- Jiangmen
-
Jiangmen
江门— Prefecture-level city — City of Jiangmen · 江门市 Outside of Jiangmen's Old Book Store Location in Guangdong Location in China Coordinates: 22°34′N 113°4′E / 22.567°N 113.067°ECoordinates: 22°34′N 113°4′E / 22.567°N 113.067°E Country  China
ChinaProvince Guangdong City Seat Pengjiang District Area – Total 9,443 km2 (3,646 sq mi) Population (2010) – Total 4,448,871 – Density 471.1/km2 (1,220.2/sq mi) Time zone China Standard Time (UTC+8) Postal code 529000 Area code(s) 750 License plate prefixes 粤J Website http://www.jiangmen.gov.cn/ (Chinese) Jiangmen (simplified Chinese: 江门; traditional Chinese: 江門; Mandarin Pinyin: Jiāngmén; Jyutping: Gong1 Mun4), is a prefecture-level city in Guangdong province in southern China with a population of about 4.48 million in 2010. The 3 urban districts are now part of Guangzhou - Shenzhen built up area.
Contents
Names
Jiangmen has various historical romanisations including Kong-Moon, Kongmoon, Kongmun[1] or Kiangmoon. The area is alternately referred to as Sze Yup or Ng Yup. The name Jiangmen is often the butt of jokes because its Cantonese pronunciation is identical to the scientific word for anus (肛門).[2] As a result there has been some proposals to change the name of the city, for example a 2009 proposal to change it to "Qiaodu" ("City of Overseas Chinese").[3]
History
The port of Jiangmen, was forced to open to western trade in 1902. One legacy of this period is an historic waterfront district lined with buildings in the treaty port style. The city has an ongoing renewal project which has restored many of these buildings.
Jiangmen was proclaimed a city in 1951, and later became the administrative capital of the prefecture for the Wu Yi region which includes Taishan, Kaiping, Xinhui, Enping and Heshan.
Geography
The city is located on the lower reaches of the Xijiang or West River, in the west of the Pearl River Delta in the middle of southern Guangdong Province. It faces the South China Sea in the south and is 100 km away from Guangzhou and Zhuhai by highway. Jiangmen city has an area of 9,260 km², about one quarter the size of the Pearl River Delta.
The climate is subtropical with monsoon influences. The annual average temperature is 21.8°C.
Economy
Jiangmen was selected by the Chinese state as a pilot city for a nationwide information programme. It was also chosen by the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC) as a trial city for the Regional Integration for Sustainable Economics (RISE) project. According to the "Report on Investment Environment in China 2003" by the World Bank, Jiangmen ranked the fourth after Shanghai, Hangzhou and Dalian of 23 cities under evaluation in China. Among various indicators, Jiangmen excelled in infrastructure, labour redundancy, proportion of joint ventures in all firms, informal payments to government, taxation, productivity and the investment rate.
The economic development strategies within Jiangmen focus on the three urban districts, and the south, middle and north lines. It is planned to develop four main economic areas: the central urban district of the city, the Yinzhou Lake (銀州湖) economic area, and two economic areas along the various transport axes.
Manufacturing industries
Similar to other cities in the western Pearl River Delta, the manufacturing sector plays a significant role in Jiangmen's economy. The chief industries include manufacturing of motorcycles, household appliances, electronics, paper, food processing, synthetic fibers and garments, as well as textiles and stainless steel products. Some worldwide brand names have factories in Jiangmen including Haojue motorcycles, Jingling fan/washing machines, Vinda toilet paper, ABB Group and Lee Kum Kee foods.
Jiangmen port
Jiangmen Port is the second largest river port in Guangdong province. The local government plans to develop a harbour industrial zone with heavy industries to include petrochemical and machinery plants, as well as an ocean-based economy.
Administration
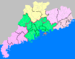
Jiangmen has jurisdiction over:
Map # Name Hanzi Hanyu Pinyin Population (2003 est.) Area (km²) Density (/km²) 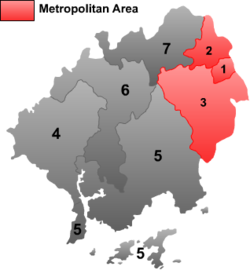
City Proper 1 Jianghai District 江海区 Jiānghǎi Qū 150,000 107 1,402 2 Pengjiang District 蓬江区 Péngjiāng Qū 440,000 325 1,354 3 Xinhui District 新会区 Xīnhuì Qū 740,000 1,260 587 Satellite cities 4 Enping 恩平市 Ēnpíng Shì 470,000 1,698 277 5 Taishan 台山市 Táishān Shì 990,000 3,286 301 6 Kaiping 开平市 Kāipíng Shì 680,000 1,659 410 7 Heshan 鹤山市 Hèshān Shì 360,000 1,108 325 Transport
Jiangmen has a mature network of inter-city highway (between Guangzhou, Foshan, Zhuhai, Zhongshan, Yangjiang etc.). It does sits astride a key route between Guangzhou and the southwest region of its home province, even Guangxi Province.
A network of intra-city roadways has been built since the late 1990s to facilitate industrial integration within the city.
Jiangmen's railway transport is relatively weak, but the condition will be changed before 2011. The Guangzhou–Zhuhai Intercity Mass Rapid Transit and Guangzhou–Zhuhai Railway will passby Jiangmen, which plan to be finished before 2011.
Making use of the Jiangmen Port facilities, Chu Kong Passenger Transport (CKS) connects Jiangmen with high speed ferry services to Hong Kong (95 nautical miles) taking about 2.5 hours each way.
Education
Wuyi University is the main university in Jiangmen.
Jiangmen No.1 Middle School is claimed to be the top middle school in the district, was one of the best middle school in Guangdong Province in 1980s~1990s. However in recent years the quality of its education has been dropping and in the district of Jiangmen, its status has been constantly challenged by Xinhui No.1 Middle School in Xinhui, Kaiqiao(Kaiping Emigrant) Middle School in Kiaping etc.
Culture
Jiangmen is the homeland of 3.68 million overseas Chinese, who live in 107 countries and regions throughout the world. Strong oversea connections are especially found in the villages.
Tourism
A significant amount of historical heritage survives from the period of mass emigration prior to World War II. The most significant are the fortified multi-story towers found mainly in Kaiping. These are known as "Gold Mountain Towers" or diaolou (碉樓).Number of natural Hotspring resorts has been developed successfully by using its wealthy natural heated ground water resources such as Gudou Hotspring Resort (古兜温泉)
The local government's economic development strategies emphasize the development of tourism and protection of the environment.
Controversy
In 2011, the city banned pet dogs after rabies killed 42 people over the preceding 3 years.[4] The city plans to remove all remaining dogs from the city centre. A government spokesman said "We hope that all citizens will cooperate with us in creating a civilised Jiangmen and send their dogs to live in the outskirts or rural areas,"[4] a 13 acre site has been set aside to allow rural chinese to adopt the dogs,[4] but the City has warned that it may be forced to seize and put down any remaining dogs left in Pengjiang, Jianghai and Xinhui districts after the 26th of August, 2011. An estimated 30,000 dogs will be affected. Dr. Tang Qing of the National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention at China's Centre for Disease Control reportedly believes that culling is not scientific, humane, or effective in preventing rabies over the long term.[5]
Reference
- ^ Ball, J. Dyer. (1900). "The Shun Tak Dialect". The China Review, or notes & queries on the Far East 25 (2): 57–68. http://sunzi1.lib.hku.hk/hkjo/view/26/2600399.pdf.
- ^ "彈指春秋:別讓江門死於肛門", Oriental Daily News, 2010-08-29, http://orientaldaily.on.cc/cnt/news/20100829/00184_001.html, retrieved 2011-11-03
- ^ "“江门”与“肛门”相距甚远", Guangzhou Net, 2009-11-05, http://www.gznet.com/news/society/shgc/200911/t20091105_1228098.html, retrieved 2011-11-03
- ^ a b c "Chinese city bans dogs". The Telegraph. 4 August 2011. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/china/8678489/Chinese-city-bans-dogs.html.
- ^ Branigan, Tania. (2011). "Cull of 30,000 pet dogs ordered after deadly rabies outbreak in Chinese city". The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2011/aug/03/chinese-city-bans-pet-dogs.
External links
- Jiangmen International Website (Chinese)
- Invest Jiangmen Government Website (Chinese)
Guangdong topics General Geography Cities • Pearl River mega-city • Leizhou Peninsula • Pearl River Delta • Northern Guangdong • East River • West River • Nanling Mountains • Pratas IslandsEducation Guangzhou Education • Shenzhen Education • Shenzhen University • Huizhou University • Guangdong Institute of Education • Guangzhou UniversityCulture Lingnan culture • Music • Guangdong music (genre) • Cantonese opera • Teochew people • Hakka people • Hailufeng dialectCuisine Cantonese cuisine • White boiled shrimp • Cantonese fried rice • Chinese steamed eggs • Beef chow fun • Chow mein • Char siu • Roasted suckling pig • Bird's nest soup • Seafood birdsnestVisitor attractions Danxia Mountain • Seven Star Crags • Dinghu Mountain • Xinfengjiang Reservoir • Zhongshan Park • Guangdong Provincial MuseumGuangdong Province county-level divisions Guangzhou: Baiyun District · Haizhu District · Huadu District · Huangpu District · Liwan District · Luogang District · Nansha District · Panyu District · Tianhe District · Yuexiu District · Conghua City · Zengcheng
Shenzhen: Bao'an District · Futian District · Longgang District · Luohu District · Nanshan District · Yantian District · Guangming New Area* · Pingshan New Area*
Zhuhai: Doumen District · Jinwan District · Xiangzhou District · Hengqin New Area*
Shantou: Chaonan District · Chaoyang District · Chenghai District · Haojiang District · Jinping District · Longhu District · Nan'ao County
Shaoguan: Qujiang District · Wujiang District · Zhenjiang District · Renhua County · Shixing County · Wengyuan County · Xinfeng County · Ruyuan Autonomous County · Lechang City · Nanxiong City
Foshan: Chancheng District · Gaoming District · Nanhai District · Sanshui District · Shunde District
Jiangmen: Xinluo District | Jianghai District · Pengjiang District · Xinhui District · Enping City · Heshan City · Kaiping City · Taishan City
Zhanjiang: Chikan District · Mazhang District · Potou District · Xiashan District · Suixi County · Xuwen County · Leizhou City · Lianjiang City · Wuchuan City
Maoming: Maogang District · Maonan District · Dianbai County · Gaozhou City · Huazhou · Xinyi City
Zhaoqing: Dinghu District · Duanzhou District · Deqing County · Fengkai County · Guangning County · Huaiji County · Gaoyao City · Sihui City
Huizhou: Huicheng District · Huiyang District · Boluo County · Huidong County · Longmen County
Meizhou: Meijiang District · Xingning City · Dabu County · Fengshun County · Jiaoling County · Mei County · Pingyuan County · Wuhua County
Shanwei: Chengqu District · Haifeng County · Luhe County · Lufeng City
Heyuan: Yuancheng District · Heping County · Lianping County · Longchuan County · Dongyuan County · Zijin County
Yangjiang: Jiangcheng District · Yangdong County · Yangxi County · Yangchun City
Qingyuan: Lianzhou City · Yingde City · Qingcheng District · Fogang County · Qingxin County · Yangshan County · Liannan Autonomous County · Lianshan Autonomous County
Dongguan: (no intermediate County-level divisions, see Administration of Dongguan)
Zhongshan: (no intermediate County-level divisions, see Administration of Zhongshan)
Chaozhou: Xiangqiao District · Chao'an County · Raoping County
Jieyang: Rongcheng District · Puning City · Huilai County · Jiedong County · Jiexi County
Yunfu: Yuncheng District · Xinxing County · Yunan County · Yun'an County · Luoding CityPearl River Delta Region Guangdong Province Special Administrative Region Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.