- Zhaoqing
-
Zhaoqing
肇庆— Prefecture-level city — 肇庆市 Location in Guangdong Location in China Coordinates: 23°3′0″N 112°28′0″E / 23.05°N 112.466667°E Country China Province Guangdong County-level divisions 8 Township divisions City seat Duanzhou District Area – Total 22,322 km2 (8,618.6 sq mi) Population (2002) – Total 3,910,000 – Density 175.2/km2 (453.7/sq mi) Time zone China Standard Area code(s) 758 GDP GDP per capita License Plate 粤H Major Nationalities Han Website Zhaoqing official site Zhaoqing (simplified Chinese: 肇庆; traditional Chinese: 肇慶; pinyin: Zhàoqìng) is a prefecture-level city of Guangdong province in southern China.
Contents
Geography
Zhaoqing is located 110 km northwest of Guangzhou, in the west Pearl River Delta. It lies on the north shores of the Xijiang River, which is flows from west to east, and opposite of Gaoyao. A plain area lies to the south and west of Zhaoqing, with mountains to the east and north.
The city lies in a south subtropical monsoon climatic zone. The yearly average temperature is 21.9 °C, and annual precipitation is 1605 mm.
Climate
Climate data for Zhaoqing (1971−2000) Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 18.0
(64.4)18.4
(65.1)21.2
(70.2)25.7
(78.3)29.6
(85.3)31.8
(89.2)33.2
(91.8)33.0
(91.4)31.5
(88.7)28.6
(83.5)24.4
(75.9)20.5
(68.9)26.33
(79.39)Average low °C (°F) 10.8
(51.4)12.2
(54.0)15.3
(59.5)19.8
(67.6)23.1
(73.6)25.1
(77.2)25.8
(78.4)25.8
(78.4)24.5
(76.1)21.2
(70.2)16.2
(61.2)12.0
(53.6)19.32
(66.77)Precipitation mm (inches) 40.9
(1.61)64.2
(2.528)81.3
(3.201)200.6
(7.898)276.0
(10.866)256.1
(10.083)229.5
(9.035)236.2
(9.299)143.0
(5.63)75.3
(2.965)37.5
(1.476)30.8
(1.213)1,671.4
(65.803)Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) 8.2 12.3 15.9 17.4 19.9 18.9 17.2 17.4 12.4 6.7 5.5 5.3 157.1 Source: Weather China History and Name
The date of Zhaoqing's founding is uncertain, but it existed as early as the Qin (221-206 B.C.) and Han (206 B.C. - 220 C.E.) Dynasties, when it was known as Gaoyao (高要). In the Sui Dynasty (581-618 C.E.), Zhaoqing became known as Duanzhou (端州) and served as an important administrative region and military base.
In C.E. 1118, Northern Song Dynasty Emperor Huizong bestowed its current name upon the city. "Zhaoqing" means "beginning of auspiciousness".
Early Jesuit mission
By the time of the Europeans arriving to Guangdong in the 16th century, Zhaoqing was an important administrative center, and the seat of Viceroy of Guangdong and Guangxi.[1]
Matteo Ricci account of the "Christian expeditions into China" tell about the early visits of Macau-based Europeans to Zhaoqing. The first visit may have been that by the Macau City Auditor Mattia Penella and the Italian Jesuit Michele Ruggieri, who went to Zhaoqing in 1582, sent there by the Macau's authorities in lieu of the Mayor and the Bishop of Macau, whom the Viceroy (named Chen Jui, 陈瑞) had summoned to report to him at his residence.[2] The Jesuits at the time were interested in expanding their missionary activity from Macau into Mainland China, so other visits by Jesuits soon followed, and by 1583, after several false starts, Michele Ruggieri and another, recently arrived Jesuit, named Matteo Ricci managed to establish residence in the city - the first Jesuit mission house in China outside Macau. Ruggieri and Ricci were able to move to the city after receiving an invitation from the governor of Zhaoqing at the time, Wang Pan, who had heard of Ricci's skill as a mathematician/cartographer.
It was in Zhaoqing that Ricci drew up the first ever map of the world in Chinese in 1584. In 1588, Ruggieri left China for Rome - not to ever return, as it turned out. But Ricci stayed in Zhaoqing until 1589, when a new viceroy decided to expel him from the city, and the Jesuit had to move to Shaozhou.[3]
There is now a memorial plaque in Zhaoqing to commemorate Ricci's six-year stay there as well as a building set up as a "Ricci Memorial Centre" although the building itself does not date back to the time of the priest as it was built in the 1860s.
The anti-Manchu resistance
After the fall of northern China to the Manchus in 1644, a sequence of Ming princes one after another established short-lived regimes at various locations in central and southern China, collectively known as the Southern Ming Dynasty. For several years until 1650, Zhaoqing was the seat of the last of these pretenders on the Ming throne, Zhu Youlang, styled the Yongli Emperor (who also made his court in Guilin and, later, at various locations in Guangxi, Yunnan, and Burma). The Jesuits Andreas Wolfgang Koffler and, later, Michał Boym stayed for some time at his court [4][5]
Administration
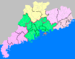
Zhaoqing has jurisdiction over 2 districts, 4 counties and 2 county-level cities:
Map # Name Hanzi Hanyu Pinyin Population (2003 est.) Area (km²) Density (/km²) 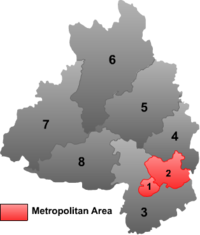
City Proper 1 Duanzhou District 端州区 Duānzhōu Qū 330,000 152 2,171 2 Dinghu District 鼎湖区 Dǐnghú Qū 150,000 506 296 Satellite cities 3 Gaoyao 高要市 Gāoyào Shì 730,000 2,206 331 4 Sihui 四会市 Sìhuì Shì 420,000 1,258 334 Rural 5 Guangning County 广宁县 Guǎngníng Xiàn 540,000 2,380 227 6 Huaiji County 怀集县 Huáijí Xiàn 930,000 3,573 260 7 Fengkai County 封开县 Fēngkāi Xiàn 470,000 2,723 173 8 Deqing County 德庆县 Déqìng Xiàn 360,000 2,258 159 Economy
Primary Industries
The rich local resources within the mountain region include coal, limestone, copper, lead, zinc, granite, gold, sulfur, gypsum and other minerals.
For agriculture sector, the fertile plain yields paddy rice, sugar cane, aquatic products, fruits, rosin, cassia bark. Horticulture possesses a large sector in farming industries. Poultry and animal husbandry are also seeking modern development and management.
The forest in mountain region is a rich source for herbal medicine in southern China, and other materials like rosin and casia bark from different forest plants.
Secondary Industries
Food and beverages, building materials, electronics, micro bioengineering, chemicals, equipments and machinery, textile and garments are the pillar industries. Duanzhou, Gaoyao and Sihui area being developed as the export-oriented industrial bases. Yunfu is a major area for the production of sulphur and iron.
To facilitate industrial development in Zhaoqing, the local government has made great efforts in establishing various industrial zones / parks in the city. The largest one is the Guangdong Zhaoqing High-tech Industrial Development Zone, with an area of 109km², that consists of two industrial parks, Sanrong Industrial Park and Dawang Industrial Park, of areas 9km² and 100km² respectively. Dawang is facilitated as an export processing and trade zone.
The 10 Projects
The Zhaoqing local government attracts capital investment by promoting the city to private and foreign investors, and by developing industrial parks in modern standard. Making the best use of its natural environment, Zhaoqing aims to become a garden city, ecological city and modernized large city in China.
In five year's time (2003-2007), the city government will implement 10 big projects:
- Expansion of urban proper towards the east and the south with the best urban planning, construction, and management.
- Developing the eastern and southern industrial areas to become a modern manufacturing base of the world.
- Promoting economic development in the hilly areas and counties and upgrade their industrial zones.
- Construction of an industrial corridor of science, technology, education and culture to nurture knowledge economy, through developing technology park and university park, and inter-university cooperation
- Increasing capital investment for infrastructure construction.
- Promoting the reform and development of state owned enterprises.
- Developing tourism spots and industry.
- Construction of an "education city" and a "cultural city" to enhance the quality of human resources.
- Construction of "digital Zhaoqing".
- Enhancing environmental protection.
Highlights
- Limestone peaks at Seven Star Crags
- Dinghu Mountain
- Song Township city walls, over 800 years old
- Chongxi Pagoda
- Tower for Reviewing the River
- Baogong Memorial Temple
Education
The city government of Zhaoqing is currently seeking to improve its higher education system and preserve cultural resources. Zhaoqing has a university and is also home to a campus of Guangdong University of Finance. There is also Zhaoqing Foreign Language College, a Canadian-American School and numerous other schools including those specialising in foreign language study.
Colleges and universities
- Zhaoqing University
Transportation
Zhaoqing is served by railways and highways. Direct train and bus services connect it to Guangzhou, Hong Kong and other cities in Guangdong. Major roadways include Interstates 321 and 324 and the Guang-Zhao and Guang-Wu Expressways. The Sanmao Railway also runs through Zhaoqing. It is connected with Hong Kong via the KCRC Guangdong Through Train service from Zhaoqing Railway Station. Hong Kong Chu Kong Passenger Transport Co., Ltd. also runs daily express catamaran ferries between Zhaoqing and Hong Kong.
Within the city, the primary form of public transportation are the 24 public bus routes.
References
- ^ De Christiana expeditione apud Sinas, Book Two, Chapter 3. Pages 136 in the English translation: Louis J. Gallagher (1953). "China in the Sixteenth Century: The Journals of Matteo Ricci", Random House, New York, 1953. The original Latin text by Nicolas Trigault, De Christiana expeditione apud Sinas suscepta ab Societate Jesu, can be found on Google Books.
- ^ Gallagher (trans.), p. 136. Chen Jui is Cinsui in Ricci's transcription
- ^ Gallagher (trans.), pp. 205-229.
- ^ Andreas Wolfgang Koffler in The Dictionary of the Ming Biography, pp. 722-723
- ^ Mungello, David E. (1989). Curious Land: Jesuit Accommodation and the Origins of Sinology. University of Hawaii Press. p. 139. ISBN 0-8248-1219-0. http://books.google.com/books?id=wb4yPw4ZgZQC.
External links
- Zhaoqing Government website
- Zhaoqing University website (in Chinese and English)
- Guangdong University of Finance website (in Chinese and English)
- News Guangdong Zhaoqing page
- The Zhaoqing Ricci center
- Matteo Ricci and his contributions to science in China
- Map of the city center
- Chu Kong Passenger Transport Co. Ltd.
Guangdong topics General Geography Cities • Pearl River mega-city • Leizhou Peninsula • Pearl River Delta • Northern Guangdong • East River • West River • Nanling Mountains • Pratas IslandsEducation Guangzhou Education • Shenzhen Education • Shenzhen University • Huizhou University • Guangdong Institute of Education • Guangzhou UniversityCulture Lingnan culture • Music • Guangdong music (genre) • Cantonese opera • Teochew people • Hakka people • Hailufeng dialectCuisine Cantonese cuisine • White boiled shrimp • Cantonese fried rice • Chinese steamed eggs • Beef chow fun • Chow mein • Char siu • Roasted suckling pig • Bird's nest soup • Seafood birdsnestVisitor attractions Danxia Mountain • Seven Star Crags • Dinghu Mountain • Xinfengjiang Reservoir • Zhongshan Park • Guangdong Provincial MuseumGuangdong Province county-level divisions Guangzhou: Baiyun District · Haizhu District · Huadu District · Huangpu District · Liwan District · Luogang District · Nansha District · Panyu District · Tianhe District · Yuexiu District · Conghua City · Zengcheng
Shenzhen: Bao'an District · Futian District · Longgang District · Luohu District · Nanshan District · Yantian District · Guangming New Area* · Pingshan New Area*
Zhuhai: Doumen District · Jinwan District · Xiangzhou District · Hengqin New Area*
Shantou: Chaonan District · Chaoyang District · Chenghai District · Haojiang District · Jinping District · Longhu District · Nan'ao County
Shaoguan: Qujiang District · Wujiang District · Zhenjiang District · Renhua County · Shixing County · Wengyuan County · Xinfeng County · Ruyuan Autonomous County · Lechang City · Nanxiong City
Foshan: Chancheng District · Gaoming District · Nanhai District · Sanshui District · Shunde District
Jiangmen: Xinluo District | Jianghai District · Pengjiang District · Xinhui District · Enping City · Heshan City · Kaiping City · Taishan City
Zhanjiang: Chikan District · Mazhang District · Potou District · Xiashan District · Suixi County · Xuwen County · Leizhou City · Lianjiang City · Wuchuan City
Maoming: Maogang District · Maonan District · Dianbai County · Gaozhou City · Huazhou · Xinyi City
Zhaoqing: Dinghu District · Duanzhou District · Deqing County · Fengkai County · Guangning County · Huaiji County · Gaoyao City · Sihui City
Huizhou: Huicheng District · Huiyang District · Boluo County · Huidong County · Longmen County
Meizhou: Meijiang District · Xingning City · Dabu County · Fengshun County · Jiaoling County · Mei County · Pingyuan County · Wuhua County
Shanwei: Chengqu District · Haifeng County · Luhe County · Lufeng City
Heyuan: Yuancheng District · Heping County · Lianping County · Longchuan County · Dongyuan County · Zijin County
Yangjiang: Jiangcheng District · Yangdong County · Yangxi County · Yangchun City
Qingyuan: Lianzhou City · Yingde City · Qingcheng District · Fogang County · Qingxin County · Yangshan County · Liannan Autonomous County · Lianshan Autonomous County
Dongguan: (no intermediate County-level divisions, see Administration of Dongguan)
Zhongshan: (no intermediate County-level divisions, see Administration of Zhongshan)
Chaozhou: Xiangqiao District · Chao'an County · Raoping County
Jieyang: Rongcheng District · Puning City · Huilai County · Jiedong County · Jiexi County
Yunfu: Yuncheng District · Xinxing County · Yunan County · Yun'an County · Luoding CityPearl River Delta Region Guangdong Province Special Administrative Region Categories:- Cities in Guangdong
- Prefecture-level divisions of Guangdong
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.