- Nutcracker syndrome
-
Nutcracker syndrome Classification and external resources 
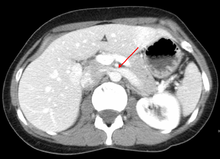
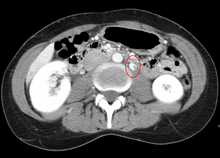
The nutcracker syndrome results from compression of the left renal vein between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery.DiseasesDB 32367 Compression of the left renal vein (marked by the arrow) between the superior mesenteric artery (above) and the aorta (below) due to nutcracker syndrome. Thrombosis in the left renal vein associated with dilation.
Thrombosis in the left renal vein associated with dilation. A nutcracker. The legs of this nutcracker, with some imagination, could represent the superior mesenteric artery and abdominal aorta in nutcracker syndrome.
A nutcracker. The legs of this nutcracker, with some imagination, could represent the superior mesenteric artery and abdominal aorta in nutcracker syndrome.
In medicine, the nutcracker syndrome (NCS) — is a clinically manifest variant of nutcracker phenomenon, renal vein entrapment syndrome, or mesoaortic compression of the left renal vein. It results most commonly from the compression of the left renal vein between the abdominal aorta (AA) and superior mesenteric artery (SMA), although other variants exist.[1][2] The name derives from the fact that, in the sagittal view, the SMA and AA (with some imagination) appear to be a nutcracker crushing a nut (the renal vein). There is a wide spectrum of clinical presentations and diagnostic criteria are not well defined, which frequently results in delayed or incorrect diagnosis.[1] This condition is not to be confused with superior mesenteric artery syndrome, which is the compression of the third portion of the duodenum by the SMA and the AA.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
NCS is associated with hematuria (which can lead to anemia[3]) and abdominal pain (classically left flank pain[4]).
Since the left gonad drains via the left renal vein it can also result in left testicular pain[5] in men or left lower quadrant pain in women. Nausea and vomiting can result due to compression of the splanchnic veins.[5] An unusual manifestation of NCS includes varicocele formation and varicose veins in the lower limbs.[6]. Another clinical study has shown that that nutcracker syndrome is a frequent finding in varicocele-affected patients and possibly, nutcracker syndrome should be routinely excluded as a possible cause of varicocele [7].
Diagnosis
Nutcracker syndrome can be diagnosed with:
- Left renal venography — considered to be the gold standard test.
- Computed tomography (CT).
- Abdominal ultrasonography — not definitive but has been found to be useful.[8]
Differential diagnosis
- Renal stones
- Genitourinary malignancy
- Loin pain hematuria syndrome[9]
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity and symptoms. Treatments include:
- Endovascular stenting.[4]
- Renal vein re-implantation.[10]
- Gonadal vein embolization.[10]
References
- ^ a b Kurklinsky A., Rooke T. (June 2010). "Nutcracker Phenomenon and Nutcracker Syndrome". Mayo Clin Proc. 85 (6): 552–559. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0586. PMC 2878259. PMID 20511485. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2878259.
- ^ Sugimoto I, Takashi O, Ishibashi H, Takeuchi N, Nagata Y, Honda Y (2001). "Left Renal Vein Entrapment Syndrome (Nutcracker Syndrome) treated with Left Renal Vein Transposition". Jnp J Vasc Surg. 10: 503–7. http://www.jsvs.org/en/journal/abstract.php?bn=20011004&no=8.[dead link]
- ^ Oteki T, Nagase S, Hirayama A, et al. (July 2004). "Nutcracker syndrome associated with severe anemia and mild proteinuria". Clin. Nephrol. 62 (1): 62–5. PMID 15267016.
- ^ a b Barnes RW, Fleisher HL, Redman JF, Smith JW, Harshfield DL, Ferris EJ (October 1988). "Mesoaortic compression of the left renal vein (the so-called nutcracker syndrome): repair by a new stenting procedure". J. Vasc. Surg. 8 (4): 415–21. doi:10.1067/mva.1988.avs0080415. PMID 3172376.
- ^ a b Hilgard P, Oberholzer K, Meyer zum Büschenfelde KH, Hohenfellner R, Gerken G (July 1998). "[The "nutcracker syndrome" of the renal vein (superior mesenteric artery syndrome) as the cause of gastrointestinal complaints]" (in German). Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 123 (31–32): 936–40. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1024101. PMID 9721569.
- ^ Little AF, Lavoipierre AM (June 2002). "Unusual clinical manifestations of the Nutcracker Syndrome". Australas Radiol 46 (2): 197–200. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1673.2001.01037.x. PMID 12060163. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0004-8461&date=2002&volume=46&issue=2&spage=197.
- ^ Mohamadi A, Ghasemi-Rad M, Mladkova N, Masudi S. (August 2010). "Varicocele and nutcracker syndrome: sonographic findings". J Ultrasound Med 29 (8): 1153–1160. PMID 20660448. http://www.jultrasoundmed.org/cgi/content/short/29/8/1153?rss=1.
- ^ Takebayashi S, Ueki T, Ikeda N, Fujikawa A (January 1999). "Diagnosis of the nutcracker syndrome with color Doppler sonography: correlation with flow patterns on retrograde left renal venography". AJR Am J Roentgenol 172 (1): 39–43. PMID 9888735. http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=9888735.
- ^ Ahmed K, Sampath R, Khan MS (2006). "Current trends in the diagnosis and management of renal nutcracker syndrome: a review". Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 31 (4): 410–6. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2005.05.045. PMID 16431142.
- ^ a b Rudloff U, Holmes RJ, Prem JT, Faust GR, Moldwin R, Siegel D (January 2006). "Mesoaortic compression of the left renal vein (nutcracker syndrome): case reports and review of the literature". Ann Vasc Surg 20 (1): 120–9. doi:10.1007/s10016-005-5016-8. PMID 16374539.
External links
- Kimura K, Araki T (July 1996). "Images in clinical medicine. Nutcracker phenomenon". N. Engl. J. Med. 335 (3): 171. doi:10.1056/NEJM199607183350305. PMID 8657215. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=8657215&promo=ONFLNS19.
Urinary system · Pathology · Urologic disease / Uropathy (N00–N39, 580–599) Abdominal Primarily
nephrotic.3 Mesangial proliferative · .4 Endocapillary proliferative .5/.6 Membranoproliferative/mesangiocapillaryBy conditionType III RPG/Pauci-immuneTubulopathy/
tubulitisAny/allAny/allGeneral syndromesOtherUreterPelvic UrethraUrethritis (Non-gonococcal urethritis) · Urethral syndrome · Urethral stricture/Meatal stenosis · Urethral caruncleAny/all Obstructive uropathy · Urinary tract infection · Retroperitoneal fibrosis · Urolithiasis (Bladder stone, Kidney stone, Renal colic) · Malacoplakia · Urinary incontinence (Stress, Urge, Overflow)Categories:- Kidney diseases
- Syndromes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.