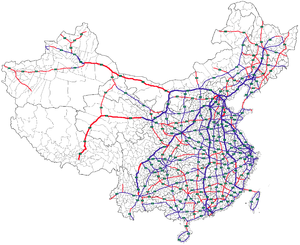
- Expressways of China
-
 Chinese expressway, complete with signage. Shown here is the G106 (Jingkai Expressway section) in southern Beijing. (Summer 2004 image)
Chinese expressway, complete with signage. Shown here is the G106 (Jingkai Expressway section) in southern Beijing. (Summer 2004 image)
The Expressway Network of the People's Republic of China (simplified Chinese: 中国高速网; traditional Chinese: 中國高速網; pinyin: Zhōngguó gāosùwǎng) is one of the longest in the world. The network is also known as National Trunk Highway System (NTHS). The total length of China's expressways was 74,000 kilometres (46,000 mi) at the end of 2010,[1] the world's second longest only after the United States and slightly longer than the total expressway length in the European Union. In 2010, 9,816 kilometres (6,099 mi) of expressways were added to the network.[2] The length of China's expressway system is expected to surpass that of the Interstate Highway System in 2011, but will remain shorter than that country's National Highway System.[3]
Expressways in China are a fairly recent addition to a complex network of roads. China's first expressway was built in 1988. Until 1993, very few expressways existed. One of the earliest expressways nationwide was the Jingshi Expressway between Beijing and Shijiazhuang in Hebei province. This expressway now forms part of the Jingzhu Expressway, currently one of the longest expressways nationwide at over 2,000 km.
History
Originally, China had been carrying out an ambitious plan to build up a 35,000 kilometer national trunk highway system. Construction of expressways began in 1988 and the network had been scheduled to be complete in 2020. The scale of the project can be seen by the fact that on January 1, 1989, the PRC had 147 km of freeways, but by January 1, 2008, it had 53,600 km of freeway, about 8,000 km of which were built in 2007. The main objective of the NTHS was to construct 12 high standard trunk roads: five longitudinal roads and seven latitudinal roads. 70% of the trunk roads are expressways. This project was completed by the end of 2007, 13 years ahead of the original plan.[4] By the end of 2007, there were already 3.57 million km of highways, which includes 53,600 km (33,300 mi) of expressways.[4] Design standards for China's National Trunk Highway System are derived from the standards used on the American Interstate Highway System, with Chinese expressway cross-sections, interchange profiles, and bridge designs closely reflecting their counterparts in the United States.
On January 13, 2005, it was announced by Zhang Chunxian, minister of communications, that China would build a network of 85,000 km expressways over the next three decades, connecting all provincial capitals and cities with a population of over 200,000. Of this total length, 68,000 km are trunk roads and 17,000 km are 5 regional ring roads. There are also 2 parallel routes and more than 30 connecting links. 32,000 km of expressway are to be built in central and western regions.
Historical development of expressway length in Mainland China
 Combined G4/G5 (formerly, G030) (Jingshi Expressway section) after Zhaoxindian/Changxindian exit (Early July 2004 image)
Combined G4/G5 (formerly, G030) (Jingshi Expressway section) after Zhaoxindian/Changxindian exit (Early July 2004 image)
Historical Development of Expressway Length in Mainland China[5] Year Distance (KM) 01-01-1988 0 01-01-1989 147 km (91 mi) 01-01-1990 271 km (168 mi) 01-01-1991 522 km (324 mi) 01-01-1992 574 km (357 mi) 01-01-1993 652 km (405 mi) 01-01-1994 1,145 km (711 mi) 01-01-1995 1,603 km (996 mi) 01-01-1996 2,141 km (1,330 mi) 01-01-1997 3,422 km (2,126 mi) 01-01-1998 4,771 km (2,965 mi) 01-01-1999 8,733 km (5,426 mi) 01-01-2000 11,605 km (7,211 mi) 01-01-2001 16,314 km (10,137 mi) 01-01-2002 19,453 km (12,088 mi) 01-01-2003 25,200 km (15,700 mi) 01-01-2004 29,800 km (18,500 mi) 01-01-2005 34,300 km (21,300 mi) 01-01-2006 41,005 km (25,479 mi) 01-01-2007 45,339 km (28,172 mi) 01-01-2008 53,913 km (33,500 mi) 01-01-2009 60,436 km (37,553 mi) 01-01-2010 65,065 km (40,430 mi) 01-01-2011 74,000 km (46,000 mi) 01-01-2016 108,000 km (67,000 mi) Costs
 G42 Hurong expressway crossing Si Du River in Enshi Prefecture, Hubei. The bridge cost around US $100 million.[6]
G42 Hurong expressway crossing Si Du River in Enshi Prefecture, Hubei. The bridge cost around US $100 million.[6]
The total costs of the national expressway network are estimated to be 2 trillion yuan (some 240 billion US dollars). From 2005 to 2010, the annual investment was planned to run from 140 billion yuan (17 billion US dollars) to 150 billion yuan (18 billion US dollars), while from 2010 to 2020, the annual investment planned is to be around 100 billion yuan (12 billion US dollars).
The construction fund will come from vehicle purchase tax, fees and taxes collected by local governments, state bonds, domestic investment and foreign investment. Unlike other freeway systems, almost all of the roads on the NTHS/"7918 Network" are toll roads that are largely financed by private companies under contract from provincial governments. The private companies raise money through bond and stock offerings and recover money through tolls.
Efforts to impose a national gasoline tax to finance construction of the tollways met with opposition and it has been very difficult for both the Communist Party of China and the State Council to pass such a tax through the National People's Congress of China.
Expressway nomenclature
 An old signpost refers the Jingshi Expressway as the Jingshi Freeway, thus hinting at its previous nomenclature. (Summer 2004 image)
An old signpost refers the Jingshi Expressway as the Jingshi Freeway, thus hinting at its previous nomenclature. (Summer 2004 image)
Neither officially named "motorway" nor "highway", the PRC used to call these roads "freeways". In this sense, the word "free" means that the traffic is free-flowing; that is, cross traffic is grade separated and the traffic on the freeway is not impeded by traffic control devices like traffic lights and stop signs. However, many misinterpret "free" as meaning "no cost", and this may be misleading because most of the expressways charge tolls. Sometime in the 1990s, "expressways" became the standardised term.
Note that "highways" refers to China National Highways, which are not expressways at all.
"Express routes" exist too; they are akin to expressways but are mainly inside cities. The "express route" name is a derivation of the Chinese name kuaisu gonglu (compare with expressway, gaosu gonglu). Officially, "expressway" is used for both expressways and express routes, which is also the standard used here.
The names of the individual expressways regularly are composed by two characters representing start and end of expressway, e.g. "Jingcheng" expressway is the expressway between "Jing" (meaning Beijing) and Chengde.
Expressway speed limits
The Road Traffic Safety Law of the People's Republic of China has raised the speed limit nationwide from 110 km/h to 120 km/h (75 mph), effective May 1, 2004. It may still take some time for local expressways to raise the speed limit accordingly.
A minimum speed limit is in force, of 70 km/h. On overtaking lanes, however, this could be as high as 100 km/h to 110 km/h. Penalties for driving both below and in excess of the prescribed speed limits are in force.
Expressway legislation
Only motor vehicles are allowed to enter expressways. As of May 1, 2004, "new drivers" (i.e., those with a PRC driver's licence for less than a year) are allowed on expressways, something that was prohibited from the mid-1990s.
Overtaking on the right, speeding, and illegal use of the emergency belt (or hard shoulder) cost violators stiff penalties.
Expressway signage
 Chinese expressway distances road sign. Shown here are some connections to the Expressways of Beijing in eastern Beijing. (Spring 2003 image)
Chinese expressway distances road sign. Shown here are some connections to the Expressways of Beijing in eastern Beijing. (Spring 2003 image)
 Chinese expressway exit sign (older version). Shown here is an exit sign to Liangxiang Airport in southwestern Beijing on the Jingshi Expressway. (Summer 2004 image)
Chinese expressway exit sign (older version). Shown here is an exit sign to Liangxiang Airport in southwestern Beijing on the Jingshi Expressway. (Summer 2004 image)
Expressways in China are signed in both Simplified Chinese and English (except for parts of the Jingshi Expressway, which relies only on Chinese characters, and some provinces, in Inner Mongolia for example signs are in Mongolian and Chinese). This sharply reduces the language barrier; however, very few toll officials at toll gates speak English.
The signs on Chinese expressways use white lettering on a green background, like Japanese highways, Swiss autobahns and United States freeways. Newer signage places the exit number in an exit tab to the upper right of the sign, making them very similar in appearance to American freeway signs.
Exits are well signed, with signs far ahead of exits. There are frequent signs that announce the next three exits. At each exit, there is a sign with the distance to the next exit. Exit signs are also posted 3000 m, 2000 m, 1000 m, and 500 m ahead of the exit, immediately before the exit, and at the exit itself.
Service areas and refreshment areas are standard on some of the older, more established expressways, and are expanding in number. Gas stations are frequent.
Signs indicate exits, toll gates, service/refreshment areas, intersections, and also warn about keeping a fair distance apart. "Distance checks" are commonplace; the idea here is to keep the two second rule (or, as PRC law requires, at least a 100 m distance between cars). Speed checks and speed traps are often signposted (in fact, on the Jingshen Expressway in the Beijing section, even the cameras have a warning sign above them), but some may just be scarecrow signs. Signs urging drivers to slow down, warning about hilly terrain, banning driving in emergency lanes, or about different road surfaces are also present. Also appearing from time to time are signs signaling the overtaking lane (which legally should only be used to pass other cars). Although most English signs are comprehensible, occasionally the English is garbled.
Some, if not most, expressways have digital displays. These displays may advise against speeding, indicate upcoming road construction, warn of traffic jams, or alert drivers to rain. Recommended detours are also signaled. The great majority of messages are only in Chinese.
Expressway exit numbering
Exit numbering has been standard in China from virtually day one, while some other nations are just catching on (e.g. Switzerland only in 2002). Most Chinese expressways, especially those in the national network, use distance-based exit numbering, with the last three numbers before the decimal point taken used as the exit number. Hence, an exit present at km 982.7 would be Exit 982, whereas an exit at km 3,121.2 would be Exit 121.
Mostly regional expressways still use sequential exit numbering, although even here, new signage feature distance-based exit numbering. Before the 2009–2010 numbering switchover, nearly all of China's expressways used sequential numbering, and a few expressways used Chinese names outright.
The exit is written inside an oval in green letters to the immediate right of the Chinese word for exit, "出口" (chukou).
Expressway tolls and financing
 Chinese expressway toll gate. Shown here is the Dujiakan toll gate on the Jingshi Expressway in southwest Beijing. (Summer 2004 image)
Chinese expressway toll gate. Shown here is the Dujiakan toll gate on the Jingshi Expressway in southwest Beijing. (Summer 2004 image)
Nearly all expressways charge tolls. Tolls are roughly around CNY 0.5 per kilometre, and minimum rates (e.g. CNY 5) usually apply regardless of distance. However, some are more expensive (the Jinji Expressway costs around CNY 0.66 per kilometre) and some are less expensive (the Jingshi Expressway in Beijing costs around CNY 0.33 per kilometre). It is noteworthy that cheaper expressways do not necessarily mean poorer roads or a greater risk of traffic congestion.
 Chinese expressway toll charges table. In many jurisdictions it is legally required that charges be openly disclosed. Shown here is the toll charges table at Doudian exit on the Jingshi Expressway in southwest Beijing. (Autumn 2004 image)
Chinese expressway toll charges table. In many jurisdictions it is legally required that charges be openly disclosed. Shown here is the toll charges table at Doudian exit on the Jingshi Expressway in southwest Beijing. (Autumn 2004 image)
Expressway planning is performed by the Ministry of Transportation of the People's Republic of China. Unlike the road networks in most nations, most Chinese expressways are not directly owned by the state, but rather are owned by for-profit corporations (which have varying amounts of public and private ownership) which borrow money from banks or securities markets based on revenue from projected tollways. One reason for this is that Chinese provinces, which are responsible for road building, have extremely limited powers to tax and even fewer powers to borrow.
Expressway construction has also been one of the rare instances in which the Communist Party of China and the State Council has had to back down on a major policy initiative. During the late-1990s, there were proposals to fund public highways by means of a fuel tax, but this was voted down by the National People's Congress.
Toll methods
Most expressways use a card system. Upon entrance to an expressway (or to a toll portion of the expressway), an entry card is handed over to the driver. The tolls to be paid are determined from the distance traveled when the driver hands the entry card back to the exit toll gate upon leaving the expressway. A small number of expressways do not use a card system but charge unitary fares. Passage through these expressways is relatively faster but it is economically less advantageous. An example of such an expressway would be the Jingtong Expressway.
China is increasingly deploying a system of ETC systems, and in the latest edition of expressway toll gate signage, a new ETC sign is now shown at an increasing number of toll gates. ETC networks based around Beijing [1], Shanghai [2] and Guangdong province [3] all feature either mixed toll passages supporting toll card payment or full-service dedicated ETC lanes. Beijing, in particular, has a dedicated ETC lane at almost all toll gates.[7]
City transit cards are not widely used; one of the first experiments with the Beijing Yikatong Card on what is now the Jingzang Expressway (G6)[8] went live for only a year before a new national standard replaced it in early 2008.
Numeric System and List by number
G000 Series
For more details on this topic, see China National Highways.A previous system, the 1992 "five vertical + seven horizontal expressways" system, was used for arterial expressways and were, in essence, G0-series expressways (e.g. G020, G025). This was replaced by the present-day new numeric system (see below).
New Numbering System
A new system, which dates from 2004 and began use on a nationwide level beginning late 2009 and early 2010, integrates itself into the present-day G-series number system. The present-day network, termed the 7918 Network (also known as the National Trunk Highway System (NTHS)), uses one, two or four digits in the G-series numbering system, leaving three-figured G roads as the China National Highways.
The new 7918 Network is composed of
- 7 radial expressways leaving Beijing (G1-G7)
- 9 vertical expressways going north to south (double digit G roads with numbers ending in an odd numeral)
- 18 horizontal expressways head west to east (double digit G roads with numbers ending in an even numeral)
The network is additionally composed of connection expressways as well as regional and metropolitan ring expressways.
On a nationwide basis, expressways use the G prefix (short for "guojia" or "nation" in Chinese), as well as the character "国家高速" (National Expressway, white letters on a red stripe on top of the sign). For regional expressways, the prefix S (short for "shengji" or "province-level") is used instead, as well as the one-character abbreviation of the province and "高速" (expressway, black letters on an orange-yellow stripe on top of the sign.) The same numbering system is used for both national and regional expressways.
Numbering Rules
- All expressways in this network begin with the letter G. (For regional expressways, the letter S is used instead.)
- All expressways have a thin band on top of the sign. For national expressways, this will be red; for regional expressways, it will be orange-yellow.
- For radial expressways leaving from or ending in Beijing, use a single digit from 1 to 9 (e.g. G1, G2).
- For north-south expressways, use an odd number from 11-89 (e.g. G13, G35).
- For west-east expressways, use an even number from 10-90 (e.g. G30, G46).
- For regional expressways in the 7918 network, use numbers from 91-99 (e.g. G91, G93)
- Note: G99 or the Taiwan Ring Expressway is currently a theoretical expressway based in Taiwan Province, which is claimed by the People's Republic of China, but is actually administered by the Republic of China. (In additional, the ROC has not built the eastern half as an expressway.) See Political status of Taiwan. See also Highway System in Taiwan for the current Republic of China-maintained Taiwan freeway system, which uses a different numbering system.
- For the parallel expressways running alongside primary expressways, add the direction signal "W", "E", "N", "S" after the primary expressway number (e.g. G4W).
- For connection expressways, use "1" plus an order number after the main line (e.g. G1511).
- For city ring expressways, use "0" plus an order number after the main line number, starting from the smallest possible number.
List
Number and Name Origin Terminus Length
(km)Notes Radial Expressways from Beijing  G1 Beijing–Harbin Expressway
G1 Beijing–Harbin ExpresswayBeijing Harbin 1,280 km (800 mi)  G2 Beijing–Shanghai Expressway
G2 Beijing–Shanghai ExpresswayBeijing Shanghai 1,245 km (774 mi)  G3 Beijing–Taipei Expressway
G3 Beijing–Taipei ExpresswayBeijing Fuzhou (Taipei) 2,030 mi (3,270 km) See also Political Status of Taiwan.  G4 Beijing–Hong Kong–Macau Expressway
G4 Beijing–Hong Kong–Macau ExpresswayBeijing Hong Kong–Mainland China border 2,285 km (1,420 mi) Extends into Shenzhen section of Hong Kong Route 10 and connects other expressways in Hong Kong. Hong Kong is a special administrative region of China.  G4W Guangzhou–Macau Expressway
G4W Guangzhou–Macau ExpresswayGuangzhou Macau–Mainland China border Connects to Macau's roads. Macao is a special administrative region of China.  G5 Beijing–Kunming Expressway
G5 Beijing–Kunming ExpresswayBeijing Kunming 2865  G6 Beijing–Lhasa Expressway
G6 Beijing–Lhasa ExpresswayBeijing Lhasa 3710  G7 Beijing–Ürümqi Expressway
G7 Beijing–Ürümqi ExpresswayBeijing Ürümqi 2540 North–South Expressways  G11 Hegang–Dalian Expressway
G11 Hegang–Dalian ExpresswayHegang Dalian 1390  G1111 Hegang–Harbin Expressway
G1111 Hegang–Harbin ExpresswayHegang Harbin  G1112 Ji’an–Shuangliao Expressway
G1112 Ji’an–Shuangliao ExpresswayJi'an Shuangliao  G1113 Dandong–Fuxin Expressway
G1113 Dandong–Fuxin ExpresswayDandong Fuxin  G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway
G15 Shenyang–Haikou ExpresswayShenyang Haikou 3710  G15W Changshu–Taizhou Expressway
G15W Changshu–Taizhou ExpresswayChangshu Taizhou  G1511 Rizhao–Lankao Expressway
G1511 Rizhao–Lankao ExpresswayRizhao Lankao  G1512 Ningbo–Jinhua Expressway
G1512 Ningbo–Jinhua ExpresswayNingbo Jinhua  G1513 Wenzhou–Lishui Expressway
G1513 Wenzhou–Lishui ExpresswayWenzhou Lishui  G1514 Ningde–Shangrao Expressway
G1514 Ningde–Shangrao ExpresswayNingde Shangrao  G25 Changchun–Shenzhen Expressway
G25 Changchun–Shenzhen ExpresswayChangchun Shenzhen 3580  G2511 Xinmin–Lubei Expressway
G2511 Xinmin–Lubei ExpresswayXinmin Lubei, Jarud Banner  G2512 Fuxin–Jinzhou Expressway
G2512 Fuxin–Jinzhou ExpresswayFuxin Jinzhou  G2513 Huai'an–Xuzhou Expressway
G2513 Huai'an–Xuzhou ExpresswayHuai'an Xuzhou  G35 Jinan–Guangzhou Expressway
G35 Jinan–Guangzhou ExpresswayJinan Guangzhou 2110  G45 Daqing–Guangzhou Expressway
G45 Daqing–Guangzhou ExpresswayDaqing Guangzhou 3550  G4511 Longnan–Heyuan Expressway
G4511 Longnan–Heyuan ExpresswayLongnan Heyuan  G55 Erenhot–Guangzhou Expressway
G55 Erenhot–Guangzhou ExpresswayErenhot Guangzhou 2685  G5511 Jining–Arun Expressway
G5511 Jining–Arun ExpresswayJining Arun (Arong) Banner  G5512 Jincheng–Xinxiang Expressway
G5512 Jincheng–Xinxiang ExpresswayJincheng Xinxiang  G5513 Changsha–Zhangjiajie Expressway
G5513 Changsha–Zhangjiajie ExpresswayChangsha Zhangjiajie  G65 Baotou–Maoming Expressway
G65 Baotou–Maoming ExpresswayBaotou Maoming 3130  G75 Lanzhou–Haikou Expressway
G75 Lanzhou–Haikou ExpresswayLanzhou Haikou 2570  G7511 Qinzhou–Dongxing Expressway
G7511 Qinzhou–Dongxing ExpresswayQinzhou Dongxing Connects Vietnamese expressway to Hanoi, Vietnam  G85 Chongqing–Kunming Expressway
G85 Chongqing–Kunming ExpresswayChongqing Kunming 838  G8511 Kunming–Mohan Expressway
G8511 Kunming–Mohan ExpresswayKunming Mohan, Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture Part of the Kunming-Bangkok Expressway via Laos and Thailand to Bangkok East–West Expressways  G10 Suifenhe–Manzhouli Expressway
G10 Suifenhe–Manzhouli ExpresswaySuifenhe Manzhouli 1520 Two terminal are both boundary cities. Connects the expressway in Russia and Mongolia  G1011 Harbin–Tongjiang Expressway
G1011 Harbin–Tongjiang ExpresswayHarbin Tongjiang, Heilongjiang  G12 Huichun–Ulanhot Expressway
G12 Huichun–Ulanhot ExpresswayHuichun Ulanhot 885 Connects the expressways in North Korea  G1211 Jilin–Heihe Expressway
G1211 Jilin–Heihe ExpresswayJilin City Heihe Connects the expressways in Russia  G1212 Shenyang–Jilin Expressway
G1212 Shenyang–Jilin ExpresswayShenyang Jilin City  G16 Dandong–Xilinhot Expressway
G16 Dandong–Xilinhot ExpresswayDandong Xilinhot 960  G18 Rongcheng–Wuhai Expressway
G18 Rongcheng–Wuhai ExpresswayRongcheng, Shandong Wuhai 1820  G1811 Huanghua–Shijiazhuang Expressway
G1811 Huanghua–Shijiazhuang ExpresswayHuanghua, Hebei Shijiazhuang  G20 Qingdao–Yinchuan Expressway
G20 Qingdao–Yinchuan ExpresswayQingdao Yinchuan 1600  G2011 Qingxin Expressway
G2011 Qingxin ExpresswayQingdao Xinhe County, Hebei  G2012 Dingwu Expressway
G2012 Dingwu ExpresswayDingbian Wuwei  G22 Qingdao–Lanzhou Expressway
G22 Qingdao–Lanzhou ExpresswayQingdao Lanzhou 1795  G30 Lianyungang–Khorgas Expressway
G30 Lianyungang–Khorgas ExpresswayLianyungang Khorgas 4280  G3011 Liuyuan–Golmud Expressway
G3011 Liuyuan–Golmud ExpresswayLiuyuan, Guazhou County, Jiuquan Golmud  G3012 Turpan–Hotan Expressway
G3012 Turpan–Hotan ExpresswayTurpan Hotan  G3013 Kashgar–Irkeshtam Expressway
G3013 Kashgar–Irkeshtam ExpresswayKashgar Irkeshtam Connects to Kyrgyzstan  G3014 Kuytun–Aksu Expressway
G3014 Kuytun–Aksu ExpresswayKuytun Aksu  G3015 Kuytun–Tacheng Expressway
G3015 Kuytun–Tacheng ExpresswayKuytun Tacheng Connects Kazakh expressways  G3016 Qingshuihe–Ghulja Expressway
G3016 Qingshuihe–Ghulja ExpresswayQingshuihe Yining  G36 Nanjing–Luoyang Expressway
G36 Nanjing–Luoyang ExpresswayNanjing Luoyang 712  G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway
G40 Shanghai–Xi'an ExpresswayShanghai Xi'an 1490  G4011 Yangzhou–Liyang Expressway
G4011 Yangzhou–Liyang ExpresswayYangzhou Liyang  G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway
G42 Shanghai–Chengdu ExpresswayShanghai Chengdu 1960  G4211 Nanjing–Wuhu Expressway
G4211 Nanjing–Wuhu ExpresswayNanjing Wuhu  G4212 Hefei–Anqing Expressway
G4212 Hefei–Anqing ExpresswayHefei Anqing  G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway
G50 Shanghai–Chongqing ExpresswayShanghai Chongqing 1900  G5011 Wuhu–Hefei Expressway
G5011 Wuhu–Hefei ExpresswayWuhu Hefei  G56 Hangzhou–Ruili Expressway
G56 Hangzhou–Ruili ExpresswayHangzhou Ruili 3405 Connects Burmese expressways  G5611 Dali–Lijiang Expressway
G5611 Dali–Lijiang ExpresswayDali Lijiang  G60 Shanghai–Kunming Expressway
G60 Shanghai–Kunming ExpresswayShanghai Kunming 2370  G70 Fuzhou–Yinchuan Expressway
G70 Fuzhou–Yinchuan ExpresswayFuzhou Yinchuan 2485  G7011 Shiyan–Tianshui Expressway
G7011 Shiyan–Tianshui ExpresswayShiyan Tianshui  G72 Quanzhou–Nanning Expressway
G72 Quanzhou–Nanning ExpresswayQuanzhou Nanning 1635  G7211 Nanning–Youyiguan Expressway
G7211 Nanning–Youyiguan ExpresswayNanning Youyiguan Connects Vietnamese expressways  G76 Xiamen–Chengdu Expressway
G76 Xiamen–Chengdu ExpresswayXiamen Chengdu 2295  G78 Shantou–Kunming Expressway
G78 Shantou–Kunming ExpresswayShantou Kunming 1710  G80 Guangzhou–Kunming Expressway
G80 Guangzhou–Kunming ExpresswayGuangzhou Kunming 1610  G8011 Kaiyuan–Hekou Expressway
G8011 Kaiyuan–Hekou ExpresswayKaiyuan Hekou County, Yunnan Connects Vietnamese expressways Zonal Ring Expressways  G91 Liaozhong Ring Expressway
G91 Liaozhong Ring ExpresswayLiaozhong Liaozhong Interconnects Tieling, Fushun, Benxi, Liaoyang,
Liaozhong, Xinmin, Tieling G92 Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway
G92 Hangzhou Bay Ring ExpresswayShanghai Ningbo Interconnects Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo  G9211 Ningbo–Zhoushan Expressway
G9211 Ningbo–Zhoushan ExpresswayNingbo Zhoushan Interconnects Ningbo and Zhoushan  G93 Chengdu–Chongqing Ring Expressway
G93 Chengdu–Chongqing Ring ExpresswayChengdu Chengdu Interconnects Chengdu, Mianyang, Suining, Chongqing,
Hejiang, Luzhou, Yibin, Leshan, Yaan, and Chengdu G94 Pearl River Delta Ring Expressway
G94 Pearl River Delta Ring ExpresswayHong Kong-Mainland China border Hong Kong-Mainland China border Interconnects Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, Foshan, Huadu, Zengcheng and Dongguan of mainland China,
Hong Kong and
Macao G9411 Dongguan–Foshan Expressway
G9411 Dongguan–Foshan ExpresswayDongguan Foshan Interconnects Dongguan, Humen, Foshan  G98 Hainan Ring Expressway
G98 Hainan Ring ExpresswayHaikou Haikou Interconnects Haikou, Qionghai, Sanya, Dongfang, Haikou  G99 Taiwan Ring Expressway (observed)
G99 Taiwan Ring Expressway (observed)
currently branded:
 TNH 1,
TNH 1,  TPH 1 [Kaohsiung-Fangshan],
TPH 1 [Kaohsiung-Fangshan],
 TPH 9 [Fangshan-Luodong], &
TPH 9 [Fangshan-Luodong], &  TNH 5 (counter clockwise)
TNH 5 (counter clockwise) Taipei Taipei Connects Taipei, Taichung, Kaoshiung, Taitung, Hualien, Taipei together
This is a theoretical expressway listed by the People's Republic of China.
Taiwan Province is currently administered by the Republic of China.
See Political Status of Taiwan. See also Highway System in Taiwan for the
current Republic of China-maintained Taiwan freeway system, which uses a different numbering system.List of expressways in China
Municipalities: All expressways are ordered by direction (starting from the north, in west-to-east direction).
Other Regions: All expressways are ordered alphabetically.Radial Expressways - Beijing
Main article: Expressways of BeijingExisting expressways
- Badaling Expressway (Madian - Kangzhuang)
- Jingda Expressway (Madian - Datong (Shanxi))
- Jingcheng Expressway (Taiyonggong/Wanghe Bridge - Gaoliying)
- Airport Expressway (Sanyuanqiao - Beijing Capital International Airport)
- Jingtong Expressway (Dawangqiao - Balizhuang/Ximazhuang)
- Jingha Expressway (Tongzhou District Beiguan Roundabout - Yanjiao (Hebei))
- Jingshen Expressway (Sifang Bridge - Shenyang (Liaoning)
- Jingjintang Expressway (Fenzhongsi - TEDA (Tianjin)
- (Jinghu Expressway (Beijing - Shanghai)
- Jingkai Expressway (Yuquanying - Yufa)
- Jingshi Expressway (Liuliqiao - Shijiazhuang)
Expressways under construction
- Jingcheng Expressway (Gaoliying - Chengde, under construction as of 2004)
- Airport Expressway (Northern Approach Route and 2nd Expressway, under construction as of 2004)
- Northern Jingjin Expressway (Tongzhou - Tianjin, under construction as of 2004)
Projected expressways
- Litian Expressway
- Jingji Expressway (Jingping Expressway)
- Southern Jingjin Expressway
- Jingbao Expressway
Radial Expressways - Tianjin
Existing expressways
- Jinji Expressway
- Tangjin Expressway
- Jinghu Expressway
- Baojin Expressway
- Jingjintang Expressway
- Jinbin Expressway
Radial Expressways - Shanghai
Main article: Expressways of ShanghaiExisting expressways
- Huhang Expressway (A8) (Xinzhuang Interchange - Hangzhou)
- Huning Expressway (A11) (Zhenbei Road Interchange - Nanjing)
- / Jinghu Expressway (Beijing - Shanghai)
- A9 Expressway (Waihuan Huqingping Interchange - Qingpu - Zhujiajiao)
- A12 Expressway (Wenshui Road - Jiading - Taicang)
- A4 Expressway (Xinzhuang Interchange - Fengxian - Jinshan)
- A5 Expressway
- A30 Expressway (Suburb circular expressway, partly G010 National Highway)
Radial Expressways - Chongqing
Existing expressways
- Changwan Expressway
- Yufu Expressway
- Yuqian Expressway
- Chengyu Expressway
Hebei Province
Main article: Expressways of HebeiExisting expressways
- Baojin Expressway
- Jinghu Expressway
- Jingjintang Expressway
- Jingshen Expressway
- Jingshi Expressway
- Jingzhang Expressway
- Shian Expressway
- Shicang Expressway
- Tangjin Expressway
- Tanggang Expressway
- Xuanda Expressway
Expressways under construction
Projected expressways
- Chengtang Expressway
- Zhangshi Expressway
- Yanhai Expressway
- Qinghong Expressway
Shanxi Province
Liaoning Province
Jilin Province
Heilongjiang Province
Jiangsu Province
- Huning Expressway (Shanghai - Nanjing)
- Yanjiang Expressway (Taicang - Changzhou)
- Ningtong Expressway (Nanjing - Nantong)
- Ningma Expressway (Nanjing - Maanshan)
- Ningjingyan Expressway (Nanjing - Jingjiang - Yancheng)
- Yanlian Expressway (Yancheng - Lianyungang)
Zhejiang Province
- Changtai Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Jiaxing - Shaoxing - Taizhou)
- Changshen Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Hangzhou - Jinhua - Lishui)
- Hangrui Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Hangzhou)
- Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Jiaxing - Hangzhou - Shaoxing - Ningbo)
- Hangzhou Ring Expressway (Hangzhou)
- Hukun Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Jiaxing - Hangzhou)
- Huyu Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Huzhou)
- Jingtai Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Quzhou)
- Ningbo Ring Expressway (Ningbo)
- Shenhai Expressway(Zhejiang section) (Jiaxing - Ningbo - Taizhou - Wenzhou)
- Wenli Expressway (Wenzhou - Lishui)
- Wenzhou Ring Expressway (Wenzhou)
- Yongjin Expressway (Ningbo - Jinhua)
- Yongzhou Expressway (Ningbo - Zhoushan)
Anhui Province
Fujian Province
Shenghai Expressway
Jiangxi Province
- Ganyue Expressway
- Hurui Expressway
- Changjiu Expressway
- Jingfu Expressway
Shandong Province
Henan Province
Hubei Province
Existing Expressways
- Airport Expressway (Jianghan District, Wuhan - Huangpi District, Wuhan)
- G70 Fuyin Expressway (Huangmei County, Huanggang - Yunxi County, Shiyan)
- Hanshi Expressway (Huangpi District, Wuhan - Zhangwan District, Shiyan)
- Xiaoxiang Expressway (Xiaonan District, Xiaogan - Xiangyang District, Xiangfan)
- Huangxiao Expressway (Huangmei County, Huanggang)
- Shiman Expressway (Zhangwan District, Shiyan - Yunxi County, Shiyan)
- Wuhuang Expressway (Hongshan District, Wuhan - Huangshigang District, Huangshi)
- Hanshi Expressway (Huangpi District, Wuhan - Zhangwan District, Shiyan)
- Hancai Expressway (Hanyang District, Wuhan - Caidian District, Wuhan)
- Han'e Expressway (Qingshan District, Wuhan - Hongshan District, Wuhan)
- Hanhong Expressway (Hanyang District, Wuhan - Hannan District, Wuhan)
- Hanhuang Expressway (Jiang'an District, Wuhan - Huangpi District, Wuhan)
- Hanma Expressway (Huangpi District, Wuhan - Hong'an County, Huanggang)
- Hanyi Expressway (Caidian District, Wuhan - Xiling District, Yichang)
- Huanghuang Expressway (Huangshigang District, Huangshi - Huangmei County, Huanggang)
- Jingdong Expressway (Jingzhou District, Jingzhou - Gong'an County, Jingzhou)
- Jingxiang Expressway (Jingzhou District, Jingzhou - Xiangyang District, Xiangfan)
- Jingzhu Expressway (Dawu County, Xiaogan - Chibi City, Xianning)
- Qingzheng Expressway (Hongshan District, Wuhan - Jiangxia District, Wuhan)
- Wuhan Middle Ring Expressway
- Wuhan Outer Ring Expressway (some parts concurrent with G4 Jinggang'ao Expressway, G42 Hurong Expressway, G50 Huyu Expressway, G70 Fuyin Expressway)
Expressways under construction
- G45 Daguang Expressway (Macheng City, Huanggang - Tongshan County, Xianning)
- G42 Hurong Expressway (Yingshan County, Huanggang - Badong County, Enshi)
- Hanying Expressway (Jiang'an District, Wuhan - Yingshan County, Huanggang)
- Suiyue Expressway (Zengdu District, Suizhou - Jianli County, Jingzhou)
Hunan Province
Guangdong Province
- Guangfo Expressway
- Guangshen Expressway
- Guangsan Expressway
- Guangqing Expressway
- Guangzhan Expressway
- Guanghui Expressway
- Guangwu Expressway
- Shenshan Expressway
Hainan Province
- Haiwen expressway
- Hainan Ring Expressway
Sichuan Province
Guizhou Province
- Yusan Expressway
- Sankai Expressway
- Kaima Expressway
- Guixin Expressway
- Qingzhen Expressway
- Zhensheng Expressway
- Chongzun Expressway
- Guizun Expressway
- Guibi Expressway
- Guanxing Expressway
- Liuhuang Expressway
- Yutong Expressway
- Guiyang City Ring Expressway
Yunnan Province
- Kunming-Bangkok Expressway
- Kunshi Expressway
Shaanxi Province
- Xiyu Expressway
- Xihan Expressway
- Hanning Expressway
- Wuzi Expressway
- Zijing Expressway
- Jingwang Expressway
- Shaanxi section of Qinglan Expressway
- Xitong Expressway
- Xibao Expressway
- Xilan Expressway
- Shanmeng Expressway
- Yujing Expressway
- Jingan Expressway
- Huangyan Expressway
- Xihuang Expressway
- Xizha Expressway
- Xilan Expressway
- Yongxian Expressway
- Yongchang Expressway
- Shaanxi section of Dingwu Expressway
- Xi'an City Ring Expressway
- Shaanxi section of Shitian Expressway
- Xi'an Airport Expressway
- Tongfeng Expressway
Gansu Province
- Liubai Expressway
- Bailan Expressway
- Lanhai Expressway
- Gansu section of Jingxin Expressway
- Tianding Expressway
- Dinglan Expressway
- Liuzhong Expressway
- Yinzhong Expressway
- Shuxu Expressway
- Xugu Expressway
- Guyong Expressway
- Yongshan Expressway
- Shanlin Expressway
- Linqing Expressway
- Qingjia Expressway
- Jia'an Expressway
- Gansu section of Fuyin Expressway
- Lanlin Expressway
- Gansu section of Dingwu Expressway
- Gansu section of Liuge Expressway
- Gansu section of Shitian Expressway
- Yinzhong Expressway
Qinghai Province
- Maping Expressway
- Pingxi Expressway
- Xihuang Expressway
- Qinghai section of Liuge Expressway
- Xita Expressway
- Ningda Expressway
- Ping'a Expressway
Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
- Jilao Expressway
- Huji Expressway
- Hubao Expressway
- Baoli Expressway
- Liwu Expressway
- Inner Mongolia section of Jingxin Expressway
- Inner Mongolia section of Suiman Expressway
- Inner Mongolia section of Hunwu Expressway
- Chida Expressway
- G109 Highway
- Chitong Expressway
- Baijifeng Expressway
- Baodong Expressway
- Dongsu Expressway
- Tonglu Northwest Ring
- Inner Mongolia section of Ji'a Expressway
- Hohhot City Ring Expressway
- Huzhun Expressway
Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
- Guiliu Expressway
- Liunan Expressway
- Nanwu Expressway
- Nanbai Expressway
- Nanyou Expressway
Tibet Autonomous Region
- Tibet section of Jingzang Expressway
Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region
- Yinchuan City Ring Expressway
- Ningxia section of Jingzang Expressway
- Ningxia section of Qingyin Expressway
- Ningxia section of Qinglan Expressway
- Ningxia section of Fuyin Expressway
- Ningxia section of Dingwu Expressway
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region
- Xinjiang section of Jingxin Expressway
- Tuwu Expressway
- Wuda Expressway
- Wukui Expressway
- Kuisai Expressway
- Saihuo Expressway
- Tuhe Expressway
- Heku Expressway
- Xinjiang section of Tuhe Expressway
- Xinjiang section of Kuia Expressway
- Xinjiang section of Kuita Expressway
- Xinjiang section of Qingyi Expressway
- Wuda Expressway
- Ürümqi/Wulumuqi Airport Expressway
See also
- China National Highways
- Transport in China
- Highway System in Taiwan
References
- ^ "China’s Highway Network Expands to 74,000 Kilometers". ChinaAutoWeb.com. http://chinaautoweb.com/2010/12/chinas-highway-network-expands-74000-kilometers/.
- ^ http://www.transdata.com.cn/info/infocontent.aspx?infoid=25620
- ^ China Expressway System to Exceed US Interstates, newgeography.com, Feb 10, 2011
- ^ a b National highway target set for year
- ^ http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/statisticaldata/yearlydata
- ^ Wang, Chongxu; Yuancheng Peng, Yinbo Liu (January 2009). "Crossing the Limits". Civil Engineering (Reston, Virginia: American Society of Civil Engineers) 79 (1): 64–69, 79–80. ISSN 0885-7024. http://pubs.asce.org/magazines/CEMag/2009/Issue_01-09/.
- ^ "365条ETC车道开通,基本实现全市收费站点全覆盖". 北京快通高速路电子收费系统有限公司. 2010-04-29. http://www.bjetc.cn/ETC_ASPX/N_XinWen_ZW.aspx?ID=117. Retrieved 2010-08-03.
- ^ "北京八达岭高速"速通卡"将停止使用". 京华时报. 2008-01-03. http://news.sohu.com/20080103/n254426805.shtml. Retrieved 2010-08-03.
External links
Expressways of the National Trunk Highway System of China Radial Expressways - Beijing
Primary G1 • G2 • G3 • G4 • G5 • G6 • G7Branch North-South ExpresswaysPrimary G11 • G15 • G25 • G35 • G45 • G55 • G65 • G75 • G85Branch Auxiliary East-West ExpresswaysPrimary G10 • G12 • G16 • G18 • G20 • G22 • G30 • G36 • G40 • G42 • G50 • G56 • G60 • G70 • G72 • G76 • G78 • G80Auxiliary Regional Ring ExpresswaysPrimary G91 • G92 • G93 • G94 • G98 • G99 (observed)Auxiliary City Ring ExpresswaysRing Categories:- Expressways in China
- Roads in the People's Republic of China
- Limited-access roads by country
- Full access controlled highways by country
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
China Southern Airlines — 中国南方航空公司 Zhōngguó Nánfāng Hángkōng Gōngsī IATA CZ ICAO CSN Callsign … Wikipedia
China Eastern Airlines — 中国东方航空公司 Zhōngguó Dōngfāng Hángkōng Gōngsī IATA MU ICAO CES Callsign … Wikipedia
China Cargo Airlines — 中国货运航空 IATA CK ICAO CKK Callsign CARGO KING … Wikipedia
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation — Type State owned Founded 1999 Headquarters Beijing, China The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (中國航天科技集團公司)(CASC) is the main c … Wikipedia
China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation — 中国船舶重工集团公司 Type State owned enterprise Industry Shipbuilding Founded 1999 Headquarters … Wikipedia
China Northern Airlines — 中國北方航空 Zhōngguó Běifāng Hángkōng IATA CJ ICAO CBF Callsign China Northern Fou … Wikipedia
China Postal Airlines — 中国货运邮政航空公司 IATA 8Y ICAO CYZ Callsign CHINA POST … Wikipedia
China General Aviation — (Corporation CGAC) was an airline based in the People s Republic of China. It was based in Nanjing and operated a fleet of 12 Yakovlev Yak 42D and later a few Boeing 737 300 aircraft. It was acquired by China Eastern Airlines in 1997.[citation… … Wikipedia
China Xinhua Airlines — 中国新华航空 IATA XW ICAO CXH Callsign XINHUA Founded 1992 Fleet size 16 Destinations … Wikipedia
China Northwest Airlines — 中国西北航空公司 IATA WH ICAO CNW Callsign CHINA NORTHWEST Founded … Wikipedia