK-Extended) and (2) when AltGr is pressed, the apostrophe key becomes an acute dead key.
Italian
Note:
- braces (right above square brackets and shown in purple) are given with both AltGr and Shift pressed.
- the tilde (~) character is not present on the Italian keyboard layout
- the standard Italian keyboard layout does not allow one to write 100% correct Italian language, since it lacks the È key. The common workaround is writing E' (E followed by an apostrophe) instead, or relying on the auto-correction feature of several word processors when available. It is possible to obtain the È symbol in Ms Word by typing Alt+ 212. Mac users, however, can write the correct accented character by pressing shift + option + E. GNU/Linux users can also write it by pressing the "è" key with Caps Lock enabled.
An alternate layout has characters accessible through AltGr in different positions and includes the tilde. It is commonly used in IBM keyboards.
Maltese
The Maltese language uses Unicode (UTF-8) to display the Maltese diacritics: ċ Ċ; ġ Ġ; ħ Ħ; ż Ż (together with à À; è È; ì Ì; ò Ò; ù Ù). There are 2 standard keyboard layouts for Maltese, according to "MSA 100:2002 Maltese Keyboard Standard". There is the 47-key and the 48-key keyboards.
- The Maltese language keyboard layout can be activated through the language bar in Microsoft, Mac, Linux and Ubuntu. To activate this language bar refer to this user's manual: [1]. For other systems/queries, send an email to the National Council for the Maltese Language.
- Type in Maltese with Google Virtual Keyboard: [[2]]
- More - ALT codes etc: [[3]]
- To install the Maltese keyboard layout in Android OS, use this application in your smartphone/tablet: [4]
We are still trying to find a similar app for Maltese in Blackberry and iPhone. If you know of any, link them here.
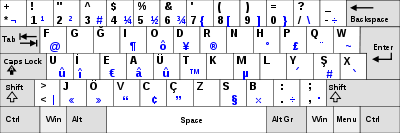
Norwegian
The Norwegian languages use the same letters as Danish, but the Norwegian layout differs from the Danish regarding the placement of Æ, Ø and \ (backslash) keys. On the Danish keyboard Ø and Æ have switched places, which many Norwegians find annoying when using Danish keyboards. The Swedish and Norwegian keyboard layouts have Ö/ö and Ø/ø and Ä/ä and Æ/æ at the same place. (Ö/ö and Ø/ø are differing glyphs representing the same letter and so is Ä/ä and Æ/æ. Ö/ö was used in Denmark and Norway as well in the not very distant past, and there are still Norwegians using Ö/ö in handwriting.)[citation needed]
On Macintosh computers holding the option/alt key while typing Ö/ö on a Swedish or Finnish keyboard gives Ø/ø and the same for Ä/ä and Æ/æ and vice versa on a Danish or Norwegian keyboard using option/alt with Ø/ø gives Ö/ö and the same with Æ/æ and Ä/ä. Unfortunately this is not yet implemented on Windows PCs, so writing Swedish on a Norwegian or Danish keyboard involves dead keys or cumbersome Alt Gr+four digit code or just using the alternative glyph (which is often seen in mails and other internet communications when people are unable to find the right glyphs). Writing Norwegian or Danish on a Swedish keyboard on a Windows PC involves Alt Gr+four digit code as there is no dead key combination for Æ/æ and Ø/ø.)
On the Norwegian or Norwegian extended keyboard layout on Macintosh computers, the signs obtained by the numerals with shift and by the numerals with option and option-shift differ slightly from the one shown in this picture. Also the keys left and right of the numerals and 29 alphabet letters are assigned to other glyphs. Noteworthy are the $ sign at Shift-4 and ¢ at Shift-Option-4, where Swedish and Danish keyboards have € at Shift-4, $ at Option-4 and ¢ at Shift-Option-4. The difference can be explained by the fact that Norway is a oil driven economy, dealing in oil prices in US$ and it is outside the European Union, while Sweden and Denmark are industrial nations within the EU, dealing more in €.[citation needed] The Norwegian keyboard layout and the Norwegian extended keyboard layout on Macintosh computers also have the frequently used @ between Æ/æ and Return, which is more handy than the Swedish, Swedish pro and Danish keyboard layouts where it is obtainable by option-2 (like the Alt Gr-2 combination of the Norwegian, Swedish and Danish keyboard layouts on Windows machines, except that the option key on a Macintosh keyboard is where the left Alt key is on a Windows PC Keyboard.)
There is also a keyboard layout called "Norwegian with Sámi", which allows for easier input of the characters required to write various Sámi (also known as Lapp) languages. All the Sámi characters are accessed through the "AltGr" key.
Persian (Farsi)
See also: Persian KeyboardThis keyboard is contributed by Desphilic group for writing Internationalized Persian language. It supports Unipers characters [ ä š ü ž] and an additional set of Desphilic extended character [ ö ķ ğ ] and their Capitals [ Ä Š Ü Ž Ö Ķ Ğ ]. These characters are added to Latin-1 character set to form Persian Roman alphabet. The keyboard is in increasing use specially in Persian chat. It is intended to be used as a base for future standards for a Universal Persian Keyboard. The keyboard is likely to be agreed by two Persian Romanization standards ( Desphilic and Unipers) and is used for transliteration of Persian and writing Persian Latin alphabet. The base and shifted layouts are identical with US-English keyboard and the AltGr layout is shown in the image to the right.
Polish
Most typewriters use a QWERTZ keyboard with Polish accented letters accessed directly (officially approved as "Typist's keyboard", Polish: klawiatura maszynistki, Polish Standard PN-87), which is mainly ignored in Poland as impractical (except custom-made, e.g., in public sector and some Apple computers); the "Polish programmer's" (Polish: polski programisty) layout has become the de facto standard, used on virtually all computers sold on the Polish market.
Polish programmers use QWERTY keyboards identical with the standard US layout. In this layout Polish letters are accessed in the same manner as the usage of keyboard shortcuts, with Latin letter keys in combination with right Alt (actually working as AltGr) key. These key combinations (excluding one for "€") obey states of both Shift and Caps Lock keys, preserving normal capitalization while typing Polish characters. For example, to obtain capital "Ź" pressing Shift-rightAlt-X is needed, with Caps Lock off. Note that usage of right Alt in Polish programmers layout may be confusive with Alt-A, Alt-C etc. (which are common shortcuts in most programs and can be obtained only with left Alt) because the key really acting as AltGr is also marked as Alt. This fact is based on usage (and thus selling) in Poland almost only US-layout keyboards (with Alt marked both keys, without AltGr) although Microsoft officially depicts it as AltGr.[10] It can be easily verified by examining the pictures of models offered everywhere in Poland.
Key combinations to obtain Polish characters Caps Lock state In combination with Keystroke A C E L N O S Z X U Off right Alt ą ć ę ł ń ó ś ż ź € Shift & right Alt Ą Ć Ę Ł Ń Ó Ś Ż Ź On right Alt Ą Ć Ę Ł Ń Ó Ś Ż Ź € Shift & right Alt ą ć ę ł ń ó ś ż ź Note: On Polish programmer keyboard, right Alt plays the role of AltGr Also, on MS Windows, the tilde character (Shift+` ) acts as a dead key to type Polish letters (with diacritical marks) thus, to obtain an "Ł", one may press ~ followed by L. The tilde character is obtained with ~ and space.
Portuguese (Brazil)
The Brazilian computer keyboard layout is specified in the ABNT NBR 10346 variant 2 (alphanumeric portion) and 10347 (numeric portion) standards.
Essentially, the Brazilian keyboard contains dead keys for five variants of diacritics in use in the language; the letter Ç, the only application of the cedilla in Portuguese has its own key. Accessible via the AltGr+C combination is the ₢ character (Unicode 0x20A2), symbol for the Cruzeiro, currency of the country from 1942 to 1967. The via AltGr+5 accessible cent sign ¢ can be used for the centavo, subunit of previous currencies as well as the current Real, which itself is represented with R$. The masculine and feminine ordinals ª and º are accessible via AltGr combinations. The section sign § (Unicode U+00A7), in Portuguese called parágrafo, is nowadays practically only used do denote sections of laws.
The variant 2 of the Brazilian keyboard, the only which gained general acceptance, has a unique mechanical layout, combining some features of the ISO 9995-3 and the JIS keyboards in order to fit 12 keys between the left and right Shift (compared to the American standard of 10 and the international of 11). Its modern, IBM PS/2-based variations, are thus known as 107-keys keyboards, and the original PS/2 variation was 104-key. The variant 1, never widely adopted, was based on the ISO 9995-2 keyboards.
Portuguese (Portugal)
During the 20th century, a different keyboard layout, HCESAR, was in widespread use in Portugal. On some QWERTY keyboards the key labels are translated, but the majority has labels in English.
Romanian (in Romania and Moldova)
The current Romanian National Standard SR 13392:2004 establishes two layouts for Romanian keyboards: a "primary" one and a "secondary" one.
The "primary" layout is intended for traditional users who have learned how to type with older, Microsoft-style implementations of the Romanian keyboard. The "secondary" layout is mainly used by programmers as it does not contradict the physical arrangement of keys on a US-style keyboard. The "secondary" arrangement is used as the default Romanian layout by GNU/Linux distributions, as defined in the "X Keyboard Configuration Database"
There are four Romanian-specific characters that are incorrectly implemented in versions of Microsoft Windows prior to Vista:
- Ș (U+0218, S with comma), incorrectly implemented as Ş (U+015E, S with cedilla)
- ș (U+0219, s with comma), incorrectly implemented as ş (U+015F, s with cedilla)
- Ț (U+021A, T with comma), incorrectly implemented as Ţ (U+0162, T with cedilla)
- ț (U+021B, t with comma), incorrectly implemented as ţ (U+0163, t with cedilla)
The cedilla-versions of the characters do not exist in the Romanian language (they came to be used due to a historic bug).[11]
Since Romanian hardware keyboards are not widely available, Cristian Secară has created a driver that allows Romanian characters to be generated with a US-style keyboard in all versions of Windows prior to Vista through the use of the AltGr key modifier. The keyboard driver is available here (in Romanian).
Windows 7 now includes the correct diacritical signs in the default Romanian Keyboard layout. This layout has the Z and Y keys mapped like in English layouts and also includes characters like the 'at' (@) and dollar ($) signs, among others. The older cedilla-version layout is still included albeit as the 'Legacy' layout.
Slovak
In Slovakia, similarly to the Czech Republic, both QWERTZ and QWERTY keyboard layouts are used. QWERTZ is the default keyboard layout for Slovak in Microsoft Windows.
Spanish (Spain), aka Spanish (International sort)
The Spanish keyboard layout is used to write in Spanish and in other languages of Spain such as Aragonese, Asturian, Catalan, Occitan, Galician and Basque. It includes Ñ for Spanish, Asturian and Galician, the acute accent, the diaeresis, the left question and exclamation marks (¿, ¡) and, finally, some characters required only for typing Catalan and Occitan that are Ç, the grave accent and the interpunct (punt volat / punt interior, used in l·l, n·h, s·h; located at Shift-3). It can also be used to write other international characters, such as the circumflex accent (used in French and Portuguese among others) and the tilde (used in Portuguese), which are available as dead keys. However, it lacks two characters used in Asturian: Ḥ and Ḷ (historically, general support for these two has been poor – they aren't present in the ISO8859-1 character encoding standard, or any other ISO/IEC 8859 standard); several alternative distributions, based on this one or created from scratch, have been created to address this issue (see the Other original layouts and layout design software section for more information).
On most keyboards, € is marked as Alt Gr + E and not Alt Gr + 5 as shown in the image.
Normally "Bloq Mayús" is used instead of "Caps Lock", and "Intro" instead of "Enter".
The c-cedilla key (Ç), instead of on the right of the acute accent key (´), is located alternatively on some keyboards one or two lines above. In some cases it's placed on the right of the plus sign key (+).[12][13] In other keyboards it's situated on the right of the inverted exclamation mark key (¡).[14][15]
Spanish (Latin America)
The Spanish (Latin America) keyboard layout is used throughout Mexico, Central and South America. In the last few years, vendors have been preferring the Spanish (Spain) layout as default; as of 2011, the latter is becoming dominant.
Its most obvious difference with the Spanish (Spain) layout is the lack of a Ç key; it also lacks a tilde (~) dead key. This is not a problem when typing in Spanish, but it is rather problematic when typing in Portuguese, which can be an issue in countries with large commercial ties to Brazil (Argentina and Paraguay).
Normally "Bloq Mayús" is used instead of "Caps Lock", and "Intro" instead of "Enter".
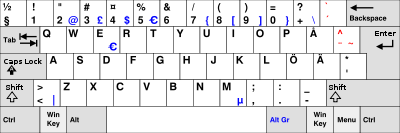
Swedish
The central characteristics of the Swedish keyboard are the three additional letters å, ä, and ö. The same visual layout is also in use in Finland, as the letters ä and ö are shared with the Finnish language, and even å is needed by Swedish-speaking Finns. However, the Finnish Multilingual Keyboard adds new letters and punctuation to the functional layout.
The Swedish and Norwegian keyboard layouts have Ö/ö and Ø/ø and Ä/ä and Æ/æ at the same place. (Ö/ö and Ø/ø are differing glyphs representing the same letter and so is Ä/ä and Æ/æ. Actually Ö/ö was used a lot in Denmark and Norway as well in the not very distant past, and there are still Norwegians using Ö/ö in handwriting.) On Macintosh computers holding the option/alt key while typing Ö/ö on a Swedish or Finnish keyboard gives Ø/ø and the same for Ä/ä and Æ/æ and vice versa on a Danish or Norwegian keyboard using option/alt with Ø/ø gives Ö/ö and the same with Æ/æ and Ä/ä. In Linux the same functionality is provided by using the alt gr key instead of the option key. Unfortunately this is not yet implemented on Windows PCs, so writing Swedish on a Norwegian or Danish keyboard involves dead keys or cumbersome Alt Gr+four digit code or just using the alternative glyph (which is often seen in mails and other internet communications when people are unable to find the right glyphs. Writing Norwegian or Danish on a Swedish keyboard on a Windows PC involves Alt Gr+four digit code as there is no dead key combination for Æ/æ and Ø/ø, unless one chooses instead to use the Finnish Multilingual keyboard layout.)
There is also a keyboard layout called "Swedish with Sámi", which allows for easier input of the characters required to write various Sámi (also known as Lapp) languages. All the Sámi characters are accessed through the "AltGr" key, and also Æ and Ø. This keyboard has the same function for all keys written on a Swedish standard keyboard, plus more using the "AltGr" key, so it can be used with a standard keyboard without bad effects .
The Swedish and Swedish Pro keyboard layouts on Macintosh computers have some variations from the pictures shown above, specially in which signs are assigned to the numerals with shift, option (corresponding to Alt Gr on Windows machines, but placed on the left side next to ctrl and command) and option-shift, and also which signs are assigned to the keys next to the 29 alphabetic keys and the numerals. The key next to delete is a dead key with ´and with shift`, the key next to it and 0 has + and with shift ?, while the key next to Ä has ' and with shift *, the one next to Å being a dead key with ¨and with shift ^. On the left of Z is < and with shift > and next to 1 on the left is § and with shift °. The numerals produce !"#€%&/()= with shift, ©@£$∞§|[]≈ with option and ¡”¥¢‰¶\{}≠ with shift-option.
The Linux keyboard layout has all of the characters the Window keyboard layout and additionally several extra characters provided by the alt gr key. Under Linux, alt gr gives ¶¡@£$€¥{[]}\± (with shift: ¾¹²³¼¢⅝÷«»°¿¬) on the first row, @ł€®þ←↓→œþ"~ (with shift: ΩŁ¢®Þ¥↑ıŒÞ°ˇ) on the second row, ªßðđŋħjĸłøæ´ (with shift: º§ÐªŊĦJ&ŁØÆ×) on the third row and |«»©“”nµ¸·̣ (with shift: ¦<>©‘’Nº˛˙˙) on the fourth row. Several of the characters are deadkeys; listed characters for deadkey keys are the ones which appear if the deadkey is directly followed by a space.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom and Ireland[16] use a keyboard layout based on the 48-key version defined in British Standard BS 4822.[17] It is very similar to that of the United States, but has an extra key and a larger Enter key, includes £ and € signs and some rarely used EBCDIC symbols (¬, ¦), and uses different positions for the characters @, ", #, ~, \, and |. See the article British and American keyboards for details.
The BS 4822:1994 standard does not make any use of the AltGr key and lacks support for any non-ASCII characters other than ¬ and £. It also assigns a key for the non-ASCII character broken bar (¦), but lacks one for the far more commonly used ASCII character vertical bar (|). It also lacks support for Welsh orthography. Therefore, various manufacturers have modified or extended the BS 4822 standard:
- The B00 key (left of Z) shifted results in vertical bar (|) on some systems (e.g., Microsoft Windows' UK/Ireland keyboard layout and GNU/Linux/X11 UK/Ireland keyboard layout), rather than the broken bar (¦) assigned by BS 4822 and provided in some systems (e.g., OS/2's UK166 keyboard layout)
- The E00 key (left of 1) with AltGr provides either vertical bar (|) (OS/2's UK166 keyboard layout, GNU/Linux/X11 UK keyboard layout) or broken bar (¦) (Microsoft Windows' UK/Ireland keyboard layout)
(Hong Kong uses US and Chinese (Traditional) keyboards rather than UK and Ireland ones. See also Technical standards in colonial Hong Kong.)
Also note that the "British" version of the Apple Keyboard does not have this layout. Instead, some older versions have the US layout below with a few differences: the £ sign is reached by shift-3 and the # sign by option-3, the opposite to the US layout. € is also present and is typed with shift-option-2.
Newer Apple "British" keyboards use a layout that is relatively unlike either the US or traditional UK keyboard. It uses an elongated return key, a shortened left-shift with ` and ~ in the newly created position, and in the upper left of the keyboard are § and ± instead of the traditional EBCDIC codes. The middle-row key that fits inside the return key has \ and |.
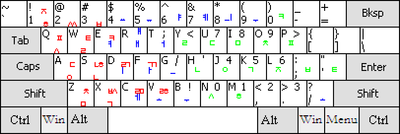
United States
This layout is used as default in the current main operating systems.[citation needed] U.S. keyboards are used not only in the United States, but also in other English-speaking places (e.g., India, Australia, English Canada, Hong Kong, New Zealand, South Africa, Malaysia, Singapore and Philippines), excluding the United Kingdom and Ireland, which use a UK standard instead. The US keyboard can be found worldwide in the stores.
The US keyboard layout has a second Alt key instead of the AltGr key and does not use any dead keys; this makes it inefficient for all but a handful of languages. On the other hand, the US or UK keyboard layout is occasionally used by programmers in countries where the keys for []{} are located in less convenient positions on the locally customary layout.[18]
On some keyboards the enter key is bigger than traditionally and takes up also a part of the line above, more or less the area of the traditional location of the backslash key (\). In these cases the backslash is located on alternative places.[19] It can be situated one line above the default location, on the right of the equals sign key (=).[20][21] Sometimes it's placed one line below its traditional situation, on the right of the apostrophe key (') (on these cases the enter key is narrower than usual on the line of its default location).[22] It may also be two lines below its default situation, below the enter key, on the right of a narrower than traditionally right shift key.[23]
Vietnamese
The Vietnamese keyboard layout is an extended Latin QWERTY layout. The letters Ă, Â, Ê, and Ô are found on what would be the number keys 1–4 on the American English keyboard, with 5–9 producing the tonal marks (grave accent, hook, tilde, acute accent, and dot below, in that order), 0 producing Đ, = producing the đồng sign (₫) when not shifted, and brackets ([]) producing Ư and Ơ.[24]
International
International layouts are available which are capable of generating a wide variety of characters used in different countries, based on UK and US physical keyboards. The UK extended keyboard retains the normal use of all keys except the rarely used grave accent (`), using the AltGr key for most functions; the US-international layout changes the effect of the apostrophe/single-quote ('), grave accent (`), double-quote ("), caret (^) and tilde (~) keys, making them dead keys used to modify the following keystroke.
United Kingdom extended
Windows XP SP2 and later also offer a "United Kingdom Extended" keyboard layout which allows input on a standard physical UK keyboard for many languages (including Welsh) without changing any of the allocations of frequently used keys (the rarely used grave accent key becomes a dead key). In particular, the apostrophe, double-quote, tilde and caret keys are not changed into dead keys modifying the character generated by the next key pressed, as used by the US International layout. The extended keyboard is software installed from the Windows control panel, and the extended characters are not normally engraved on keyboards.
The layout provides support for adding diacritics to the vowels a, e, i, o, u, w and y (the last two being used in Welsh) as well as capitals:
- The grave accent key (left of 1) becomes a dead key which adds a grave accent to a subsequent vowel, generating à, è, etc. Pressing the key followed by a character which does not take a grave accent behaves as on a standard keyboard; grave followed by spacebar generates a grave accent character.
- Vowels with acute accents are generated either by pressing AltGr and the relevant character key simultaneously, or AltGr and apostrophe (acting as a dead key combination) followed by the character. Some programs use the combination of AltGr and a letter for other functions, in which case the AltGr and apostrophe method must be used to generate acute accents.
- AltGr + 6 acts as a dead key combination to add a circumflex to a subsequent vowel (â, ê, etc.). Use of the shifted 6 key is intended to be mnemonic as the key is marked with the caret (^), which looks like a circumflex.
- AltGr + 2 acts as a dead key combination to add a diaeresis to a subsequent vowel (ä, ë, etc.). Use of the shifted 2 key is intended to be mnemonic as on UK keyboards the key is marked with the double quote ("), which looks a bit like a diaeresis.
AltGr + # (hash) acts as a dead key combination to add a tilde (~) to a subsequent a, n, o, A, N, or O (ã, ñ, õ etc.), as used in Spanish and Portuguese. This is mnemonic again; the # key on a UK keyboard is marked with the tilde character (~).
With Windows versions newer than Windows XP SP2, AltGr and c generates lower-case c with cedilla (ç), and AltGr and C (shift-c) generates the capital letter (Ç).
The UK extended layout is almost entirely transparent to users familiar with the UK layout; a machine with the extended layout will behave exactly as with the standard UK except for the rarely used grave accent key. This makes this layout suitable for a machine for shared or public use by a user population in which some, but not all, are aware of the extended functionality.
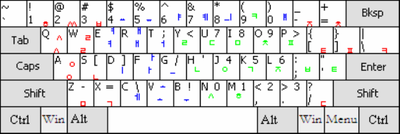
US-International
There is an alternative layout that uses the physical US keyboard to type diacritics in some operating systems (including Windows). This is the US-International layout, which uses the right Alt key as an AltGr key which supports many additional characters directly as an additional shift key, and uses keys ', `, ", ^ and ~ as dead keys used to generate characters with diacritics by pressing the appropriate key, then the letter on the keyboard. The international keyboard is a software setting installed from the Windows control panel[25] or similar; the additional functions (shown in blue) may or may not be engraved on the keyboard, but are always functional.
A diacritic key is activated by pressing and releasing it, then pressing the letter that requires a diacritic. After the two strokes, the single character with diacritics is generated. Note that only certain letters (such as vowels and n) can have diacritics in this way. To use the dead keys to generate the symbols marked on them, ', `, ", ^ and ~, when the following character is capable of having a diacritic, the spacebar should be pressed after the key.
Characters with diacritics can be typed with the following combinations:
- ' + vowel → vowel with acute accent, e.g., ' + e → é
- ` + vowel → vowel with grave accent, e.g., ` + e → è
- " + vowel → vowel with diaeresis (or umlaut), e.g., " + e → ë
- ^ + vowel → vowel with circumflex accent, e.g., ^ + e → ê
- ~ + a, n or o → letter with tilde, e.g. ~ + n → ñ, ~ + o → õ
- ' + c → ç
The US-International layout is not entirely transparent to users familiar with the US layout; when using a machine with the international layout the commonly used single- and double-quote keys and the less commonly used grave accent, tilde, and caret keys will behave differently than expected. This could be disconcerting on a machine for shared or public use
There are also alternative US-International formats, whereby modifier keys such as shift and alt are used, and the keys for the characters with diacritics are in different places than their unmodified counterparts.
US-International in the Netherlands
In the Netherlands the US-International keyboard layout is nearly always used. The Dutch layout is historical, and keyboards with this layout are rarely used. Many US keyboards sold do not have the extra US-International characters or "AltGr" (blue in the image) engraved on the keyboard, although € (AltGr+5) always is; however the keys work as expected although not marked. Many computer-experienced Dutch people have retained the habit of using alt+number codes to type accented characters, though use of a spelling checker to replace words typed without diacritics by the correct form is common.
Windows 2003 has an error by which the (obsolete) Dutch layout is set as default if the Windows location is set to the Netherlands, and will even install this every time the system boots, replacing the US International layout. This causes many issues, but has not been patched.
QWERTZ
The QWERTZ layout is fairly widely used in Germany and much of Central Europe. The main difference between it and QWERTY is that Y and Z are swapped, and most special characters such as brackets are replaced by diacritical characters.
Czech
The QWERTZ keyboard layout is commonly used in the Czech Republic. (The layout on the picture is in fact a combination of the US and CZ keyboard layout.)
Hungary
Note that on some keyboards "ű" is found to the right of the right Shift key. Also, many Hungarians who were not exposed to typewriters, but started using computers when Hungarian keyboards were uncommon or unavailable, still prefer the layout with the y/z keys in their QWERTY locations because that is what they are used to. The same applies to Hungarians who frequently switch between a QWERTY and a Hungarian layout (for example because they write in several different languages).
Germany and Austria (but not Switzerland)
The PC keyboard layout commonly used in Germany and Austria is based on one defined in an old (October 1988) version of the German standard DIN 2137-2. The characters ², ³, {, [, ], }, \, @, €, |, µ, and ~ are accessed by holding the Alt Gr key and tapping the other key. The Alt key on the left will not access these additional characters. Alternatively Ctrl+Alt and pressing the respective key also produce the alternative characters on some operating systems.
The accent keys ^, `, ´ are dead keys: press and release an accent key, then press a vowel key to produce accented characters (ô, á, ù, etc.). One problem with German keyboards when used to type English text is that users frequently mistype a spacing accent instead of an apostrophe (e.g., it´s or it`s instead of correctly it's).[26]
The keyboard lacks some important characters like the German style quotation marks („ and “ and ‚ ‘ respectively). As a consequence, these are seldom used in Internet communication, " and ' are used instead (which is technically incorrect).
Note that the semi-colon and colon are accessed by using the Shift key.
Contrary to many other languages, German keyboards are usually not labeled in English (a notable exception is the layout on the Schneider EURO PC series, which did in fact use English abbreviations like Ctrl). Abbreviations on a German keyboard:
German label English equivalent Steuerung (Strg) Control (Ctrl) Alternate Graphic (Alt Gr) See Alt Gr key Einfügen (Einfg) Insert (Ins) Entfernen (Entf) Delete (Del) Bild auf (Bild↑) Page up (PgUp) Bild ab (Bild↓) Page down (PgDn) Position eins (Pos1) Home ("position one") Ende (Ende) End (end) Drucken / Systemabfrage (Druck/S-Abf) Print Screen/SysRq Rollen Scroll Lock ("to roll") Pause/Unterbrechen (Pause/Untbr) Pause/Break On some keyboards, the asterisk (*) key on the numeric keypad is instead labeled with the multiplication sign (×) and the divide-key is labeled with the division sign (÷) instead of slash (/).
The behaviour of Caps Lock according to the DIN standard is inherited from mechanical typewriters: Pressing it once shifts all keys including numbers and special characters until the Caps Lock key is pressed again. Holding Shift while Caps Lock is active unshifts all keys. Both Shift and Caps Lock lack any textual labels. The Caps Lock key is simply labeled with a large down-arrow (on newer designs pointing to an uppercase A key) and Shift is labeled with a large up-arrow.
In IT, an alternative behaviour is often preferred, usually described as "IBM", which is the same as Caps Lock on English keyboards – only letters are shifted, and hitting Caps Lock again releases it.
Slovak
The QWERTZ keyboard layout is used in Slovakia as well; QWERTY layout being an option though.
Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian Latin and Slovene
The Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian Latin and Slovene keyboard layout has five additional special characters Č, Ć, Ž, Š and Đ. This keyboard layout was standardized in the 1980s in Yugoslavia. Characters Ć and Đ are not part of the Slovene alphabet however they are used for historical reasons and for writing words in the closely related Croatian, Serbian and Bosnian languages. The Ž is on the right side of the Ć key on keyboards which have a longer Backspace key, and the usual inverted L shaped Enter key.
Serbian Cyrillic
Apart from a set of characters common to most Cyrillic alphabets, the Serbian Cyrillic layout uses six additional special characters unique or nearly unique to the Serbian Cyrillic alphabet: Љ, Њ, Ћ, Ђ, Џ and Ј.
Due to the bialphabetic nature of the language, actual physical keyboards with the Serbian Cyrillic layout printed on the keys are somewhat uncommon today. Typical keyboards sold in Serbian-speaking markets are marked with Serbian Latin characters and used with both the Latin and Cyrillic layout configured in the software. What makes the two layouts this readily interchangeable is that the non-alphabetic keys are identical between them, and alphabetic keys always correspond directly to their counterparts (except the Latin letters Q, W, X, and Y that have no Cyrillic equivalents, and the Cyrillic letters Љ, Њ and Џ whose Latin counterparts are digraphs LJ, NJ and DŽ). This also makes the Serbian Cyrillic layout a rare example of a non-Latin layout based on QWERTZ.
Switzerland(German, French, Italian, Romansh), Liechtenstein, Luxembourg
The layout of the Swiss keyboard is designed to allow easy access to frequently used accents of the French, German and Italian languages. The difference between the Swiss German (sg) and the Swiss French (sf) layout is that the German variety has the German umlauts (ä, ö, ü) accessible without dead keys, while the French version has the French accented characters (é, à, è) accessible in the unshifted state. The actual keyboards have the keys engraved for both variations; the difference is only in the driver setting. In the latest versions of Windows there are also separately listed driver settings for Swiss Italian and Swiss Romansh, but they correspond to the Swiss French and Swiss German layout, respectively. In Mac OS X 10.6 only Swiss French and Swiss German is available.
Swiss German does not include the esszett (ß) ligature, which is only used in Germany and Austria, and so that letter is not found on the keyboard.
While the German keyboard uses German-language abbreviations (e.g. Strg for German Steuerung instead of Ctrl for Control), Swiss keyboards use the English abbreviations as a "neutral" solution, as they are used for all the national languages of Switzerland.
Luxembourg does not have a keyboard layout of its own. Public education uses the Swiss-French keyboard, while the banking sector prefers the Belgian layout. Other places use either or the US layout. Liechtenstein, which also has no keyboard layout of its own, uses the Swiss German keyboard.
AZERTY
The AZERTY layout is used in France, Belgium and some African countries. It differs from the QWERTY layout thus:
- A and Q are swapped,
- Z and W are swapped,
- M is moved to the right of L (where colon/semicolon is on a US keyboard),
- The digits 0 to 9 are on the same keys, but to be typed the shift key must be pressed. The unshifted positions are used for accented characters,
- Caps lock is replaced by Shift lock, thus affects non-letter keys as well. But there is an evolution going towards a Caps lock key instead of a Shift lock.
The French and Belgian AZERTY keyboards also have special characters used in the French language, such as ç, à, é and è, and other characters such as &, ", ' and §, all located under the numbers.
Some French people use the Canadian Multilingual standard keyboard. The Portuguese (Portugal) keyboard layout may also be preferred, as it provides all French accents (acute, grave, diaeresis, circumflex, cedilla, and also French quotation marks or guillemets, «») and its dead-letter option for all the accent keys allow for easy input of all the possibilities in French and most other languages (áàäãâéèëêíìïîóòöõôúùüû). Ç is, however, a separate key, as can be seen above. The US-International keyboard is also used for the same reason. An alternative to azerty is the "bépo" layout (see below).
French
Belgian
The Belgian AZERTY keyboard was developed from the French AZERTY keyboard, but some adaptations were made in the 1980s.
All letters remain in the same positions as on the French keyboard, but there are :
- some additional symbols ( ³ , ´ , ` )
- some other symbols are in different locations ( ! , @ , - , _ , + , = , § )
Lithuanian
Lithuanian keyboards use a layout known as ĄŽERTY, where Ą appears in place of Q above A, Ž in place of W above S, with Q and W being available either on the far right-hand side or by use of the Alt Gr key. Depending on the software used, the Lithuanian symbols can also be positioned in the place of digits: 1 for Ą, 2 for Č, 3 for Ę, 4 for Ė, 5 for Į, 6 for Š, 7 for Ų, 8 for Ū and = for Ž.
QZERTY
The QZERTY layout is used mostly, if not exclusively, in Italy, where it is very common on typewriters[citation needed]. Computer keyboards are usually QWERTY, although non-alphanumeric characters vary.
- Z and W are swapped
- M is moved from the right of N to the right of L, as in AZERTY
Apple supported QZERTY layout in its early Italian keyboards, and currently iPod Touch also has it available.[27]
Non-QWERTY keyboards for Latin scripts
There are also keyboard layouts that do not resemble QWERTY very closely, if at all. These are designed to reduce finger movement and are claimed by some proponents to offer higher typing speed along with ergonomic benefits.
Some languages use the Latin script but with non-QWERTY-based keyboard layouts, such as Latvian and Turkish (the majority of Turkish keyboards are QWERTY, though the "Turkish-F keyboard layout" is older and said to be better suited to the language).
Dvorak
The Dvorak Simplified Keyboard (DSK) is the best-known alternative to QWERTY, also known as the American Simplified Keyboard, ASK layout. It was named after its inventor, August Dvorak. There are also numerous adaptations for languages other than English, and single-handed variants. Dvorak's original layout had the numerals rearranged, but the present-day layout has them in numerical order. The Dvorak Simplified Keyboard has numerous properties designed to increase typing speed, decrease errors, and increase comfort[citation needed]. The most prominent property involves concentrating the most used English letters in the home row where the fingers rest, thus having 70% of typing done in the home row (compared to 32% in QWERTY).
The Dvorak Simplified Keyboard is available out of the box on most operating systems, making switching through software very easy. "Hardwired" Dvorak keyboards are also available, though only from specialized hardware companies.
Colemak
The Colemak keyboard layout is another alternative to the standard QWERTY layout, offering a more incremental change for users already accustomed to the standard layout.[28] It builds upon the QWERTY layout as a base, changing the positions of eighteen keys while retaining the QWERTY positions of most non-alphabetic characters and many popular keyboard shortcuts, making it easier to learn than Dvorak for people who already type in QWERTY. Despite this, statistics show it to be equal to, if not a slight improvement over, Dvorak, disproving the thought that it is less optimized for ultimate typing performance.[29]
An additional defining feature of the Colemak layout is the lack of a Caps Lock key; an additional Backspace key occupies the position typically occupied by Caps Lock on modern keyboards.[28]
The Colemak layout is supported out-of-the-box in the NetBSD,[30] FreeBSD,[31] DragonFly BSD,[32] Haiku,[33] Chrome and GNU/Linux[34] operating systems, as well as the X.org implementation of the X Window System.[35] It is also included with Mac OS X and iOS (hardware keyboards), starting with Mac OS X Lion and iOS 5.0.[36]
JCUKEN
Main article: JCUKENThe JCUKEN layout was used in the USSR for all computers (both domestically produced and imported such as Japan-made MSX-compatible systems) due to its phonetic compatibility with Russian ЙЦУКЕН layout (see below). The layout has advantage of having punctuation marks on Latin and Cyrillic layouts mapped on the same keys.
Neo
The Neo layout is an optimized German keyboard layout developed by the Neo Users Group, supporting nearly all Latin-based languages, including the International Phonetic Alphabet,[37] the Vietnamese language and some African languages.[38] The positions of the letters are not only optimized for German letter frequency, but also for typical groups of two or three letters. English is considered a major target as well. The design tries to enforce the alternating usage of both hands to increase typing speed. It is based on ideas from de-ergo and other ergonomic layouts. Typing with it is usually easier due to the high frequency keys being in the home row. The current layout Neo 2.0 has unique features not present in other layouts, making it extremely suited for many target groups such as programmers, mathematicians, scientists or authors. Neo is grouped in different layers, each designed for a special purpose. Most special characters inherit the meaning of the lower layers — for example the ⟨¿⟩ character is one layer above the ⟨?⟩, or the Greek ⟨α⟩ is above the ⟨a⟩ character. Neo uses a total of six layers with the following general use:
Layer Usage 1 Lowercase characters 2 Uppercase characters, typographical characters 3 Special characters for programming, etc. 4 WASD-like movement keys and number block 5 Greek characters 6 Mathematical symbols and Greek uppercase characters Bépo
The Bépo layout is an optimized French keyboard layout developed by the BÉPO community, supporting all Latin-based languages of the European Union, Greek and Esperanto.[41] It is also designed to ease programming. It is based on ideas from the Dvorak and other ergonomic layouts. Typing with it is usually easier due to the high frequency keys being in the home row.
Turkish
The Turkish language uses the Turkish Latin alphabet, and a dedicated keyboard layout was designed in 1955 by İhsan Sıtkı Yener.[42] During its design, letter frequencies in the Turkish language were investigated with the aid of Turkish Language Association. These statistics were then combined with studies on bone and muscle anatomy of the fingers to design the Turkish-F keyboard. The keyboard provides a balanced distribution of typing effort between the hands: 49% for the left hand and 51% for the right. With this scientific preparation, Turkey has broken 14 world records in typewriting championships between 1957 and 1995.[43] In 2009, Recep Ertaş from Turkey came in first at the 47th Intersteno congress at Beijing.[44] Despite the greater efficiency of the Turkish-F keyboard however, the modified QWERTY keyboard is the one that is used on most computers in Turkey.
Chorded keyboards and mobile devices
The multi-touch screens of mobile devices allow implementation of virtual on-screen Chorded keyboards. Buttons are fewer, so they can be made larger. Symbols on the keys can be changed dynamically depending on what other keys are pressed, thus eliminating the need to memorize combos for characters and functions before use. For example, in the chorded GKOS Keyboard which has been adapted for Android and iPhone platforms, thumbs are used for chording by pressing one or two keys at the same time. In the layout, the keys are divided in two separate pads which are located towards the sides of the screen and the text appears in the middle.
Some other layouts have also been designed specifically for use with mobile devices. The FITALY layout, which is optimised for use with a stylus to place the most commonly used letters closest to the centre and minimise the distance travelled when entering words. A similar concept was followed to research and develop the MessagEase keyboard layout for fast text entry with stylus or finger. The ATOMIK layout, designed for stylus use, was developed by IBM using the Metropolis Algorithm to mathematically minimize the movement necessary to spell words in English.[45] The ATOMIK keyboard layout is an alternative to QWERTY in ShapeWriter's WritingPad software.[46]
Chorded keyboards in general, such as the Stenotype and Velotype, allow letters and words to be entered using combinations of keys in a single stroke. Users of stenotype machines can often reach rates as high as 300 words per minute and these systems are commonly used for realtime transcription by court reporters and in live closed captioning systems.
Other original layouts and layout design software
Several other alternative keyboard layouts have been designed either for use with specialist commercial keyboards (e.g. Maltron and PLUM) or by hobbyists (e.g. Asset, Arensito); however, none of them are in widespread use, and many of them are merely proofs of concept. Principles commonly used in their design include maximising use of the home row, minimising finger movement, maximising hand alternation or inward rolls (where successive letters are typed moving towards the centre of the keyboard), minimising changes from QWERTY to ease the learning curve, and so on.
Maltron also has a single-handed keyboard layout.
Programs such as the Microsoft Keyboard Layout Creator,[47] KbdEdit[48] and Keyman Developer[49] make it very easy to create custom keyboard layouts for regular keyboards;[50] users may satisfy their own typing patterns or specific needs by creating new ones from scratch (like the IPA[51] or pan-iberian[52] layouts) or modify existing ones (for example, the Latin American Extended[53] or Gaelic[54] layouts).
Some high end keyboards such as the Kinesis Advantage contoured keyboard allow users total flexibility to reprogram keyboard mappings at the hardware level.
A few companies offer "ABC" (alphabetical) layout keyboards.[55][56]
Keyboard layouts for non-Latin alphabetic scripts
Some keyboard layouts for non-Latin alphabetic scripts, most notably the Greek layout, are based on the QWERTY layout, in that glyphs are assigned as far as possible to keys that bear similar-sounding or appearing glyphs in QWERTY. This saves learning time for those familiar with QWERTY.
This is not a general rule, and many non-Latin keyboard layouts have been invented from scratch.
All non-Latin computer keyboard layouts can also input Latin letters as well as the script of the language, for example, when typing in URLs or names. This may be done through a special key on the keyboard devoted to this task, or through some special combination of keys, or through software programs that do not interact with the keyboard much.
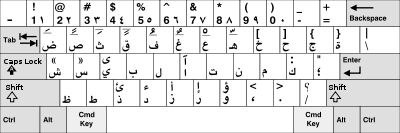
Arabic
Main article: Arabic keyboardThe above layout was developed by Microsoft from the classic Arabic typewriter layout and is used by IBM PCs.
The above layout was developed by Apple.
The above layout is built to maximize knowledge transfer. Intellark is designed to allow QWERTY, AZERTY or any Latin-derived keyboard layout users to retain and reuse their knowledge of key locations. In Intellark, a relationship is established between Latin-based and Arabic-based characters based on phonetic sound. For example, typing the English element in the pairs (a, ا), (s, س), (d, د), (f, ف), or (w, و) produces the Arabic one. Next, further relationships are drawn among the Arabic characters themselves, where double pressing the element on the right in each pair in (و، ؤ) ,(د، ذ) ,(س، ش) ,(ا، أ) produces a dependent character as based on shape, phonetic sound, or both, and so on.
Armenian
The Armenian keyboard is similar to the Greek in that in most (but not all) cases, a given Armenian letter is at the same location as the corresponding Latin letter on the QWERTY keyboard.
Greek
The usual Greek layout follows the U.K. layout for letters related to Latin letters (ABDEHIKLMNOPRSTXYZ), substitutes visually or phonetically similar letters (Φ at F; Γ at G) and uses the remaining slots for the remaining Greek letters: Ξ at J; Ψ at C; Ω at V; Θ at U).
Greek has two fewer letters than English, but has two accents which, because of their frequency, are placed on the home row at the U.K. ";" position; they are dead keys. Word-final sigma has its own position as well, and semicolon (which is used as a question mark in Greek) and colon move to the position of Q.
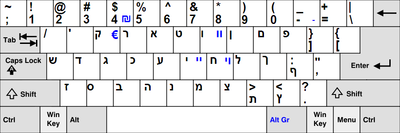
Hebrew
All keyboards in Israel are fitted with both Latin and Hebrew letters. Some include Arabic or Russian Cyrillic as well, creating two unique keyboards which include three different alphabets.
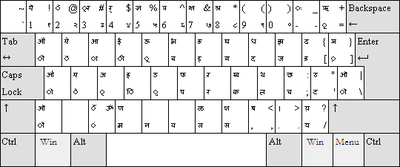
InScript
InScript is the standard keyboard for 12 Indian scripts including Devanagari, Bengali, Gujarati, Gurmukhi, Kannada, Malayalam, Oriya, Tamil and Telugu etc.
Most Indian scripts are derived from Brahmi, therefore their alphabetic order is same. On the basis of this property, the InScript keyboard layout scheme was prepared. So a person who knows InScript typing in one language can type in other scripts using dictation even without knowledge of that script.
An InScript keyboard is inbuilt in most modern operating systems including Windows, Linux and Mac OS. It is also available in some mobile phones.
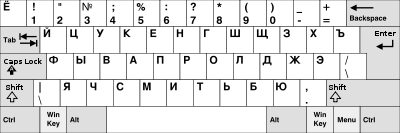
Russian
The most common keyboard layout in modern Russia is the so-called Windows layout. It is the default Russian layout used in the Windows operating system. This layout allows using keyboards of the same physical design as in many other countries but has some usability issues for Russian-language users. Because of an unfortunate design decision, the comma and full stop symbols are on the same key in this layout, and users need to hold Shift every time they enter a comma despite the fact that the comma is much more frequent in the language.[57]
There are some other Russian keyboard layouts in use: in particular, the traditional Russian Typewriter layout (punctuation symbols are placed on numerical keys, one needs to press Shift to enter numbers) and the Russian DOS layout (similar to the Russian Typewriter layout with common punctuation symbols on numerical keys, but numbers are entered without Shift). The Russian Typewriter layout can be found on many Russian typewriters produced before the 1990s, and it is the default Russian keyboard layout in the OpenSolaris operating system.[58]
Keyboards in Russia always have Cyrillic letters on the keytops as well as Latin letters. Usually Cyrillic and Latin letters are labeled with different colors.
The Russian Phonetic Keyboard Layout (also called homophonic or transliterated) is widely used outside Russia, where normally there are no Russian letters drawn on keyboard buttons. This layout is made for typists who are more familiar with other layouts, like the common English QWERTY keyboard, and follows the Greek and Armenian layouts in placing most letters at the corresponding Latin letter locations. It is famous among both native speakers and people who use, teach, or are learning Russian, and is recommended - along with the Standard Layout - by the linguists, translators, teachers and students of AATSEEL.org.[5]
There are several different Russian Phonetic layouts, for example YaZhERT (яжерт), YaWERT (яверт), and YaShERT (яшерт) (also sometimes with the 'ы'/'y' - i.e. YaZhERTY (яжерты), YaWERTY (яверты), etc.). They are named after the first several letters that take over the 'QWERTY' row on the Latin keyboard. They differ by where a few of the letters are placed. For example, some have Cyrillic 'B' (which is pronounced 'V') on the Latin 'W' key (after the German transliteration of B), while others have it on the Latin 'V' key. There are also variations within these variations; for example the Mac OS X Phonetic Russian layout is YaShERT but differs in placement of ж and э.[59][60]
A virtual (on-screen) Russian keyboard[61] allows entering Cyrillic directly in a browser without installing Russian drivers. Another virtual keyboard[62] supports both traditional (Windows and Typewriter) and some phonetic keyboard layouts.
Sinhalese
The Sinhala Keyboard Layout is based on the Wijesekara typewriter for Sinhala script
Moldovan
The Moldovan Cyrillic keyboard layout is based on a mixture of Russian phonetic and Serbian keyboard layout while adding a unique letter Ӂ to the layout in place of the letter Џ on the Serbian Cyrillic layout. This is the ЭЖЕРТ (EZhERT) layout. The letter Я is mapped the same as on the standard Russian layout, while letter Й is mapped where J is in Serbian layout. Also, letters Ь and Ы are remapped. This unofficial keyboard layout can be found here.
Ukrainian
Ukrainian keyboards, based on a slight modification of Russian Standard Layout, often also have the Russian Standard ("Windows") layout marked on them, making it easy to switch from one language to another. This keyboard layout had several problems, one of which was the omission of the letter Ґ, which does not exist in Russian. The other long-standing problem was the omission of the apostrophe, which is used in Ukrainian almost as commonly as in English (though with a different value), but which also does not exist in Russian. Both of these problems were resolved with the "improved Ukrainian" keyboard layout for Windows available with Vista and subsequent Windows versions.
Bulgarian
The current official Bulgarian keyboard layout for both typewriters and computer keyboards is described in BDS (Bulgarian State/National Standard) 5237:1978.[63] It superseded the old standard, BDS 5237:1968, on 1 January 1978.[63] Like the Dvorak keyboard, it has been designed to optimize typing speed and efficiency, placing the most common letters in the Bulgarian language - О, Н, Т and А - under the strongest fingers. In addition to the standard 30 letters of the Bulgarian alphabet, the layout includes the non-Bulgarian Cyrillic symbols Э and ы and the Roman numerals I and V (the X is supposed to be represented by the Cyrillic capital Х, which is acceptable in typewriters but problematic in computers).
There is also a second, informal layout in widespread use - the so-called "phonetic" layout, in which Cyrillic letters are mapped to the QWERTY keys for Latin letters that "sound" or "look" the same, with several exceptions (Я is mapped to Q, Ж is mapped to V, etc. - see this image and compare it to the standard QWERTY layout). This layout is available as an alternative to the BDS one in some operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Ubuntu.
In 2006, Prof. Dimiter Skordev from the Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics of Sofia University and Dimitar Dobrev from the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences proposed a new standard, prBDS 5237:2006, including a revised version of the old BDS layout and a standardization of the informal "phonetic" layout. After some controversy and a public discussion in 2008, the proposal was not accepted,[64] although it had been already used in several places - the "Bulgarian Phonetic" layout in Windows Vista is based on it.
Devanagari
InScript is the standard keyboard layout for Devanagari. Some other layouts also exist for Devanāgarī. See Devanagari keyboard layouts for additional configurations.
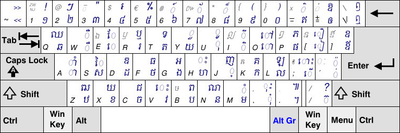
Thai
The less frequently used characters are accessed by the Shift key. Despite their wide usage in Thai, Arabic numbers are not present on the main section of the keyboard. Instead they are accessed via the numeric keypad. The backtick (`) key is blank, because this key is typically used to switch between input languages.
Khmer
Khmer uses its own layout roughly matched to the equivalent of its QWERTY counterpart. For example, the letter ល [lɔ] is typed on the same space as the letter L on the English based qwerty. Since most Khmer consonants have two forms, the shift key is used to switch between the first and second forms. The glyph below the letter ញ [ɲɔ] is used to type in subscripts when they occur in a cluster. Since spaces are used in Khmer to separate sentences and not words, the space option is activated when pressed with the shift key only. Otherwise it has no effect.
Tibetan
Tibetan (China)
The Chinese National Standard on Tibetan Keyboard Layout standardises a layout for the Tibetan language in China.[65]
The first version of Microsoft Windows to support the Tibetan keyboard layout is Windows Vista. The layout has been available in GNU/Linux since September 2007.
Dzongkha (Bhutan)
The Bhutanese Standard for a Dzongkha keyboard layout standardizes the layout for typing Dzongkha, and other languages using the Tibetan script, in Bhutan. This standard layout was formulated by the Dzongkha Development Commission and Department of Information Technology in Bhutan. The Dzongkha keyboard layout is very easy to learn as the key sequence essentially follows the order of letters in the Dzongkha and Tibetan alphabet. The layout has been available in GNU/Linux since 2004.
East Asian languages
Chinese, Japanese and Korean require special input methods, often abbreviated to CJK IMEs (Input Method Editors), due to the thousands of possible characters in these languages. Various methods have been invented to fit all these possibilities into a QWERTY keyboard, so East Asian keyboards are essentially the same as those in other countries. However, their input methods are considerably more complex, without one-to-one mappings between keys and characters.
In general, first the range of possibilities is narrowed down (most often by entering the desired character's pronunciation), then, if there remains more than one possibility, selecting the desired ideogram either by typing the number before the character, or using a graphical menu to select it. The computer assists the typist by using heuristics to guess which character is most likely desired. Although this may sound clumsy, East Asian input methods are today sufficiently sophisticated that, even for beginners, typing in these languages is only slightly slower than typing English.
In Japanese, the QWERTY-based JIS keyboard layout is used, and the pronunciation of each character is entered using Hepburn romanization or Kunrei-shiki romanization. There are several kana-based typing methods. See also Japanese language and computers.
Chinese has the most complex and varied input methods. Characters can be entered by pronunciation (like Japanese and Hanja in Korean) or by structure. Most of the structural methods are the most difficult to learn, but they are extremely fast for experienced typists, as they do away with the need for selecting characters from a menu. For a detailed treatment, see Chinese input methods for computers.
There exist a variety of other, slower ways a character may be entered. If the pronunciation of a character is not known, the selection can be narrowed down by giving its component shapes, radicals, and stroke count. Also, many input systems include a "drawing pad" permitting "handwriting" of a character using a mouse. Finally, if the computer does not have CJK software installed, it may be possible to enter a character directly through its encoding number (e.g. Unicode).
In contrast to Chinese and Japanese, Korean is typed in a similar way to Western languages. There are two major kinds of keyboard layouts: dubeolsik and sebeolsik. Dubeolsik, which shares its symbol layout with the QWERTY layout, is more commonly used. While Korean consonants and vowels (jamo) are grouped together into syllabic grids when written, the script is essentially alphabetical, and therefore typing in Korean is quite simple for those who understand the Korean alphabet Hangul. Each jamo is assigned to a single key. As the user types letters, the computer automatically groups them into syllabic characters. Given a sequence of jamo, there is only one unambiguous way letters can be validly grouped into syllables, so the computer seamlessly groups them together as the user types.
Japanese
The JIS standard layout includes Japanese kana in addition to a QWERTY style layout.
 Example of Microsoft's IME in Windows
Example of Microsoft's IME in Windows
For entering Japanese, the most common method is entering text phonetically, as romanized (transliterated) kana, which are then converted to kanji as appropriate by an input method editor. It is also possible to type kana directly, depending on the mode used. For example, to type たかはし, "Takahashi", a Japanese name, one could type either "takahas(h)i" in Romanized (Rōmaji) input mode, or "qtfd" in kana input mode. Then the user can proceed to the conversion step to convert the input into the appropriate kanji.
The extra keys in the bottom row, and the changed keys in the leftmost column, control various aspects of the conversion process and select different modes of input.
For more details, see the section on East Asian languages above, and the articles Japanese language and computers, Japanese input methods, and Language input keys.
Chinese
A Chinese keyboard is simply a US layout with Chinese input method labels printed on the keys. Without an input method handler, these keyboards would respond to Latin characters, provided that US keyboard layout is selected in the operating system.
Most modern input methods allow input of both simplified and traditional characters, and will simply default to one or the other based on the locale setting.
See the section on Chinese languages, and also Chinese input methods for computers.
Mainland China
Keyboards used in the mainland of the People's Republic of China typically use an English US (QWERTY) keyboard and input Chinese characters using Hanyu pinyin, which represents the sounds of Chinese characters using Latin letters. Keyboards can occasionally be found with labels for alternative input methods such as Wubi method, but those are rare.
Taiwan
Computers in Taiwan often use Zhuyin (bopomofo) style keyboards (US keyboards with bopomofo labels), many also with Cangjie method key labels, as Cangjie is the standard method for speed-typing in Traditional Chinese. The bopomofo style keyboards are in lexicographical order, top-to-bottom left-to-right. The codes of three input methods are typically printed on the Chinese (traditional) keyboard: Zhuyin (upper right); Cangjie (lower left); and Dayi (lower right).
Hong Kong
In Hong Kong, both Chinese (Taiwan) and US keyboards are found. Japanese keyboards are occasionally found, but UK keyboards are rare.
Other input methods include the Cantonese Input Method for the Cantonese language speakers. The romanisation, which mirrors the Hong Kong government romanisation of Cantonese, requires users to spell out the Cantonese sound of each character without tone marks, e.g. 'heung' and 'kong' (or 'gong') for 'Hong Kong'/香港 and to choose the characters from a list.
- Chinese writing characters are pieces of ideograms / monographs organised in structured strokes. A Chinese word may be composed of a single ideogram, or two ideograms in combinations. Each monograph can have only one single syllable to pronounce it. However, the same monograph may carry more than one different syllable to denote an entirely different contextual meaning.
The disadvantage of the Cantonese Input Method is that there are many characters that can have the same syllable in the spelling only (they sound the same but are written with different characters) that needed to be differentiated by different intonations for speech communication. Unless a user has also input a phonetic intonation or an accent numeral (i.e., 1, 2, 3, or 4.) to narrow down the list of possible combinations, he or she can have a substantial set of ambiguous Chinese characters of the same pronunciation to select. The selection process can slow down the input speed for those do have not input an accent numeral after each and every Cantonese spelling.
The advantage of the Cantonese Input Method is that nearly all Cantonese Speakers can input Traditional Chinese characters on their very instinct; no particular training and practice is required at all. The advantage available to a Hanyu Pinyin user is that any keyboard with just an English layout, i.e., without BoPoMoFo markings engraved, can deploy the Pinyin IME for bilingual (both Chinese and English on the same document) input. All those who have received formal education in Mainland China can easily input with Hanyu Pinyin without any formal training. The drawback of Hanyu Pinyin to a Hong Kong native Cantonese speaker is that the alphabets are not pronounced exactly in the same way as the common English language syllables should be pronounced because it is only the Latin letters in the keyboard that have been used by the Hanyu Pinyin Method.
Thorough training and practice are required to input correctly with Changjie or Cangjie, yet it is, by impression, the quickest Chinese input method[clarification needed]. Many Cantonese speakers have taken Changjie or Cangjie input courses because of the fast typing speed availed by the input method. This method is the fastest because it has the capability to fetch the exact, unambiguous Chinese character which the user has in mind to input, pinpointing to only one character in most cases. This is also the reason why no provision for an input of phonetic accent is needed to complement this Input Method. The Changjie or Cangjie character feature is available on both Mac OS X and Windows. On Mac OS X the use of the multitouch pads of modern Macs makes it possible to write a glyph with a finger and the correct character is recognised by the computer.[clarification needed]
The clumsiest Chinese Input method is the Stroke Input Method which is ideal for those who are not so proficient in spelling the Cantonese language in English Alphabets nor Mandarin in Pinyin. The method is widely installed in mobile phones with small screens because the method only requires five key taps for the 5,000 commonly used Chinese characters. It is also considered too tedious requiring a user to type out all the strokes constituting a single Chinese character. Chinese characters sharing the same 3 to 5 beginning brush strokes are grouped to response to users' tapping sequences. Thus, there yields a lengthly list of more than 40 some Chinese characters having these similar beginning strokes for the user to confirm which one of the listed characters should be the intended one to input.
The character picking process is a must for the Stroke Input Method users regardless of whether the Traditional or Simplified Chinese character set is to be used. To a native Hong Kong Cantonese speaker who can spell the Cantonese dialect fairly accurately in English alphabets and, who types Chinese in ad-hoc occasions only; Cantonese Input Method is, by far, the most convenient Chinese input method both for phone book searching and for word processing using laptops and smart phones.
Hangul (for Korean)
Dubeolsik
Dubeolsik (두벌식) is the most common and the sole national standard of Hangul keyboard layout in use in South Korea since 1969. Pressing the Ha/En (한/영) key once switches between Hangul as shown, and QWERTY. There is another key to the left of the space bar for Hanja input. But, if using a 104-key keyboard, the left Alt key will become the Ha/En key, and the right Ctrl key will become the Hanja key. Consonants occupy the left side of the layout, while vowels are on the right.
Sebeolsik 390
Sebeolsik 390 (세벌식 390) was released in 1990. It is based on Dr. Kong's earlier work. This layout is notable for its compatibility with the QWERTY layout; almost all QWERTY symbols that are not alphanumeric are available in Hangul mode. Numbers are placed in three rows. Syllable-initial consonants are on the right (shown green in the picture), and syllable-final consonants and consonant clusters are on the left (shown red). Some consonant clusters are not printed on the keyboard; the user has to press multiple consonant keys to input some consonant clusters, unlike Sebeolsik Final. It is more ergonomic than the dubeolsik, but is not in wide use.
Sebeolsik Final
Sebeolsik Final (세벌식 최종) is another Hangul keyboard layout in use in South Korea. It is the final Sebulsik layout designed Dr. Kong Byung Woo, hence the name. Numbers are placed on two rows. Syllable-initial consonants are on the right, and syllable-final consonants and consonant clusters are on the left. Vowels are in the middle. All consonant clusters are available on the keyboard, unlike the Sebeolsik 390 which does not include all of them. It is more ergonomic than the dubeolsik, but is not in wide use.
Sebeolsik Noshift
Sebeolsik Noshift is a variant of sebeolsik which can be used without pressing the shift key. Its advantage is that people with disabilities who cannot press two keys at the same time will still be able to use it to type in Hangul.
See also
- Alphanumeric keyboard
- British and American keyboards
- Chinese input methods for computers
- Computer keyboard
- FITALY Layout
- IBM Personal Computer
- Inscript (Indian Script)
- ISO/IEC 9995
- Japanese language and computers
- Keyboard (computing)
- Language code
- Maltron
- Model M keyboard
- Telephone (phone, mobile phone) keypad character (letter) layout (mapping)
- Scancode
- Technical standards in colonial Hong Kong
- Unicode
- Urdu keyboard
Notes and references
- ^ Alain Souloumiac, Les perspectives de l'informatique, La Documentation Francaise 1983, p.72
- ^ George M. Phelps, U.S. Patent 0,026,003 Improvement in Telegraphic Machines issued November 1, 1859
- ^ "The House Printing Telegraph". telegraph-history.org. http://www.telegraph-history.org/george-m-phelps/house.htm. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ^ "Latkey: Defining keyboard layouts with stickers". http://www.latkey.com. Retrieved 2010-10-31.
- ^ An introduction to Linux Mint 8 – Main Edition (Helena) (Liberian Geek )
- ^ "Spanish/Español". iragination.com. http://www.iragination.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2007/10/spankey.jpg. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ^ "Fren-Canadian keyboard". uakron.edu. http://www3.uakron.edu/modlang/french/images/kbd4.gif. Retrieved 27 November 2010.
- ^ SFS 5966 Keyboard layout. Finnish-Swedish multilingual keyboard setting. Finnish Standards Association SFS. (2008-11-03.)
- ^ Kotoistus: Uusi näppäinasettelu = Status of the new Keyboard Layout. A bi-lingual (Finnish + English) presentation page collecting drafts of the Finnish Multilingual Keyboard. CSC – IT Center for Science Ltd. (Page updated 2006-12-28.)
- ^ Microsoft.com
- ^ Secarica.ro
- ^ Spanish Keyboard layout and special alt characters Spain (Spanish) version (MyLingos.com)
- ^ Spanish (Traditional Sort) Keyboard Overlays (Trantor)
- ^ (PNG) Flyff Distrib esp (image), Wikimedia Commons, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Flyff_Distrib_esp.png.
- ^ Foreign language Keyboard layout: type foreign languages, spanish keyboard layout, french, german, italian, Translation Software, http://www.translationsoftware4u.com/keyboard-layout.php.
- ^ There is a separate Irish Gaelic keyboard layout, but this is rarely used. In all common operating systems that have a different selection for Irish, this refers to the layout that is identical with the UK layout (with the exception of Windows, where the grave dead key is enabled by default, and when AltGr is pressed, apostrophe becomes an acute dead key), not the Irish Gaelic layout; the latter tends to be called Gaelic or similar.
- ^ British Standard BS 4822: Keyboard allocation of graphic characters for data processing. British Standards Institution, 1994. Note that "[t]his standard has been declared obsolescent as it is no longer felt to be relevant."
- ^ "CLiki: Editing Lisp Code with Emacs". http://www.cliki.net/Editing%20Lisp%20Code%20with%20Emacs. Retrieved 2008-01-04.
- ^ Where is the backslash key located on my keyboard? (Sharpened.net)
- ^ Taken from http://stackoverflow.mobi/question687_Keyboard-for-programmers.aspx (Stackoverflow.mobi)
- ^ Taken from http://doc.opensuse.org/products/SLES/SLES-admin/cha.trouble.html (openSUSE.org)
- ^ Typing accented letters and other special characters on a PC (or Mac) (Department of Foreign Languages, Salem State University: Jon Aske)
- ^ :::online in4mation gmbh ::: us keyboard design - US Tastaturbelegung ::: amerikanische Tastatur (online in4mation gmbh)
- ^ Just.nicepeople.free.fr
- ^ How to use the United States-International keyboard layout in Windows 7, in Windows Vista, and in Windows XP, Microsoft, August 17, 2009
- ^ Markus Kuhn: Apostrophe and acute accent confusion, 2001.
- ^ iPod touch Features Guide
- ^ a b "Colemak keyboard layout". http://www.colemak.com/. Retrieved 2011-08-29.
- ^ Krzywinski, Martin. "Colemak - Popular Alternative". Carpalx - keyboard layout optimizer. Canada's Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre. http://mkweb.bcgsc.ca/carpalx/?colemak. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
- ^ CVS commit: src
- ^ FreeBSD — CVS log for src/share/syscons/keymaps/colemak.iso15.acc.kbd
- ^ Colemak keymap for syscons(4)
- ^ Haiku Trac — #3944 (support for Colemak keyboard layout)
- ^ kbd ChangeLog, git.altlinux.org
- ^ Xkeyboard-config — "added us(colemak), b.fd.o#11416"
- ^ http://forum.colemak.com/viewtopic.php?id=1031
- ^ https://wiki.neo-layout.org/wiki/IPA%20mit%20Neo
- ^ https://wiki.neo-layout.org/wiki/Sprachen%20mit%20Neo
- ^ Phillip H. Poll, Neu verteilt. Ergonomischeres Tastaturlayout mit Neo, LinuxUser 05/2009
- ^ Daniel Knittl-Frank, Neo – Ergonomisch optimiert, Yalm-Magazine 07/2009
- ^ Characters and languages supported by the bépo layout
- ^ "F klavye (Turkish)". http://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/F_klavye.
- ^ "Biography of Ihsan Sıtkı Yener (Turkish)". http://www.msxlabs.org/forum/bilim-tr/276542-ihsan-sitki-yener-ihsan-sitki-yener-kimdir-ihsan-sitki-yener-hakkinda.html.
- ^ "Results list of 47th Intersteno congress". http://www.intersteno.it/uploads/BEIJING_RESULTLIST.pdf.
- ^ Almaden.ibm.com
- ^ Shapewriter.com
- ^ "Microsoft Keyboard Layout Creator". http://msdn.microsoft.com/goglobal/bb964665. Retrieved 2011-02-03.
- ^ "KbdEdit". http://www.kbdedit.com. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "Tavultesoft Keyman Developer". http://www.tavultesoft.com/keymandev/. Retrieved 2009-05-14.
- ^ Kaplan, Michael (2006-11-28). "Your layout (in all likelihood) bores me". http://blogs.msdn.com/michkap/archive/2006/11/28/1170048.aspx. Retrieved 2007-07-26.
- ^ "IPA Keyboard Layout for Windows". http://www.rejc2.co.uk/ipakeyboard/. Retrieved 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Keyboard layouts for Windows: pan-iberian.". http://www.farah.cl/DistribucionesDeTeclado/PaniberN_en.html. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
- ^ "Keyboard layouts for Windows: latin american extended.". http://www.farah.cl/DistribucionesDeTeclado/LatAmExt_en.html. Retrieved 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Gaelic Keyboards for MS Windows". http://www.smo.uhi.ac.uk/~oduibhin/mearchlar/windows.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-26.
- ^ "The ABCkeyboard". http://www.abckeyboard.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
- ^ "BIG KEY KEYBOARDS ABC Layout or QWERTY Layout". http://www.fentek-ind.com/bigkey.htm. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
- ^ Artemy Lebedev. Where once was a comma, 2004, arlebedev.com.
- ^ ru:Русская раскладка клавиатуры
- ^ Teaching and Learning with Technology (2009-03-06). "Mac OS X Keyboards". Penn State University. http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/international/keyboards/mackey.html. Retrieved 2009 9 13.
- ^ SIL International (2009-03-06). "Mac OS X Keyboard Layout Editor". SIL International. http://scripts.sil.org/cms/scripts/page.php?site_id=nrsi&item_id=ukelele. Retrieved 2009 9 13.
- ^ "Russian Keyboard OnLine (On-Screen Cyrillic Virtual Keyboard) with Russian Spellcheck". http://www.softcorporation.com/products/cyrillic/.
- ^ Paul Gorodyansky. "On-line Cyrillic keyboard". http://winrus.com/screen_e.htm.
- ^ a b "БДС 5237:1978". Official site of the Bulgarian Institute for Standardization. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization. http://www.bds-bg.org/standard/info.php?standard_id=14264. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
- ^ "Състоя се една ползотворна дискусия" (in Bulgarian). News, Official site of the Bulgarian Institute for Standardization. Bulgarian Institute for Standardization. 2008-06-20. http://www.bds-bg.org/news/?news_id=56. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
- ^ Yalasoo.com
External links
Custom Layouts
- Official for Microsoft Windows
- Unofficial for GNU/Linux | UNIX
- Unofficial for Mac OS X
- Russian Translit - converting Latin characters into Russian
Keyboard keys Dead keys Modifier keys Lock keys Navigation Editing Misc. System request/Print screen · Break/Pause · Escape · Menu · Numeric keypad · Function · Power management (Power, Sleep, Wake) · Language input · any key · Macro key · EjectAlternative layouts Non-Roman Arabic · Dzongkha (Tibetan) · Hebrew · InScript (Indian languages Hindi, Telugu etc) · Urdu · Russian (pre-reform) · Russian (post-reform)For mobile devices Chorded keyboards Historical Categories:- Computer keyboards
- Keyboard layouts
- Internationalization and localization
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.