- Chengde
-
Chéngdé
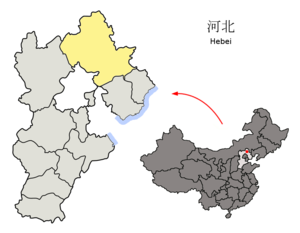
承德— Prefecture-level city — 承德市 Location of Chengde in Hebei Province, and location of Hebei Province within the People's Republic of China Location of Chengde in Hebei Province, and location of Hebei Province within the People's Republic of China Coordinates: 40°58′N 117°56′E / 40.967°N 117.933°ECoordinates: 40°58′N 117°56′E / 40.967°N 117.933°E Country China Province Hebei Area – Prefecture-level city 39,519 km2 (15,258.4 sq mi) – Urban 709 km2 (273.7 sq mi) Population (2004) – Prefecture-level city 3,610,000 – Density 91/km2 (235.7/sq mi) – Urban 457,300 – Urban density 645/km2 (1,670.5/sq mi) License Plate Prefix 冀H GDP (2004) CNY 30 billion Website http://www.chengde.gov.cn City tree
Pagoda TreeCity flower
Rugosa RoseChengde (Chinese: 承德; pinyin: Chéngdé), previously known as Jehol or Re He (Chinese: 热河; pinyin: Rèhé), is a prefecture-level city in Hebei province, People's Republic of China, situated northeast of Beijing. It is best known as the site of the Mountain Resort, a vast imperial garden and palace formerly used by the Qing emperors as summer residence.[1] The urban center had a population of approximately 450,000 as of 2009.
Contents
History
In 1703, Chengde was chosen by the Kangxi Emperor as the location for his summer residence. Constructed throughout the eighteenth century, the Mountain Resort (避暑山庄; literally "avoiding the heat mountain villa") was used by both the Yongzheng and Qianlong emperors. The site is currently an UNESCO World Heritage Site. Since the seat of government followed the emperor, Chengde was a political center of the Chinese empire during these times.
The city of Jehol reached its height under the Qianlong Emperor 1735-1796 (died 1799). The great monastery temple of the Potala, loosely based on the Potala in Lhasa, was completed after just four years of work in 1771. It was heavily decorated with gold and the emperor worshipped in the Golden Pavilion. In the temple itself was a bronze-gilt statue of Tsongkhapa, the Reformer of the Gelugpa sect.
Under the Republic of China, Chengde was the capital of Rehe province. From 1933 to 1945 the city was under Japanese control as a part of the Manchurian puppet state known as Manchukuo. After World War II the Kuomintang regained jurisdiction. In 1948, the People's Liberation Army took control of Chengde. It would remain a part of Rehe until 1955, when the province was abolished, and the city was incorporated into Hebei.
The city is home to large populations of ethnic minorities, Mongol and Manchu in particular. The name for Chengde in Manchu is Erdemu be aliha fu.
Administrative divisions
Chengde comprises:
Map 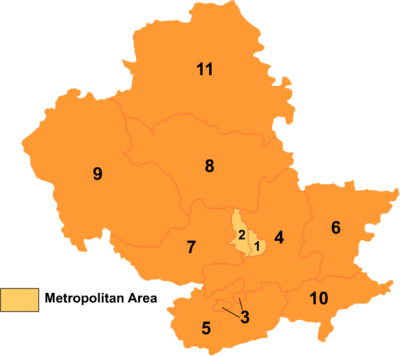
# Name Hanzi Hanyu Pinyin Population (2004 est.) Area (km²) Density (/km²) 1 Shuangqiao District 双桥区 Shuāngqiáo Qū 290,000 311 932 2 Shuangluan District 双滦区 Shuāngluán Qū 100,000 250 400 3 Yingshouyingzi Mining District 鹰手营子矿区 Yīngshǒuyíngzi
Kuàngqū70,000 148 473 4 Chengde County 承德县 Chéngdé Xiàn 470,000 3,990 118 5 Xinglong County 兴隆县 Xīnglóng Xiàn 320,000 3,116 103 6 Pingquan County 平泉县 Píngquán Xiàn 470,000 3,297 143 7 Luanping County 滦平县 Luánpíng Xiàn 320,000 3,195 100 8 Longhua County 隆化县 Lónghuà Xiàn 420,000 5,474 77 9 Fengning Manchu
Autonomous County丰宁满族
自治县Fēngníng Mǎnzú
Zìzhìxiàn380,000 8,747 43 10 Kuancheng Manchu
Autonomous County宽城满族
自治县Kuānchéng Mǎnzú
Zìzhìxiàn230,000 1,933 119 11 Weichang Manchu and
Mongol Autonomous County围场满族
蒙古族自治县Wéichǎng Mǎnzú
Měnggǔzú Zìzhìxiàn520,000 9,058 57 Geography
Chengde Climate chart (explanation) J F M A M J J A S O N D 2.5−2−143.62−118.310−41919550251187291614530201182918482411211747.57−52.50−12Average max. and min. temperatures in °C Precipitation totals in mm Source: CMA [2] Imperial conversion J F M A M J J A S O N D 0.12860.136130.349260.766411.977523.484625.786674.784641.976520.863390.345240.13111Average max. and min. temperatures in °F Precipitation totals in inches Chengde is located in the northeastern portion of Hebei province, with latitude 40°12′-42°37′ North, and longitude 115°54′-119°15′ East. It borders Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Beijing, and Tianjin. Neighbouring prefecture-level provincial cities are Qinhuangdao and Tangshan on the Bohai Gulf, and land-locked Zhangjiakou. Due to its Liaoning border, it is often considered a part of both Northern and Northeastern China. From north to south the prefecture stretches 269 kilometres (167 mi), and from west to east 280 kilometres (174 mi), for a total area of 39,702.4 square kilometres (15,329.2 sq mi), thus occupying 21.2% of the total provincial area. It is by area the largest prefecture in the province, though as most of its terrain is mountainous, its population density is low.
Climate
Chengde has a four-season, monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen Dwa), with widely varying conditions through the prefecture due to its size: winters are moderately long, cold and windy, but dry, and summers are hot and humid. Near the city, however, temperatures are much cooler than they are in Beijing, due to the high altitude of at least 1000 metres: Monthly means range from −9.1 °C (15.6 °F) in January to 24.5 °C (76.1 °F) in July. Spring warming is rapid, but dust storms can blow in from the Mongolian steppe; autumn cooling is similarly quick. Precipitation averages at 512 millimetres (20.2 in) for the year, with more than two-thirds of it falling during the three summer months.
Climate data for Chengde (1971−2000) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) −2.2
(28.0)2.2
(36.0)9.6
(49.3)19.0
(66.2)25.2
(77.4)29.1
(84.4)30.1
(86.2)28.7
(83.7)24.2
(75.6)17.3
(63.1)7.2
(45.0)−0.3
(31.5)15.8 Average low °C (°F) −14.4
(6.1)−10.6
(12.9)−3.6
(25.5)4.9
(40.8)11.3
(52.3)16.4
(61.5)19.5
(67.1)17.8
(64.0)11.2
(52.2)3.8
(38.8)−4.6
(23.7)−11.8
(10.8)3.3 Precipitation mm (inches) 2.5
(0.098)3.6
(0.142)8.3
(0.327)18.9
(0.744)49.5
(1.949)86.8
(3.417)144.7
(5.697)118.2
(4.654)48.2
(1.898)21.3
(0.839)7.5
(0.295)2.5
(0.098)512.0
(20.157)% humidity 51 46 44 39 46 58 71 74 67 58 56 54 55.3 Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) 1.6 2.1 3.7 4.5 7.8 11.1 14.2 12.6 7.7 5.0 2.5 1.4 74.2 Sunshine hours 195.6 202.3 240.6 258.7 276.4 262.0 229.1 234.0 240.2 236.2 193.5 177.2 2,745.8 Source: China Meteorological Administration [2] Economy
With road and railroad links to Beijing, Chengde has developed into a distribution hub, and its economy is growing rapidly. The newly-built Jingcheng Expressway connects Chengde directly to central Beijing, and more freeways are planned for the city.
Sights
The project of building Chengde Mountain Resort started in 1703 and finished in 1790. The whole mountain resort covers an area 5,640,000 square meters. It is the largest royal garden in China. The wall of the mountain resort is over 10,000 meters in length. In summers, emperors of Qing Dynasty came to the mountain resort to relax themselves and escape from the high temperature in Beijing.
The whole Resort can be divided into three areas which are lakes area, plains area and hills area. The lakes area, which includes 8 lakes, covers an area of 496,000 square meters. The plains area covers an area of 607,000 square meters. The emperors held horse races and hunted in the area. The largest area of the three is the hills area. It covers an area of 4,435,000 square meters. Hundreds of palaces and temples were built on the hills in this area.
The elaborate Mountain Resort features large parks with lakes, pagodas, and palaces ringed by a wall. Outside the wall are the Eight Outer Temples (外八庙), built in varying architectural styles drawn from throughout China. One of the best-known of these is the Putuo Zongcheng Temple, built to resemble the Potala Palace in Lhasa, Tibet. The resort and outlying temples were made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The nearby Puning Temple, built in 1755, houses the world's tallest wooden statue of the Bodhisattva Avalokiteśvara.
Chengde's older name of Rehe (or Jehol) came from the name for the local river (热河; Pinyin: Rèhé) which translates as "hot river." The river was so named because it did not freeze in the winter. Most sections of the river are currently dry because of a new damming project.
Another popular attraction of the Chengde area is Sledgehammer Peak (磬锤峰), a large rock formation in the shape of an inverted sledgehammer. A variety of other mountains, valleys, and grasslands lie within the borders of the city.
Gallery
-
Downtown Chengde, seen from the Mountain Resort.
-
Saihanba National Park, in northern Chengde, near the border with Inner Mongolia.
Sister cities
Chengde has city partnerships with the following cities:
 Santo André, Brazil
Santo André, Brazil Takasaki, Japan
Takasaki, Japan Dakota County, Minnesota, USA
Dakota County, Minnesota, USA
References
Footnotes
- ^ Hedin (1933), pp. 1, 14.
- ^ a b "中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年)". China Meteorological Administration. http://cdc.cma.gov.cn/shuju/search1.jsp?dsid=SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MMON_19712000_CES&tpcat=SURF&type=table&pageid=3. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
Sources
- Hedin, Sven (1933). Jehol: City of Emperors. Reprint (2000): Pilgrim's Book House, Varanasi. ISBN 81-7769-009-4.
External links
Hebei topics General Geography Cities • North China Plain • Taihang Mountains • Yan Mountains • Shanhai Pass • Bohai Sea • Hai River watershed • Luan He watershed • Baiyangdian LakeEducation Culture Visitor attractions Beidaihe beach resort • Chengde Mountain Resort • Eastern Qing Tombs • Western Qing Tombs • Anji BridgeHebei Province county-level divisions Shijiazhuang: Chang'an District • Qiaodong District • Qiaoxi District • Xinhua District • Yuhua District • Jingxing Mining District • Luquan City • Xinji City • Gaocheng City • Jinzhou City • Xinle City • Shenze County • Wuji County • Zhao County • Lingshou County • Gaoyi County • Yuanshi County • Zanhuang County • Pingshan County • Jingxing County • Luancheng County • Zhengding County • Xingtang County
Tangshan: Lubei District • Lunan District • Guye District • Kaiping District • Fengrun District • Fengnan District • Zunhua City • Qian'an City • Luan County • Luannan County • Laoting County • Qianxi County • Yutian County • Tanghai County
Qinhuangdao: Haigang District • Shanhaiguan District • Beidaihe District • Changli County • Funing County • Lulong County • Qinglong Autonomous County
Handan: Congtai District • Hanshan District • Fuxing District • Fengfeng Mining District • Wu'an City • Handan County • Linzhang County • Cheng'an County • Daming County • She County • Ci County • Feixiang County • Yongnian County • Qiu County • Jize County • Guangping County • Guantao County • Wei County • Quzhou County
Xingtai: Qiaodong District • Qiaoxi District • Nangong City • Shahe City • Xingtai County • Lincheng County • Neiqiu County • Baixiang County • Longyao County • Ren County • Nanhe County • Ningjin County • Julu County • Xinhe County • Guangzong County • Pingxiang County • Wei County • Qinghe County • Linxi County
Baoding: Xinshi District • Beishi District • Nanshi District • Dingzhou City • Zhuozhou City • Anguo City • Gaobeidian City • Mancheng County • Qingyuan County • Yi County • Xushui County • Laiyuan County • Dingxing County • Shunping County • Tang County • Wangdu County • Laishui County • Gaoyang County • Anxin County • Xiong County • Rongcheng County • Quyang County • Fuping County • Boye County • Li County
Zhangjiakou: Qiaoxi District • Qiaodong District • Xuanhua District • Xiahuayuan District • Zhangbei County • Kangbao County • Xuanhua County • Shangyi County • Guyuan County • Yu County • Yangyuan County • Huai'an County • Wanquan County • Huailai County • Zhuolu County • Chicheng County • Chongli County
Chengde: Shuangqiao District • Shuangluan District • Yingshouyingzi Mining District • Chengde County • Xinglong County • Pingquan County • Luanping County • Longhua County • Fengning Autonomous County • Kuancheng Autonomous County • Weichang Autonomous County
Cangzhou: Yunhe District • Xinhua District • Botou City • Renqiu City • Huanghua City • Hejian City • Cang County • Qing County • Dongguang County • Haixing County • Yanshan County • Suning County • Nanpi County • Wuqiao County • Xian County • Mengcun Autonomous County
Langfang: Anci District • Guangyang District • Bazhou City • Sanhe City • Gu'an County • Yongqing County • Xianghe County • Dacheng County • Wen'an County • Dachang Autonomous County
Hengshui: Taocheng District • Jizhou City • Shenzhou City • Zaoqiang County • Wuyi County • Wuqiang County • Raoyang County • Anping County • Gucheng County • Jing County • Fucheng CountyCategories:- Cities in Hebei
- Prefecture-level divisions of Hebei
- Chengde
- Populated places established in the 18th century
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.