- Zhangjiakou
-
"Kalgan" redirects here. For other uses, see Kalgan (disambiguation).
Zhangjiakou
张家口— Prefecture-level city — 张家口市 General view of Zhangjiakou Location in Hebei and the PRC Coordinates: 40°46′N 114°53′E / 40.767°N 114.883°ECoordinates: 40°46′N 114°53′E / 40.767°N 114.883°E Country People's Republic of China Province Hebei Government – Mayor Wang Xiaodong (王晓东) – Party Secretary Xu Ning (许宁) Area – Prefecture-level city 36,829 km2 (14,219.8 sq mi) – Urban 254 km2 (98.1 sq mi) Elevation 716 m (2,349 ft) Population (2010 census) – Prefecture-level city 4,345,491 – Density 118/km2 (305.6/sq mi) – Urban 473,193 – Urban density 1,863/km2 (4,825.1/sq mi) Time zone China Standard (UTC+9) License Plate Prefix 冀G Website http://www.zjk.gov.cn/ Zhangjiakou, also known also by several other names, is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Hebei province of North China, adjacent to Beijing to the southeast. Its administrative area has a population of 4.35 million, and covers 36,947 square kilometres (14,265 sq mi). The urban area of Zhangjiakou is divided into Qiaoxi and Qiaodong Districts which have 473,193 inhabitants in 2010, but the prefecture-level city is much larger, spanning around 36,800 square kilometres (14,200 sq mi).
Contents
Names
Zhangjiakou is written 张家口 in simplified Chinese and 張家口 in traditional Chinese. It is Zhāngjiākǒu in pinyin and the name means "Zhang family gate." Older names for the town in Chinese include Zhāngyuán (張垣), used in the Republican era, and Zhāngjiābǎo (張家堡).
Zhangjiakou was historically known to the Europeans as Kalgan until the mid 20th century. This name derives from the Mongolian name of the city,
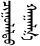 , "Chuulalt haalga" or shorter,
, "Chuulalt haalga" or shorter, 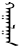 , "haalga" which means "gate" (in the Great Wall). In Manchu, the city is known as
, "haalga" which means "gate" (in the Great Wall). In Manchu, the city is known as 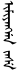 (Imiyangga jase).
(Imiyangga jase).Because of its strategic position above and northwest of Beijing, Zhangjiakou has been nicknamed "Beijing's Northern Door".
History
The water-scarce city was historically the chief northern gate in the Great Wall to China for Europeans travelling along the Tea Road (such as Ivan Petlin (1619)[1] or Nicolae Milescu).
In August 1211, there raised the Badger's Mount Campaign, Genghis Khan 90,000 strong force destroyed the 450,000 strong Jin Dynasty army.
In the 19th century, the town was the seat of a very extensive transit trade. In early autumn long lines of camels would come in from all quarters for the conveyance of the tea chests from Zhangjiakou, the Kalgan, to Kyakhta; and each caravan usually made three journeys in the winter. Some Russian merchants had permanent residences and warehouses just outside the gate.
In October 1909, Kalgan was connected by railway with Peking. The 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica noted that, in Kalgan, "the ordinary houses have an unusual appearance, from the fact that they are mostly roofed with earth and become covered with green-sward" and that "on the way to Peking the road passes over a beautiful bridge of seven arches, ornamented with marble figures of animals".
In 1937 the Japanese occupied the region and made Kalgan the capital of the autonomous Cha-nan (South Chahar) Province. The Federated Mengjiang Commission was set up to supervise the economic affairs, banking, communications, and industry of Japanese-occupied Inner Mongolia (Mengjiang).
In the early 1960s at the height of Sino-Soviet tensions, Zhangjiakou was considered one of the most important cities in China for military strategy reasons. Zhangjiakou was aptly nicknamed, "Beijing's Northern Door", because whoever controlled Zhangjiakou was in a good position to either attack (in the case of the Soviets) or defend (in the case of the Chinese) Beijing.
Economy
The vicinity of Zhangjiakou is rich in coal and iron ore, making it an ideal location for developing iron and steel industry. Apart from metallurgy, the city is home to one of China's most important grape wine industries, with the Great Wall Wine Company being located in Shacheng (沙城镇), Huailai County. [1]
Transportation
- The city lies in the northwestern corner of the province and is linked from Datong in Shanxi by the Xuanda Expressway and from Beijing by means of the Jingzhang Expressway.
- Zhangjiakou is further linked by a freeway to Inner Mongolia which opened on September 7, 2005.
- China National Highway 207
- A heavy-haul railway is under construction, to transport coal from Zhangjiakou to Tangshan. Construction is expected to finish in 2015; the railway is planned to carry 200 million tons of coal per year.[2] Another heavy-haul railway, Junggar-Zhangjiakou, is expected to connect to it.[3]
Military
Zhangjiakou is headquarters of the 65th Group Army of the People's Liberation Army, one of the three group armies that comprise the Beijing Military Region responsible for defending China's capital.
Education
Zhangjiakou is home to Hebei North University. The university has been improving its international network and many foreign students are now studying there.
Geography and climate
Zhangjiakou is located in the northwest part of Hebei province, and is defined by mostly rough terrain created by the Yin Mountains, with elevations increasing from southeast to northwest. The east of the prefecture marks the Yan Mountains The bordering prefectures in the province are Chengde to the northeast and Baoding to the south. It also borders Shanxi to the west and southwest and Inner Mongolia to the northwest. The prefecture's latitude ranges from 39° 30' to 42° 10' N, or 289.2 kilometres (179.7 mi), while its longitude spans 113° 50' to 116° 30' E, or 216.2 kilometres (134.3 mi).
Zhangjiakou City is divided into three topographical regions: plateau, mountains, and basin. The former has elevations generally above 1,400 metres (4,600 ft), and consists of all of Guyuan and Kangbao Counties as well as part of Shangyi and Zhangbei Counties. This area is part of the southern end of the Inner Mongolia Plateau (内蒙古高原) and accounts for one-third of the prefecture's area.[4] The basin area has elevations of 500 to 1,000 metres (1,600 to 3,300 ft) and supports a few rivers.
Zhangjiakou has a monsoon-influenced, continental semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk), with long, cold, dry, and windy winters due to the Siberian anticyclone, and hot, humid summers driven by the East Asian monsoon; in between spring and autumn are dry and brief. Conditions are much cooler than in Beijing due in part to the elevation. Winters last from mid-November to late March and at their height in January, temperatures typically remain below freezing all day. In summer, temperatures often reach or surpass 30 °C (86 °F).
Climate data for Zhangjiakou (1971−2000) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) −2.2
(28.0)1.5
(34.7)8.4
(47.1)17.9
(64.2)24.8
(76.6)28.5
(83.3)29.4
(84.9)27.7
(81.9)23.2
(73.8)16.3
(61.3)6.6
(43.9)−0.4
(31.3)15.1 Average low °C (°F) −12.9
(8.8)−10
(14)−3.6
(25.5)4.6
(40.3)11.2
(52.2)16.0
(60.8)18.7
(65.7)17.2
(63.0)11.2
(52.2)4.3
(39.7)−4
(24.8)−10.5
(13.1)3.5 Precipitation mm (inches) 2.0
(0.079)4.1
(0.161)9.1
(0.358)14.0
(0.551)33.1
(1.303)60.6
(2.386)109.9
(4.327)100.5
(3.957)45.0
(1.772)16.9
(0.665)6.3
(0.248)2.1
(0.083)403.6
(15.89)Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) 1.7 2.5 4.6 4.8 7.6 10.2 13.4 12.8 9.1 4.3 2.6 1.7 75.3 Source: Weather China Administrative divisions
Map 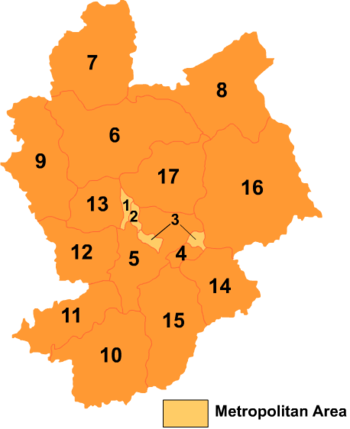
# Name Hanzi Hanyu Pinyin Population (2004 est.) Area (km²) Density (/km²) County-level divisions 1 Qiaoxi District 桥西区 Qiáoxī Qū 230,000 141 1,631 2 Qiaodong District 桥东区 Qiáodōng Qū 260,000 113 2,301 3 Xuanhua District 宣化区 Xuānhuà Qū 290,000 276 1,051 4 Xiahuayuan District 下花园区 Xiàhuāyuán Qū 70,000 315 222 5 Xuanhua County 宣化县 Xuānhuà Xiàn 300,000 2,095 143 6 Zhangbei County 张北县 Zhāngběi Xiàn 370,000 4,232 87 7 Kangbao County 康保县 Kāngbǎo Xiàn 280,000 3,365 83 8 Guyuan County 沽源县 Gūyuán Xiàn 230,000 3,601 64 9 Shangyi County 尚义县 Shàngyì Xiàn 190,000 2,621 72 10 Yu County 蔚县 Yù Xiàn 460,000 3,216 143 11 Yangyuan County 阳原县 Yángyuán Xiàn 280,000 1,834 153 12 Huai'an County 怀安县 Huái'ān Xiàn 250,000 1,706 147 13 Wanquan County 万全县 Wànquán Xiàn 220,000 1,158 190 14 Huailai County 怀来县 Huáilái Xiàn 340,000 1,793 190 15 Zhuolu County 涿鹿县 Zhuōlù Xiàn 330,000 2,799 118 16 Chicheng County 赤城县 Chìchéng Xiàn 280,000 5,238 53 17 Chongli County 崇礼县 Chónglǐ Xiàn 120,000 2,326 52 Zhangjiakou in fiction
- In the novel The Legend of the Condor Heroes, the two main characters, Guo Jing and Huang Rong first met in this city.
- Zhangjiakou was the setting for Zhang Yimou's film Not One Less (1999).
Notes
- ^ "A Relation of two Russe Cossacks travailes, out of Siberia to Catay, and other Countries adjoyning thereunto. Also a Copie of the last Patent from the Muscovite. A Copie of a Letter written to the Emperour from his Governours out of Siberia". Published as Chapter XI in: Samuel Purchas, Haklutyus Posthumus (or, Purchas His Pilgrimes), vol. XIV, p. 280. 1625. Full Text on archive.org. The city name reported by Petlin appears in Purchas' English translation as "Shirokalga".
- ^ "Railway Gazette: News in Brief". http://www.railwaygazette.com/nc/news/single-view/view/news-in-brief-47.html. Retrieved 2011-01-02.
- ^ "COALWorld". http://www.coalworld.net/indexnews/info.jsp?id=65780. Retrieved 2011-01-02.
- ^ 地理环境. Accessed 2011-05-20
See also
External links
Hebei topics General Geography Cities • North China Plain • Taihang Mountains • Yan Mountains • Shanhai Pass • Bohai Sea • Hai River watershed • Luan He watershed • Baiyangdian LakeEducation Culture Visitor attractions Beidaihe beach resort • Chengde Mountain Resort • Eastern Qing Tombs • Western Qing Tombs • Anji BridgeHebei Province county-level divisions Shijiazhuang: Chang'an District • Qiaodong District • Qiaoxi District • Xinhua District • Yuhua District • Jingxing Mining District • Luquan City • Xinji City • Gaocheng City • Jinzhou City • Xinle City • Shenze County • Wuji County • Zhao County • Lingshou County • Gaoyi County • Yuanshi County • Zanhuang County • Pingshan County • Jingxing County • Luancheng County • Zhengding County • Xingtang County
Tangshan: Lubei District • Lunan District • Guye District • Kaiping District • Fengrun District • Fengnan District • Zunhua City • Qian'an City • Luan County • Luannan County • Laoting County • Qianxi County • Yutian County • Tanghai County
Qinhuangdao: Haigang District • Shanhaiguan District • Beidaihe District • Changli County • Funing County • Lulong County • Qinglong Autonomous County
Handan: Congtai District • Hanshan District • Fuxing District • Fengfeng Mining District • Wu'an City • Handan County • Linzhang County • Cheng'an County • Daming County • She County • Ci County • Feixiang County • Yongnian County • Qiu County • Jize County • Guangping County • Guantao County • Wei County • Quzhou County
Xingtai: Qiaodong District • Qiaoxi District • Nangong City • Shahe City • Xingtai County • Lincheng County • Neiqiu County • Baixiang County • Longyao County • Ren County • Nanhe County • Ningjin County • Julu County • Xinhe County • Guangzong County • Pingxiang County • Wei County • Qinghe County • Linxi County
Baoding: Xinshi District • Beishi District • Nanshi District • Dingzhou City • Zhuozhou City • Anguo City • Gaobeidian City • Mancheng County • Qingyuan County • Yi County • Xushui County • Laiyuan County • Dingxing County • Shunping County • Tang County • Wangdu County • Laishui County • Gaoyang County • Anxin County • Xiong County • Rongcheng County • Quyang County • Fuping County • Boye County • Li County
Zhangjiakou: Qiaoxi District • Qiaodong District • Xuanhua District • Xiahuayuan District • Zhangbei County • Kangbao County • Xuanhua County • Shangyi County • Guyuan County • Yu County • Yangyuan County • Huai'an County • Wanquan County • Huailai County • Zhuolu County • Chicheng County • Chongli County
Chengde: Shuangqiao District • Shuangluan District • Yingshouyingzi Mining District • Chengde County • Xinglong County • Pingquan County • Luanping County • Longhua County • Fengning Autonomous County • Kuancheng Autonomous County • Weichang Autonomous County
Cangzhou: Yunhe District • Xinhua District • Botou City • Renqiu City • Huanghua City • Hejian City • Cang County • Qing County • Dongguang County • Haixing County • Yanshan County • Suning County • Nanpi County • Wuqiao County • Xian County • Mengcun Autonomous County
Langfang: Anci District • Guangyang District • Bazhou City • Sanhe City • Gu'an County • Yongqing County • Xianghe County • Dacheng County • Wen'an County • Dachang Autonomous County
Hengshui: Taocheng District • Jizhou City • Shenzhou City • Zaoqiang County • Wuyi County • Wuqiang County • Raoyang County • Anping County • Gucheng County • Jing County • Fucheng CountyCategories:- Cities in Hebei
- Prefecture-level divisions of Hebei
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.