- Daqing
-
Daqing
大庆— Prefecture-level city — Daqing (red) in Heilongjiang province (orange) and China Location in Heilongjiang Coordinates: 46°35′N 125°0′E / 46.583°N 125°E Country People's Republic of China Province Heilongjiang Area – Prefecture-level city 8,556.4 sq mi (22,161 km2) – Urban 2,123.6 sq mi (5,500 km2) – Metro 1,260.6 sq mi (3,265 km2) Population (2010 census) – Prefecture-level city 2,904,532 – Density 339.5/sq mi (131.1/km2) – Urban 1,323,252 – Urban density 623.1/sq mi (240.6/km2) – Metro 1,042,902 – Metro density 827.3/sq mi (319.4/km2) Time zone China standard time (UTC+8) Website http://www.daqing.gov.cn/ Daqing (simplified Chinese: 大庆; traditional Chinese: 大慶; pinyin: Dàqìng; formerly spelled "Taching") (pronounced Da Tshing) is a prefecture-level city in the west of Heilongjiang province of Northeast China. The name literally means "Great Celebration". Located in China’s Harbin-Daqing-Qiqihar Industrial Corridor, Daqing is known as the Oil Capital of China and has experienced a phenomenal boom. Since oil was discovered here in the 1960s, Daqing was originally used as a settlement for petroleum workers, and became the most important city for the petrochemicals industry and petroleum extraction in China.
Its population is 2,904,532 at the 2010 census whom 1,042,902 in the built up area made of 4 out of 5 urban districts (Sartu, Longfeng, Ranghulu and Honggang)
Contents
Administrative divisions
Daqing is divided into 9 county-level divisions: 5 districts, 3 counties and 1 autonomous county.
Map 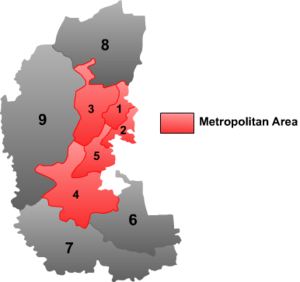
# Name Hanzi Hanyu Pinyin Population (2003 est.) Area (km²) Density (/km²) 1 Sartu District 萨尔图区 Sà'ěrtú Qū 260,000 549 474 2 Longfeng District 龙凤区 Lóngfèng Qū 160,000 510 314 3 Ranghulu District 让胡路区 Rànghúlù Qū 380,000 1,394 273 4 Datong District 大同区 Dàtóng Qū 250,000 2,235 112 5 Honggang District 红岗区 Hónggǎng Qū 130,000 812 160 6 Zhaozhou County 肇州县 Zhàozhōu Xiàn 440,000 2,445 180 7 Zhaoyuan County 肇源县 Zhàoyuán Xiàn 450,000 4,198 107 8 Lindian County 林甸县 Líndiàn Xiàn 270,000 3,591 75 9 Dorbod Mongol Autonomous County 杜尔伯特蒙古族自治县 Dù'ěrbótè Měnggǔzú Zìzhìxiàn 250,000 6,427 39 History
Until the Qing Dynasty, the area now known as Daqing was a reasonably insignificant place, known only as a hunting ground due to its wetland and prairies, and consequently it remained unsettled. It grew slightly after Russia constructed the Chinese Eastern Railway through the area with a stop at Saertu. Daqing was founded in 1959 to house workers extracting oil and gas from the Daqing oilfield and to host industries which could take advantage of the energy and petrochemicals. Since its foundation it has been advocated as a model of good practice in industry and healthcare by the Chinese government. The fact that Mao Zedong promulgated his Supreme Directive, In industry, learn from Daqing, in the 1960s reflects how important a role Daqing has historically played in industry in China. The film Entrepreneurial Pioneers (Chinese: 创业), made in the early 1970s, is a literary rendition of the history of Daqing. During the Mao era, Daqing's agricultural counterpart was Dazhai, a village in the hilly Xiyang county, Shanxi Province, for which Chairman Mao issued the directive In agriculture, learn from Dazhai, also in the 1960s.
Demographics
Daqing has a population of 2.58 million, urban population 901,840 of them mainly Han Chinese, with a few population of other 31 minority ethnic groups including Manchu, Mongolian, Korean, and Hui nationalities. The population density is 112.69/km², urban population density 205.07/km².
Climate
Located in the north temperate zone, Daqing belongs to the continental monsoon climate and is affected by the cold air mass from the inland of Mongolia and the monsoon resulted from the warm air mass of the ocean. Generally, the winter is cold with occasional snowfalls, and spring and autumn are prevailed by monsoons. A shorter frost free period, and plenty of rainfall comes in step with the heat, all of which are good for crops and herbage. The yearly average temperature is 5.6 degrees Celsius with a summer average of 22 degrees Celsius, and 2658.1 hours of sunshine, 229 days[dubious ] free of frost in average.[citation needed] The daily difference in temperature can be up to 14 degrees Celsius during the growth period of crops.
Economy
Daqing's economy highly depends on petroleum and related industries. Daqing's oilfield is China's largest oilfield, and the world's fourth most productive oil field. Petroleum accounts for 60.8% of GDP. In 2008 Gross Domestic Product was RMB 222 billion yuan, while GDP Per capita RMB 80,092 (US$11,532), so Daqing is ranked eighth by GDP per capita among 659 Chinese cities. Being the most important petrochemical base in China, Daqing has established five pillar industries, including extraction of petroleum and natural gas, petrochemicals, agricultural product processing, building materials and equipment manufacturing.
Transportation
Daqing is located on the Harbin-Manzhouli Railway.
Culture
Daqing spirit
Daqing has a unique culture centering around the Iron man spirit, which was generated by the history of this city. It consists of patriotism, truth-seeking, entrepreneurial spirit and dedication. Wang Jinxi, a petroleum worker on the Daqing Oilfield who was know as the Iron Man, was honored as a national hero due to his contributions to the petroleum industry of China. In the 1960s, Daqing was established by the central government as a model for the secondary industry. Its entrepreneurial process has two stages: the first involves discovering a large oilfield in the wasteland; the second concerns itself with building a modern city near the oilfield. Films have been made to illuminate the entrepreneurial history of both Daqing and its people.
International relations
Main article: List of twin towns and sister cities in ChinaTwin towns — Sister cities
Daqing is twinned with:
External links
- Daqing Government Website
- Daqing Oilfield Company Ltd.
- Daqing Petroleum Administrative Bureau
- Northeast Petroleum University
- Heilongjiang August First Land Reclamation Institute
Heilongjiang topics General Geography Cities • Greater Khingan mountain range • Lesser Khingan mountain range • Wanda Mountains • Huma River • Muling River • Naoli River • Songhua River • Nen River • Mudan River • Amur RiverEducation Visitor attractions Heilongjiang Province county-level divisions Harbin: Daoli District · Nangang District · Daowai District · Xiangfang District · Pingfang District · Songbei District · Hulan District · Acheng District · Shuangcheng City · Shangzhi City · Wuchang City · Yilan County · Fangzheng County · Bin County · Bayan County · Mulan County · Yanshou County · Tonghe County
Qiqihar: Longsha District · Jianhua District · Tiefeng District · Ang'angxi District · Fularji District · Nianzishan District · Meilisi Daur District · Nehe City · Longjiang County · Yi'an County · Tailai County · Gannan County · Fuyu County · Keshan County · Kedong County · Baiquan County
Hegang: Xingshan District · Xiangyang District · Gongnong District · Nanshan District · Xing'an District · Dongshan District · Luobei County · Suibin County
Shuangyashan: Jianshan District · Lingdong District · Sifangtai District · Baoshan District · Jixian County · Youyi County · Baoqing County · Raohe County
Jixi: Jiguan District · Hengshan District · Didao District · Lishu District · Chengzihe District · Mashan District · Hulin City · Mishan City · Jidong County
Daqing: Sartu District · Longfeng District · Ranghulu District · Datong District · Honggang District · Zhaozhou County · Zhaoyuan County · Lindian County · Dorbod Mongol Autonomous County
Yichun: Yichun District · Nancha District · Youhao District · Xilin District · Cuiluan District · Xinqing District · Meixi District · Jinshantun District · Wuying District · Wumahe District · Tangwanghe District · Dailing District · Wuyiling District · Hongxing District · Shangganling District · Tieli City · Jiayin County
Mudanjiang: Aimin District · Dong'an District · Yangming District · Xi'an District · Muling City · Suifenhe City · Hailin City · Ning'an City · Dongning County · Linkou County
Jiamusi: Qianjin District · Xiangyang District · Dongfeng District · Jiaoqu District · Tongjiang City · Fujin City · Huanan County · Huachuan County · Tangyuan County · Fuyuan County
Qitaihe: Taoshan District · Xinxing District · Qiezihe District · Boli County
Heihe: Aihui District · Bei'an City · Wudalianchi City · Nenjiang County · Xunke County · Sunwu County
Suihua: Beilin District · Anda City · Zhaodong City · Hailun City · Wangkui County · Lanxi County · Qinggang County · Qing'an County · Mingshui County · Suileng County
Da Hinggan Ling: Jiagedaqi District · Songling District · Huzhong District · Xinlin District · Huma County · Tahe County · Mohe CountyCategories:- Cities in Heilongjiang
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.